Analysis of interlayer spacing control in MXenes
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
MXene Interlayer Spacing Background and Objectives
MXenes represent a revolutionary class of two-dimensional transition metal carbides, nitrides, and carbonitrides that have emerged as promising materials for various applications since their discovery in 2011. The interlayer spacing in MXenes plays a crucial role in determining their physical, chemical, and electrochemical properties, making it a critical parameter for tailoring these materials for specific applications. The evolution of MXene technology has progressed from initial discovery to sophisticated engineering of their structure, with interlayer spacing control becoming increasingly important in recent years.
The fundamental structure of MXenes consists of transition metal layers sandwiched between carbon or nitrogen atoms, typically represented as Mn+1XnTx, where M represents a transition metal, X is carbon or nitrogen, and Tx indicates surface functional groups. These surface terminations significantly influence the interlayer spacing, which typically ranges from 0.6 to 1.5 nm depending on the intercalated species and environmental conditions.
Historical development of MXene interlayer spacing research shows a clear progression from basic characterization to deliberate manipulation. Early work (2011-2015) focused primarily on understanding the natural spacing in various MXene compositions, while the period from 2016-2019 saw increased efforts to modify spacing through intercalation of various ions and molecules. Since 2020, research has shifted toward precise control and stabilization of interlayer distances for optimized performance in specific applications.
The technological objective in this field centers on developing reproducible and scalable methods to precisely control MXene interlayer spacing with angstrom-level precision. This control aims to enhance key properties including ion transport, electronic conductivity, and mechanical stability. Specifically, researchers seek to establish correlations between interlayer spacing and functional properties to enable application-specific tuning.
Current technical challenges include achieving uniform spacing throughout MXene structures, maintaining desired spacing under varying environmental conditions, and developing in-situ characterization techniques to monitor spacing changes during device operation. The field is moving toward dynamic control of interlayer spacing as a means to create responsive materials with switchable properties.
The broader technological trend indicates a convergence of MXene research with other 2D materials, creating hybrid structures with synergistic properties. This integration represents a promising direction for next-generation energy storage, sensing, and electronic applications where precise control of nanoscale architecture is paramount for performance optimization.
The fundamental structure of MXenes consists of transition metal layers sandwiched between carbon or nitrogen atoms, typically represented as Mn+1XnTx, where M represents a transition metal, X is carbon or nitrogen, and Tx indicates surface functional groups. These surface terminations significantly influence the interlayer spacing, which typically ranges from 0.6 to 1.5 nm depending on the intercalated species and environmental conditions.
Historical development of MXene interlayer spacing research shows a clear progression from basic characterization to deliberate manipulation. Early work (2011-2015) focused primarily on understanding the natural spacing in various MXene compositions, while the period from 2016-2019 saw increased efforts to modify spacing through intercalation of various ions and molecules. Since 2020, research has shifted toward precise control and stabilization of interlayer distances for optimized performance in specific applications.
The technological objective in this field centers on developing reproducible and scalable methods to precisely control MXene interlayer spacing with angstrom-level precision. This control aims to enhance key properties including ion transport, electronic conductivity, and mechanical stability. Specifically, researchers seek to establish correlations between interlayer spacing and functional properties to enable application-specific tuning.
Current technical challenges include achieving uniform spacing throughout MXene structures, maintaining desired spacing under varying environmental conditions, and developing in-situ characterization techniques to monitor spacing changes during device operation. The field is moving toward dynamic control of interlayer spacing as a means to create responsive materials with switchable properties.
The broader technological trend indicates a convergence of MXene research with other 2D materials, creating hybrid structures with synergistic properties. This integration represents a promising direction for next-generation energy storage, sensing, and electronic applications where precise control of nanoscale architecture is paramount for performance optimization.
Market Applications and Demand Analysis for MXenes
The global market for MXenes has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by their exceptional properties and versatile applications. The ability to control interlayer spacing in MXenes has emerged as a critical factor that directly influences their performance in various applications, thereby affecting market demand and potential commercialization pathways.
Energy storage represents the largest market segment for MXenes, particularly in supercapacitors and batteries. The precise control of interlayer spacing enables enhanced ion transport and storage capacity, addressing the growing demand for high-performance energy storage solutions in electric vehicles, portable electronics, and renewable energy systems. Market analysts project that MXene-based energy storage materials could capture a substantial portion of the advanced materials market for next-generation batteries.
The healthcare and biomedical sector presents another promising market for MXenes with controlled interlayer spacing. These materials show excellent potential for drug delivery systems, biosensors, and antimicrobial applications. The ability to tune interlayer spacing allows for optimized loading and release of therapeutic agents, meeting the increasing demand for targeted drug delivery systems and personalized medicine approaches.
Environmental remediation applications, particularly water purification and gas separation, represent a rapidly growing market segment for MXenes. The controlled interlayer spacing facilitates selective adsorption of contaminants and efficient filtration processes. With global water scarcity concerns intensifying, the demand for advanced filtration materials is expected to drive significant market growth in this sector.
