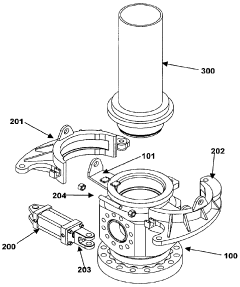
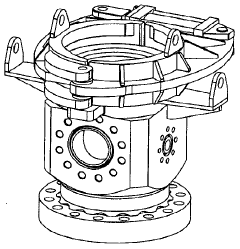
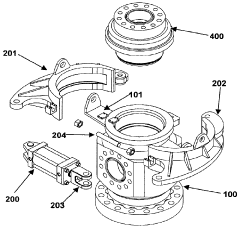
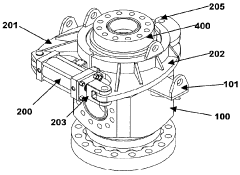
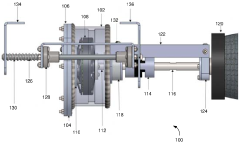
Application of 4140 Steel in Deep-Sea ROV Equipment
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
4140 Steel in ROV: Background and Objectives
The application of 4140 steel in deep-sea Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) equipment represents a significant advancement in underwater exploration and offshore operations. This high-strength low-alloy steel has gained prominence in the marine industry due to its exceptional mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, making it particularly suitable for the harsh deep-sea environment.
The development of ROVs has been driven by the increasing demand for underwater operations in various sectors, including oil and gas exploration, scientific research, and marine archaeology. As these operations extend to greater depths and more challenging environments, the materials used in ROV construction must meet increasingly stringent requirements. 4140 steel has emerged as a preferred material due to its ability to withstand high pressures, resist corrosion, and maintain structural integrity in extreme conditions.
The evolution of 4140 steel application in ROVs can be traced back to the early stages of underwater robotics. Initially, ROVs were primarily constructed using conventional marine-grade materials. However, as operations moved into deeper waters and more corrosive environments, the limitations of these materials became apparent. This led to the exploration of alternative materials, with 4140 steel emerging as a promising candidate due to its superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent fatigue resistance.
The objectives of utilizing 4140 steel in deep-sea ROV equipment are multifaceted. Primarily, it aims to enhance the operational capabilities of ROVs by enabling them to withstand greater depths and pressures. This, in turn, expands the range of underwater tasks that can be performed, from deep-sea oil and gas exploration to scientific research in previously inaccessible areas of the ocean.
Another key objective is to improve the longevity and reliability of ROV components. The corrosive nature of seawater, combined with the high pressures encountered in deep-sea operations, can rapidly degrade conventional materials. 4140 steel's superior corrosion resistance and mechanical properties offer the potential for extended operational life and reduced maintenance requirements, leading to more cost-effective and efficient underwater operations.
Furthermore, the application of 4140 steel in ROVs aligns with the broader trend towards more sustainable and environmentally responsible underwater operations. By enhancing the durability and efficiency of ROV equipment, it contributes to reducing the environmental impact of underwater activities and minimizes the need for frequent equipment replacement.
The development of ROVs has been driven by the increasing demand for underwater operations in various sectors, including oil and gas exploration, scientific research, and marine archaeology. As these operations extend to greater depths and more challenging environments, the materials used in ROV construction must meet increasingly stringent requirements. 4140 steel has emerged as a preferred material due to its ability to withstand high pressures, resist corrosion, and maintain structural integrity in extreme conditions.
The evolution of 4140 steel application in ROVs can be traced back to the early stages of underwater robotics. Initially, ROVs were primarily constructed using conventional marine-grade materials. However, as operations moved into deeper waters and more corrosive environments, the limitations of these materials became apparent. This led to the exploration of alternative materials, with 4140 steel emerging as a promising candidate due to its superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent fatigue resistance.
The objectives of utilizing 4140 steel in deep-sea ROV equipment are multifaceted. Primarily, it aims to enhance the operational capabilities of ROVs by enabling them to withstand greater depths and pressures. This, in turn, expands the range of underwater tasks that can be performed, from deep-sea oil and gas exploration to scientific research in previously inaccessible areas of the ocean.
