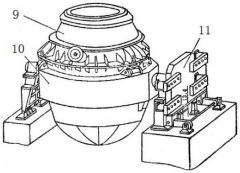
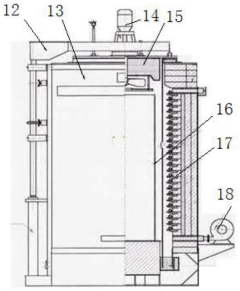
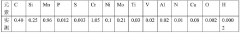
Developments in 4140 Steel Recycling Technologies
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
4140 Steel Recycling Background and Objectives
4140 steel, also known as AISI 4140 or SCM440, is a medium carbon chromium-molybdenum alloy steel widely used in various industries due to its excellent combination of strength, toughness, and wear resistance. The recycling of 4140 steel has become increasingly important in recent years, driven by environmental concerns, resource conservation, and economic factors.
The development of 4140 steel recycling technologies has its roots in the broader field of metal recycling, which has been practiced for centuries. However, the specific focus on 4140 steel recycling has gained momentum in the past few decades as the demand for this alloy has grown in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. The primary objective of 4140 steel recycling is to recover and reuse this valuable material while minimizing energy consumption and environmental impact.
The evolution of 4140 steel recycling technologies has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, recycling efforts were limited to basic sorting and melting processes. As technology advanced, more sophisticated methods emerged, including improved sorting techniques, advanced melting furnaces, and precise alloying processes to maintain the material's specific composition and properties.
Current trends in 4140 steel recycling focus on increasing efficiency and purity in the recycling process. This includes the development of automated sorting systems using artificial intelligence and machine learning, as well as advanced spectroscopic techniques for rapid and accurate material identification. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on closed-loop recycling systems within manufacturing facilities to maximize material recovery and minimize waste.
The technical goals for 4140 steel recycling technologies are multifaceted. They include improving the quality of recycled 4140 steel to match or exceed that of virgin material, reducing energy consumption in the recycling process, minimizing material loss during recycling, and developing more efficient methods for separating 4140 steel from other alloys and contaminants.
Looking ahead, the future of 4140 steel recycling technologies is likely to involve further integration of digital technologies, such as blockchain for traceability and Internet of Things (IoT) devices for real-time monitoring of recycling processes. There is also a push towards developing more environmentally friendly recycling methods, including the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of harmful emissions during the recycling process.
The development of 4140 steel recycling technologies has its roots in the broader field of metal recycling, which has been practiced for centuries. However, the specific focus on 4140 steel recycling has gained momentum in the past few decades as the demand for this alloy has grown in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. The primary objective of 4140 steel recycling is to recover and reuse this valuable material while minimizing energy consumption and environmental impact.
The evolution of 4140 steel recycling technologies has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, recycling efforts were limited to basic sorting and melting processes. As technology advanced, more sophisticated methods emerged, including improved sorting techniques, advanced melting furnaces, and precise alloying processes to maintain the material's specific composition and properties.
Current trends in 4140 steel recycling focus on increasing efficiency and purity in the recycling process. This includes the development of automated sorting systems using artificial intelligence and machine learning, as well as advanced spectroscopic techniques for rapid and accurate material identification. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on closed-loop recycling systems within manufacturing facilities to maximize material recovery and minimize waste.
The technical goals for 4140 steel recycling technologies are multifaceted. They include improving the quality of recycled 4140 steel to match or exceed that of virgin material, reducing energy consumption in the recycling process, minimizing material loss during recycling, and developing more efficient methods for separating 4140 steel from other alloys and contaminants.
Looking ahead, the future of 4140 steel recycling technologies is likely to involve further integration of digital technologies, such as blockchain for traceability and Internet of Things (IoT) devices for real-time monitoring of recycling processes. There is also a push towards developing more environmentally friendly recycling methods, including the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of harmful emissions during the recycling process.
Market Analysis for Recycled 4140 Steel
The market for recycled 4140 steel has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing environmental concerns and the push for sustainable manufacturing practices. As industries seek to reduce their carbon footprint and optimize resource utilization, the demand for recycled 4140 steel has surged across various sectors.
The automotive industry stands as a primary consumer of recycled 4140 steel, utilizing it in the production of critical components such as crankshafts, axles, and gears. The high strength and durability of 4140 steel make it an ideal choice for these applications, even in its recycled form. The aerospace sector has also shown increased interest in recycled 4140 steel, particularly for non-critical components where weight reduction is less crucial.
