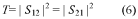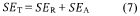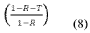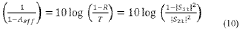MXenes for electromagnetic interference shielding in electronics
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
MXenes EMI Shielding Background and Objectives
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) has emerged as a critical challenge in modern electronics, with the proliferation of wireless communication systems, high-speed digital circuits, and miniaturized electronic devices. The need for effective EMI shielding materials has never been more pressing, as electromagnetic pollution continues to grow exponentially across consumer, industrial, and military applications.
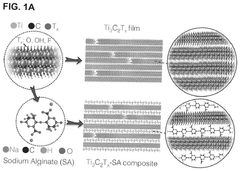
MXenes, a relatively new class of two-dimensional transition metal carbides and nitrides, have attracted significant attention since their discovery at Drexel University in 2011. These materials, with the general formula Mn+1XnTx (where M represents a transition metal, X is carbon or nitrogen, and Tx stands for surface terminations), have demonstrated exceptional properties that make them particularly promising for EMI shielding applications.
The historical development of EMI shielding materials has progressed from traditional metals to carbon-based materials such as graphene and carbon nanotubes, and now to MXenes. This evolution has been driven by the increasing demand for lightweight, flexible, and highly effective shielding materials that can be integrated into next-generation electronic devices without compromising performance or adding substantial weight.
MXenes offer a unique combination of high electrical conductivity, hydrophilicity, and mechanical flexibility. Their layered structure, coupled with abundant surface terminations, provides an ideal platform for electromagnetic wave absorption and reflection. Initial research has demonstrated that MXene-based composites can achieve shielding effectiveness values exceeding 70 dB, which is substantially higher than many conventional materials at comparable thicknesses.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate the potential of MXenes for EMI shielding applications in electronics. This includes understanding the fundamental mechanisms behind their exceptional shielding properties, exploring various synthesis methods and processing techniques to optimize their performance, and investigating practical implementation strategies for different electronic applications.
Additionally, this research aims to identify the key challenges and limitations associated with MXene-based EMI shielding materials, such as long-term stability, scalable production, and integration with existing manufacturing processes. By addressing these challenges, we seek to accelerate the transition of MXenes from laboratory curiosities to commercially viable EMI shielding solutions.
The ultimate goal is to establish a clear technological roadmap for the development and implementation of MXene-based EMI shielding materials, positioning them as next-generation solutions for the increasingly complex electromagnetic environments of modern electronic systems.
MXenes, a relatively new class of two-dimensional transition metal carbides and nitrides, have attracted significant attention since their discovery at Drexel University in 2011. These materials, with the general formula Mn+1XnTx (where M represents a transition metal, X is carbon or nitrogen, and Tx stands for surface terminations), have demonstrated exceptional properties that make them particularly promising for EMI shielding applications.
The historical development of EMI shielding materials has progressed from traditional metals to carbon-based materials such as graphene and carbon nanotubes, and now to MXenes. This evolution has been driven by the increasing demand for lightweight, flexible, and highly effective shielding materials that can be integrated into next-generation electronic devices without compromising performance or adding substantial weight.
MXenes offer a unique combination of high electrical conductivity, hydrophilicity, and mechanical flexibility. Their layered structure, coupled with abundant surface terminations, provides an ideal platform for electromagnetic wave absorption and reflection. Initial research has demonstrated that MXene-based composites can achieve shielding effectiveness values exceeding 70 dB, which is substantially higher than many conventional materials at comparable thicknesses.
The primary objective of this technical research is to comprehensively evaluate the potential of MXenes for EMI shielding applications in electronics. This includes understanding the fundamental mechanisms behind their exceptional shielding properties, exploring various synthesis methods and processing techniques to optimize their performance, and investigating practical implementation strategies for different electronic applications.
Additionally, this research aims to identify the key challenges and limitations associated with MXene-based EMI shielding materials, such as long-term stability, scalable production, and integration with existing manufacturing processes. By addressing these challenges, we seek to accelerate the transition of MXenes from laboratory curiosities to commercially viable EMI shielding solutions.
The ultimate goal is to establish a clear technological roadmap for the development and implementation of MXene-based EMI shielding materials, positioning them as next-generation solutions for the increasingly complex electromagnetic environments of modern electronic systems.