Another key objective is to improve the longevity and reliability of ROV components. The corrosive nature of seawater, combined with the high pressures encountered in deep-sea operations, can rapidly degrade conventional materials. 4140 steel's superior corrosion resistance and mechanical properties offer the potential for extended operational life and reduced maintenance requirements, leading to more cost-effective and efficient underwater operations.
Furthermore, the application of 4140 steel in ROVs aligns with the broader trend towards more sustainable and environmentally responsible underwater operations. By enhancing the durability and efficiency of ROV equipment, it contributes to reducing the environmental impact of underwater activities and minimizes the need for frequent equipment replacement.
Deep-Sea ROV Market Analysis
The deep-sea Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for underwater exploration, offshore oil and gas operations, and marine research activities. The global deep-sea ROV market was valued at approximately $2.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $3.9 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 7.8% during the forecast period.
The market is segmented based on vehicle type, application, and region. Work-class ROVs dominate the market, accounting for over 60% of the total market share, due to their versatility and ability to perform complex tasks in deep-sea environments. Observation-class ROVs are also gaining traction, particularly in marine research and environmental monitoring applications.
Key application areas for deep-sea ROVs include oil and gas exploration, scientific research, defense and security, and offshore wind farm maintenance. The oil and gas sector remains the largest end-user, contributing to approximately 45% of the market revenue. However, the renewable energy sector, particularly offshore wind, is emerging as a rapidly growing segment for ROV applications.
Geographically, North America holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The Gulf of Mexico and the North Sea are major hubs for deep-sea ROV operations, primarily driven by extensive offshore oil and gas activities. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate, fueled by increasing offshore exploration activities in countries like China, India, and Australia.
The market is characterized by the presence of several established players and a growing number of new entrants. Key market players include Oceaneering International, Fugro, Saab Seaeye, and Forum Energy Technologies. These companies are focusing on technological advancements to enhance ROV capabilities, such as improved sensors, higher depth ratings, and increased autonomy.
The adoption of advanced materials, including 4140 steel, in ROV construction is a growing trend in the market. The use of high-strength, corrosion-resistant materials like 4140 steel is crucial for enhancing the durability and performance of ROVs in harsh deep-sea environments. This trend is driving collaborations between ROV manufacturers and material suppliers to develop customized solutions that meet the specific requirements of deep-sea operations.
Looking ahead, the deep-sea ROV market is poised for continued growth, driven by technological advancements, increasing deep-sea exploration activities, and the expansion of offshore renewable energy projects. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities in ROVs is expected to open up new opportunities and applications in the coming years.
The market is segmented based on vehicle type, application, and region. Work-class ROVs dominate the market, accounting for over 60% of the total market share, due to their versatility and ability to perform complex tasks in deep-sea environments. Observation-class ROVs are also gaining traction, particularly in marine research and environmental monitoring applications.
Key application areas for deep-sea ROVs include oil and gas exploration, scientific research, defense and security, and offshore wind farm maintenance. The oil and gas sector remains the largest end-user, contributing to approximately 45% of the market revenue. However, the renewable energy sector, particularly offshore wind, is emerging as a rapidly growing segment for ROV applications.
Geographically, North America holds the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The Gulf of Mexico and the North Sea are major hubs for deep-sea ROV operations, primarily driven by extensive offshore oil and gas activities. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate, fueled by increasing offshore exploration activities in countries like China, India, and Australia.
The market is characterized by the presence of several established players and a growing number of new entrants. Key market players include Oceaneering International, Fugro, Saab Seaeye, and Forum Energy Technologies. These companies are focusing on technological advancements to enhance ROV capabilities, such as improved sensors, higher depth ratings, and increased autonomy.
The adoption of advanced materials, including 4140 steel, in ROV construction is a growing trend in the market. The use of high-strength, corrosion-resistant materials like 4140 steel is crucial for enhancing the durability and performance of ROVs in harsh deep-sea environments. This trend is driving collaborations between ROV manufacturers and material suppliers to develop customized solutions that meet the specific requirements of deep-sea operations.
