MXenes for enhancing thermal management in electronic devices
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
MXenes Background and Thermal Management Goals
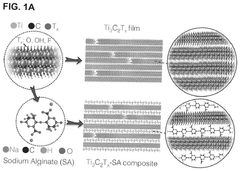
MXenes represent a relatively new class of two-dimensional (2D) transition metal carbides, nitrides, and carbonitrides that were first discovered in 2011 by researchers at Drexel University. These materials are derived from MAX phases through selective etching of the A-layer atoms, resulting in a layered structure with the general formula Mn+1XnTx, where M represents a transition metal, X is carbon or nitrogen, and Tx stands for surface terminations such as -OH, -O, or -F. Since their discovery, MXenes have attracted significant attention due to their unique combination of metallic conductivity and hydrophilic surfaces.
The evolution of MXenes has progressed rapidly over the past decade, with researchers developing various synthesis methods beyond the original HF etching approach, including milder etching protocols and delamination techniques that preserve the 2D structure while enhancing processability. The family of MXenes has expanded to include more than 30 different compositions, each with distinct properties that can be further tuned through surface modifications and compositional engineering.
In the context of thermal management for electronic devices, MXenes have emerged as promising candidates due to their exceptional thermal conductivity, which can exceed 1000 W/m·K in certain compositions—comparable to or even surpassing traditional thermal management materials like copper (400 W/m·K) and aluminum (237 W/m·K). This high thermal conductivity, combined with their 2D nature, makes MXenes particularly suitable for addressing the critical challenge of heat dissipation in increasingly miniaturized and powerful electronic components.
The primary technical goal for MXenes in thermal management applications is to develop scalable, cost-effective solutions that can efficiently transfer heat away from hotspots in electronic devices, thereby preventing performance degradation and extending device lifespan. Specific objectives include enhancing the in-plane and cross-plane thermal conductivity of MXene-based composites, improving their integration with existing electronic packaging materials, and ensuring long-term stability under operating conditions.
Current trends in MXene research for thermal management focus on several key areas: optimizing synthesis methods for large-scale production, developing MXene-polymer composites with enhanced thermal interfaces, creating hierarchical structures that maximize heat transfer pathways, and exploring hybrid systems that combine MXenes with other high-thermal-conductivity materials such as graphene or boron nitride.
As electronic devices continue to advance toward higher power densities and smaller form factors, the demand for innovative thermal management solutions becomes increasingly urgent. MXenes, with their tunable properties and exceptional thermal characteristics, represent a promising frontier in addressing these challenges, potentially enabling the next generation of high-performance, thermally efficient electronic systems.
The evolution of MXenes has progressed rapidly over the past decade, with researchers developing various synthesis methods beyond the original HF etching approach, including milder etching protocols and delamination techniques that preserve the 2D structure while enhancing processability. The family of MXenes has expanded to include more than 30 different compositions, each with distinct properties that can be further tuned through surface modifications and compositional engineering.
In the context of thermal management for electronic devices, MXenes have emerged as promising candidates due to their exceptional thermal conductivity, which can exceed 1000 W/m·K in certain compositions—comparable to or even surpassing traditional thermal management materials like copper (400 W/m·K) and aluminum (237 W/m·K). This high thermal conductivity, combined with their 2D nature, makes MXenes particularly suitable for addressing the critical challenge of heat dissipation in increasingly miniaturized and powerful electronic components.
The primary technical goal for MXenes in thermal management applications is to develop scalable, cost-effective solutions that can efficiently transfer heat away from hotspots in electronic devices, thereby preventing performance degradation and extending device lifespan. Specific objectives include enhancing the in-plane and cross-plane thermal conductivity of MXene-based composites, improving their integration with existing electronic packaging materials, and ensuring long-term stability under operating conditions.
Current trends in MXene research for thermal management focus on several key areas: optimizing synthesis methods for large-scale production, developing MXene-polymer composites with enhanced thermal interfaces, creating hierarchical structures that maximize heat transfer pathways, and exploring hybrid systems that combine MXenes with other high-thermal-conductivity materials such as graphene or boron nitride.
