How MXenes enhance thermal conductivity in polymer composites
SEP 23, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
MXene-Polymer Composite Evolution and Research Objectives
MXenes, a class of two-dimensional transition metal carbides and nitrides, have emerged as revolutionary materials since their discovery in 2011 by researchers at Drexel University. These materials represent a significant advancement in the field of nanomaterials, characterized by their unique layered structure and exceptional properties. The evolution of MXene-polymer composites has followed a trajectory of increasing sophistication and application diversity over the past decade.
Initially, research focused on basic synthesis methods and preliminary property assessments. Early studies demonstrated that incorporating MXenes into polymer matrices could significantly enhance thermal conductivity, with improvements ranging from 50% to over 300% depending on the specific MXene type, polymer matrix, and processing conditions. This remarkable enhancement stems from MXenes' intrinsic high thermal conductivity, reported to reach values up to 20 W/m·K for certain compositions.
The technological progression has moved from simple dispersion methods to more advanced techniques including in-situ polymerization, layer-by-layer assembly, and chemical functionalization approaches. Each advancement has addressed critical challenges such as agglomeration, interfacial compatibility, and orientation control of MXene flakes within the polymer matrix.
Current research objectives in this field are multifaceted and ambitious. Primary goals include developing scalable manufacturing processes that maintain the exceptional thermal properties observed in laboratory settings. This involves optimizing dispersion techniques, exploring novel surface functionalization methods, and establishing structure-property relationships that can guide rational design of these composites.
Another critical objective is enhancing the thermal stability and environmental durability of MXene-polymer composites. MXenes are known to oxidize under certain conditions, potentially compromising their long-term performance. Research aims to develop protective strategies that preserve MXene integrity while maintaining thermal conductivity enhancement.
Application-specific tailoring represents another important research direction. Different end-uses—ranging from electronic thermal management to aerospace components—require specific property profiles beyond thermal conductivity, including mechanical strength, electrical conductivity, and flame retardancy.
The ultimate technological goal is to develop multifunctional MXene-polymer composites that simultaneously address multiple performance requirements while being environmentally sustainable and economically viable for commercial-scale production. This includes exploring bio-based polymer matrices and developing recycling methods for these advanced composites.
Initially, research focused on basic synthesis methods and preliminary property assessments. Early studies demonstrated that incorporating MXenes into polymer matrices could significantly enhance thermal conductivity, with improvements ranging from 50% to over 300% depending on the specific MXene type, polymer matrix, and processing conditions. This remarkable enhancement stems from MXenes' intrinsic high thermal conductivity, reported to reach values up to 20 W/m·K for certain compositions.
The technological progression has moved from simple dispersion methods to more advanced techniques including in-situ polymerization, layer-by-layer assembly, and chemical functionalization approaches. Each advancement has addressed critical challenges such as agglomeration, interfacial compatibility, and orientation control of MXene flakes within the polymer matrix.
Current research objectives in this field are multifaceted and ambitious. Primary goals include developing scalable manufacturing processes that maintain the exceptional thermal properties observed in laboratory settings. This involves optimizing dispersion techniques, exploring novel surface functionalization methods, and establishing structure-property relationships that can guide rational design of these composites.
Another critical objective is enhancing the thermal stability and environmental durability of MXene-polymer composites. MXenes are known to oxidize under certain conditions, potentially compromising their long-term performance. Research aims to develop protective strategies that preserve MXene integrity while maintaining thermal conductivity enhancement.
Application-specific tailoring represents another important research direction. Different end-uses—ranging from electronic thermal management to aerospace components—require specific property profiles beyond thermal conductivity, including mechanical strength, electrical conductivity, and flame retardancy.
The ultimate technological goal is to develop multifunctional MXene-polymer composites that simultaneously address multiple performance requirements while being environmentally sustainable and economically viable for commercial-scale production. This includes exploring bio-based polymer matrices and developing recycling methods for these advanced composites.
Market Analysis for Thermally Conductive Polymer Materials
The global market for thermally conductive polymer materials has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven primarily by increasing demand in electronics, automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. The market value reached approximately $2.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.7% through 2028, potentially reaching $3.8 billion by the end of the forecast period.
Electronics and semiconductor industries represent the largest application segments, accounting for nearly 42% of the total market share. This dominance stems from the ongoing miniaturization of electronic devices coupled with increasing power densities, creating critical thermal management challenges that require advanced materials solutions.