In the energy sector, recycled 4140 steel finds applications in the manufacturing of drilling equipment, valves, and other components used in oil and gas exploration. The renewable energy industry, particularly wind power, has also begun incorporating recycled 4140 steel in the production of turbine components, contributing to the overall sustainability of clean energy technologies.
The construction industry represents another significant market for recycled 4140 steel, using it in the fabrication of high-strength structural elements and reinforcement materials. As green building practices gain traction globally, the demand for recycled materials in construction is expected to rise, further boosting the market for recycled 4140 steel.
Market analysis indicates that the Asia-Pacific region, led by China and India, is the largest consumer of recycled 4140 steel, driven by rapid industrialization and infrastructure development. North America and Europe follow closely, with their mature manufacturing sectors and stringent environmental regulations promoting the use of recycled materials.
The global recycled 4140 steel market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5-6% over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of circular economy principles, government initiatives promoting recycling, and the cost-effectiveness of recycled steel compared to virgin materials.
However, challenges remain in the market, including the need for improved sorting and processing technologies to ensure consistent quality of recycled 4140 steel. Additionally, fluctuations in raw material prices and the availability of scrap steel can impact market dynamics. Despite these challenges, the overall outlook for the recycled 4140 steel market remains positive, with opportunities for innovation and expansion in recycling technologies driving future growth.
The automotive industry stands as a primary consumer of recycled 4140 steel, utilizing it in the production of critical components such as crankshafts, axles, and gears. The high strength and durability of 4140 steel make it an ideal choice for these applications, even in its recycled form. The aerospace sector has also shown increased interest in recycled 4140 steel, particularly for non-critical components where weight reduction is less crucial.
In the energy sector, recycled 4140 steel finds applications in the manufacturing of drilling equipment, valves, and other components used in oil and gas exploration. The renewable energy industry, particularly wind power, has also begun incorporating recycled 4140 steel in the production of turbine components, contributing to the overall sustainability of clean energy technologies.
The construction industry represents another significant market for recycled 4140 steel, using it in the fabrication of high-strength structural elements and reinforcement materials. As green building practices gain traction globally, the demand for recycled materials in construction is expected to rise, further boosting the market for recycled 4140 steel.
Market analysis indicates that the Asia-Pacific region, led by China and India, is the largest consumer of recycled 4140 steel, driven by rapid industrialization and infrastructure development. North America and Europe follow closely, with their mature manufacturing sectors and stringent environmental regulations promoting the use of recycled materials.
The global recycled 4140 steel market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5-6% over the next five years. This growth is attributed to the increasing adoption of circular economy principles, government initiatives promoting recycling, and the cost-effectiveness of recycled steel compared to virgin materials.
However, challenges remain in the market, including the need for improved sorting and processing technologies to ensure consistent quality of recycled 4140 steel. Additionally, fluctuations in raw material prices and the availability of scrap steel can impact market dynamics. Despite these challenges, the overall outlook for the recycled 4140 steel market remains positive, with opportunities for innovation and expansion in recycling technologies driving future growth.
Current Challenges in 4140 Steel Recycling
The recycling of 4140 steel presents several significant challenges that hinder the efficiency and effectiveness of the process. One of the primary obstacles is the presence of alloying elements, particularly chromium and molybdenum, which complicate the separation and purification stages. These elements, while essential for the steel's desirable properties, make it difficult to achieve high-purity recycled material without specialized techniques.
Contamination from other materials during the recycling process poses another major challenge. 4140 steel components often come into contact with various substances during their lifecycle, such as lubricants, coatings, or other metals. These contaminants can compromise the quality of the recycled steel if not properly removed, potentially affecting its mechanical properties and performance in subsequent applications.
The energy-intensive nature of 4140 steel recycling is a significant hurdle from both economic and environmental perspectives. The high melting point of this alloy steel necessitates substantial energy input during the remelting process, contributing to increased costs and carbon emissions. This challenge is particularly pronounced in regions where energy prices are high or where there is a push for more sustainable manufacturing practices.
Sorting and identification of 4140 steel from mixed scrap streams remain problematic. Unlike some other materials, 4140 steel cannot be easily distinguished from other steel grades through visual inspection alone. This necessitates the use of advanced sorting technologies, such as X-ray fluorescence or laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, which can be costly and may not be widely available in all recycling facilities.