As electronic devices continue to advance toward higher power densities and smaller form factors, the demand for innovative thermal management solutions becomes increasingly urgent. MXenes, with their tunable properties and exceptional thermal characteristics, represent a promising frontier in addressing these challenges, potentially enabling the next generation of high-performance, thermally efficient electronic systems.
Market Demand for Advanced Electronic Cooling Solutions
The electronic device market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with global shipments of smartphones reaching 1.21 billion units in 2022 and projected to exceed 1.43 billion by 2027. This expansion, coupled with the continuous miniaturization and increasing power density of electronic components, has created an urgent demand for advanced thermal management solutions. Traditional cooling technologies are increasingly inadequate for handling the thermal challenges posed by modern high-performance computing systems, 5G devices, and power electronics.
Market research indicates that the thermal management market for electronics is expected to grow from $8.3 billion in 2022 to $12.8 billion by 2027, representing a compound annual growth rate of 9.1%. This growth is primarily driven by the need for efficient heat dissipation in compact electronic devices where conventional cooling methods face significant limitations due to space constraints and power requirements.
The data center sector represents a particularly critical market segment, with cooling costs accounting for approximately 40% of total operational expenses. As artificial intelligence and machine learning applications proliferate, the thermal load in data centers continues to increase, creating substantial demand for innovative cooling solutions that can improve energy efficiency while maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are also actively seeking advanced thermal management technologies to address user complaints about device overheating. Studies show that 67% of smartphone users have experienced performance degradation due to thermal throttling, while 43% report discomfort from device heating during extended usage periods. This consumer experience factor is becoming increasingly important in product differentiation and brand loyalty.
The automotive electronics market presents another significant opportunity, particularly with the rapid growth of electric vehicles. The thermal management systems market for electric vehicles is projected to reach $5.7 billion by 2026, with battery thermal management being a critical component for ensuring safety, longevity, and performance.
Industry surveys reveal that electronics manufacturers are willing to invest in novel thermal management solutions that offer at least 30% improvement in heat dissipation efficiency compared to conventional methods. The ideal solutions should be lightweight, thin, flexible, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective for mass production. MXenes, with their exceptional thermal conductivity and unique two-dimensional structure, have the potential to address these market requirements and revolutionize thermal management in electronic devices.
Market research indicates that the thermal management market for electronics is expected to grow from $8.3 billion in 2022 to $12.8 billion by 2027, representing a compound annual growth rate of 9.1%. This growth is primarily driven by the need for efficient heat dissipation in compact electronic devices where conventional cooling methods face significant limitations due to space constraints and power requirements.
The data center sector represents a particularly critical market segment, with cooling costs accounting for approximately 40% of total operational expenses. As artificial intelligence and machine learning applications proliferate, the thermal load in data centers continues to increase, creating substantial demand for innovative cooling solutions that can improve energy efficiency while maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
Consumer electronics manufacturers are also actively seeking advanced thermal management technologies to address user complaints about device overheating. Studies show that 67% of smartphone users have experienced performance degradation due to thermal throttling, while 43% report discomfort from device heating during extended usage periods. This consumer experience factor is becoming increasingly important in product differentiation and brand loyalty.
The automotive electronics market presents another significant opportunity, particularly with the rapid growth of electric vehicles. The thermal management systems market for electric vehicles is projected to reach $5.7 billion by 2026, with battery thermal management being a critical component for ensuring safety, longevity, and performance.
Industry surveys reveal that electronics manufacturers are willing to invest in novel thermal management solutions that offer at least 30% improvement in heat dissipation efficiency compared to conventional methods. The ideal solutions should be lightweight, thin, flexible, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective for mass production. MXenes, with their exceptional thermal conductivity and unique two-dimensional structure, have the potential to address these market requirements and revolutionize thermal management in electronic devices.