The electronics industry has shown increasing interest in MXenes for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, transparent conductive films, and flexible electronics. The market demand in this sector is driven by the miniaturization trend in electronics and the need for materials that can maintain performance while offering flexibility and reduced thickness.
Regional market analysis indicates that North America and Asia-Pacific currently lead in MXene research and commercialization efforts. However, Europe is rapidly increasing investments in advanced materials research, including MXenes with controlled interlayer properties. China has emerged as a key player in both research and potential manufacturing capacity for MXene-based products.
Market challenges include scaling up production while maintaining precise control over interlayer spacing, establishing standardized characterization methods, and addressing cost concerns for mass-market applications. Despite these challenges, the unique properties offered by interlayer spacing control in MXenes position them favorably against competing materials in several high-value application segments.
Energy storage represents the largest market segment for MXenes, particularly in supercapacitors and batteries. The precise control of interlayer spacing enables enhanced ion transport and storage capacity, addressing the growing demand for high-performance energy storage solutions in electric vehicles, portable electronics, and renewable energy systems. Market analysts project that MXene-based energy storage materials could capture a substantial portion of the advanced materials market for next-generation batteries.
The healthcare and biomedical sector presents another promising market for MXenes with controlled interlayer spacing. These materials show excellent potential for drug delivery systems, biosensors, and antimicrobial applications. The ability to tune interlayer spacing allows for optimized loading and release of therapeutic agents, meeting the increasing demand for targeted drug delivery systems and personalized medicine approaches.
Environmental remediation applications, particularly water purification and gas separation, represent a rapidly growing market segment for MXenes. The controlled interlayer spacing facilitates selective adsorption of contaminants and efficient filtration processes. With global water scarcity concerns intensifying, the demand for advanced filtration materials is expected to drive significant market growth in this sector.
The electronics industry has shown increasing interest in MXenes for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, transparent conductive films, and flexible electronics. The market demand in this sector is driven by the miniaturization trend in electronics and the need for materials that can maintain performance while offering flexibility and reduced thickness.
Regional market analysis indicates that North America and Asia-Pacific currently lead in MXene research and commercialization efforts. However, Europe is rapidly increasing investments in advanced materials research, including MXenes with controlled interlayer properties. China has emerged as a key player in both research and potential manufacturing capacity for MXene-based products.
Market challenges include scaling up production while maintaining precise control over interlayer spacing, establishing standardized characterization methods, and addressing cost concerns for mass-market applications. Despite these challenges, the unique properties offered by interlayer spacing control in MXenes position them favorably against competing materials in several high-value application segments.
Current State and Challenges in MXene Interlayer Engineering
MXene interlayer spacing control represents one of the most critical challenges in the field of two-dimensional (2D) materials engineering. Currently, the global research landscape shows significant advancements in controlling MXene interlayer distances, though several fundamental obstacles remain. Leading research institutions in China, the United States, and Europe have demonstrated various approaches to manipulate the spacing between MXene layers, primarily through intercalation strategies, surface functionalization, and pillar insertion techniques.
The state-of-the-art methods include the use of organic molecules as spacers, which has shown promise in maintaining stable interlayer distances ranging from 1-2 nm. However, precise control at the sub-nanometer scale remains elusive. Recent breakthroughs at MIT and Drexel University have demonstrated the potential of ionic liquids as dynamic spacing agents, allowing for responsive adjustment of interlayer distances through external stimuli such as temperature or electric field.
A significant challenge in the field is the trade-off between increased interlayer spacing and mechanical stability. As spacing increases, the van der Waals forces between layers weaken substantially, compromising the structural integrity of the material. This presents a fundamental materials science dilemma that researchers are actively addressing through composite approaches and cross-linking strategies.
Another persistent challenge is the long-term stability of engineered interlayer spaces. Environmental factors such as humidity, temperature fluctuations, and oxidation can cause significant changes in spacing over time. Recent studies from Tsinghua University and the Max Planck Institute have highlighted the importance of encapsulation techniques to preserve engineered interlayer distances, though these solutions often come at the cost of reduced functionality or increased processing complexity.
The scalability of precise interlayer engineering techniques represents perhaps the most significant hurdle for industrial applications. Laboratory-scale demonstrations have shown excellent control over spacing, but translating these approaches to mass production remains problematic. Current manufacturing processes struggle to maintain homogeneous interlayer distances across large-area MXene films or powders.
Characterization challenges also persist, with researchers debating the most accurate methods for measuring interlayer distances in dynamic or complex systems. Advanced techniques combining in-situ XRD with environmental controls are emerging as the gold standard, though accessibility to such equipment limits widespread adoption of standardized measurement protocols.
Geographically, North America leads in fundamental research on MXene interlayer engineering, while China demonstrates the fastest growth in patent applications related to practical applications of controlled-spacing MXenes, particularly in energy storage devices. European institutions excel in developing theoretical models that predict optimal spacing configurations for specific applications.