Market Analysis for EMI Shielding Solutions
The global electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by the proliferation of electronic devices and the increasing need for signal integrity in compact electronic systems. As of 2023, the EMI shielding market was valued at approximately 7 billion USD, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% through 2030, potentially reaching 10.4 billion USD by the end of the forecast period.
The demand for EMI shielding solutions is particularly strong in consumer electronics, which accounts for nearly 35% of the total market share. This is followed by automotive electronics (22%), telecommunications (18%), healthcare devices (12%), and aerospace applications (8%). The remaining market share is distributed among various industrial applications and emerging sectors.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific dominates the EMI shielding market, representing over 45% of global demand, primarily due to the concentration of electronics manufacturing in countries like China, South Korea, Japan, and Taiwan. North America follows with approximately 25% market share, driven by advanced telecommunications infrastructure and defense applications. Europe accounts for about 20% of the market, with strong demand from automotive and industrial sectors.
Traditional EMI shielding materials such as copper, aluminum, and various conductive polymers currently dominate the market landscape, collectively accounting for over 70% of all shielding solutions deployed. However, there is a clear shift toward advanced materials that offer superior performance characteristics while addressing limitations of conventional options.
MXenes, as emerging two-dimensional materials for EMI shielding, are positioned to disrupt this established market. The potential market for MXene-based EMI shielding solutions is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 15-18% over the next five years, significantly outpacing the overall market growth. This accelerated adoption is driven by MXenes' exceptional shielding effectiveness (reaching up to 70-90 dB) at significantly lower thicknesses compared to traditional materials.
Key market drivers for MXene-based EMI shielding include the miniaturization trend in electronics, increasing operating frequencies in 5G and upcoming 6G networks, and stringent electromagnetic compatibility regulations across major markets. Additionally, the growing emphasis on lightweight components in electric vehicles and portable electronics creates a favorable environment for MXene adoption.
Despite promising growth prospects, challenges remain in scaling production, standardizing material properties, and reducing manufacturing costs to achieve price parity with established solutions. Current production costs for MXene-based shielding materials are estimated to be 3-5 times higher than conventional alternatives, presenting a significant barrier to widespread commercial adoption.
The demand for EMI shielding solutions is particularly strong in consumer electronics, which accounts for nearly 35% of the total market share. This is followed by automotive electronics (22%), telecommunications (18%), healthcare devices (12%), and aerospace applications (8%). The remaining market share is distributed among various industrial applications and emerging sectors.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific dominates the EMI shielding market, representing over 45% of global demand, primarily due to the concentration of electronics manufacturing in countries like China, South Korea, Japan, and Taiwan. North America follows with approximately 25% market share, driven by advanced telecommunications infrastructure and defense applications. Europe accounts for about 20% of the market, with strong demand from automotive and industrial sectors.
Traditional EMI shielding materials such as copper, aluminum, and various conductive polymers currently dominate the market landscape, collectively accounting for over 70% of all shielding solutions deployed. However, there is a clear shift toward advanced materials that offer superior performance characteristics while addressing limitations of conventional options.
MXenes, as emerging two-dimensional materials for EMI shielding, are positioned to disrupt this established market. The potential market for MXene-based EMI shielding solutions is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 15-18% over the next five years, significantly outpacing the overall market growth. This accelerated adoption is driven by MXenes' exceptional shielding effectiveness (reaching up to 70-90 dB) at significantly lower thicknesses compared to traditional materials.
Key market drivers for MXene-based EMI shielding include the miniaturization trend in electronics, increasing operating frequencies in 5G and upcoming 6G networks, and stringent electromagnetic compatibility regulations across major markets. Additionally, the growing emphasis on lightweight components in electric vehicles and portable electronics creates a favorable environment for MXene adoption.
Despite promising growth prospects, challenges remain in scaling production, standardizing material properties, and reducing manufacturing costs to achieve price parity with established solutions. Current production costs for MXene-based shielding materials are estimated to be 3-5 times higher than conventional alternatives, presenting a significant barrier to widespread commercial adoption.