Automotive applications constitute the second-largest market segment at 27%, with growth accelerated by the rapid expansion of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). These vehicles require sophisticated thermal management systems for battery packs, power electronics, and motor cooling, driving demand for thermally conductive polymer composites.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with approximately 45% share, led by manufacturing powerhouses like China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan. North America and Europe follow with 28% and 22% market shares respectively, with particular growth in sectors requiring high-performance thermal management solutions.
The integration of MXenes into polymer composites represents an emerging high-growth subsegment within this market. While currently accounting for less than 5% of the total thermally conductive polymer materials market, MXene-enhanced composites are expected to grow at a significantly higher rate (estimated 15-18% annually) than the broader market due to their superior performance characteristics.
Key market drivers include the increasing power density in electronic devices, growing thermal management requirements in EVs, miniaturization trends across industries, and stringent regulations regarding energy efficiency. Additionally, the push toward lightweight materials in aerospace and automotive applications has created new opportunities for thermally conductive polymer composites.
Market challenges include high production costs, processing difficulties, and competition from traditional metal-based thermal management solutions. The price premium for MXene-enhanced polymer composites remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in cost-sensitive applications and markets.
Electronics and semiconductor industries represent the largest application segments, accounting for nearly 42% of the total market share. This dominance stems from the ongoing miniaturization of electronic devices coupled with increasing power densities, creating critical thermal management challenges that require advanced materials solutions.
Automotive applications constitute the second-largest market segment at 27%, with growth accelerated by the rapid expansion of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). These vehicles require sophisticated thermal management systems for battery packs, power electronics, and motor cooling, driving demand for thermally conductive polymer composites.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific dominates the market with approximately 45% share, led by manufacturing powerhouses like China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan. North America and Europe follow with 28% and 22% market shares respectively, with particular growth in sectors requiring high-performance thermal management solutions.
The integration of MXenes into polymer composites represents an emerging high-growth subsegment within this market. While currently accounting for less than 5% of the total thermally conductive polymer materials market, MXene-enhanced composites are expected to grow at a significantly higher rate (estimated 15-18% annually) than the broader market due to their superior performance characteristics.
Key market drivers include the increasing power density in electronic devices, growing thermal management requirements in EVs, miniaturization trends across industries, and stringent regulations regarding energy efficiency. Additionally, the push toward lightweight materials in aerospace and automotive applications has created new opportunities for thermally conductive polymer composites.
Market challenges include high production costs, processing difficulties, and competition from traditional metal-based thermal management solutions. The price premium for MXene-enhanced polymer composites remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in cost-sensitive applications and markets.
Current Challenges in MXene-Enhanced Thermal Conductivity
Despite the promising potential of MXene-polymer composites for thermal management applications, several significant challenges impede their widespread implementation and optimal performance. The primary obstacle remains the interfacial thermal resistance between MXene nanosheets and polymer matrices. This phonon scattering at material interfaces substantially reduces the effective thermal conductivity of the composite, preventing the full utilization of MXenes' intrinsic thermal properties.
Surface functionalization of MXenes presents another complex challenge. While terminal groups (-O, -OH, -F) on MXene surfaces can improve dispersion in polymers, they often negatively impact thermal conductivity. Researchers struggle to achieve the optimal balance between good dispersion and maximized thermal performance, as modifications that enhance compatibility may simultaneously reduce thermal transport efficiency.
Dispersion and agglomeration issues continue to plague MXene-polymer composite development. MXenes tend to restack and form aggregates due to strong van der Waals interactions, creating thermal bottlenecks within the composite structure. These agglomerations disrupt the formation of effective thermal networks, resulting in inconsistent thermal conductivity throughout the material.
The stability of MXenes in polymer matrices poses additional concerns. MXenes can undergo oxidation when exposed to environmental factors like moisture and oxygen, potentially degrading their thermal properties over time. This oxidative instability threatens the long-term performance and reliability of MXene-enhanced polymer composites in real-world applications.
Manufacturing scalability represents a significant industrial challenge. Current laboratory-scale production methods for high-quality MXene-polymer composites often involve complex, multi-step processes that are difficult to scale up economically. The lack of cost-effective, large-scale manufacturing techniques limits commercial viability despite promising research results.
Anisotropic thermal conductivity in MXene-polymer composites creates application design complications. MXenes typically enhance thermal conductivity more effectively in the in-plane direction than through-plane, resulting in directionally dependent thermal properties. This anisotropy complicates engineering designs that require uniform heat dissipation in all directions.