The market dynamics for recycled 4140 steel present additional challenges. Fluctuations in demand for high-quality recycled alloy steel can impact the economic viability of recycling operations. Moreover, the perception of recycled steel as potentially inferior to virgin material can limit its acceptance in certain high-performance applications, despite evidence to the contrary when proper recycling techniques are employed.
Regulatory compliance and quality control pose ongoing challenges in the 4140 steel recycling industry. Stringent standards for recycled materials, particularly for use in critical applications, require rigorous testing and certification processes. Meeting these standards consistently while managing the variability inherent in recycled feedstock can be technically challenging and resource-intensive.
Lastly, the development of efficient and cost-effective technologies for removing or managing tramp elements during the recycling process remains an area of active research. These unwanted elements, which accumulate over multiple recycling cycles, can negatively impact the steel's properties if not properly addressed, limiting the number of times 4140 steel can be effectively recycled without degradation in quality.
Contamination from other materials during the recycling process poses another major challenge. 4140 steel components often come into contact with various substances during their lifecycle, such as lubricants, coatings, or other metals. These contaminants can compromise the quality of the recycled steel if not properly removed, potentially affecting its mechanical properties and performance in subsequent applications.
The energy-intensive nature of 4140 steel recycling is a significant hurdle from both economic and environmental perspectives. The high melting point of this alloy steel necessitates substantial energy input during the remelting process, contributing to increased costs and carbon emissions. This challenge is particularly pronounced in regions where energy prices are high or where there is a push for more sustainable manufacturing practices.
Sorting and identification of 4140 steel from mixed scrap streams remain problematic. Unlike some other materials, 4140 steel cannot be easily distinguished from other steel grades through visual inspection alone. This necessitates the use of advanced sorting technologies, such as X-ray fluorescence or laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, which can be costly and may not be widely available in all recycling facilities.
The market dynamics for recycled 4140 steel present additional challenges. Fluctuations in demand for high-quality recycled alloy steel can impact the economic viability of recycling operations. Moreover, the perception of recycled steel as potentially inferior to virgin material can limit its acceptance in certain high-performance applications, despite evidence to the contrary when proper recycling techniques are employed.
Regulatory compliance and quality control pose ongoing challenges in the 4140 steel recycling industry. Stringent standards for recycled materials, particularly for use in critical applications, require rigorous testing and certification processes. Meeting these standards consistently while managing the variability inherent in recycled feedstock can be technically challenging and resource-intensive.
Lastly, the development of efficient and cost-effective technologies for removing or managing tramp elements during the recycling process remains an area of active research. These unwanted elements, which accumulate over multiple recycling cycles, can negatively impact the steel's properties if not properly addressed, limiting the number of times 4140 steel can be effectively recycled without degradation in quality.
Existing 4140 Steel Recycling Methods
01 Composition and properties of 4140 steel
4140 steel is a medium carbon, low alloy steel known for its high strength and toughness. It typically contains chromium and molybdenum as alloying elements, which contribute to its improved hardenability and wear resistance. This steel grade is widely used in various applications due to its balanced combination of strength, ductility, and machinability.- Composition and properties of 4140 steel: 4140 steel is a medium carbon, low alloy steel known for its high strength and toughness. It typically contains chromium and molybdenum as alloying elements, which contribute to its improved hardenability and wear resistance. This steel grade is widely used in various applications due to its balanced combination of strength, ductility, and machinability.
- Heat treatment processes for 4140 steel: Various heat treatment processes can be applied to 4140 steel to enhance its mechanical properties. These may include quenching and tempering, normalizing, or annealing. The specific heat treatment process chosen depends on the desired final properties and application requirements. Proper heat treatment can significantly improve the steel's strength, hardness, and toughness.
- Applications of 4140 steel in oil and gas industry: 4140 steel is commonly used in the oil and gas industry due to its excellent mechanical properties and resistance to harsh environments. It is often employed in the manufacturing of drilling equipment, wellhead components, and various downhole tools. The steel's high strength-to-weight ratio and good fatigue resistance make it suitable for these demanding applications.
- Machining and fabrication of 4140 steel: 4140 steel can be machined and fabricated using various techniques, including turning, milling, drilling, and welding. While it offers good machinability compared to some other high-strength steels, proper tooling and cutting parameters are essential for optimal results. Heat treatment may be required before or after machining to achieve the desired final properties.