The state-of-the-art methods include the use of organic molecules as spacers, which has shown promise in maintaining stable interlayer distances ranging from 1-2 nm. However, precise control at the sub-nanometer scale remains elusive. Recent breakthroughs at MIT and Drexel University have demonstrated the potential of ionic liquids as dynamic spacing agents, allowing for responsive adjustment of interlayer distances through external stimuli such as temperature or electric field.
A significant challenge in the field is the trade-off between increased interlayer spacing and mechanical stability. As spacing increases, the van der Waals forces between layers weaken substantially, compromising the structural integrity of the material. This presents a fundamental materials science dilemma that researchers are actively addressing through composite approaches and cross-linking strategies.
Another persistent challenge is the long-term stability of engineered interlayer spaces. Environmental factors such as humidity, temperature fluctuations, and oxidation can cause significant changes in spacing over time. Recent studies from Tsinghua University and the Max Planck Institute have highlighted the importance of encapsulation techniques to preserve engineered interlayer distances, though these solutions often come at the cost of reduced functionality or increased processing complexity.
The scalability of precise interlayer engineering techniques represents perhaps the most significant hurdle for industrial applications. Laboratory-scale demonstrations have shown excellent control over spacing, but translating these approaches to mass production remains problematic. Current manufacturing processes struggle to maintain homogeneous interlayer distances across large-area MXene films or powders.
Characterization challenges also persist, with researchers debating the most accurate methods for measuring interlayer distances in dynamic or complex systems. Advanced techniques combining in-situ XRD with environmental controls are emerging as the gold standard, though accessibility to such equipment limits widespread adoption of standardized measurement protocols.
Geographically, North America leads in fundamental research on MXene interlayer engineering, while China demonstrates the fastest growth in patent applications related to practical applications of controlled-spacing MXenes, particularly in energy storage devices. European institutions excel in developing theoretical models that predict optimal spacing configurations for specific applications.
Current Approaches for MXene Interlayer Spacing Modification
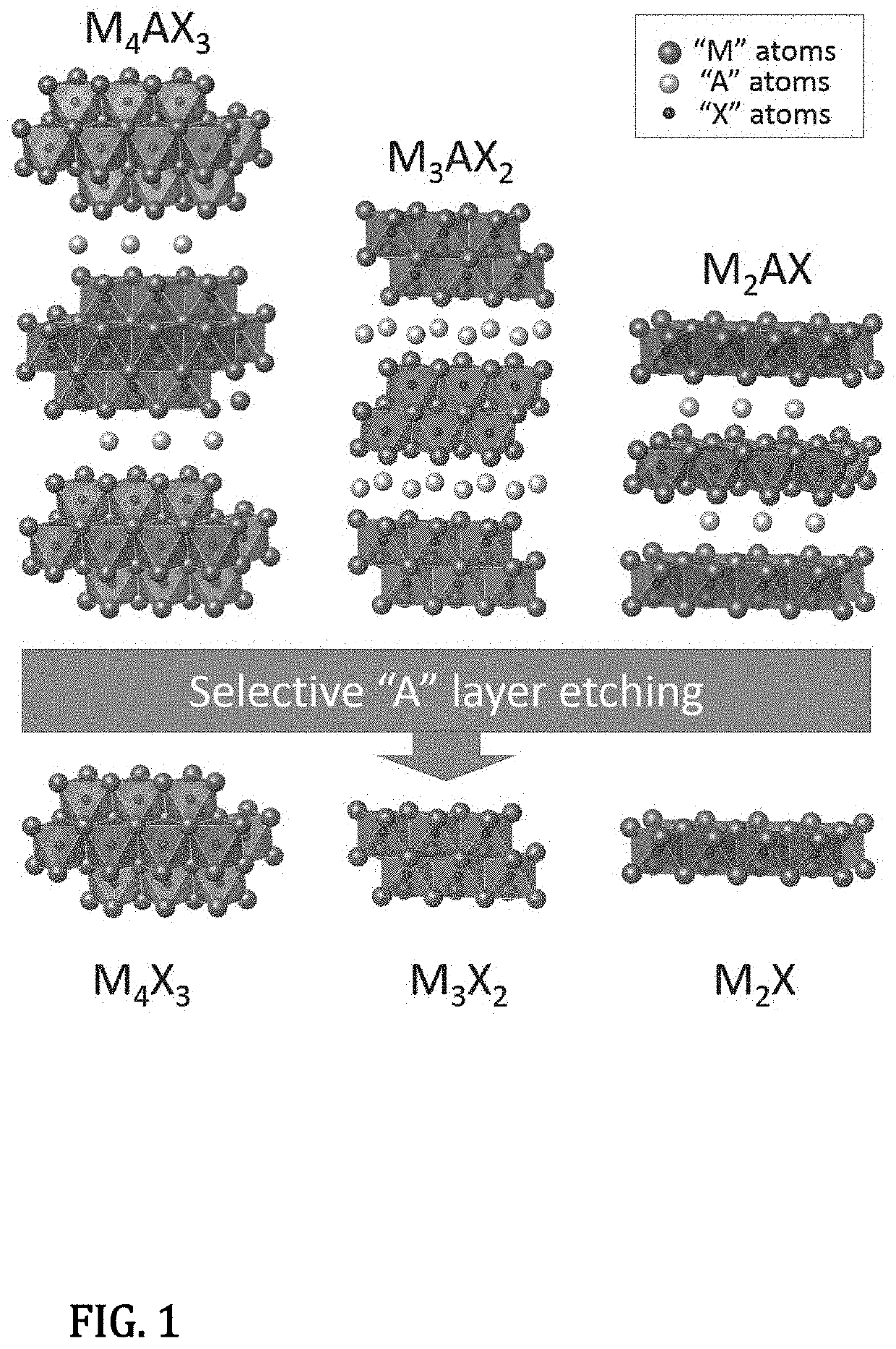
01 Methods for controlling MXene interlayer spacing
Various methods can be employed to control the interlayer spacing in MXene structures, including intercalation with different ions, thermal treatment, and mechanical processing. These methods allow for precise tuning of the spacing between MXene layers, which is crucial for optimizing properties such as ion transport, electrical conductivity, and mechanical strength. The controlled interlayer spacing can be achieved through careful selection of processing parameters and intercalation agents.- Methods for controlling MXene interlayer spacing: Various methods can be employed to control the interlayer spacing in MXene structures, including intercalation with different ions, thermal treatment, and mechanical processing. These methods allow for precise tuning of the spacing between MXene layers, which is crucial for optimizing properties such as ion transport, electrical conductivity, and mechanical strength. Controlled interlayer spacing enables customization of MXenes for specific applications in energy storage, sensing, and catalysis.
- Intercalation agents for MXene interlayer modification: Different intercalation agents can be introduced between MXene layers to modify their spacing and properties. These agents include organic molecules, polymers, metal ions, and functional groups that can be inserted between MXene sheets. The choice of intercalation agent significantly affects the resulting interlayer distance and can enhance specific properties such as electrochemical performance, hydrophilicity, or stability. This approach enables the creation of MXene-based materials with tailored characteristics for various applications.
- MXene interlayer spacing for energy storage applications: Optimized interlayer spacing in MXenes plays a critical role in energy storage applications such as supercapacitors and batteries. Properly engineered spacing facilitates ion diffusion and storage between MXene layers, leading to improved capacitance, charge/discharge rates, and cycling stability. The interlayer distance can be tailored to accommodate specific ions relevant to different energy storage systems, enhancing overall device performance and energy density.