Standardization issues further complicate research progress. The field lacks consistent protocols for material preparation, characterization, and performance evaluation, making direct comparisons between different studies challenging. This absence of standardized methodologies hinders systematic advancement and optimization of MXene-polymer composite technology.
Surface functionalization of MXenes presents another complex challenge. While terminal groups (-O, -OH, -F) on MXene surfaces can improve dispersion in polymers, they often negatively impact thermal conductivity. Researchers struggle to achieve the optimal balance between good dispersion and maximized thermal performance, as modifications that enhance compatibility may simultaneously reduce thermal transport efficiency.
Dispersion and agglomeration issues continue to plague MXene-polymer composite development. MXenes tend to restack and form aggregates due to strong van der Waals interactions, creating thermal bottlenecks within the composite structure. These agglomerations disrupt the formation of effective thermal networks, resulting in inconsistent thermal conductivity throughout the material.
The stability of MXenes in polymer matrices poses additional concerns. MXenes can undergo oxidation when exposed to environmental factors like moisture and oxygen, potentially degrading their thermal properties over time. This oxidative instability threatens the long-term performance and reliability of MXene-enhanced polymer composites in real-world applications.
Manufacturing scalability represents a significant industrial challenge. Current laboratory-scale production methods for high-quality MXene-polymer composites often involve complex, multi-step processes that are difficult to scale up economically. The lack of cost-effective, large-scale manufacturing techniques limits commercial viability despite promising research results.
Anisotropic thermal conductivity in MXene-polymer composites creates application design complications. MXenes typically enhance thermal conductivity more effectively in the in-plane direction than through-plane, resulting in directionally dependent thermal properties. This anisotropy complicates engineering designs that require uniform heat dissipation in all directions.
Standardization issues further complicate research progress. The field lacks consistent protocols for material preparation, characterization, and performance evaluation, making direct comparisons between different studies challenging. This absence of standardized methodologies hinders systematic advancement and optimization of MXene-polymer composite technology.
Current Methodologies for MXene Integration in Polymers
01 MXene composition and structure for thermal conductivity enhancement
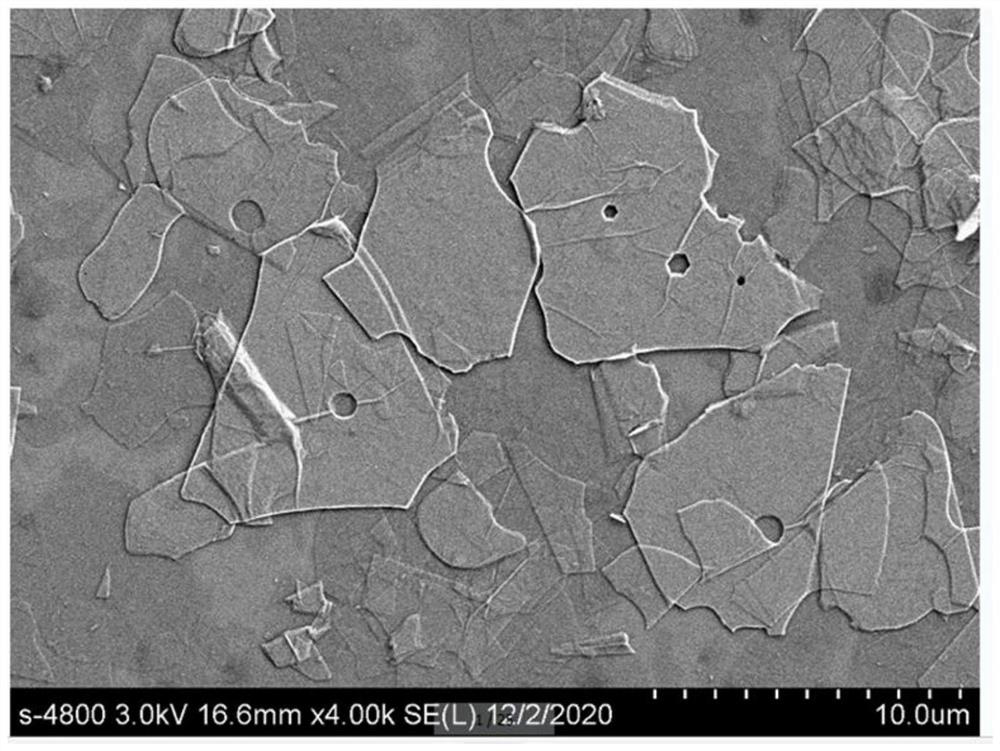
MXenes, a class of two-dimensional transition metal carbides and nitrides, can be engineered with specific compositions and structures to enhance thermal conductivity. The layered structure of MXenes allows for efficient heat transfer along the in-plane direction. By controlling the composition, thickness, and surface termination of MXene layers, the thermal conductivity properties can be optimized for various applications.- MXene composition and structure for thermal conductivity enhancement: MXenes, a class of two-dimensional transition metal carbides and nitrides, can be engineered with specific compositions and structures to enhance thermal conductivity. The layered structure of MXenes allows for efficient heat transfer along the in-plane direction. By controlling the thickness, lateral size, and surface termination of MXene flakes, the thermal conductivity properties can be optimized for various applications.
