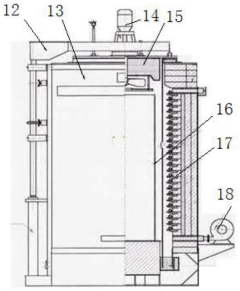
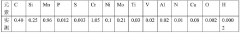
Role of 4140 Steel in Fire Safety Equipment Manufacturing
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
4140 Steel in Fire Safety: Background and Objectives
The role of 4140 steel in fire safety equipment manufacturing has become increasingly significant over the years, driven by the growing emphasis on robust and reliable fire protection systems. This alloy steel, known for its exceptional strength and heat resistance properties, has emerged as a crucial material in the production of various fire safety components and equipment.
The evolution of fire safety standards and regulations has played a pivotal role in shaping the demand for high-performance materials like 4140 steel. As building codes and safety requirements have become more stringent, manufacturers have sought materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and maintain structural integrity under fire conditions. 4140 steel, with its unique combination of mechanical properties, has proven to be an ideal candidate for such applications.
Historically, the use of 4140 steel in fire safety equipment can be traced back to the mid-20th century when advancements in metallurgy allowed for the development of alloy steels with enhanced properties. Since then, continuous improvements in steel production techniques and heat treatment processes have further refined the characteristics of 4140 steel, making it even more suitable for fire safety applications.
The primary objective of utilizing 4140 steel in fire safety equipment manufacturing is to enhance the overall performance and reliability of fire protection systems. This includes improving the durability of components exposed to high temperatures, increasing the load-bearing capacity of structural elements, and extending the operational lifespan of critical safety devices.
Another key goal is to develop fire safety equipment that can provide extended protection times, allowing for safer evacuation procedures and more effective firefighting operations. The superior strength-to-weight ratio of 4140 steel enables the design of lighter yet stronger components, which is particularly advantageous in portable fire safety equipment and mobile firefighting units.
Furthermore, the use of 4140 steel aims to address the challenges posed by modern building designs and materials. As architectural trends evolve and new construction materials emerge, fire safety equipment must adapt to provide adequate protection in diverse environments. The versatility of 4140 steel allows for the creation of customized solutions that can meet the specific requirements of different industries and building types.
In the context of technological advancements, the integration of 4140 steel with smart fire safety systems represents an emerging trend. The material's compatibility with various sensors and electronic components opens up possibilities for developing intelligent fire detection and suppression systems that can respond more effectively to fire incidents.
The evolution of fire safety standards and regulations has played a pivotal role in shaping the demand for high-performance materials like 4140 steel. As building codes and safety requirements have become more stringent, manufacturers have sought materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and maintain structural integrity under fire conditions. 4140 steel, with its unique combination of mechanical properties, has proven to be an ideal candidate for such applications.
Historically, the use of 4140 steel in fire safety equipment can be traced back to the mid-20th century when advancements in metallurgy allowed for the development of alloy steels with enhanced properties. Since then, continuous improvements in steel production techniques and heat treatment processes have further refined the characteristics of 4140 steel, making it even more suitable for fire safety applications.
The primary objective of utilizing 4140 steel in fire safety equipment manufacturing is to enhance the overall performance and reliability of fire protection systems. This includes improving the durability of components exposed to high temperatures, increasing the load-bearing capacity of structural elements, and extending the operational lifespan of critical safety devices.
Another key goal is to develop fire safety equipment that can provide extended protection times, allowing for safer evacuation procedures and more effective firefighting operations. The superior strength-to-weight ratio of 4140 steel enables the design of lighter yet stronger components, which is particularly advantageous in portable fire safety equipment and mobile firefighting units.
Furthermore, the use of 4140 steel aims to address the challenges posed by modern building designs and materials. As architectural trends evolve and new construction materials emerge, fire safety equipment must adapt to provide adequate protection in diverse environments. The versatility of 4140 steel allows for the creation of customized solutions that can meet the specific requirements of different industries and building types.
In the context of technological advancements, the integration of 4140 steel with smart fire safety systems represents an emerging trend. The material's compatibility with various sensors and electronic components opens up possibilities for developing intelligent fire detection and suppression systems that can respond more effectively to fire incidents.
Market Analysis for 4140 Steel in Fire Safety Equipment
The market for 4140 steel in fire safety equipment manufacturing has shown significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of fire safety measures and stringent regulations across various industries. This alloy steel, known for its high strength, toughness, and wear resistance, has become a preferred material for critical components in fire safety equipment.