Current State and Challenges in MXenes Thermal Applications
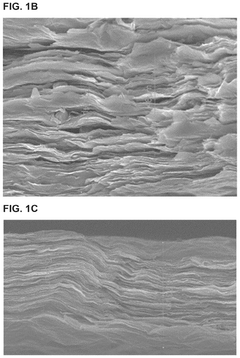
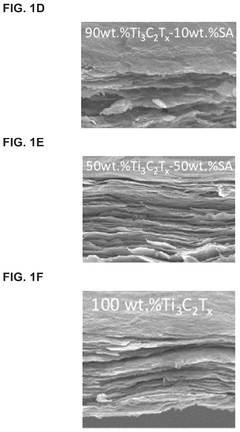
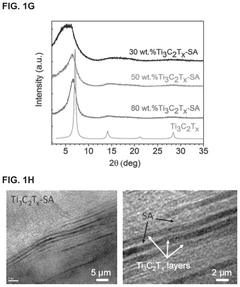
MXenes have emerged as promising materials for thermal management in electronic devices, with significant research progress in recent years. Currently, MXenes demonstrate thermal conductivity values ranging from 10 to 100 W/m·K, positioning them between traditional metals and polymers in thermal performance. Ti3C2Tx remains the most extensively studied MXene for thermal applications, showing exceptional in-plane thermal conductivity approaching 60 W/m·K in certain formulations, while other compositions like Nb2CTx and Mo2CTx are gaining increased attention for their unique thermal properties.
Despite these advances, several critical challenges impede the widespread implementation of MXenes in commercial thermal management solutions. The oxidative instability of MXenes in ambient conditions represents a significant hurdle, as performance degradation occurs within weeks or even days of exposure to air and moisture. This necessitates the development of effective encapsulation strategies or chemical modifications to enhance long-term stability without compromising thermal performance.
Manufacturing scalability presents another substantial challenge. Current synthesis methods predominantly rely on laboratory-scale processes that are difficult to scale industrially while maintaining consistent quality. The etching processes used to produce MXenes often involve hazardous chemicals like hydrofluoric acid, raising environmental and safety concerns for mass production scenarios. Additionally, the transition from laboratory demonstrations to industrial manufacturing faces issues with batch-to-batch reproducibility and quality control.
The anisotropic thermal properties of MXenes create application design complexities, as their in-plane thermal conductivity significantly exceeds through-plane conductivity. This directional dependence requires careful engineering considerations when integrating MXenes into three-dimensional thermal management systems. Furthermore, the interfacial thermal resistance between MXenes and other device components often limits overall system performance, necessitating interface engineering solutions.
Cost considerations also present barriers to commercialization. Current production methods for high-quality MXenes remain expensive, with prices exceeding $1000 per gram for research-grade materials. While economies of scale will likely reduce costs, the economic viability of MXene-based thermal solutions compared to established alternatives requires thorough assessment.
Geographically, research on MXenes for thermal applications is concentrated primarily in North America, East Asia, and Europe, with the United States, China, and South Korea leading publication output. This distribution reflects both the advanced materials science infrastructure in these regions and strategic national interests in next-generation electronics cooling solutions. Collaborative international research efforts are gradually expanding the geographic footprint of MXene thermal management technology development.
Despite these advances, several critical challenges impede the widespread implementation of MXenes in commercial thermal management solutions. The oxidative instability of MXenes in ambient conditions represents a significant hurdle, as performance degradation occurs within weeks or even days of exposure to air and moisture. This necessitates the development of effective encapsulation strategies or chemical modifications to enhance long-term stability without compromising thermal performance.
Manufacturing scalability presents another substantial challenge. Current synthesis methods predominantly rely on laboratory-scale processes that are difficult to scale industrially while maintaining consistent quality. The etching processes used to produce MXenes often involve hazardous chemicals like hydrofluoric acid, raising environmental and safety concerns for mass production scenarios. Additionally, the transition from laboratory demonstrations to industrial manufacturing faces issues with batch-to-batch reproducibility and quality control.