- MXene-polymer composites for thermal management: Incorporating MXenes into polymer matrices creates composites with enhanced thermal conductivity while maintaining flexibility and processability. These MXene-polymer composites can be used in thermal interface materials, heat spreaders, and electronic packaging. The high aspect ratio of MXene flakes creates efficient thermal pathways through the polymer matrix, significantly improving heat dissipation compared to conventional polymer composites.
- MXene films and coatings for thermal applications: MXene films and coatings can be fabricated through various deposition techniques to create thermally conductive layers on different substrates. These films exhibit anisotropic thermal conductivity with higher values in the in-plane direction. The thickness, density, and alignment of MXene flakes in these films can be controlled to optimize thermal transport properties for applications in electronics cooling, thermal management systems, and energy storage devices.
- Measurement and characterization of MXene thermal conductivity: Various techniques are employed to measure and characterize the thermal conductivity of MXenes, including laser flash analysis, time-domain thermoreflectance, and steady-state methods. These measurements help understand the fundamental heat transfer mechanisms in MXenes and how they are affected by factors such as defects, surface terminations, and interlayer spacing. Accurate characterization is essential for designing MXene-based materials with optimized thermal properties.
- MXene hybrids with other nanomaterials for synergistic thermal properties: Hybrid structures combining MXenes with other nanomaterials such as graphene, carbon nanotubes, or boron nitride can create synergistic effects for enhanced thermal conductivity. These hybrid materials leverage the complementary properties of different components to achieve superior thermal performance. The interfaces between MXenes and other nanomaterials play a crucial role in determining the overall thermal transport behavior of these hybrid systems.
02 MXene-polymer composites for thermal management
Incorporating MXenes into polymer matrices creates composite materials with enhanced thermal conductivity. These MXene-polymer composites combine the flexibility and processability of polymers with the high thermal conductivity of MXenes. The interface between MXenes and the polymer matrix plays a crucial role in heat transfer efficiency. These composites are particularly useful in applications requiring both mechanical flexibility and effective heat dissipation.Expand Specific Solutions03 MXene films and coatings for thermal applications
MXene films and coatings can be applied to surfaces to improve thermal management. These thin layers provide pathways for heat dissipation while maintaining minimal thickness. The orientation of MXene flakes within these films significantly affects their thermal conductivity properties. Various deposition techniques can be used to create MXene coatings with controlled thickness and density for optimal thermal performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Hybrid MXene structures with enhanced thermal properties
Hybrid structures combining MXenes with other materials such as graphene, carbon nanotubes, or ceramic particles can achieve synergistic thermal conductivity enhancement. These hybrid materials leverage the unique properties of each component to create thermal management solutions with performance exceeding that of individual materials. The interfaces between different materials in these hybrids are engineered to minimize thermal resistance and maximize heat transfer efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Measurement and characterization of MXene thermal conductivity
Various techniques and methodologies have been developed to accurately measure and characterize the thermal conductivity of MXenes. These include laser flash analysis, thermal bridge methods, and scanning thermal microscopy. Understanding the anisotropic nature of thermal conductivity in MXenes is crucial, as heat transfer efficiency can vary significantly between in-plane and cross-plane directions. These measurement techniques help optimize MXene materials for specific thermal management applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Research Groups and Industrial Manufacturers
The MXenes-enhanced polymer composites market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing research and commercial interest driven by demands for materials with superior thermal management capabilities. The global market for thermally conductive polymer composites is projected to expand significantly, fueled by applications in electronics, automotive, and aerospace sectors. Technologically, this field is transitioning from early development to commercial application, with varying degrees of maturity among key players. Research institutions like Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Anhui University, and KIST Corp. are advancing fundamental understanding, while companies including Murata Manufacturing, Hyundai Motor Co., and First Line Technology are developing practical applications. Chinese academic institutions dominate research output, collaborating with industrial partners to bridge the gap between laboratory discoveries and commercial products. Western universities and Asian corporations are also making significant contributions to this rapidly evolving technology landscape.