Looking ahead, the deep-sea ROV market is poised for continued growth, driven by technological advancements, increasing deep-sea exploration activities, and the expansion of offshore renewable energy projects. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities in ROVs is expected to open up new opportunities and applications in the coming years.
4140 Steel: Current Status and Challenges
The application of 4140 steel in deep-sea ROV equipment presents both significant opportunities and challenges. Currently, 4140 steel is widely recognized for its high strength, good toughness, and excellent wear resistance, making it a suitable candidate for various components in remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) operating in harsh deep-sea environments.
One of the primary advantages of 4140 steel in deep-sea applications is its ability to withstand high pressures and corrosive conditions. The material's chromium and molybdenum content contributes to its enhanced corrosion resistance, which is crucial for equipment exposed to saltwater for extended periods. However, despite these favorable properties, the use of 4140 steel in deep-sea ROVs still faces several challenges that require ongoing research and development.
A significant concern is the potential for hydrogen embrittlement, which can occur when the steel is exposed to hydrogen-rich environments, such as those found in deep-sea operations. This phenomenon can lead to a reduction in the material's ductility and load-bearing capacity, potentially compromising the structural integrity of ROV components. Researchers are actively working on developing surface treatments and coatings to mitigate this issue and improve the long-term reliability of 4140 steel in underwater applications.
Another challenge lies in optimizing the heat treatment processes for 4140 steel to achieve the ideal balance between strength and toughness required for deep-sea operations. The extreme pressure and temperature variations encountered in deep-sea environments necessitate careful consideration of the material's microstructure and mechanical properties. Ongoing studies are focused on refining heat treatment protocols to enhance the steel's performance under these demanding conditions.
The weight of 4140 steel components in ROVs is also a concern, as it affects the vehicle's maneuverability and energy efficiency. Engineers are exploring ways to reduce weight without compromising strength, such as through the use of advanced design techniques and the integration of composite materials in certain non-critical areas.
Furthermore, the joining of 4140 steel components in ROV construction presents challenges related to maintaining material properties and preventing corrosion at weld joints. Research is underway to develop improved welding techniques and filler materials specifically tailored for deep-sea applications.
As the demand for deep-sea exploration and resource extraction continues to grow, addressing these challenges in the application of 4140 steel for ROV equipment remains a priority. Collaborative efforts between materials scientists, engineers, and ROV manufacturers are driving innovation in this field, with the goal of enhancing the performance, durability, and reliability of deep-sea equipment.
One of the primary advantages of 4140 steel in deep-sea applications is its ability to withstand high pressures and corrosive conditions. The material's chromium and molybdenum content contributes to its enhanced corrosion resistance, which is crucial for equipment exposed to saltwater for extended periods. However, despite these favorable properties, the use of 4140 steel in deep-sea ROVs still faces several challenges that require ongoing research and development.
A significant concern is the potential for hydrogen embrittlement, which can occur when the steel is exposed to hydrogen-rich environments, such as those found in deep-sea operations. This phenomenon can lead to a reduction in the material's ductility and load-bearing capacity, potentially compromising the structural integrity of ROV components. Researchers are actively working on developing surface treatments and coatings to mitigate this issue and improve the long-term reliability of 4140 steel in underwater applications.
Another challenge lies in optimizing the heat treatment processes for 4140 steel to achieve the ideal balance between strength and toughness required for deep-sea operations. The extreme pressure and temperature variations encountered in deep-sea environments necessitate careful consideration of the material's microstructure and mechanical properties. Ongoing studies are focused on refining heat treatment protocols to enhance the steel's performance under these demanding conditions.
The weight of 4140 steel components in ROVs is also a concern, as it affects the vehicle's maneuverability and energy efficiency. Engineers are exploring ways to reduce weight without compromising strength, such as through the use of advanced design techniques and the integration of composite materials in certain non-critical areas.