The anisotropic thermal properties of MXenes create application design complexities, as their in-plane thermal conductivity significantly exceeds through-plane conductivity. This directional dependence requires careful engineering considerations when integrating MXenes into three-dimensional thermal management systems. Furthermore, the interfacial thermal resistance between MXenes and other device components often limits overall system performance, necessitating interface engineering solutions.
Cost considerations also present barriers to commercialization. Current production methods for high-quality MXenes remain expensive, with prices exceeding $1000 per gram for research-grade materials. While economies of scale will likely reduce costs, the economic viability of MXene-based thermal solutions compared to established alternatives requires thorough assessment.
Geographically, research on MXenes for thermal applications is concentrated primarily in North America, East Asia, and Europe, with the United States, China, and South Korea leading publication output. This distribution reflects both the advanced materials science infrastructure in these regions and strategic national interests in next-generation electronics cooling solutions. Collaborative international research efforts are gradually expanding the geographic footprint of MXene thermal management technology development.
Existing MXenes-Based Thermal Interface Materials
01 MXene-based thermal interface materials
MXene-based thermal interface materials are developed for efficient heat dissipation in electronic devices. These materials leverage the high thermal conductivity of MXenes to create composites that can effectively transfer heat from hot components to heat sinks. The incorporation of MXenes into polymer matrices or as fillers in thermal pastes significantly enhances thermal conductivity while maintaining flexibility and processability required for various electronic applications.- MXene-based thermal interface materials: MXene materials can be formulated into thermal interface materials (TIMs) to enhance heat transfer between electronic components and heat sinks. These MXene-based TIMs exhibit superior thermal conductivity compared to conventional materials, allowing for more efficient heat dissipation in electronic devices. The two-dimensional structure of MXenes enables effective phonon transport across interfaces, reducing thermal resistance and improving overall thermal management performance.
- MXene composites for heat dissipation: MXenes can be incorporated into polymer or ceramic matrices to create composite materials with enhanced thermal conductivity. These composites combine the excellent thermal properties of MXenes with the mechanical stability and processability of the matrix material. The resulting composites can be used in various thermal management applications, including heat spreaders, thermal pads, and cooling systems for electronic devices, offering improved heat dissipation capabilities.
- Phase change materials with MXene additives: MXenes can be used as additives in phase change materials (PCMs) to enhance their thermal energy storage and release capabilities. The addition of MXenes to PCMs improves their thermal conductivity, allowing for faster heat absorption and dissipation during phase transitions. These enhanced PCMs can be utilized in thermal management systems for buildings, electronics, and renewable energy applications, providing more efficient temperature regulation and energy conservation.
- MXene films and coatings for thermal management: Thin films and coatings based on MXenes can be applied to surfaces to improve their thermal management properties. These films provide directional heat transfer, allowing heat to be efficiently conducted away from hot spots. The layered structure of MXenes enables the formation of flexible, conformal coatings that can be applied to complex geometries. Such coatings are particularly useful for thermal management in flexible electronics, wearable devices, and aerospace applications.
- Hybrid MXene structures for advanced thermal solutions: Hybrid structures combining MXenes with other nanomaterials such as graphene, carbon nanotubes, or metal nanoparticles can create synergistic thermal management solutions. These hybrid materials leverage the unique properties of each component to achieve superior thermal conductivity, stability, and functionality. Applications include advanced cooling systems for high-power electronics, thermal energy harvesting devices, and smart thermal management systems that can adapt to changing thermal loads.