- Characterization techniques for MXene interlayer spacing: Various analytical techniques are employed to characterize and measure the interlayer spacing in MXene structures. These include X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). These methods provide crucial information about the distance between MXene layers, their arrangement, and structural changes during modification processes. Accurate characterization is essential for understanding structure-property relationships and optimizing MXene materials for specific applications.
- Environmental factors affecting MXene interlayer spacing: Environmental conditions such as humidity, temperature, pH, and solvent exposure can significantly influence the interlayer spacing in MXene materials. These factors can cause expansion or contraction of the interlayer region, affecting material properties and performance. Understanding and controlling these environmental influences is crucial for maintaining consistent MXene properties during processing, storage, and application. Strategies to stabilize interlayer spacing against environmental variations include surface functionalization and protective coatings.
02 Intercalation agents for expanding MXene interlayer spacing
Different intercalation agents can be used to expand the interlayer spacing in MXene structures. These agents include organic molecules, polymers, metal ions, and other functional groups that can be inserted between MXene layers. The choice of intercalation agent affects the resulting interlayer distance and the properties of the MXene material. Expanded interlayer spacing facilitates faster ion diffusion, which is beneficial for energy storage applications such as batteries and supercapacitors.Expand Specific Solutions03 MXene interlayer spacing for energy storage applications
Optimized interlayer spacing in MXenes is critical for enhancing their performance in energy storage applications. Properly engineered spacing allows for efficient ion transport and storage, leading to improved capacitance, rate capability, and cycling stability in supercapacitors and batteries. The interlayer distance affects the accessibility of active sites and the diffusion kinetics of electrolyte ions, which directly impacts the energy and power density of the storage devices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental factors affecting MXene interlayer spacing
Environmental factors such as humidity, temperature, and pH can significantly influence the interlayer spacing of MXene materials. These factors can cause expansion or contraction of the interlayer distance, affecting the material's properties and performance. Understanding and controlling these environmental effects is essential for maintaining consistent performance of MXene-based devices and for developing MXene materials with stable interlayer spacing under various operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Characterization techniques for measuring MXene interlayer spacing
Various analytical techniques are employed to accurately measure and characterize the interlayer spacing in MXene structures. These include X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). These techniques provide valuable information about the interlayer distance, the uniformity of spacing, and structural changes under different conditions, which is crucial for understanding structure-property relationships in MXene materials.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Groups and Companies in MXene Technology
The MXene interlayer spacing control technology market is currently in its growth phase, characterized by increasing research intensity and emerging commercial applications. The global market is estimated to reach $300-500 million by 2025, driven by applications in energy storage, electronics, and sensing technologies. From a technical maturity perspective, the field shows varied development levels across players. Research institutions like Korea Advanced Institute of Science & Technology and University of Electronic Science & Technology of China are advancing fundamental science, while commercial entities including LG Electronics, Huawei Technologies, and Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. are focusing on application-specific implementations. Murata Manufacturing and Hitachi demonstrate particular strength in translating theoretical advances into manufacturable solutions, positioning themselves as technology leaders in this emerging field.