- Surface treatments and coatings for 4140 steel: To further enhance the performance of 4140 steel, various surface treatments and coatings can be applied. These may include nitriding, carburizing, or the application of wear-resistant coatings. Such treatments can improve the steel's surface hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance, extending its service life in demanding applications.
02 Heat treatment processes for 4140 steel
Various heat treatment processes can be applied to 4140 steel to enhance its mechanical properties. These may include quenching and tempering, normalizing, and annealing. The specific heat treatment process chosen depends on the desired final properties and intended application of the steel component.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of 4140 steel in machinery and equipment
4140 steel is commonly used in the manufacturing of machinery components and equipment parts that require high strength and wear resistance. It is often employed in the production of gears, shafts, axles, and other critical components in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and oil and gas.Expand Specific Solutions04 Welding and fabrication techniques for 4140 steel
Specific welding and fabrication techniques are employed when working with 4140 steel to ensure optimal joint strength and prevent issues such as cracking or distortion. These may include preheating, controlled cooling, and the use of appropriate filler materials. Proper handling and processing are crucial to maintain the steel's desirable properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Surface treatment and coating methods for 4140 steel
Various surface treatment and coating methods can be applied to 4140 steel components to enhance their performance characteristics. These may include nitriding, carburizing, or the application of protective coatings to improve wear resistance, corrosion resistance, or other specific properties required for the intended application.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in 4140 Steel Recycling Industry
The development of 4140 steel recycling technologies is in a growth phase, driven by increasing environmental concerns and resource scarcity. The market size is expanding, with a growing emphasis on circular economy principles in the steel industry. Technologically, the field is advancing, but still has room for maturation. Key players like Angang Steel Co., Ltd., Hyundai Steel Co., and Shougang Group Co., Ltd. are investing in research and development to improve recycling processes and enhance the quality of recycled 4140 steel. Universities such as Chongqing University and the University of Science & Technology Beijing are contributing to technological advancements through academic research. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established steel manufacturers and specialized recycling companies, with increasing collaboration between industry and academia to drive innovation.
Angang Steel Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Angang Steel has developed an advanced 4140 steel recycling technology that utilizes a combination of magnetic separation and eddy current separation techniques. Their process involves shredding the steel scrap, followed by a series of sorting steps to remove non-ferrous materials. The company has implemented a state-of-the-art electric arc furnace (EAF) system that can efficiently melt and refine the recycled 4140 steel, maintaining its high-quality properties[1]. Additionally, Angang Steel has invested in advanced slag management techniques to minimize waste and recover valuable alloying elements during the recycling process[3].
Strengths: High efficiency in separating and recovering 4140 steel from mixed scrap, maintaining material quality. Weaknesses: High initial investment costs for advanced separation and EAF technologies.
University of Science & Technology Beijing
Technical Solution: The University of Science & Technology Beijing has developed a cutting-edge 4140 steel recycling technology based on advanced material characterization and separation techniques. Their process utilizes X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) for rapid and accurate identification of steel grades in mixed scrap[7]. The university has also developed a novel electrochemical recycling method that allows for selective dissolution and recovery of alloying elements from 4140 steel scrap, potentially enabling more efficient recycling of high-value components[8]. Additionally, they have made significant progress in the development of machine learning algorithms for optimizing the recycling process parameters based on scrap composition and desired output quality.
Strengths: Highly accurate scrap sorting, potential for selective element recovery. Weaknesses: Technology still at research stage, may face challenges in scaling up to industrial levels.
Innovative Approaches in 4140 Steel Recycling
Recycling method for manufacturing HSS master alloy by using ferro silicon from waste of HSS processing process
PatentWO2024158078A1
Innovation
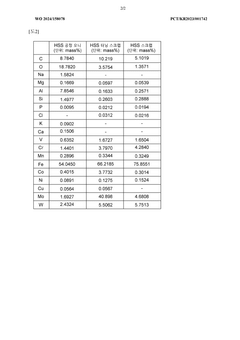
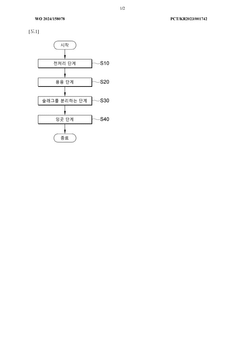
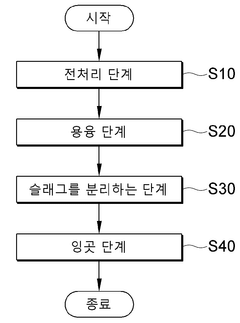
- A recycling method involving a pretreatment step to remove cutting oil by heating HSS processing waste, followed by a melting step with flux and ferrosilicon at high temperatures, and subsequent slag separation and ingot casting, which includes the use of ferro molybdenum, ferro tungsten, ferro cobalt, and ferro vanadium to control alloy composition and minimize chromium loss.