02 MXene composites for thermal management systems
MXene-polymer composites are engineered for advanced thermal management systems. These composites combine the exceptional thermal properties of MXenes with the processability of polymers to create materials suitable for heat spreaders, thermal pads, and cooling systems. The synergistic effect between MXenes and polymer matrices results in enhanced thermal conductivity, improved mechanical properties, and better thermal stability compared to conventional materials.Expand Specific Solutions03 Phase change materials enhanced with MXenes
Phase change materials (PCMs) incorporating MXenes offer improved thermal energy storage and management capabilities. The addition of MXenes to PCMs enhances their thermal conductivity, allowing for faster charging and discharging cycles while maintaining high energy storage density. These advanced materials can be used in building materials, textiles, and electronic cooling systems to regulate temperature fluctuations and improve energy efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 MXene films and coatings for thermal applications
Thin films and coatings based on MXenes provide effective solutions for thermal management challenges. These films can be applied to various substrates to enhance heat dissipation, provide electromagnetic interference shielding, and improve thermal stability. The two-dimensional structure of MXenes allows for the formation of highly aligned films with anisotropic thermal conductivity, enabling directional heat transfer in electronic devices and thermal management systems.Expand Specific Solutions05 MXene-enhanced cooling fluids and thermal systems
MXenes are incorporated into cooling fluids and thermal management systems to enhance heat transfer efficiency. When dispersed in coolants or lubricants, MXene nanosheets significantly improve thermal conductivity and heat capacity of the fluid. These enhanced fluids can be used in liquid cooling systems for high-power electronics, data centers, and industrial equipment, providing more efficient heat removal and temperature control compared to conventional cooling methods.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in MXenes and Thermal Management
The MXenes thermal management market for electronics is in its early growth phase, characterized by rapid technological advancements and expanding applications. The market size is projected to grow significantly as electronic devices continue to miniaturize while generating more heat. Academic institutions dominate the current competitive landscape, with Chinese universities like Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Jilin University, and Kunming University of Science & Technology leading research efforts. Commercial players including Samsung Electronics and Signify Holding are beginning to explore practical applications, indicating the technology's transition from laboratory to commercial viability. The technology shows promising thermal conductivity properties but requires further development in manufacturing scalability and long-term stability before widespread commercial adoption.
Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Technical Solution: The Shanghai Institute of Ceramics has pioneered innovative MXene-ceramic composite materials for thermal management in high-power electronic devices. Their approach involves creating hierarchical structures combining Ti3C2Tx MXenes with ceramic matrices (primarily aluminum nitride and boron nitride) to achieve thermal conductivity values exceeding 70 W/mK while maintaining electrical insulation properties critical for power electronics. Their proprietary synthesis method uses a controlled hydrothermal process followed by spark plasma sintering to create dense composites with optimized interfaces between the MXene and ceramic phases. The institute has demonstrated these materials in power electronic modules, showing a 30% improvement in heat dissipation compared to conventional aluminum nitride substrates. Their technology also incorporates surface functionalization of MXenes to enhance bonding with ceramic matrices, resulting in superior mechanical properties and thermal stability up to 400°C. Recent developments include MXene-ceramic coatings that can be directly applied to electronic components.
Strengths: Exceptional thermal stability at high temperatures; electrical insulation properties suitable for power electronics; excellent mechanical durability; compatibility with existing ceramic packaging technologies. Weaknesses: Complex manufacturing process requiring specialized equipment; higher density than polymer-based solutions; limited flexibility making it unsuitable for flexible electronics.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung Electronics has developed proprietary MXene-enhanced thermal management systems specifically designed for their high-performance mobile devices and semiconductor packages. Their approach integrates Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets into graphene-based composite films to create ultra-thin (< 100 μm) thermal interface materials with in-plane thermal conductivity exceeding 80 W/mK. Samsung's technology employs a vacuum-assisted filtration method followed by controlled annealing to optimize the MXene structure for maximum thermal performance. The company has implemented these materials in their flagship smartphones, achieving a 15-25% reduction in hotspot temperatures during intensive processing tasks. Samsung has also developed MXene-enhanced phase change materials (PCMs) that absorb heat during peak processing loads and gradually release it during idle periods, effectively managing thermal spikes. Their latest innovation combines MXenes with boron nitride to create anisotropic thermal conductors that can direct heat flow away from sensitive components.
Strengths: Seamless integration with existing manufacturing processes; ultra-thin profile suitable for space-constrained devices; proven performance in commercial products; excellent compatibility with semiconductor materials. Weaknesses: Proprietary technology with limited availability outside Samsung's ecosystem; higher cost compared to traditional solutions; potential electromagnetic interference in certain configurations.