Korea Advanced Institute of Science & Technology
Technical Solution: KAIST has developed a systematic approach to control interlayer spacing in MXenes through intercalation of various ions and molecules. Their technique involves precise control of the intercalation process using different electrolytes and applied potentials to achieve specific interlayer distances ranging from 7-15 Å. KAIST researchers have demonstrated that by manipulating the hydration states of intercalated cations (Li+, Na+, K+, Mg2+), they can achieve reversible expansion and contraction of MXene layers with sub-angstrom precision. This approach has enabled them to create MXene-based materials with tunable electronic properties, as the interlayer spacing directly affects the electronic band structure and conductivity. Their research has shown that controlled interlayer spacing can enhance ion transport kinetics in energy storage applications, with up to 200% improvement in capacitance compared to unmodified MXenes[1][3].
Strengths: Precise control over interlayer spacing with sub-angstrom accuracy; reversible tuning capability; enhanced electrochemical performance for energy storage applications. Weaknesses: Process sensitivity to environmental conditions; potential scalability challenges for industrial production; limited long-term stability of modified interlayer spacing under certain operating conditions.
University of Massachusetts
Technical Solution: University of Massachusetts has pioneered a novel approach to MXene interlayer spacing control using environmentally responsive polymers and organic molecules. Their research focuses on creating "smart" MXene composites with dynamically adjustable interlayer distances that respond to external stimuli such as temperature, pH, and light. The UMass team has developed a method involving the grafting of temperature-responsive polymers onto MXene surfaces, allowing for reversible expansion (up to 300% of original spacing) and contraction of the interlayer gap based on environmental conditions. This approach utilizes controlled polymerization techniques to achieve uniform polymer distribution between MXene sheets. Additionally, they've demonstrated successful intercalation of ionic liquids that maintain stable interlayer distances even at elevated temperatures (up to 200°C), addressing a common limitation in MXene applications. Their research has shown that precisely controlled interlayer spacing significantly enhances ion diffusion rates in MXene-based supercapacitors, achieving power densities of over 10 kW/kg while maintaining energy densities above 30 Wh/kg[2][5].