The global fire safety equipment market, which includes products made with 4140 steel, is experiencing steady expansion. Key factors contributing to this growth include urbanization, industrialization, and the implementation of strict building safety codes. The market encompasses a wide range of products such as fire extinguishers, sprinkler systems, fire alarms, and protective gear, many of which utilize 4140 steel in their construction.
In the fire extinguisher segment, 4140 steel is commonly used for high-pressure cylinders due to its ability to withstand extreme pressures and temperatures. The demand for these cylinders has been rising, particularly in commercial and industrial sectors where large-capacity fire extinguishers are required. The automotive and aerospace industries also contribute significantly to the market demand, as they require fire suppression systems that can withstand harsh operating conditions.
The construction industry plays a crucial role in driving the demand for fire safety equipment incorporating 4140 steel. As building codes become more stringent, there is an increased need for robust fire protection systems in both residential and commercial structures. This has led to a higher adoption of fire sprinkler systems and other fire safety devices that often utilize 4140 steel components.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market for fire safety equipment, including those manufactured with 4140 steel. These regions have well-established regulatory frameworks and high awareness levels regarding fire safety. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and increasing government initiatives to improve fire safety standards.
The oil and gas industry represents another significant market for 4140 steel in fire safety applications. Offshore platforms, refineries, and petrochemical plants require specialized fire suppression systems that can withstand corrosive environments and high pressures, making 4140 steel an ideal material choice.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as fluctuating raw material prices and the emergence of alternative materials could impact the growth of 4140 steel usage in fire safety equipment. However, ongoing technological advancements and the development of more efficient manufacturing processes are expected to maintain the competitiveness of 4140 steel in this sector.
The global fire safety equipment market, which includes products made with 4140 steel, is experiencing steady expansion. Key factors contributing to this growth include urbanization, industrialization, and the implementation of strict building safety codes. The market encompasses a wide range of products such as fire extinguishers, sprinkler systems, fire alarms, and protective gear, many of which utilize 4140 steel in their construction.
In the fire extinguisher segment, 4140 steel is commonly used for high-pressure cylinders due to its ability to withstand extreme pressures and temperatures. The demand for these cylinders has been rising, particularly in commercial and industrial sectors where large-capacity fire extinguishers are required. The automotive and aerospace industries also contribute significantly to the market demand, as they require fire suppression systems that can withstand harsh operating conditions.
The construction industry plays a crucial role in driving the demand for fire safety equipment incorporating 4140 steel. As building codes become more stringent, there is an increased need for robust fire protection systems in both residential and commercial structures. This has led to a higher adoption of fire sprinkler systems and other fire safety devices that often utilize 4140 steel components.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the market for fire safety equipment, including those manufactured with 4140 steel. These regions have well-established regulatory frameworks and high awareness levels regarding fire safety. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by rapid industrialization, infrastructure development, and increasing government initiatives to improve fire safety standards.
The oil and gas industry represents another significant market for 4140 steel in fire safety applications. Offshore platforms, refineries, and petrochemical plants require specialized fire suppression systems that can withstand corrosive environments and high pressures, making 4140 steel an ideal material choice.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as fluctuating raw material prices and the emergence of alternative materials could impact the growth of 4140 steel usage in fire safety equipment. However, ongoing technological advancements and the development of more efficient manufacturing processes are expected to maintain the competitiveness of 4140 steel in this sector.
Current Challenges in Fire Safety Equipment Manufacturing
The fire safety equipment manufacturing industry faces several significant challenges in its current landscape. One of the primary issues is the increasing complexity of fire safety regulations and standards across different regions and countries. Manufacturers must navigate a maze of evolving requirements, which often vary significantly between jurisdictions, making it difficult to create standardized products for global markets.
Material selection and performance under extreme conditions remain critical challenges. While 4140 steel offers excellent strength and heat resistance, manufacturers struggle to balance these properties with weight considerations, especially in portable fire safety equipment. The need for materials that can withstand high temperatures while remaining lightweight and durable continues to drive research and development efforts in the industry.
Cost pressures present another significant hurdle. As demand for more sophisticated fire safety equipment grows, manufacturers must find ways to incorporate advanced technologies and materials without substantially increasing production costs. This challenge is particularly acute in developing markets, where price sensitivity can limit the adoption of state-of-the-art fire safety solutions.