Furthermore, the joining of 4140 steel components in ROV construction presents challenges related to maintaining material properties and preventing corrosion at weld joints. Research is underway to develop improved welding techniques and filler materials specifically tailored for deep-sea applications.
As the demand for deep-sea exploration and resource extraction continues to grow, addressing these challenges in the application of 4140 steel for ROV equipment remains a priority. Collaborative efforts between materials scientists, engineers, and ROV manufacturers are driving innovation in this field, with the goal of enhancing the performance, durability, and reliability of deep-sea equipment.
Current 4140 Steel Applications in ROVs
01 Composition and properties of 4140 steel
4140 steel is a medium carbon, low alloy steel known for its high strength, toughness, and wear resistance. It typically contains chromium and molybdenum as key alloying elements, which contribute to its improved hardenability and mechanical properties. This steel grade is widely used in various industrial applications due to its balanced combination of strength and ductility.- Composition and properties of 4140 steel: 4140 steel is a medium carbon, low alloy steel known for its high strength and toughness. It typically contains chromium and molybdenum as alloying elements, which contribute to its improved hardenability and wear resistance. This steel grade is widely used in various applications due to its balanced combination of strength, ductility, and machinability.
- Heat treatment processes for 4140 steel: Various heat treatment processes can be applied to 4140 steel to enhance its mechanical properties. These may include quenching and tempering, normalizing, or annealing. The specific heat treatment process chosen depends on the desired final properties and application requirements. Proper heat treatment can significantly improve the steel's strength, hardness, and toughness.
- Applications of 4140 steel in manufacturing: 4140 steel finds extensive use in manufacturing various components and products. It is commonly employed in the production of automotive parts, such as crankshafts, gears, and axles. Additionally, this steel grade is utilized in the fabrication of tools, machinery components, and structural elements in construction and engineering applications.
- Welding and fabrication techniques for 4140 steel: Welding and fabrication of 4140 steel require specific techniques to ensure optimal results. Preheating and post-weld heat treatment are often necessary to prevent cracking and maintain desired mechanical properties. Various welding methods, such as shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) and gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), can be employed depending on the application and desired outcomes.
- Surface treatment and coating of 4140 steel: Surface treatments and coatings can be applied to 4140 steel to enhance its performance in specific applications. These treatments may include nitriding, carburizing, or the application of protective coatings to improve wear resistance, corrosion resistance, or other surface properties. The choice of surface treatment depends on the intended use and environmental conditions the steel will be exposed to.
02 Heat treatment processes for 4140 steel
Various heat treatment processes can be applied to 4140 steel to enhance its mechanical properties. These may include quenching and tempering, normalizing, and annealing. The specific heat treatment process chosen depends on the desired final properties and application requirements. Proper heat treatment can significantly improve the steel's strength, hardness, and toughness.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of 4140 steel in oil and gas industry
4140 steel is commonly used in the oil and gas industry due to its excellent mechanical properties and resistance to harsh environments. It is often employed in the manufacturing of drilling equipment, wellhead components, and other downhole tools. The steel's high strength-to-weight ratio and good fatigue resistance make it suitable for these demanding applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Machining and fabrication of 4140 steel
4140 steel can be machined and fabricated using various techniques, including turning, milling, drilling, and welding. However, due to its high strength and hardness, especially after heat treatment, specialized tooling and machining parameters may be required. Proper cooling and lubrication during machining processes are essential to achieve optimal results and extend tool life.Expand Specific Solutions05 Surface treatments for 4140 steel
Various surface treatments can be applied to 4140 steel to enhance its performance in specific applications. These may include nitriding, carburizing, or the application of protective coatings. Such treatments can improve the steel's wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and fatigue strength, extending its service life in demanding environments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in ROV and Steel Industries
The application of 4140 steel in deep-sea ROV equipment is at a mature stage of development, with a growing market driven by increasing offshore exploration and production activities. The technology's maturity is evident from the involvement of established players like China National Offshore Oil Corp. and Offshore Oil Engineering Co., Ltd. These companies have extensive experience in offshore operations and are likely to be at the forefront of implementing advanced materials like 4140 steel in ROV equipment. The market size is substantial, given the global demand for deep-sea exploration and the critical role of ROVs in these operations. Companies such as Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and Cummins are also potential contributors to this field, bringing their expertise in heavy machinery and power systems to enhance ROV capabilities using 4140 steel.