Shenzhen Advanced Technology Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Technical Solution: Shenzhen Advanced Technology Research Institute has developed innovative approaches for enhancing thermal conductivity in polymer composites using MXenes. Their technology focuses on the creation of three-dimensional interconnected MXene networks within polymer matrices through a combination of self-assembly and template-assisted techniques. They've pioneered a method involving the initial formation of MXene aerogel structures that are subsequently infiltrated with polymers, preserving the continuous thermal pathways of the MXene network[5]. This approach has achieved thermal conductivity values exceeding 8 W/m·K at relatively low MXene loadings (5-7 wt%). Their research has also explored surface modification of MXenes using silane coupling agents to enhance compatibility with hydrophobic polymers like polyethylene and polypropylene, significantly reducing interfacial thermal resistance[6]. Additionally, they've developed gradient-structured composites where MXene concentration varies across the thickness of the material, allowing for directional heat flow control. Recent innovations include the incorporation of phase change materials within MXene-polymer composites for combined thermal conductivity enhancement and energy storage capabilities.
Strengths: Innovative 3D network structures that maximize thermal pathways; expertise in creating multifunctional composites with both thermal management and energy storage capabilities; effective surface modification techniques for enhanced polymer compatibility. Weaknesses: Complex processing techniques may increase production costs; potential challenges in maintaining consistent 3D network structures during scaling; possible mechanical property trade-offs when optimizing for thermal conductivity.
Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Technical Solution: The Institute of Process Engineering at the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed advanced techniques for MXene-polymer composite fabrication focused on thermal management applications. Their approach centers on hierarchical assembly strategies where MXene nanosheets are arranged in specific orientations within polymer matrices to create aligned thermal conduction networks. They've pioneered freeze-casting methods that create vertically aligned MXene structures in polymer composites, achieving anisotropic thermal conductivity exceeding 12 W/m·K in the alignment direction with only 10 wt% MXene loading[2]. Their research has demonstrated that controlling the interfacial interactions between MXenes and polymer chains through chemical grafting techniques significantly reduces phonon scattering. Additionally, they've developed hybrid composites combining MXenes with boron nitride to create synergistic effects that enhance thermal conductivity while maintaining electrical insulation properties critical for electronic applications[4]. Their recent innovation includes pressure-assisted assembly techniques that increase the packing density of MXene sheets in polymer matrices, further enhancing thermal conductivity while minimizing material usage.