The integration of smart technologies into fire safety equipment introduces new complexities. Manufacturers are tasked with developing products that not only perform their primary safety functions but also incorporate features like real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and connectivity with building management systems. This shift towards smart fire safety solutions requires new expertise in electronics, software development, and data analytics, areas traditionally outside the core competencies of many fire safety equipment manufacturers.
Environmental concerns and sustainability requirements are increasingly shaping the industry. Manufacturers must consider the entire lifecycle of their products, from raw material sourcing to end-of-life disposal. This includes developing fire suppression agents with minimal environmental impact and designing equipment for easier recycling or refurbishment.
The global supply chain disruptions experienced in recent years have exposed vulnerabilities in the manufacturing process. Ensuring a stable supply of critical components and materials, including specialized alloys like 4140 steel, has become a significant challenge. Manufacturers are reevaluating their supply chain strategies to build resilience against future disruptions.
Lastly, the industry faces a skills gap as it evolves. The convergence of traditional manufacturing with advanced technologies requires a workforce with a diverse skill set. Attracting and retaining talent with expertise in both mechanical engineering and emerging technologies like IoT and data analytics poses a significant challenge for many companies in the sector.
Material selection and performance under extreme conditions remain critical challenges. While 4140 steel offers excellent strength and heat resistance, manufacturers struggle to balance these properties with weight considerations, especially in portable fire safety equipment. The need for materials that can withstand high temperatures while remaining lightweight and durable continues to drive research and development efforts in the industry.
Cost pressures present another significant hurdle. As demand for more sophisticated fire safety equipment grows, manufacturers must find ways to incorporate advanced technologies and materials without substantially increasing production costs. This challenge is particularly acute in developing markets, where price sensitivity can limit the adoption of state-of-the-art fire safety solutions.
The integration of smart technologies into fire safety equipment introduces new complexities. Manufacturers are tasked with developing products that not only perform their primary safety functions but also incorporate features like real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and connectivity with building management systems. This shift towards smart fire safety solutions requires new expertise in electronics, software development, and data analytics, areas traditionally outside the core competencies of many fire safety equipment manufacturers.
Environmental concerns and sustainability requirements are increasingly shaping the industry. Manufacturers must consider the entire lifecycle of their products, from raw material sourcing to end-of-life disposal. This includes developing fire suppression agents with minimal environmental impact and designing equipment for easier recycling or refurbishment.
The global supply chain disruptions experienced in recent years have exposed vulnerabilities in the manufacturing process. Ensuring a stable supply of critical components and materials, including specialized alloys like 4140 steel, has become a significant challenge. Manufacturers are reevaluating their supply chain strategies to build resilience against future disruptions.
Lastly, the industry faces a skills gap as it evolves. The convergence of traditional manufacturing with advanced technologies requires a workforce with a diverse skill set. Attracting and retaining talent with expertise in both mechanical engineering and emerging technologies like IoT and data analytics poses a significant challenge for many companies in the sector.
4140 Steel Properties and Manufacturing Processes
01 Composition and properties of 4140 steel
4140 steel is a medium carbon, low alloy steel known for its high strength and toughness. It typically contains chromium and molybdenum as alloying elements, which contribute to its improved hardenability and wear resistance. This steel grade is widely used in various applications due to its balanced combination of strength, ductility, and machinability.- Composition and properties of 4140 steel: 4140 steel is a medium carbon, low alloy steel known for its high strength, toughness, and wear resistance. It typically contains chromium and molybdenum as key alloying elements, which contribute to its improved hardenability and mechanical properties. This steel grade is widely used in various applications requiring high strength and durability.
- Heat treatment processes for 4140 steel: Various heat treatment processes can be applied to 4140 steel to enhance its mechanical properties. These may include quenching and tempering, normalizing, or annealing. The specific heat treatment process chosen depends on the desired final properties and intended application of the steel.
- Applications of 4140 steel in machinery and equipment: 4140 steel is commonly used in the manufacturing of machinery components, automotive parts, and industrial equipment. Its high strength and wear resistance make it suitable for applications such as gears, shafts, axles, and other stressed parts in various mechanical systems.
- Welding and fabrication techniques for 4140 steel: Specific welding and fabrication techniques are often employed when working with 4140 steel to maintain its desirable properties. These may include preheating, controlled cooling, and post-weld heat treatment to minimize the risk of cracking and ensure optimal performance of the welded components.