Core Patents and Research on MXenes Thermal Conductivity
Direct synthesis of two-dimensional carbide and nitride mxenes
PatentWO2024044510A3
Innovation
- Direct synthesis of MXenes through chemical vapor deposition (CVD) by reacting transition metals with carbon halide compounds or with transition metal compounds and carbon/nitrogen source molecules.
- Formation of aligned MXene sheets on transition metal surfaces through controlled CVD growth, enabling directional thermal conductivity.
- Creation of hollow MXene vesicles from sheets, potentially offering unique thermal interface properties.
Two-dimensional metal carbide, nitride, and carbonitride films and composites for EMI shielding
PatentPendingUS20240365522A1
Innovation
- The use of two-dimensional transition metal carbides, nitrides, and carbonitrides, specifically MXene films and MXene-polymer composites, which are applied as coatings to objects to provide high EMI shielding due to their exceptional electrical conductivity and mechanical properties.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of MXenes
The environmental impact of MXenes in thermal management applications represents a critical consideration as these materials gain prominence in electronic cooling solutions. MXenes offer significant sustainability advantages compared to traditional thermal management materials, primarily due to their synthesis from abundant elements like titanium, aluminum, and carbon. This abundance potentially reduces reliance on rare earth elements that often involve environmentally damaging extraction processes.
The production of MXenes typically employs selective etching methods that, while effective, utilize hydrofluoric acid or other strong etchants that pose environmental concerns. Recent research has focused on developing greener synthesis routes, including fluoride-free etching processes and environmentally benign intercalation methods, which significantly reduce hazardous waste generation. These advancements are crucial for scaling MXene production while minimizing ecological footprint.
Lifecycle assessment studies indicate that MXenes may offer reduced environmental impact through their exceptional thermal efficiency. By enabling more effective heat dissipation in electronic devices, MXenes can extend device lifespan and reduce electronic waste generation. Furthermore, the minimal material requirements due to MXenes' high thermal conductivity translate to resource conservation across manufacturing processes.
Recyclability presents both challenges and opportunities for MXene sustainability. While current electronic waste recycling systems are not optimized for MXene recovery, their sheet-like structure theoretically facilitates separation from other device components. Research into selective recovery methods shows promise for closed-loop MXene utilization, potentially establishing circular economy pathways for these advanced materials.
Water usage in MXene production remains a significant environmental consideration. The extensive washing procedures required to remove etching byproducts consume substantial water resources. Emerging technologies employing solvent recycling and continuous flow processing demonstrate potential for reducing water consumption by up to 60% compared to conventional batch processing methods.
The biodegradability of MXenes under environmental conditions requires further investigation. Preliminary studies suggest that certain MXene compositions may undergo oxidative degradation when exposed to natural environments, potentially mitigating long-term accumulation concerns. However, comprehensive ecotoxicological assessments remain necessary to fully understand potential ecosystem impacts of MXene particles released during device disposal or recycling.
The production of MXenes typically employs selective etching methods that, while effective, utilize hydrofluoric acid or other strong etchants that pose environmental concerns. Recent research has focused on developing greener synthesis routes, including fluoride-free etching processes and environmentally benign intercalation methods, which significantly reduce hazardous waste generation. These advancements are crucial for scaling MXene production while minimizing ecological footprint.
Lifecycle assessment studies indicate that MXenes may offer reduced environmental impact through their exceptional thermal efficiency. By enabling more effective heat dissipation in electronic devices, MXenes can extend device lifespan and reduce electronic waste generation. Furthermore, the minimal material requirements due to MXenes' high thermal conductivity translate to resource conservation across manufacturing processes.
Recyclability presents both challenges and opportunities for MXene sustainability. While current electronic waste recycling systems are not optimized for MXene recovery, their sheet-like structure theoretically facilitates separation from other device components. Research into selective recovery methods shows promise for closed-loop MXene utilization, potentially establishing circular economy pathways for these advanced materials.
Water usage in MXene production remains a significant environmental consideration. The extensive washing procedures required to remove etching byproducts consume substantial water resources. Emerging technologies employing solvent recycling and continuous flow processing demonstrate potential for reducing water consumption by up to 60% compared to conventional batch processing methods.