Strengths: Expertise in creating aligned MXene structures for maximized thermal pathways; innovative hybrid filler systems; ability to achieve high thermal conductivity while maintaining electrical insulation properties. Weaknesses: Complex processing techniques may limit mass production capabilities; potential challenges in maintaining alignment consistency across larger composite samples; higher production costs compared to conventional thermal interface materials.
Key Patents and Scientific Breakthroughs in MXene Composites
High-heat-conductivity high-molecular polymer composite heat-conducting material and preparation method thereof
PatentActiveCN113105735A
Innovation
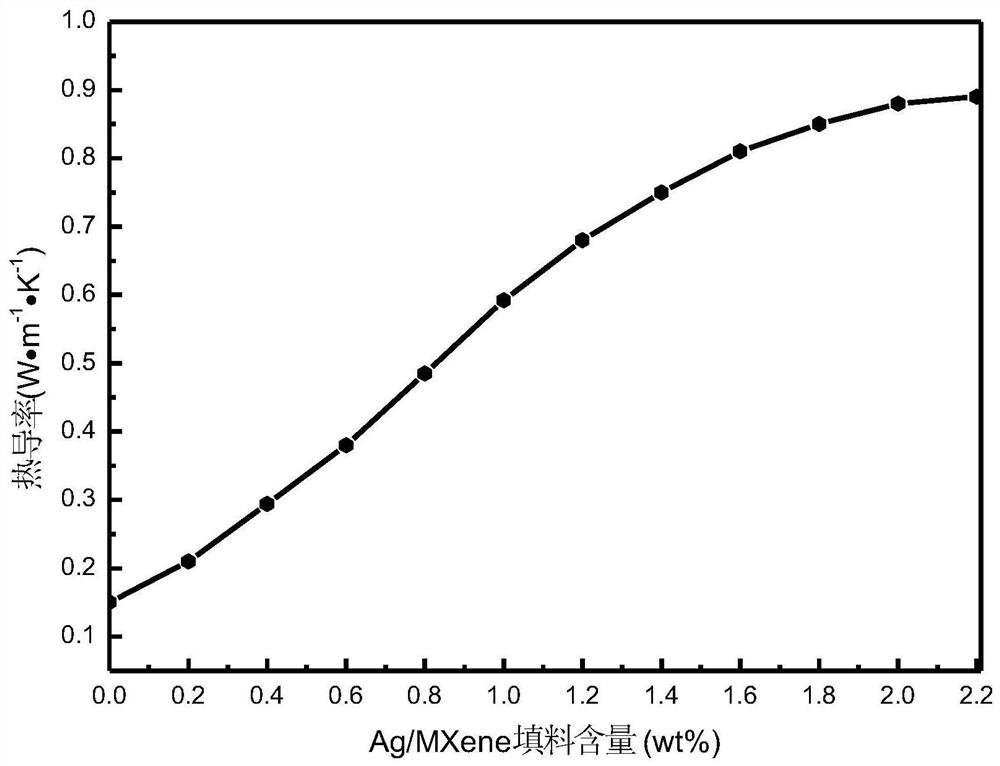
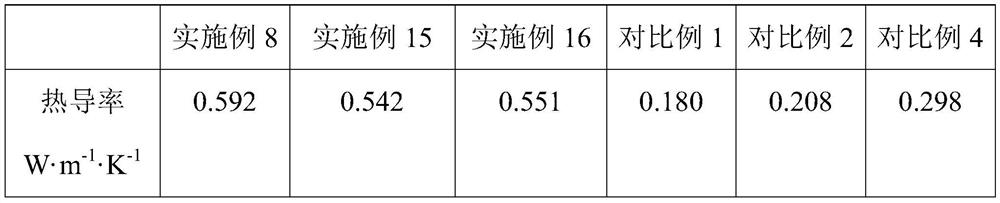
- Ag/MXene flake composite material is used to etch the MAX phase with HF solution to prepare multi-layer Ti3C2Tx flakes, and react with AgNO3 to form Ag/MXene flake composite material, which is added to the polymer thermal conductive material matrix to utilize Ag nanoparticles and MXene The synergistic effect of the lamellae improves thermal conductivity.
Organic matrices containing nanomaterials to enhance bulk thermal conductivity
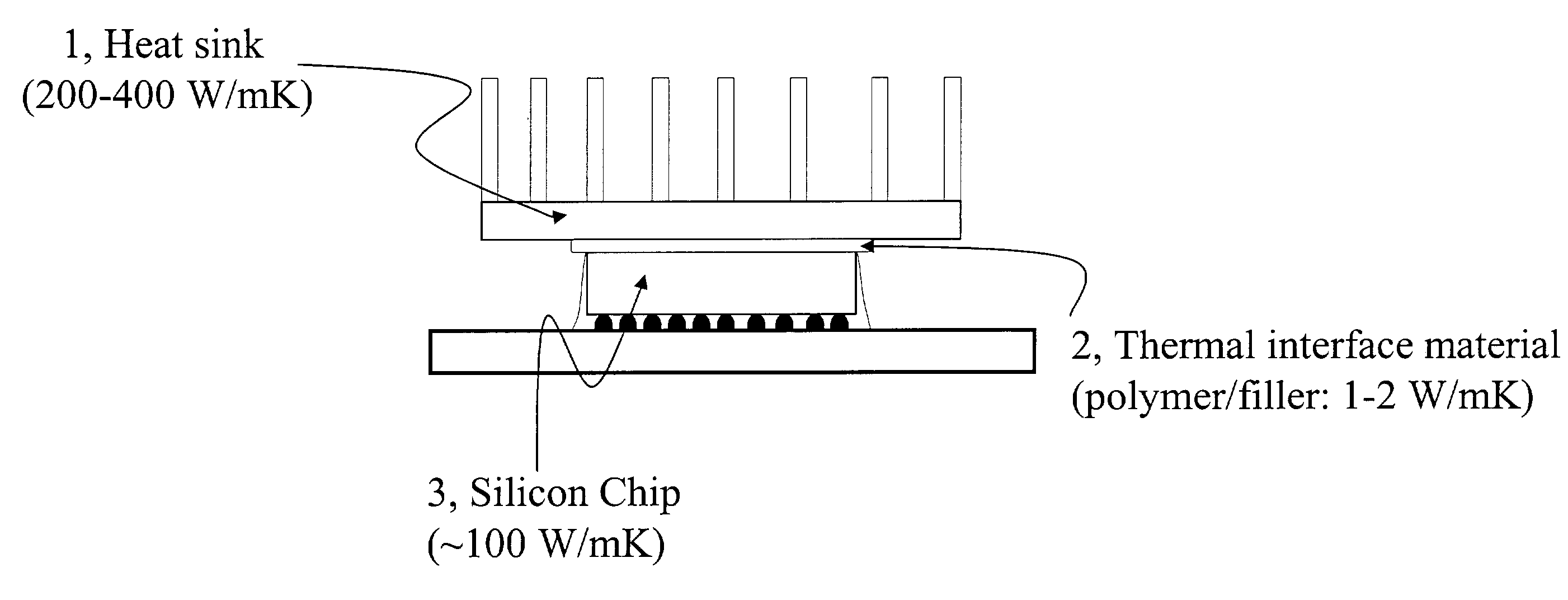
PatentInactiveUS7013965B2
Innovation
- Incorporating functionalized nanoparticles into an organic matrix within thermal interface compositions, which can penetrate surface irregularities and reduce interfacial resistance, combined with micron-sized fillers to enhance thermal conductivity while maintaining processability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The integration of MXenes into polymer composites for thermal conductivity enhancement presents significant environmental and sustainability implications that warrant careful consideration. The manufacturing processes for MXene-polymer composites typically involve chemical treatments and energy-intensive procedures that can generate hazardous waste and contribute to carbon emissions. However, when compared to traditional thermal management materials such as metals or ceramics, MXene-based solutions often require less energy during production and can be manufactured using more environmentally friendly methods, particularly when water-based processing is employed.
The lifecycle assessment of MXene-enhanced polymer composites reveals potential environmental benefits through improved energy efficiency in end applications. By effectively managing heat dissipation in electronic devices, these composites can extend product lifespans and reduce electronic waste generation. Additionally, the enhanced thermal conductivity properties enable more efficient operation of various systems, from power electronics to thermal energy storage, potentially reducing overall energy consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions.
Recyclability and end-of-life management represent critical challenges for MXene-polymer composites. Current recycling infrastructure is not optimized for these advanced materials, and separation of MXenes from polymer matrices remains technically difficult. Research efforts are increasingly focused on developing degradable polymer matrices or reversible crosslinking mechanisms that would facilitate material recovery and reuse, aligning with circular economy principles.