Current State and Challenges in MXenes EMI Shielding
MXenes have emerged as promising materials for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding applications due to their exceptional electrical conductivity, tunable surface chemistry, and high aspect ratio. Currently, the global research landscape shows significant advancements in MXene-based EMI shielding materials, with pioneering work primarily concentrated in the United States, China, and several European countries.
The state-of-the-art MXene EMI shielding materials demonstrate remarkable shielding effectiveness, with Ti3C2Tx (the most studied MXene) exhibiting values exceeding 90 dB at thicknesses below 100 μm. This performance significantly surpasses traditional metal-based and carbon-based shielding materials, positioning MXenes as frontrunners in next-generation EMI shielding solutions.
Despite these promising results, several critical challenges impede the widespread industrial adoption of MXene-based EMI shielding materials. The primary obstacle remains the oxidative instability of MXenes in ambient conditions, with most variants showing significant degradation in electrical conductivity and consequently shielding effectiveness over time. This instability is particularly pronounced in humid environments, limiting practical applications.
Scalable synthesis represents another major hurdle. Current production methods, primarily based on selective etching of MAX phases, face limitations in terms of yield, purity, and batch-to-batch consistency. The use of hazardous etchants like hydrofluoric acid (HF) further complicates large-scale manufacturing, raising environmental and safety concerns.
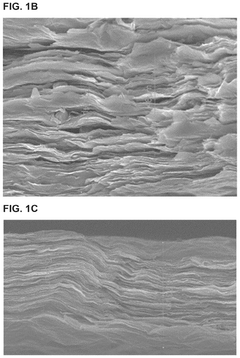
The mechanical properties of pure MXene films present additional challenges. While MXenes exhibit excellent flexibility, their relatively poor mechanical strength and durability under repeated bending or stretching limit their application in flexible electronics. This necessitates the development of MXene composites with enhanced mechanical resilience.
Cost factors also significantly constrain commercial viability. The multi-step synthesis process, coupled with expensive precursors and purification requirements, results in high production costs that currently outweigh the performance benefits for mass-market applications.
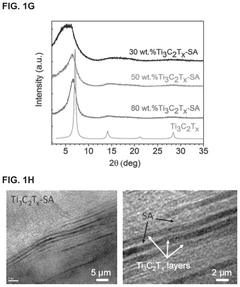
From a technical perspective, controlling the thickness, density, and microstructure of MXene-based shielding materials remains challenging. These parameters critically influence the EMI shielding mechanism, which involves reflection, absorption, and multiple reflections of electromagnetic waves. Optimizing these structural features to achieve the ideal balance between reflection and absorption-dominated shielding is an ongoing research focus.
Standardization issues further complicate progress in the field. The lack of universally accepted testing protocols and standards for MXene-based EMI shielding materials makes direct comparison between different research outputs difficult, hindering systematic advancement of the technology.
The state-of-the-art MXene EMI shielding materials demonstrate remarkable shielding effectiveness, with Ti3C2Tx (the most studied MXene) exhibiting values exceeding 90 dB at thicknesses below 100 μm. This performance significantly surpasses traditional metal-based and carbon-based shielding materials, positioning MXenes as frontrunners in next-generation EMI shielding solutions.
Despite these promising results, several critical challenges impede the widespread industrial adoption of MXene-based EMI shielding materials. The primary obstacle remains the oxidative instability of MXenes in ambient conditions, with most variants showing significant degradation in electrical conductivity and consequently shielding effectiveness over time. This instability is particularly pronounced in humid environments, limiting practical applications.
Scalable synthesis represents another major hurdle. Current production methods, primarily based on selective etching of MAX phases, face limitations in terms of yield, purity, and batch-to-batch consistency. The use of hazardous etchants like hydrofluoric acid (HF) further complicates large-scale manufacturing, raising environmental and safety concerns.
The mechanical properties of pure MXene films present additional challenges. While MXenes exhibit excellent flexibility, their relatively poor mechanical strength and durability under repeated bending or stretching limit their application in flexible electronics. This necessitates the development of MXene composites with enhanced mechanical resilience.
Cost factors also significantly constrain commercial viability. The multi-step synthesis process, coupled with expensive precursors and purification requirements, results in high production costs that currently outweigh the performance benefits for mass-market applications.