China National Offshore Oil Corp.
Technical Solution: China National Offshore Oil Corp. (CNOOC) has developed advanced applications of 4140 steel in deep-sea ROV equipment. Their approach involves using 4140 steel for critical components of ROVs, such as frames, manipulator arms, and tool skids. CNOOC has implemented a proprietary heat treatment process that enhances the steel's corrosion resistance and strength, crucial for withstanding high-pressure deep-sea environments. The company has also developed a specialized coating technology that further protects the 4140 steel components from seawater corrosion, extending the operational life of ROVs[1][3]. CNOOC's ROVs equipped with 4140 steel components have successfully operated at depths exceeding 3000 meters, demonstrating the material's reliability in extreme conditions[2].
Strengths: Enhanced corrosion resistance and strength for deep-sea operations, extended operational life of ROVs. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs due to specialized heat treatment and coating processes.
Itrec BV
Technical Solution: Itrec BV, a Dutch company specializing in offshore and subsea equipment, has innovatively applied 4140 steel in their deep-sea ROV designs. Their approach focuses on optimizing the weight-to-strength ratio of ROV components. Itrec has developed a proprietary manufacturing process that allows for the creation of hollow 4140 steel structures, significantly reducing the overall weight of the ROV while maintaining structural integrity[4]. This process involves precision machining and advanced welding techniques to create complex geometries. Additionally, Itrec has implemented a unique surface treatment method that enhances the fatigue resistance of 4140 steel components, crucial for long-term operations in the dynamic deep-sea environment[5]. Their ROVs featuring 4140 steel components have demonstrated improved maneuverability and extended operational capabilities at depths of up to 4000 meters[6].
Strengths: Optimized weight-to-strength ratio, improved ROV maneuverability, and extended operational depth. Weaknesses: Complex manufacturing process may lead to higher production costs and longer lead times.
Key Innovations in 4140 Steel for Deep-Sea Use
Rotating device having high Anti-corrosion properties for controlling pressures in well heads
PatentWO2015133884A1
Innovation
- A rotary device with high anticorrosive properties, featuring a 4140 material sleeve for wear resistance, polyurethane sealing elements, and a hydraulic piston mechanism, designed to withstand pressures from 1000 to 5000 psi and temperatures up to 300°C, using SKF GRA-EP2-60 grease for lubrication and ISO 68 oil for superior protection against oxidation and wear.
Underwater spot cleaning equipment for observational class rovs
PatentActiveIN201641040231A
Innovation
- A compact underwater spot cleaning arrangement for observational class ROVs, comprising an actuation system with a pressure hull cylinder housing a motor, a damping system to absorb vibrations, and a processor for controlling the motor, integrated with a plug-n-play hardware for easy connection, utilizing a flexible coupler and brush shaft assembly for efficient biofouling removal.
Environmental Impact of 4140 Steel in Marine Applications
The environmental impact of 4140 steel in marine applications, particularly in deep-sea ROV equipment, is a critical consideration for sustainable ocean exploration and resource management. This high-strength, low-alloy steel offers excellent mechanical properties, but its interaction with the marine environment warrants careful examination.
In deep-sea applications, 4140 steel is exposed to extreme conditions, including high pressure, low temperatures, and corrosive saltwater. The primary environmental concern is the potential for corrosion and subsequent release of metal ions into the surrounding water. While 4140 steel has good corrosion resistance compared to some other steels, it is not immune to degradation in marine environments.
The corrosion process can lead to the release of iron, chromium, and molybdenum ions into the water. These metals, in high concentrations, can have detrimental effects on marine ecosystems. Iron, for instance, can promote algal blooms, which may disrupt the balance of marine food chains. Chromium and molybdenum, while present in smaller quantities, can accumulate in marine organisms and potentially enter the food web.