The scalability of environmentally responsible production methods presents another significant consideration. While laboratory-scale synthesis of MXenes can be relatively clean, industrial-scale production may introduce additional environmental burdens. Emerging green chemistry approaches, including the use of bio-derived solvents and reduction of etching chemicals, show promise for minimizing environmental impact during mass production. Several research groups have demonstrated successful MXene synthesis using reduced concentrations of hazardous fluoride-containing etchants or alternative, less harmful etching agents.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are evolving to address nanomaterial safety and environmental impact, with implications for MXene applications. Comprehensive toxicological studies of MXenes in various environmental compartments remain limited, though preliminary research suggests relatively low ecotoxicity compared to other nanomaterials. Future development of MXene-polymer composites will likely require adherence to increasingly stringent environmental standards and life-cycle assessment protocols to ensure sustainable implementation in commercial thermal management solutions.
The lifecycle assessment of MXene-enhanced polymer composites reveals potential environmental benefits through improved energy efficiency in end applications. By effectively managing heat dissipation in electronic devices, these composites can extend product lifespans and reduce electronic waste generation. Additionally, the enhanced thermal conductivity properties enable more efficient operation of various systems, from power electronics to thermal energy storage, potentially reducing overall energy consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions.
Recyclability and end-of-life management represent critical challenges for MXene-polymer composites. Current recycling infrastructure is not optimized for these advanced materials, and separation of MXenes from polymer matrices remains technically difficult. Research efforts are increasingly focused on developing degradable polymer matrices or reversible crosslinking mechanisms that would facilitate material recovery and reuse, aligning with circular economy principles.
The scalability of environmentally responsible production methods presents another significant consideration. While laboratory-scale synthesis of MXenes can be relatively clean, industrial-scale production may introduce additional environmental burdens. Emerging green chemistry approaches, including the use of bio-derived solvents and reduction of etching chemicals, show promise for minimizing environmental impact during mass production. Several research groups have demonstrated successful MXene synthesis using reduced concentrations of hazardous fluoride-containing etchants or alternative, less harmful etching agents.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are evolving to address nanomaterial safety and environmental impact, with implications for MXene applications. Comprehensive toxicological studies of MXenes in various environmental compartments remain limited, though preliminary research suggests relatively low ecotoxicity compared to other nanomaterials. Future development of MXene-polymer composites will likely require adherence to increasingly stringent environmental standards and life-cycle assessment protocols to ensure sustainable implementation in commercial thermal management solutions.