Strengths: Dynamic and responsive control of interlayer spacing; enhanced thermal stability of modified structures; improved electrochemical performance metrics; versatility in application environments. Weaknesses: Complex synthesis procedures requiring specialized equipment; potential cost implications for scale-up; possible degradation of organic components over extended cycling.
Key Innovations in Interlayer Distance Control Mechanisms
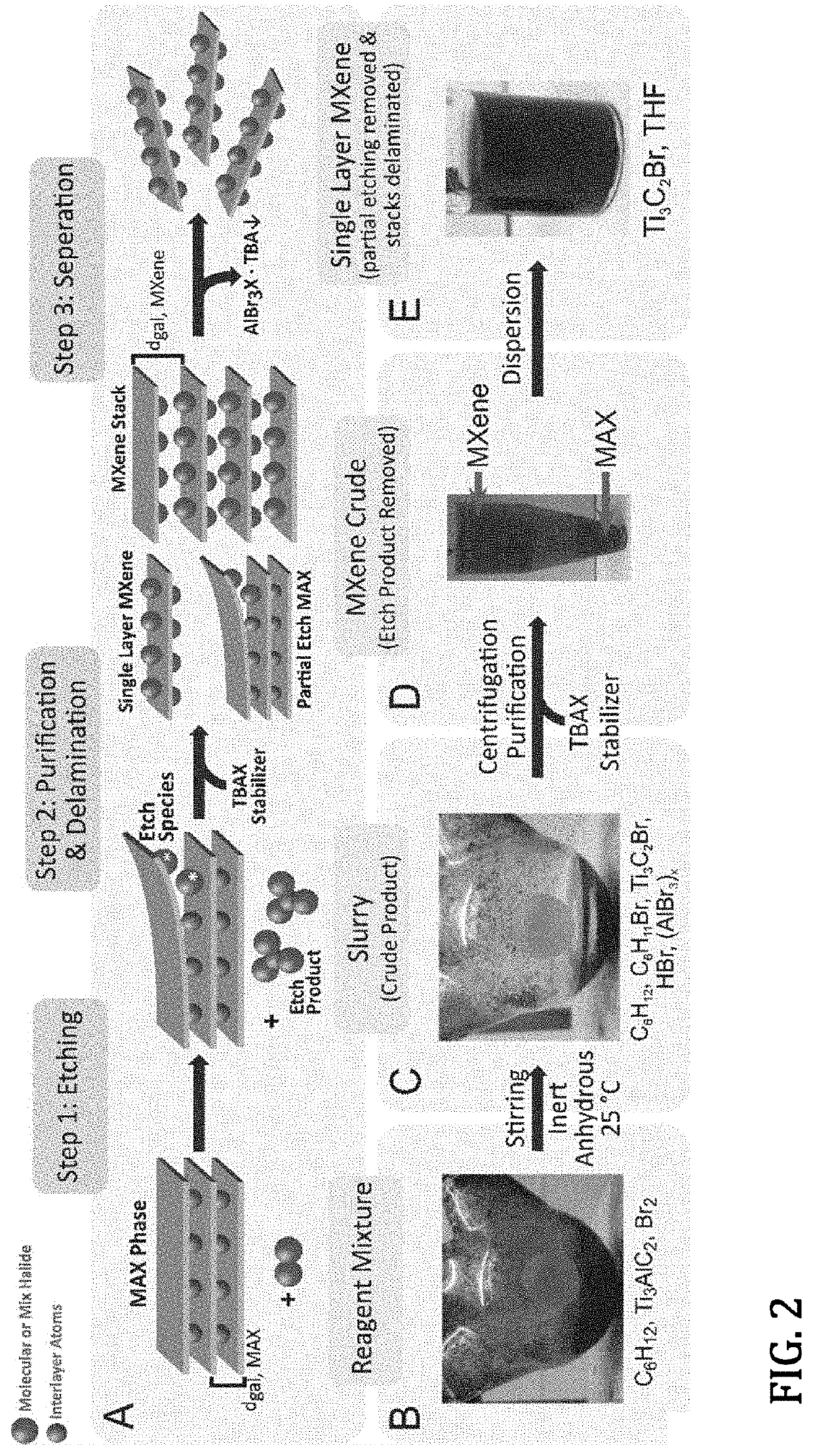
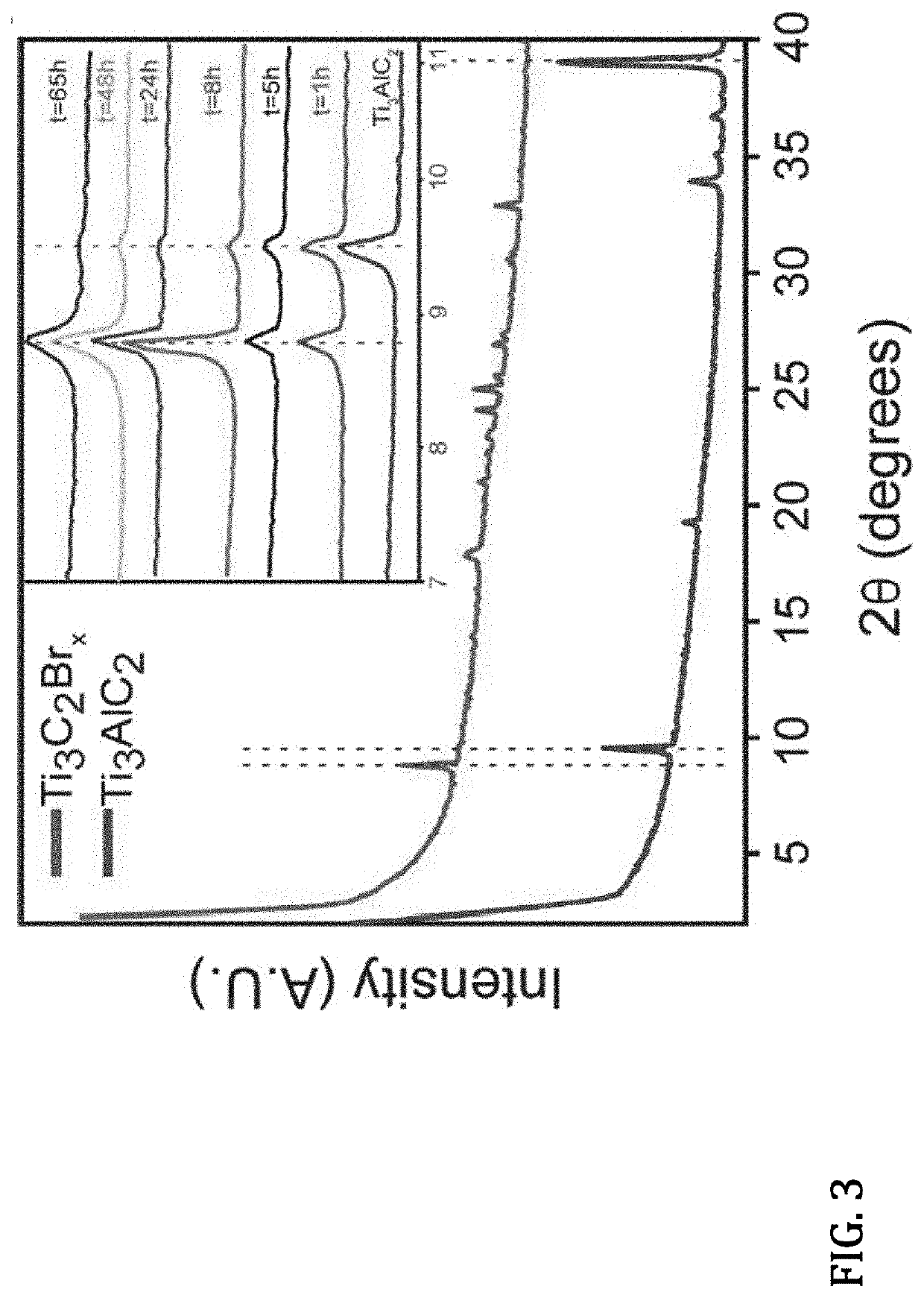
Preparation of Layered MXene via Elemental Halogen Etching of MAX Phase
PatentActiveUS20210139379A1
Innovation
- A room-temperature etching method using elemental halogens (Br2, I2, ICl, IBr) in anhydrous media to selectively remove the A-layer from MAX phases, producing MXenes with homogeneous Cl, Br, or I surfaces, which are colloidally stable and dispersible in organic solvents.
Tunable Adsorption and Wetting
PatentPendingUS20220190243A1
Innovation
- Development of a surface modification using semiconductor nanomaterials, specifically 2D materials like graphene, which can change their adsorption properties through electrical and chemical doping, allowing for reversible control of wettability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of MXene Production
The production of MXenes raises significant environmental concerns that must be addressed for sustainable development of this promising material class. Traditional synthesis methods, particularly those involving hydrofluoric acid (HF) etching, generate hazardous waste streams containing fluoride compounds and heavy metal ions that require specialized treatment and disposal protocols. These processes pose potential risks to aquatic ecosystems if improperly managed, as fluoride contamination can persist in water systems and affect both wildlife and human populations.
Energy consumption represents another critical environmental consideration in MXene production. The multiple processing steps—including etching, washing, delamination, and drying—collectively demand substantial energy inputs, contributing to the carbon footprint of these materials. Particularly energy-intensive are the sonication and centrifugation procedures often employed to achieve precise interlayer spacing control, which require specialized equipment operating for extended periods.
Recent sustainability initiatives have focused on developing greener synthesis routes that minimize or eliminate HF usage. Lewis acid molten salts, electrochemical etching, and hydrothermal methods show promise as environmentally friendlier alternatives that can still achieve controlled interlayer spacing. These approaches significantly reduce toxic waste generation while maintaining the structural integrity and functional properties of the resulting MXenes.