To mitigate these environmental risks, protective coatings and cathodic protection systems are often employed on 4140 steel components used in ROVs. These measures significantly reduce the rate of corrosion and metal ion release, thereby minimizing the environmental impact. Additionally, regular maintenance and inspection of ROV equipment can help identify and address corrosion issues before they become severe.
The use of 4140 steel in ROVs also has indirect environmental implications. The durability and strength of this material allow for the construction of robust equipment capable of withstanding deep-sea conditions. This enables more efficient and less frequent ROV deployments, potentially reducing the overall environmental footprint of deep-sea operations.
Furthermore, the longevity of 4140 steel components in ROVs contributes to reduced waste generation. Longer-lasting equipment means fewer replacements and less frequent disposal of materials, which is particularly important given the challenges of waste management in marine environments.
However, it's crucial to consider the end-of-life disposal of 4140 steel components. Proper recycling and disposal practices are essential to prevent these materials from becoming marine debris or contaminating coastal areas. The recyclability of 4140 steel is a positive factor, as it can be reprocessed and reused, reducing the demand for new raw materials and the associated environmental impacts of steel production.
In conclusion, while the use of 4140 steel in deep-sea ROV equipment presents some environmental challenges, particularly regarding corrosion and potential metal ion release, these can be effectively managed through proper design, maintenance, and protective measures. The material's durability and recyclability offer environmental benefits that, when balanced against its potential risks, make it a viable option for marine applications when used responsibly.
In deep-sea applications, 4140 steel is exposed to extreme conditions, including high pressure, low temperatures, and corrosive saltwater. The primary environmental concern is the potential for corrosion and subsequent release of metal ions into the surrounding water. While 4140 steel has good corrosion resistance compared to some other steels, it is not immune to degradation in marine environments.
The corrosion process can lead to the release of iron, chromium, and molybdenum ions into the water. These metals, in high concentrations, can have detrimental effects on marine ecosystems. Iron, for instance, can promote algal blooms, which may disrupt the balance of marine food chains. Chromium and molybdenum, while present in smaller quantities, can accumulate in marine organisms and potentially enter the food web.
To mitigate these environmental risks, protective coatings and cathodic protection systems are often employed on 4140 steel components used in ROVs. These measures significantly reduce the rate of corrosion and metal ion release, thereby minimizing the environmental impact. Additionally, regular maintenance and inspection of ROV equipment can help identify and address corrosion issues before they become severe.
The use of 4140 steel in ROVs also has indirect environmental implications. The durability and strength of this material allow for the construction of robust equipment capable of withstanding deep-sea conditions. This enables more efficient and less frequent ROV deployments, potentially reducing the overall environmental footprint of deep-sea operations.
Furthermore, the longevity of 4140 steel components in ROVs contributes to reduced waste generation. Longer-lasting equipment means fewer replacements and less frequent disposal of materials, which is particularly important given the challenges of waste management in marine environments.
However, it's crucial to consider the end-of-life disposal of 4140 steel components. Proper recycling and disposal practices are essential to prevent these materials from becoming marine debris or contaminating coastal areas. The recyclability of 4140 steel is a positive factor, as it can be reprocessed and reused, reducing the demand for new raw materials and the associated environmental impacts of steel production.
In conclusion, while the use of 4140 steel in deep-sea ROV equipment presents some environmental challenges, particularly regarding corrosion and potential metal ion release, these can be effectively managed through proper design, maintenance, and protective measures. The material's durability and recyclability offer environmental benefits that, when balanced against its potential risks, make it a viable option for marine applications when used responsibly.
Corrosion Resistance Strategies for 4140 Steel in ROVs
In the realm of deep-sea Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs), the application of 4140 steel presents unique challenges, particularly in terms of corrosion resistance. The harsh marine environment, characterized by high pressure, salinity, and potential temperature fluctuations, necessitates robust strategies to protect 4140 steel components from degradation.