From a technical perspective, controlling the thickness, density, and microstructure of MXene-based shielding materials remains challenging. These parameters critically influence the EMI shielding mechanism, which involves reflection, absorption, and multiple reflections of electromagnetic waves. Optimizing these structural features to achieve the ideal balance between reflection and absorption-dominated shielding is an ongoing research focus.
Standardization issues further complicate progress in the field. The lack of universally accepted testing protocols and standards for MXene-based EMI shielding materials makes direct comparison between different research outputs difficult, hindering systematic advancement of the technology.
Current MXenes-Based EMI Shielding Solutions
01 MXene-based composites for EMI shielding
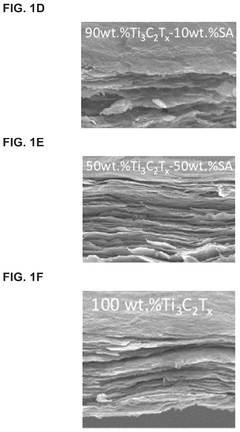
MXene-based composites can be formulated with various polymers or materials to create effective electromagnetic interference shielding solutions. These composites leverage the high conductivity and 2D structure of MXenes to absorb and reflect electromagnetic waves. The combination of MXenes with polymers or other materials can enhance flexibility, processability, and durability while maintaining excellent shielding effectiveness across a wide frequency range.- MXene-based composites for EMI shielding: MXene-based composites combine the excellent electromagnetic interference shielding properties of MXenes with other materials to enhance performance. These composites typically incorporate polymers, carbon materials, or metal oxides to create flexible, lightweight, and highly effective EMI shielding materials. The synergistic effect between MXenes and other components results in improved mechanical properties, thermal stability, and broader frequency range protection.
- Multilayer MXene structures for enhanced EMI shielding: Multilayer structures incorporating MXenes can significantly improve electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness. These structures typically consist of alternating layers of MXenes and other materials, creating a gradient or sandwich-like configuration. The multilayer design enables multiple reflection and absorption mechanisms, effectively blocking electromagnetic waves across a wide frequency range while maintaining flexibility and reduced thickness compared to traditional shielding materials.
- Surface-modified MXenes for EMI shielding applications: Surface modification of MXenes can enhance their electromagnetic interference shielding properties. Various functionalization methods, including chemical treatment, doping, and surface decoration with nanoparticles, can be employed to tailor the electronic properties and improve the interaction with electromagnetic waves. These modifications can increase the electrical conductivity, create additional interfaces for wave reflection, and enhance the absorption capabilities of MXenes.
- MXene-based coatings and films for flexible electronics shielding: MXene-based coatings and films provide effective electromagnetic interference shielding for flexible electronics. These thin, lightweight, and conformable materials can be applied to various substrates through methods such as spray coating, dip coating, or vacuum filtration. The resulting films offer excellent EMI shielding effectiveness while maintaining flexibility, making them ideal for wearable devices, flexible displays, and other applications where traditional rigid shielding materials are unsuitable.
- MXene-based foams and aerogels for lightweight EMI shielding: MXene-based foams and aerogels represent a class of ultralight materials with exceptional electromagnetic interference shielding capabilities. These three-dimensional porous structures combine the high electrical conductivity of MXenes with low density, creating effective EMI shields with minimal weight. The porous architecture provides multiple pathways for electromagnetic wave reflection and absorption, while the large surface area enhances the interaction with incident radiation, resulting in superior shielding performance.