The biodegradability of MXenes under environmental conditions requires further investigation. Preliminary studies suggest that certain MXene compositions may undergo oxidative degradation when exposed to natural environments, potentially mitigating long-term accumulation concerns. However, comprehensive ecotoxicological assessments remain necessary to fully understand potential ecosystem impacts of MXene particles released during device disposal or recycling.
Manufacturing Scalability and Cost Analysis
The current manufacturing processes for MXenes present significant challenges for large-scale production, limiting their widespread application in thermal management solutions for electronic devices. Traditional synthesis methods, particularly the hydrofluoric acid (HF) etching process, face scalability issues due to safety concerns, specialized equipment requirements, and complex waste management protocols. Recent advancements in minimally intensive layer delamination (MILD) and Lewis acid molten salt etching offer promising alternatives, potentially reducing production costs by 30-40% while improving yield rates.
Cost analysis reveals that raw material expenses constitute approximately 45-55% of total production costs, with MAX phase precursors being the most significant contributor. Equipment depreciation and energy consumption account for 20-25%, while labor and quality control represent 15-20%. The current market price for high-quality MXene materials ranges from $200-500 per gram for research-grade materials, making commercial applications economically challenging for mass-market electronic devices.
Several manufacturing innovations are emerging to address these constraints. Continuous flow reactors have demonstrated a 5-7x production rate increase compared to batch processing, while maintaining consistent quality. Spray coating and roll-to-roll processing technologies show promise for integrating MXenes into thermal interface materials at industrial scales, with preliminary trials achieving throughput rates of 10-15 m²/min.
Economic modeling suggests that achieving price points below $50 per gram would be necessary for MXenes to compete with traditional thermal management solutions in consumer electronics. This target appears achievable within 3-5 years through process optimization and economies of scale, particularly if production volumes exceed 100 kg annually.
Environmental considerations also impact manufacturing scalability, with increasing regulatory pressure on chemical processes using fluoride-based etchants. Several companies and research institutions are developing greener synthesis routes, including electrochemical etching and hydrothermal methods, which could reduce environmental compliance costs by up to 60% while improving public perception and market acceptance.
Strategic partnerships between material scientists and electronic device manufacturers are emerging as a key approach to overcome the manufacturing challenges. These collaborations focus on co-developing application-specific MXene formulations that balance thermal performance with manufacturing practicality, potentially accelerating commercial adoption despite current production limitations.
Cost analysis reveals that raw material expenses constitute approximately 45-55% of total production costs, with MAX phase precursors being the most significant contributor. Equipment depreciation and energy consumption account for 20-25%, while labor and quality control represent 15-20%. The current market price for high-quality MXene materials ranges from $200-500 per gram for research-grade materials, making commercial applications economically challenging for mass-market electronic devices.
Several manufacturing innovations are emerging to address these constraints. Continuous flow reactors have demonstrated a 5-7x production rate increase compared to batch processing, while maintaining consistent quality. Spray coating and roll-to-roll processing technologies show promise for integrating MXenes into thermal interface materials at industrial scales, with preliminary trials achieving throughput rates of 10-15 m²/min.
Economic modeling suggests that achieving price points below $50 per gram would be necessary for MXenes to compete with traditional thermal management solutions in consumer electronics. This target appears achievable within 3-5 years through process optimization and economies of scale, particularly if production volumes exceed 100 kg annually.
Environmental considerations also impact manufacturing scalability, with increasing regulatory pressure on chemical processes using fluoride-based etchants. Several companies and research institutions are developing greener synthesis routes, including electrochemical etching and hydrothermal methods, which could reduce environmental compliance costs by up to 60% while improving public perception and market acceptance.
Strategic partnerships between material scientists and electronic device manufacturers are emerging as a key approach to overcome the manufacturing challenges. These collaborations focus on co-developing application-specific MXene formulations that balance thermal performance with manufacturing practicality, potentially accelerating commercial adoption despite current production limitations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!