4140 medium-thick-wall seamless steel pipe and production method
PatentActiveCN113862556A
Innovation
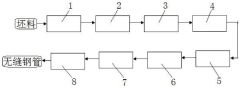
- Using the optimized 4140 composition and the new Diesel hot rolling unit rolling combined with water quenching instead of oil quenching, medium-thick wall seamless products are produced through converter smelting, continuous casting, annealing, heating, rolling, water quenching, tempering and straightening processes. steel pipe.
Environmental Impact of 4140 Steel Recycling
The environmental impact of 4140 steel recycling is a critical consideration in the development of sustainable manufacturing practices. Recycling 4140 steel, a high-strength alloy commonly used in automotive and industrial applications, offers significant environmental benefits compared to primary production.
One of the primary advantages of recycling 4140 steel is the reduction in energy consumption. The recycling process requires approximately 60-70% less energy compared to producing new steel from raw materials. This energy saving translates directly into reduced greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide, which is a major contributor to climate change.
Water conservation is another important environmental benefit of 4140 steel recycling. The recycling process uses significantly less water compared to primary steel production, helping to preserve this vital resource. Additionally, recycling reduces the need for mining activities, which often have detrimental effects on local water systems through pollution and habitat disruption.
The reduction in air pollution is a notable environmental impact of 4140 steel recycling. Primary steel production releases various pollutants, including sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. By recycling 4140 steel, these emissions are substantially reduced, contributing to improved air quality and reduced health risks for surrounding communities.
Recycling 4140 steel also plays a crucial role in waste reduction and landfill conservation. By diverting steel scrap from landfills, recycling helps extend the lifespan of existing waste disposal facilities and reduces the need for new landfill sites. This is particularly important given the limited space available for waste disposal in many urban areas.
The conservation of natural resources is a significant environmental benefit of 4140 steel recycling. By reducing the demand for virgin raw materials such as iron ore and coal, recycling helps preserve these finite resources and minimizes the environmental impact associated with their extraction and processing.
However, it's important to note that the recycling process itself is not without environmental impacts. The transportation of scrap steel, the energy used in melting and refining processes, and the potential release of contaminants during recycling operations all contribute to the overall environmental footprint. Ongoing research and technological advancements aim to further minimize these impacts and improve the efficiency of 4140 steel recycling processes.
In conclusion, while there are some environmental considerations in the recycling process itself, the overall environmental impact of 4140 steel recycling is overwhelmingly positive. The significant reductions in energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and natural resource depletion make it a crucial component of sustainable manufacturing practices and circular economy initiatives in the steel industry.
One of the primary advantages of recycling 4140 steel is the reduction in energy consumption. The recycling process requires approximately 60-70% less energy compared to producing new steel from raw materials. This energy saving translates directly into reduced greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide, which is a major contributor to climate change.
Water conservation is another important environmental benefit of 4140 steel recycling. The recycling process uses significantly less water compared to primary steel production, helping to preserve this vital resource. Additionally, recycling reduces the need for mining activities, which often have detrimental effects on local water systems through pollution and habitat disruption.
The reduction in air pollution is a notable environmental impact of 4140 steel recycling. Primary steel production releases various pollutants, including sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. By recycling 4140 steel, these emissions are substantially reduced, contributing to improved air quality and reduced health risks for surrounding communities.
Recycling 4140 steel also plays a crucial role in waste reduction and landfill conservation. By diverting steel scrap from landfills, recycling helps extend the lifespan of existing waste disposal facilities and reduces the need for new landfill sites. This is particularly important given the limited space available for waste disposal in many urban areas.
The conservation of natural resources is a significant environmental benefit of 4140 steel recycling. By reducing the demand for virgin raw materials such as iron ore and coal, recycling helps preserve these finite resources and minimizes the environmental impact associated with their extraction and processing.
However, it's important to note that the recycling process itself is not without environmental impacts. The transportation of scrap steel, the energy used in melting and refining processes, and the potential release of contaminants during recycling operations all contribute to the overall environmental footprint. Ongoing research and technological advancements aim to further minimize these impacts and improve the efficiency of 4140 steel recycling processes.