02 Multilayer MXene structures for enhanced shielding
Multilayered structures incorporating MXenes can significantly improve electromagnetic interference shielding performance. These structures typically consist of alternating layers of MXenes and other materials, creating multiple interfaces that enhance reflection and absorption of electromagnetic waves. The layered architecture allows for tunable shielding properties and can be optimized for specific frequency ranges, making them suitable for various applications including electronic devices and aerospace components.Expand Specific Solutions03 MXene-metal hybrid materials for EMI shielding
Hybrid materials combining MXenes with metals offer superior electromagnetic interference shielding capabilities. The synergistic effect between MXenes and metallic components enhances electrical conductivity and creates multiple reflection and absorption mechanisms for electromagnetic waves. These hybrid materials can be fabricated as coatings, films, or bulk composites and provide exceptional shielding effectiveness while maintaining lightweight properties compared to traditional metal-only shields.Expand Specific Solutions04 Flexible and lightweight MXene films for portable electronics
Flexible and lightweight MXene films can be specifically designed for electromagnetic interference shielding in portable electronic devices. These films combine the excellent conductivity of MXenes with mechanical flexibility, allowing them to be integrated into curved surfaces and compact designs. The films can be fabricated through various methods including vacuum filtration, spray coating, or layer-by-layer assembly, resulting in thin yet effective shielding layers that do not significantly increase the weight or bulk of electronic devices.Expand Specific Solutions05 MXene-based coatings for EMI shielding applications
MXene-based coatings provide an effective solution for applying electromagnetic interference shielding to various substrates. These coatings can be formulated as paints, sprays, or dip-coating solutions that adhere well to different materials including plastics, textiles, and metals. The thin MXene coatings offer significant shielding effectiveness while adding minimal weight and thickness to the protected components. Additionally, these coatings can be engineered to provide other functionalities such as heat dissipation or corrosion resistance alongside EMI shielding.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in MXenes Development
The electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding market using MXenes is in a rapid growth phase, driven by increasing demand for electronic device protection. The market is projected to expand significantly as electronics miniaturization continues, with an estimated value reaching billions by 2030. Technologically, MXenes are transitioning from laboratory research to commercial applications, with Drexel University leading fundamental research as the pioneer of MXene technology. Chinese institutions like Beihang University and Sichuan University are advancing application development, while companies including Murata Manufacturing and SK Hynix are exploring industrial implementation. The competitive landscape features academic-industrial collaborations, with research institutions providing innovation and companies focusing on scalable manufacturing processes and integration into existing product lines.
Drexel University
Technical Solution: Drexel University pioneered MXene technology and leads research in electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding applications. Their approach focuses on two-dimensional titanium carbide MXenes (Ti3C2Tx) with exceptional conductivity properties. The university has developed synthesis methods yielding MXene films and coatings with EMI shielding effectiveness exceeding 45 dB at minimal thicknesses (<10 μm), outperforming traditional metal shields. Their technology leverages MXenes' unique combination of high electrical conductivity and hydrophilicity, enabling solution processing into flexible, lightweight shields. Drexel researchers have demonstrated that MXene-based composites can achieve effective EMI shielding through multiple mechanisms including reflection and absorption of electromagnetic waves. Recent innovations include spray-coated MXene films that maintain shielding performance even after mechanical deformation and environmental exposure[1][3], making them suitable for next-generation flexible electronics.
Strengths: World-leading expertise in MXene synthesis and characterization; pioneered fundamental understanding of MXene EMI shielding mechanisms; extensive intellectual property portfolio. Weaknesses: Scalability challenges for industrial production; potential oxidative stability issues in certain environmental conditions; relatively higher production costs compared to conventional materials.
Murata Manufacturing Co. Ltd.
Technical Solution: Murata Manufacturing has developed proprietary MXene-based EMI shielding solutions for electronics components and modules. Their approach integrates MXene materials into their existing multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) and RF modules manufacturing processes. Murata's technology utilizes MXene's exceptional conductivity and 2D structure to create ultra-thin shielding layers (typically 1-5 μm) that can be directly applied to electronic components. Their innovation includes specialized MXene-polymer composites optimized for different frequency ranges (from MHz to GHz), particularly targeting 5G applications. Murata has successfully commercialized MXene-enhanced EMI shields that demonstrate shielding effectiveness of 30-40 dB across broad frequency spectra while maintaining flexibility and adhesion to various substrate materials. The company has integrated these solutions into their miniaturized components for smartphones, wearables, and automotive electronics, where space constraints make traditional shielding methods impractical[5]. Their manufacturing process includes proprietary surface functionalization techniques that enhance MXene's environmental stability and compatibility with existing electronics assembly processes.
Strengths: Strong manufacturing infrastructure for scaled production; established supply chain integration; ability to customize solutions for specific electronic applications; extensive experience in electronics packaging. Weaknesses: Relatively new to MXene technology compared to academic leaders; dependence on external MXene supply; limited fundamental research capabilities compared to university competitors.