- Surface treatment and coating methods for 4140 steel: Various surface treatment and coating methods can be applied to 4140 steel to further enhance its properties or provide additional functionality. These may include nitriding, carburizing, or the application of protective coatings to improve wear resistance, corrosion resistance, or other surface-dependent properties.
02 Heat treatment processes for 4140 steel
Various heat treatment processes can be applied to 4140 steel to enhance its mechanical properties. These may include quenching and tempering, normalizing, and annealing. The specific heat treatment process chosen depends on the desired final properties and application requirements. Proper heat treatment can significantly improve the steel's strength, hardness, and toughness.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of 4140 steel in machinery and equipment
4140 steel is commonly used in the manufacturing of machinery components and equipment parts due to its excellent mechanical properties. It is often employed in the production of gears, shafts, axles, and other high-stress components in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and oil and gas. The steel's ability to withstand high loads and resist wear makes it suitable for these applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Welding and fabrication techniques for 4140 steel
Welding and fabrication of 4140 steel require specific techniques to ensure optimal results. Preheating and post-weld heat treatment are often necessary to prevent cracking and maintain desired properties. Various welding methods, such as shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) and gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), can be used with appropriate filler materials and procedures to achieve strong, durable welds in 4140 steel components.Expand Specific Solutions05 Surface treatment and coating methods for 4140 steel
To enhance the surface properties of 4140 steel, various treatment and coating methods can be applied. These may include nitriding, carburizing, or the application of protective coatings such as chrome plating or PVD coatings. These surface treatments can improve wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and overall durability of 4140 steel components, extending their service life in demanding applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Manufacturers and Suppliers of 4140 Steel
The role of 4140 steel in fire safety equipment manufacturing is characterized by a competitive landscape in a mature industry with steady market growth. The global fire safety equipment market is estimated to be worth several billion dollars, with a compound annual growth rate of around 5-7%. Major players like Cummins, Inc. and The Boeing Co. have established strong positions, leveraging their expertise in engineering and manufacturing. Technological advancements focus on improving material properties, durability, and fire resistance. Companies such as NIPPON STEEL CORP. and Tata Steel Ltd. are investing in research and development to enhance 4140 steel's performance in fire safety applications. The market is moderately fragmented, with both large multinational corporations and specialized manufacturers competing for market share.
NIPPON STEEL CORP.
Technical Solution: NIPPON STEEL CORP. has developed advanced 4140 steel alloys specifically tailored for fire safety equipment manufacturing. Their proprietary heat treatment process enhances the steel's strength and toughness while maintaining excellent machinability. The company's 4140 steel exhibits superior resistance to high temperatures, with a melting point of approximately 1,416°C (2,581°F)[1]. This allows for the production of fire-resistant components that can withstand extreme heat conditions. NIPPON STEEL's 4140 steel also demonstrates improved corrosion resistance, crucial for long-term durability in fire safety applications. The company has implemented stringent quality control measures, ensuring consistent mechanical properties across batches, which is vital for reliable performance in critical fire safety equipment.
Strengths: High temperature resistance, improved corrosion resistance, and consistent mechanical properties. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost compared to standard 4140 steel grades, and limited availability outside of Japan.
Tata Steel Ltd.
Technical Solution: Tata Steel Ltd. has developed a specialized grade of 4140 steel optimized for fire safety equipment manufacturing. Their proprietary alloying process enhances the steel's fire-resistant properties while maintaining its excellent mechanical characteristics. Tata's 4140 steel grade exhibits a unique microstructure that provides improved thermal stability up to temperatures of 900°C (1,652°F)[4]. The company has implemented advanced rolling and heat treatment techniques to ensure uniform grain structure throughout the steel, resulting in consistent performance across different batches. Tata Steel's 4140 grade also demonstrates superior weldability, crucial for fabricating complex fire safety equipment. The company has conducted extensive fire simulation tests, proving that their 4140 steel retains over 70% of its room temperature yield strength at 600°C (1,112°F), significantly outperforming standard 4140 grades[5].
Strengths: Enhanced thermal stability, superior weldability, and high-temperature strength retention. Weaknesses: Limited global availability and potentially higher cost due to specialized production processes.