In conclusion, while there are some environmental considerations in the recycling process itself, the overall environmental impact of 4140 steel recycling is overwhelmingly positive. The significant reductions in energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and natural resource depletion make it a crucial component of sustainable manufacturing practices and circular economy initiatives in the steel industry.
Economic Viability of 4140 Steel Recycling
The economic viability of 4140 steel recycling is a critical factor in determining the sustainability and profitability of this process. As the demand for high-quality steel continues to grow, recycling 4140 steel presents both opportunities and challenges for the industry.
One of the primary economic drivers for 4140 steel recycling is the potential cost savings compared to producing new steel from raw materials. The recycling process typically requires less energy and fewer resources, which can lead to reduced production costs. Additionally, as natural resources become scarcer and environmental regulations become stricter, the economic advantages of recycling are likely to increase.
However, the economic viability of 4140 steel recycling is also influenced by market fluctuations and global economic conditions. The price of scrap steel, which is the primary input for recycling, can vary significantly based on supply and demand dynamics. When scrap prices are high, it may become more economically attractive to use virgin materials, potentially impacting the viability of recycling operations.
The quality of recycled 4140 steel is another crucial factor affecting its economic viability. High-quality recycled steel that meets or exceeds the properties of virgin 4140 steel can command premium prices in the market. Achieving this level of quality requires advanced sorting and processing technologies, which may involve significant initial investments but can lead to higher long-term profitability.
Energy costs play a substantial role in the economic equation of 4140 steel recycling. The recycling process, while generally less energy-intensive than primary steel production, still requires considerable energy input. Fluctuations in energy prices can therefore have a significant impact on the overall economic viability of recycling operations.
The development of more efficient recycling technologies can further enhance the economic attractiveness of 4140 steel recycling. Innovations in sorting, melting, and refining processes can reduce operational costs and improve the quality of the recycled product. These technological advancements may require initial capital investments but can lead to improved long-term economic performance.
Government policies and regulations also play a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape of 4140 steel recycling. Incentives for recycling, such as tax breaks or subsidies, can improve the economic viability of recycling operations. Conversely, stringent environmental regulations may increase operational costs but can also drive innovation and efficiency improvements in the recycling process.
The global market for recycled 4140 steel is another important consideration. As industries worldwide increasingly prioritize sustainability and circular economy principles, the demand for high-quality recycled steel is likely to grow. This expanding market can create new economic opportunities for recyclers and potentially lead to more stable and profitable operations.
One of the primary economic drivers for 4140 steel recycling is the potential cost savings compared to producing new steel from raw materials. The recycling process typically requires less energy and fewer resources, which can lead to reduced production costs. Additionally, as natural resources become scarcer and environmental regulations become stricter, the economic advantages of recycling are likely to increase.
However, the economic viability of 4140 steel recycling is also influenced by market fluctuations and global economic conditions. The price of scrap steel, which is the primary input for recycling, can vary significantly based on supply and demand dynamics. When scrap prices are high, it may become more economically attractive to use virgin materials, potentially impacting the viability of recycling operations.
The quality of recycled 4140 steel is another crucial factor affecting its economic viability. High-quality recycled steel that meets or exceeds the properties of virgin 4140 steel can command premium prices in the market. Achieving this level of quality requires advanced sorting and processing technologies, which may involve significant initial investments but can lead to higher long-term profitability.
Energy costs play a substantial role in the economic equation of 4140 steel recycling. The recycling process, while generally less energy-intensive than primary steel production, still requires considerable energy input. Fluctuations in energy prices can therefore have a significant impact on the overall economic viability of recycling operations.
The development of more efficient recycling technologies can further enhance the economic attractiveness of 4140 steel recycling. Innovations in sorting, melting, and refining processes can reduce operational costs and improve the quality of the recycled product. These technological advancements may require initial capital investments but can lead to improved long-term economic performance.
Government policies and regulations also play a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape of 4140 steel recycling. Incentives for recycling, such as tax breaks or subsidies, can improve the economic viability of recycling operations. Conversely, stringent environmental regulations may increase operational costs but can also drive innovation and efficiency improvements in the recycling process.
The global market for recycled 4140 steel is another important consideration. As industries worldwide increasingly prioritize sustainability and circular economy principles, the demand for high-quality recycled steel is likely to grow. This expanding market can create new economic opportunities for recyclers and potentially lead to more stable and profitable operations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!