Critical Patents and Research in MXenes EMI Applications
Two-dimensional metal carbide, nitride, and carbonitride films and composites for EMI shielding
PatentWO2017184957A1
Innovation
- The use of two-dimensional (2D) transition metal carbides, nitrides, and carbonitrides, specifically MXene films and MXene-polymer composites, which provide high EMI shielding effectiveness due to their exceptional electrical conductivity and mechanical properties, outperforming traditional materials by offering lightweight, flexible, and easily fabricated solutions.
Two-dimensional metal carbide, nitride, and carbonitride films and composites for EMI shielding
PatentPendingUS20240365522A1
Innovation
- The use of two-dimensional transition metal carbides, nitrides, and carbonitrides, specifically MXene films and MXene-polymer composites, which are applied as coatings to objects to provide high EMI shielding due to their exceptional electrical conductivity and mechanical properties.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental implications of MXenes in electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding applications represent a critical dimension of their technological assessment. MXenes offer potential sustainability advantages over traditional EMI shielding materials like metals and carbon-based composites. Their exceptional shielding effectiveness at lower thicknesses translates to material efficiency, potentially reducing resource consumption in electronics manufacturing. This material efficiency extends to weight reduction in portable electronics, which can decrease energy requirements during transportation and use phases.
Manufacturing processes for MXenes, however, present environmental challenges that require careful consideration. The synthesis typically involves etching procedures using hydrofluoric acid or other strong etchants, generating hazardous waste streams that demand proper treatment and disposal protocols. Recent research has focused on developing greener synthesis routes, including less toxic etchants and more environmentally benign processing methods, though these alternatives often face trade-offs between environmental impact and material performance.
The life cycle assessment of MXene-based EMI shielding materials reveals both advantages and concerns. While their durability may extend product lifespans, questions remain regarding their long-term stability in various environmental conditions. The potential for MXene particles to leach into the environment during product use or disposal represents an emerging concern that requires further toxicological and ecological impact studies.
End-of-life management presents another critical sustainability consideration. The complex integration of MXenes into electronic components may complicate recycling efforts, potentially contributing to electronic waste challenges. Research into recovery methods for MXenes from discarded electronics remains in nascent stages, though their metallic components theoretically offer recycling potential if effective separation techniques can be developed.
Energy efficiency gains represent a significant positive environmental impact of MXene-based EMI shielding. By enabling more compact electronic designs with reduced interference issues, MXenes can contribute to overall device energy efficiency. This efficiency improvement, when scaled across millions of electronic devices, could translate to meaningful energy conservation and associated carbon emission reductions.
Regulatory frameworks governing nanomaterials in electronics are evolving to address these emerging materials. Compliance with regulations such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) will influence the commercial viability of MXene-based EMI shielding solutions. Proactive engagement with evolving regulatory standards will be essential for successful market integration.
Manufacturing processes for MXenes, however, present environmental challenges that require careful consideration. The synthesis typically involves etching procedures using hydrofluoric acid or other strong etchants, generating hazardous waste streams that demand proper treatment and disposal protocols. Recent research has focused on developing greener synthesis routes, including less toxic etchants and more environmentally benign processing methods, though these alternatives often face trade-offs between environmental impact and material performance.
The life cycle assessment of MXene-based EMI shielding materials reveals both advantages and concerns. While their durability may extend product lifespans, questions remain regarding their long-term stability in various environmental conditions. The potential for MXene particles to leach into the environment during product use or disposal represents an emerging concern that requires further toxicological and ecological impact studies.
End-of-life management presents another critical sustainability consideration. The complex integration of MXenes into electronic components may complicate recycling efforts, potentially contributing to electronic waste challenges. Research into recovery methods for MXenes from discarded electronics remains in nascent stages, though their metallic components theoretically offer recycling potential if effective separation techniques can be developed.
Energy efficiency gains represent a significant positive environmental impact of MXene-based EMI shielding. By enabling more compact electronic designs with reduced interference issues, MXenes can contribute to overall device energy efficiency. This efficiency improvement, when scaled across millions of electronic devices, could translate to meaningful energy conservation and associated carbon emission reductions.