Innovations in 4140 Steel for Fire Resistance
Special steels; cryogenic process for the production thereof; use of special steels in a saline and/or high-pressure environment
PatentWO2014008564A1
Innovation
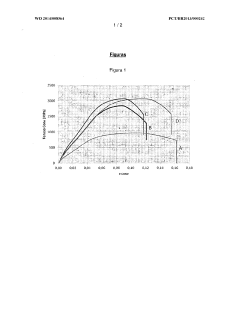
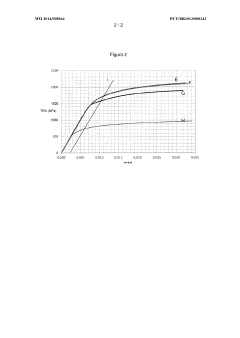
- A specific cryogenic treatment process involving tempering, cooling, immersion in cryogenic material, and subsequent tempering is applied to carbon steels, reducing retained austenite content and precipitating carbides, transforming martensite morphology and improving mechanical properties.
4140 medium-thick-wall seamless steel pipe and production method
PatentActiveCN113862556A
Innovation
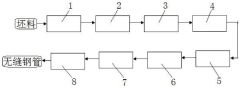
- Using the optimized 4140 composition and the new Diesel hot rolling unit rolling combined with water quenching instead of oil quenching, medium-thick wall seamless products are produced through converter smelting, continuous casting, annealing, heating, rolling, water quenching, tempering and straightening processes. steel pipe.
Regulatory Standards for Fire Safety Equipment Materials
The regulatory landscape for fire safety equipment materials is complex and stringent, reflecting the critical importance of these components in protecting lives and property. For 4140 steel, a material commonly used in fire safety equipment manufacturing, compliance with various standards is paramount.
In the United States, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) sets forth numerous codes and standards that directly impact the use of materials like 4140 steel in fire safety equipment. NFPA 1901, for instance, outlines the standards for automotive fire apparatus, which may incorporate 4140 steel components. This standard specifies requirements for material strength, durability, and performance under extreme conditions.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) also plays a crucial role in regulating fire safety equipment materials. OSHA's standards, particularly those found in 29 CFR 1910 Subpart L, detail the requirements for fire protection equipment in workplace settings. These regulations often reference material specifications that 4140 steel must meet to be deemed suitable for use in fire safety applications.
Internationally, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides guidelines that influence the use of materials in fire safety equipment. ISO 23932, which focuses on fire safety engineering principles, includes considerations for material selection and performance that manufacturers using 4140 steel must address.
The European Committee for Standardization (CEN) has developed EN 54, a series of standards for fire detection and fire alarm systems. While not directly addressing 4140 steel, these standards set performance criteria that materials used in fire safety equipment must meet, influencing the selection and application of steels like 4140 in European markets.
Material-specific standards also apply to 4140 steel when used in fire safety equipment. ASTM International's A29 standard specification for general requirements for steel bars, carbon and alloy, hot-wrought, provides guidelines that 4140 steel must meet. This standard ensures the material's consistency and quality, which are crucial for fire safety applications.
Manufacturers utilizing 4140 steel must also consider environmental regulations, such as the European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive, which limits the use of certain hazardous materials in electrical and electronic equipment, including some fire safety devices.
Compliance with these regulatory standards is not only a legal requirement but also a critical factor in ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of fire safety equipment. Manufacturers must continuously monitor and adapt to evolving regulations to maintain the integrity of their products and the safety of end-users.
In the United States, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) sets forth numerous codes and standards that directly impact the use of materials like 4140 steel in fire safety equipment. NFPA 1901, for instance, outlines the standards for automotive fire apparatus, which may incorporate 4140 steel components. This standard specifies requirements for material strength, durability, and performance under extreme conditions.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) also plays a crucial role in regulating fire safety equipment materials. OSHA's standards, particularly those found in 29 CFR 1910 Subpart L, detail the requirements for fire protection equipment in workplace settings. These regulations often reference material specifications that 4140 steel must meet to be deemed suitable for use in fire safety applications.
Internationally, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides guidelines that influence the use of materials in fire safety equipment. ISO 23932, which focuses on fire safety engineering principles, includes considerations for material selection and performance that manufacturers using 4140 steel must address.
The European Committee for Standardization (CEN) has developed EN 54, a series of standards for fire detection and fire alarm systems. While not directly addressing 4140 steel, these standards set performance criteria that materials used in fire safety equipment must meet, influencing the selection and application of steels like 4140 in European markets.
Material-specific standards also apply to 4140 steel when used in fire safety equipment. ASTM International's A29 standard specification for general requirements for steel bars, carbon and alloy, hot-wrought, provides guidelines that 4140 steel must meet. This standard ensures the material's consistency and quality, which are crucial for fire safety applications.