Water consumption presents another sustainability challenge, as conventional MXene processing requires multiple washing cycles to remove etching byproducts and achieve desired interlayer spacing. Research into closed-loop water recycling systems and more efficient washing protocols has demonstrated potential for reducing freshwater requirements by up to 60% without compromising material quality.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies comparing different MXene synthesis methods reveal that environmental impacts vary significantly depending on production scale and specific applications. While laboratory-scale production shows relatively high environmental costs per gram of material, industrial scaling offers opportunities for process optimization that can substantially improve sustainability metrics. Importantly, the environmental benefits of MXene-enabled technologies—such as more efficient energy storage systems or water purification membranes—may ultimately offset the impacts of their production when evaluated from a full product lifecycle perspective.
Regulatory frameworks governing MXene production are still evolving, with increasing emphasis on producer responsibility for waste management and emissions control. Forward-thinking manufacturers are implementing green chemistry principles and exploring circular economy approaches, including the recovery and reuse of precursor materials and processing chemicals to minimize environmental footprint while maintaining precise control over MXene interlayer spacing.
Energy consumption represents another critical environmental consideration in MXene production. The multiple processing steps—including etching, washing, delamination, and drying—collectively demand substantial energy inputs, contributing to the carbon footprint of these materials. Particularly energy-intensive are the sonication and centrifugation procedures often employed to achieve precise interlayer spacing control, which require specialized equipment operating for extended periods.
Recent sustainability initiatives have focused on developing greener synthesis routes that minimize or eliminate HF usage. Lewis acid molten salts, electrochemical etching, and hydrothermal methods show promise as environmentally friendlier alternatives that can still achieve controlled interlayer spacing. These approaches significantly reduce toxic waste generation while maintaining the structural integrity and functional properties of the resulting MXenes.