Regulatory frameworks governing nanomaterials in electronics are evolving to address these emerging materials. Compliance with regulations such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) will influence the commercial viability of MXene-based EMI shielding solutions. Proactive engagement with evolving regulatory standards will be essential for successful market integration.
Manufacturing Scalability and Cost Analysis
The scalability of MXene manufacturing represents a critical challenge for its widespread adoption in electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding applications. Current laboratory-scale synthesis methods predominantly rely on selective etching of MAX phases using hydrofluoric acid (HF), which presents significant safety concerns and scalability limitations. Alternative synthesis routes using fluoride salts (LiF + HCl) have improved safety profiles but still face throughput constraints. Industrial-scale production would require reactor designs capable of handling corrosive chemicals while maintaining precise control over reaction parameters.
Cost analysis reveals that raw material expenses constitute approximately 40-50% of total production costs, with titanium-based precursors being particularly price-sensitive. Energy consumption during synthesis and subsequent processing (delamination, filtration, drying) accounts for an additional 20-30% of costs. Current estimates place MXene production costs between $200-500 per gram for high-quality material, significantly higher than conventional EMI shielding materials like copper ($0.01/g) or carbon-based composites ($0.1-5/g).
Manufacturing yield remains a persistent challenge, with typical conversion efficiencies of 60-75% from MAX phase to final MXene products. Process optimization could potentially improve yields to 85-90%, substantially reducing per-unit costs. Waste management represents another significant cost factor, as the acidic byproducts require neutralization and proper disposal, adding 10-15% to overall production expenses.
Recent advancements in continuous flow processing show promise for scaling production. Several research groups have demonstrated semi-continuous synthesis methods capable of producing gram-scale quantities per hour, representing a significant improvement over batch processing. Industry partnerships between academic institutions and materials manufacturers are exploring pilot-scale facilities with projected capacities of 1-10 kg/month.
Economic viability analysis indicates that MXene-based EMI shielding solutions become cost-competitive with traditional materials at production volumes exceeding 100 kg/year. This threshold could be reached within 3-5 years given current scaling trajectories. The development of recycling methodologies for production waste streams could further improve economic feasibility by recovering valuable precursor materials and reducing environmental impact.
For commercial adoption, standardization of MXene quality metrics and processing protocols remains essential. Current variations in flake size, oxidation state, and surface termination between production batches create challenges for consistent performance in EMI shielding applications. Industry-wide quality standards and testing protocols would accelerate manufacturing scale-up and market acceptance.
Cost analysis reveals that raw material expenses constitute approximately 40-50% of total production costs, with titanium-based precursors being particularly price-sensitive. Energy consumption during synthesis and subsequent processing (delamination, filtration, drying) accounts for an additional 20-30% of costs. Current estimates place MXene production costs between $200-500 per gram for high-quality material, significantly higher than conventional EMI shielding materials like copper ($0.01/g) or carbon-based composites ($0.1-5/g).
Manufacturing yield remains a persistent challenge, with typical conversion efficiencies of 60-75% from MAX phase to final MXene products. Process optimization could potentially improve yields to 85-90%, substantially reducing per-unit costs. Waste management represents another significant cost factor, as the acidic byproducts require neutralization and proper disposal, adding 10-15% to overall production expenses.
Recent advancements in continuous flow processing show promise for scaling production. Several research groups have demonstrated semi-continuous synthesis methods capable of producing gram-scale quantities per hour, representing a significant improvement over batch processing. Industry partnerships between academic institutions and materials manufacturers are exploring pilot-scale facilities with projected capacities of 1-10 kg/month.
Economic viability analysis indicates that MXene-based EMI shielding solutions become cost-competitive with traditional materials at production volumes exceeding 100 kg/year. This threshold could be reached within 3-5 years given current scaling trajectories. The development of recycling methodologies for production waste streams could further improve economic feasibility by recovering valuable precursor materials and reducing environmental impact.
For commercial adoption, standardization of MXene quality metrics and processing protocols remains essential. Current variations in flake size, oxidation state, and surface termination between production batches create challenges for consistent performance in EMI shielding applications. Industry-wide quality standards and testing protocols would accelerate manufacturing scale-up and market acceptance.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!