Manufacturers utilizing 4140 steel must also consider environmental regulations, such as the European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive, which limits the use of certain hazardous materials in electrical and electronic equipment, including some fire safety devices.
Compliance with these regulatory standards is not only a legal requirement but also a critical factor in ensuring the reliability and effectiveness of fire safety equipment. Manufacturers must continuously monitor and adapt to evolving regulations to maintain the integrity of their products and the safety of end-users.
Environmental Impact of 4140 Steel Production and Use
The production and use of 4140 steel in fire safety equipment manufacturing have significant environmental implications. The steel-making process, particularly for alloy steels like 4140, is energy-intensive and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. The primary production method involves electric arc furnaces or basic oxygen furnaces, both of which require substantial electricity or fossil fuel inputs. This energy consumption leads to considerable CO2 emissions, contributing to global climate change concerns.
Mining of raw materials for 4140 steel, including iron ore, chromium, and molybdenum, can result in habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. The extraction processes often involve heavy machinery and chemical treatments, which can have long-lasting impacts on local ecosystems. Additionally, the transportation of raw materials and finished products adds to the carbon footprint of 4140 steel production.
Water usage is another critical environmental factor in 4140 steel manufacturing. The production process requires large volumes of water for cooling and cleaning, potentially straining local water resources. While many modern steel plants implement water recycling systems, there is still a net consumption and potential for thermal pollution in nearby water bodies.
The use of 4140 steel in fire safety equipment does offer some environmental benefits. Its high strength and durability mean that products made from this steel have longer lifespans, reducing the need for frequent replacements and thereby lowering the overall environmental impact over time. The steel's resistance to corrosion and high temperatures also contributes to the longevity of fire safety equipment, further enhancing its sustainability profile.
Recycling plays a crucial role in mitigating the environmental impact of 4140 steel. Steel is one of the most recycled materials globally, and the recycling process for alloy steels like 4140 requires significantly less energy than primary production. This closed-loop system helps conserve natural resources and reduce overall emissions associated with steel production.
In the context of fire safety equipment, the use of 4140 steel contributes to improved safety standards and potentially reduces the environmental impact of fire incidents. By manufacturing more effective and durable fire safety equipment, the steel indirectly helps prevent or mitigate fires, which can have devastating environmental consequences.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, steel manufacturers are increasingly adopting cleaner technologies and more efficient processes. This includes the use of renewable energy sources, implementation of carbon capture and storage technologies, and development of novel steel-making processes that reduce emissions and resource consumption. These advancements are gradually improving the environmental profile of 4140 steel production and its application in fire safety equipment manufacturing.
Mining of raw materials for 4140 steel, including iron ore, chromium, and molybdenum, can result in habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. The extraction processes often involve heavy machinery and chemical treatments, which can have long-lasting impacts on local ecosystems. Additionally, the transportation of raw materials and finished products adds to the carbon footprint of 4140 steel production.
Water usage is another critical environmental factor in 4140 steel manufacturing. The production process requires large volumes of water for cooling and cleaning, potentially straining local water resources. While many modern steel plants implement water recycling systems, there is still a net consumption and potential for thermal pollution in nearby water bodies.
The use of 4140 steel in fire safety equipment does offer some environmental benefits. Its high strength and durability mean that products made from this steel have longer lifespans, reducing the need for frequent replacements and thereby lowering the overall environmental impact over time. The steel's resistance to corrosion and high temperatures also contributes to the longevity of fire safety equipment, further enhancing its sustainability profile.
Recycling plays a crucial role in mitigating the environmental impact of 4140 steel. Steel is one of the most recycled materials globally, and the recycling process for alloy steels like 4140 requires significantly less energy than primary production. This closed-loop system helps conserve natural resources and reduce overall emissions associated with steel production.
In the context of fire safety equipment, the use of 4140 steel contributes to improved safety standards and potentially reduces the environmental impact of fire incidents. By manufacturing more effective and durable fire safety equipment, the steel indirectly helps prevent or mitigate fires, which can have devastating environmental consequences.
As environmental regulations become more stringent, steel manufacturers are increasingly adopting cleaner technologies and more efficient processes. This includes the use of renewable energy sources, implementation of carbon capture and storage technologies, and development of novel steel-making processes that reduce emissions and resource consumption. These advancements are gradually improving the environmental profile of 4140 steel production and its application in fire safety equipment manufacturing.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!