Water consumption presents another sustainability challenge, as conventional MXene processing requires multiple washing cycles to remove etching byproducts and achieve desired interlayer spacing. Research into closed-loop water recycling systems and more efficient washing protocols has demonstrated potential for reducing freshwater requirements by up to 60% without compromising material quality.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies comparing different MXene synthesis methods reveal that environmental impacts vary significantly depending on production scale and specific applications. While laboratory-scale production shows relatively high environmental costs per gram of material, industrial scaling offers opportunities for process optimization that can substantially improve sustainability metrics. Importantly, the environmental benefits of MXene-enabled technologies—such as more efficient energy storage systems or water purification membranes—may ultimately offset the impacts of their production when evaluated from a full product lifecycle perspective.
Regulatory frameworks governing MXene production are still evolving, with increasing emphasis on producer responsibility for waste management and emissions control. Forward-thinking manufacturers are implementing green chemistry principles and exploring circular economy approaches, including the recovery and reuse of precursor materials and processing chemicals to minimize environmental footprint while maintaining precise control over MXene interlayer spacing.
Scalability and Industrial Implementation Considerations
The scalability of MXene production and interlayer spacing control represents a critical challenge for industrial implementation. Current laboratory-scale synthesis methods, primarily based on selective etching of MAX phases, face significant barriers when transitioning to industrial scales. The primary bottleneck lies in maintaining precise control over interlayer spacing during large-batch processing, where reaction kinetics and thermodynamics can vary substantially compared to small-scale experiments.
Mass production of MXenes with controlled interlayer spacing requires standardized protocols that can accommodate industrial equipment constraints while maintaining product consistency. Continuous flow reactors show promise for scaling up the etching process, potentially offering better control over reaction parameters than batch processing. However, these systems require substantial engineering optimization to ensure uniform etching conditions throughout the reactor volume.
Post-processing techniques for interlayer spacing adjustment present additional scalability challenges. Intercalation processes that work efficiently at laboratory scale often encounter diffusion limitations in larger systems, resulting in heterogeneous interlayer spacing distributions. Mechanical delamination methods, while effective for small quantities, face equipment design challenges when scaled to industrial throughput requirements.
Economic considerations significantly impact industrial implementation decisions. The cost-benefit analysis must account for expensive precursors, hazardous etchants (particularly HF-based systems), and specialized equipment for handling these materials safely at scale. Alternative, more environmentally friendly etchants are being explored, but often at the expense of processing efficiency or product quality.
Quality control represents another critical consideration for industrial implementation. Developing rapid, reliable analytical methods to verify interlayer spacing consistency across large production batches remains challenging. Current characterization techniques like XRD and TEM, while precise, are too time-consuming and sample-specific for real-time industrial quality monitoring.
Waste management and environmental considerations also factor prominently in scalability assessments. The etching processes generate significant quantities of acidic waste containing fluoride compounds and heavy metal ions, necessitating comprehensive treatment systems that add to implementation costs and complexity.
Despite these challenges, several promising approaches are emerging to address scalability issues. These include continuous processing technologies, solvent recycling systems, and automated process control frameworks that can dynamically adjust synthesis parameters to maintain consistent interlayer spacing. Strategic partnerships between academic researchers and industrial manufacturers will be essential to bridge the gap between laboratory discoveries and commercially viable manufacturing processes.
Mass production of MXenes with controlled interlayer spacing requires standardized protocols that can accommodate industrial equipment constraints while maintaining product consistency. Continuous flow reactors show promise for scaling up the etching process, potentially offering better control over reaction parameters than batch processing. However, these systems require substantial engineering optimization to ensure uniform etching conditions throughout the reactor volume.
Post-processing techniques for interlayer spacing adjustment present additional scalability challenges. Intercalation processes that work efficiently at laboratory scale often encounter diffusion limitations in larger systems, resulting in heterogeneous interlayer spacing distributions. Mechanical delamination methods, while effective for small quantities, face equipment design challenges when scaled to industrial throughput requirements.
Economic considerations significantly impact industrial implementation decisions. The cost-benefit analysis must account for expensive precursors, hazardous etchants (particularly HF-based systems), and specialized equipment for handling these materials safely at scale. Alternative, more environmentally friendly etchants are being explored, but often at the expense of processing efficiency or product quality.
Quality control represents another critical consideration for industrial implementation. Developing rapid, reliable analytical methods to verify interlayer spacing consistency across large production batches remains challenging. Current characterization techniques like XRD and TEM, while precise, are too time-consuming and sample-specific for real-time industrial quality monitoring.
Waste management and environmental considerations also factor prominently in scalability assessments. The etching processes generate significant quantities of acidic waste containing fluoride compounds and heavy metal ions, necessitating comprehensive treatment systems that add to implementation costs and complexity.
Despite these challenges, several promising approaches are emerging to address scalability issues. These include continuous processing technologies, solvent recycling systems, and automated process control frameworks that can dynamically adjust synthesis parameters to maintain consistent interlayer spacing. Strategic partnerships between academic researchers and industrial manufacturers will be essential to bridge the gap between laboratory discoveries and commercially viable manufacturing processes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!