One primary approach to enhancing corrosion resistance is through surface treatments. Electroplating with corrosion-resistant metals such as nickel or chromium can significantly improve the steel's durability. These coatings form a protective barrier, isolating the underlying 4140 steel from direct contact with corrosive seawater. Additionally, advanced ceramic coatings have shown promise in providing excellent protection against both chemical and mechanical wear.
Cathodic protection systems offer another effective strategy for mitigating corrosion in ROV equipment. By introducing sacrificial anodes or implementing impressed current cathodic protection (ICCP) systems, the 4140 steel components can be maintained at a potential where corrosion is thermodynamically unfavorable. This approach is particularly beneficial for larger ROV structures and components that are continuously exposed to seawater.
The use of corrosion inhibitors in hydraulic fluids and lubricants specific to ROV operations can provide an additional layer of protection. These inhibitors form protective films on metal surfaces, reducing the rate of electrochemical reactions that lead to corrosion. Careful selection of inhibitors compatible with 4140 steel and the operating conditions of deep-sea environments is crucial for optimal performance.
Material modification techniques, such as nitriding or carburizing, can enhance the surface properties of 4140 steel without compromising its core mechanical characteristics. These processes create a hardened surface layer with improved corrosion resistance, extending the operational life of ROV components in aggressive marine environments.
Implementing proper design considerations is equally important in corrosion prevention. This includes avoiding crevices and stagnant areas where corrosive agents can accumulate, ensuring proper drainage, and utilizing modular designs that allow for easy inspection and replacement of vulnerable components. Furthermore, the strategic use of corrosion-resistant alloys in critical areas can complement the 4140 steel structure, creating a more resilient overall system.
Regular maintenance and monitoring protocols are essential components of any corrosion resistance strategy. Implementing advanced corrosion monitoring systems, such as electrochemical sensors or ultrasonic thickness gauges, allows for real-time assessment of component integrity. This proactive approach enables timely interventions and helps optimize maintenance schedules, ultimately extending the operational lifespan of 4140 steel components in deep-sea ROV applications.
One primary approach to enhancing corrosion resistance is through surface treatments. Electroplating with corrosion-resistant metals such as nickel or chromium can significantly improve the steel's durability. These coatings form a protective barrier, isolating the underlying 4140 steel from direct contact with corrosive seawater. Additionally, advanced ceramic coatings have shown promise in providing excellent protection against both chemical and mechanical wear.
Cathodic protection systems offer another effective strategy for mitigating corrosion in ROV equipment. By introducing sacrificial anodes or implementing impressed current cathodic protection (ICCP) systems, the 4140 steel components can be maintained at a potential where corrosion is thermodynamically unfavorable. This approach is particularly beneficial for larger ROV structures and components that are continuously exposed to seawater.
The use of corrosion inhibitors in hydraulic fluids and lubricants specific to ROV operations can provide an additional layer of protection. These inhibitors form protective films on metal surfaces, reducing the rate of electrochemical reactions that lead to corrosion. Careful selection of inhibitors compatible with 4140 steel and the operating conditions of deep-sea environments is crucial for optimal performance.
Material modification techniques, such as nitriding or carburizing, can enhance the surface properties of 4140 steel without compromising its core mechanical characteristics. These processes create a hardened surface layer with improved corrosion resistance, extending the operational life of ROV components in aggressive marine environments.
Implementing proper design considerations is equally important in corrosion prevention. This includes avoiding crevices and stagnant areas where corrosive agents can accumulate, ensuring proper drainage, and utilizing modular designs that allow for easy inspection and replacement of vulnerable components. Furthermore, the strategic use of corrosion-resistant alloys in critical areas can complement the 4140 steel structure, creating a more resilient overall system.
Regular maintenance and monitoring protocols are essential components of any corrosion resistance strategy. Implementing advanced corrosion monitoring systems, such as electrochemical sensors or ultrasonic thickness gauges, allows for real-time assessment of component integrity. This proactive approach enables timely interventions and helps optimize maintenance schedules, ultimately extending the operational lifespan of 4140 steel components in deep-sea ROV applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!