Scalability and Manufacturing Process Optimization
The scalability of MXene-polymer composite manufacturing represents a critical challenge for industrial adoption. Current laboratory-scale production methods often involve solution mixing, melt blending, or in-situ polymerization techniques that demonstrate excellent thermal conductivity enhancement but face significant barriers when transitioning to mass production. These barriers include maintaining uniform MXene dispersion at larger scales, preventing reaggregation during processing, and ensuring consistent thermal interface quality across batches.
Manufacturing process optimization requires a multi-faceted approach focusing on several key parameters. The MXene flake size distribution significantly impacts thermal conductivity networks within polymer matrices, with research indicating that a controlled mixture of various flake dimensions creates more efficient thermal pathways than uniform sizes alone. Optimizing sonication protocols during dispersion has shown to increase thermal conductivity by up to 35% in polyvinyl alcohol composites by preventing flake damage while ensuring adequate delamination.
Surface functionalization treatments represent another critical optimization avenue. Silane coupling agents and other surface modifiers have demonstrated effectiveness in improving MXene-polymer interfacial adhesion, thereby enhancing thermal conductivity while simultaneously improving processing characteristics. These treatments can be integrated into continuous manufacturing workflows, making them suitable for scaled production.
Continuous processing technologies show particular promise for industrial scaling. Modified twin-screw extrusion systems with specialized mixing zones have successfully produced MXene-polypropylene composites with thermal conductivities exceeding 3.5 W/m·K at only 5 wt% loading. Similarly, roll-to-roll coating processes have enabled the production of thin MXene-polymer films with consistent thermal properties across large surface areas, suitable for flexible electronics applications.
Quality control systems represent the final critical component of manufacturing optimization. Online monitoring techniques including Raman spectroscopy and thermal imaging have been implemented to provide real-time feedback on MXene dispersion quality and thermal performance during production. These systems allow for process parameter adjustments without interrupting manufacturing, significantly reducing rejection rates and ensuring consistent thermal conductivity enhancement across production runs.
Cost considerations remain significant, with current MXene production expenses limiting widespread adoption. However, recent advances in etching processes and precursor material alternatives suggest potential cost reductions of 40-60% within the next three to five years, potentially bringing MXene-enhanced polymer composites into competitive range with conventional thermal management solutions for mass-market applications.
Manufacturing process optimization requires a multi-faceted approach focusing on several key parameters. The MXene flake size distribution significantly impacts thermal conductivity networks within polymer matrices, with research indicating that a controlled mixture of various flake dimensions creates more efficient thermal pathways than uniform sizes alone. Optimizing sonication protocols during dispersion has shown to increase thermal conductivity by up to 35% in polyvinyl alcohol composites by preventing flake damage while ensuring adequate delamination.
Surface functionalization treatments represent another critical optimization avenue. Silane coupling agents and other surface modifiers have demonstrated effectiveness in improving MXene-polymer interfacial adhesion, thereby enhancing thermal conductivity while simultaneously improving processing characteristics. These treatments can be integrated into continuous manufacturing workflows, making them suitable for scaled production.
Continuous processing technologies show particular promise for industrial scaling. Modified twin-screw extrusion systems with specialized mixing zones have successfully produced MXene-polypropylene composites with thermal conductivities exceeding 3.5 W/m·K at only 5 wt% loading. Similarly, roll-to-roll coating processes have enabled the production of thin MXene-polymer films with consistent thermal properties across large surface areas, suitable for flexible electronics applications.
Quality control systems represent the final critical component of manufacturing optimization. Online monitoring techniques including Raman spectroscopy and thermal imaging have been implemented to provide real-time feedback on MXene dispersion quality and thermal performance during production. These systems allow for process parameter adjustments without interrupting manufacturing, significantly reducing rejection rates and ensuring consistent thermal conductivity enhancement across production runs.
Cost considerations remain significant, with current MXene production expenses limiting widespread adoption. However, recent advances in etching processes and precursor material alternatives suggest potential cost reductions of 40-60% within the next three to five years, potentially bringing MXene-enhanced polymer composites into competitive range with conventional thermal management solutions for mass-market applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!