Application of 4140 Steel in Drill Bit Manufacturing
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
4140 Steel Evolution
The evolution of 4140 steel in drill bit manufacturing represents a significant advancement in the oil and gas industry. This medium carbon, low alloy steel has undergone several iterations since its inception, each improving its suitability for drill bit applications.
In the early stages of oil exploration, drill bits were primarily made from carbon steel, which lacked the durability required for deep drilling operations. The introduction of 4140 steel in the mid-20th century marked a turning point in drill bit manufacturing. Its composition of chromium, molybdenum, and manganese provided a superior balance of strength, toughness, and wear resistance.
The 1960s and 1970s saw further refinements in the heat treatment processes for 4140 steel, enhancing its mechanical properties. Quenching and tempering techniques were optimized to achieve a microstructure that could withstand the extreme conditions encountered in drilling operations. This period also witnessed the development of more precise alloying methods, allowing for tighter control over the steel's chemical composition.
During the 1980s and 1990s, advancements in metallurgy led to improvements in the cleanliness of 4140 steel. Reduced impurities and inclusions resulted in more consistent performance and increased fatigue resistance. Simultaneously, surface treatment technologies such as carburizing and nitriding were adapted for 4140 steel, further enhancing the wear resistance of drill bit components.
The turn of the millennium brought about a focus on customizing 4140 steel for specific drilling environments. Manufacturers began tailoring the steel's properties to suit different geological formations and drilling conditions. This era also saw the integration of computer modeling and simulation in the design process, allowing for more precise prediction of steel behavior under various stress conditions.
Recent years have witnessed the emergence of nano-engineering techniques applied to 4140 steel. These innovations aim to manipulate the steel's microstructure at the nanoscale, potentially leading to unprecedented improvements in strength and toughness. Additionally, research into advanced coating technologies compatible with 4140 steel is ongoing, promising to further extend the lifespan and performance of drill bits in increasingly challenging drilling scenarios.
The evolution of 4140 steel in drill bit manufacturing continues to be driven by the demands of deeper, more complex drilling operations. As the industry pushes the boundaries of exploration, the development of this versatile steel remains crucial in meeting the ever-increasing performance requirements of modern drill bits.
In the early stages of oil exploration, drill bits were primarily made from carbon steel, which lacked the durability required for deep drilling operations. The introduction of 4140 steel in the mid-20th century marked a turning point in drill bit manufacturing. Its composition of chromium, molybdenum, and manganese provided a superior balance of strength, toughness, and wear resistance.
The 1960s and 1970s saw further refinements in the heat treatment processes for 4140 steel, enhancing its mechanical properties. Quenching and tempering techniques were optimized to achieve a microstructure that could withstand the extreme conditions encountered in drilling operations. This period also witnessed the development of more precise alloying methods, allowing for tighter control over the steel's chemical composition.
During the 1980s and 1990s, advancements in metallurgy led to improvements in the cleanliness of 4140 steel. Reduced impurities and inclusions resulted in more consistent performance and increased fatigue resistance. Simultaneously, surface treatment technologies such as carburizing and nitriding were adapted for 4140 steel, further enhancing the wear resistance of drill bit components.
The turn of the millennium brought about a focus on customizing 4140 steel for specific drilling environments. Manufacturers began tailoring the steel's properties to suit different geological formations and drilling conditions. This era also saw the integration of computer modeling and simulation in the design process, allowing for more precise prediction of steel behavior under various stress conditions.
Recent years have witnessed the emergence of nano-engineering techniques applied to 4140 steel. These innovations aim to manipulate the steel's microstructure at the nanoscale, potentially leading to unprecedented improvements in strength and toughness. Additionally, research into advanced coating technologies compatible with 4140 steel is ongoing, promising to further extend the lifespan and performance of drill bits in increasingly challenging drilling scenarios.
The evolution of 4140 steel in drill bit manufacturing continues to be driven by the demands of deeper, more complex drilling operations. As the industry pushes the boundaries of exploration, the development of this versatile steel remains crucial in meeting the ever-increasing performance requirements of modern drill bits.
Drill Bit Market Demand
The global drill bit market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand in various industries such as oil and gas, mining, construction, and manufacturing. The market for drill bits is closely tied to the overall drilling activity across these sectors, with the oil and gas industry being a major contributor to market demand.
In recent years, the drill bit market has seen a shift towards more advanced and durable materials, with 4140 steel emerging as a popular choice for drill bit manufacturing. This high-strength alloy steel offers an excellent combination of hardness, toughness, and wear resistance, making it ideal for the demanding conditions encountered in drilling operations.
The oil and gas industry remains the largest consumer of drill bits, accounting for a significant portion of market demand. As exploration and production activities continue to expand into more challenging environments, such as deep-water and unconventional reservoirs, there is a growing need for drill bits that can withstand higher pressures, temperatures, and abrasive formations. This trend has led to increased demand for drill bits made from high-performance materials like 4140 steel.
The mining sector is another key driver of drill bit market demand. As easily accessible mineral deposits become depleted, mining companies are forced to explore deeper and in more challenging geological conditions. This has created a need for more robust and efficient drill bits that can maintain performance in harsh environments, further boosting the demand for 4140 steel-based drill bits.
In the construction industry, the growing trend towards urbanization and infrastructure development has led to an increased demand for drilling equipment, including drill bits. The use of 4140 steel in drill bit manufacturing for construction applications has gained traction due to its ability to handle diverse soil and rock conditions encountered in foundation work, tunneling, and other construction projects.
The manufacturing sector also contributes to the drill bit market demand, particularly in industries requiring precision drilling operations, such as aerospace, automotive, and machinery production. The superior mechanical properties of 4140 steel make it an attractive option for manufacturing drill bits used in these high-precision applications.
As environmental concerns and regulations become more stringent, there is a growing emphasis on developing drill bits that can improve drilling efficiency and reduce environmental impact. This trend has further fueled the demand for advanced materials like 4140 steel, which can contribute to longer bit life, reduced drilling time, and improved overall drilling performance.
In recent years, the drill bit market has seen a shift towards more advanced and durable materials, with 4140 steel emerging as a popular choice for drill bit manufacturing. This high-strength alloy steel offers an excellent combination of hardness, toughness, and wear resistance, making it ideal for the demanding conditions encountered in drilling operations.
The oil and gas industry remains the largest consumer of drill bits, accounting for a significant portion of market demand. As exploration and production activities continue to expand into more challenging environments, such as deep-water and unconventional reservoirs, there is a growing need for drill bits that can withstand higher pressures, temperatures, and abrasive formations. This trend has led to increased demand for drill bits made from high-performance materials like 4140 steel.
The mining sector is another key driver of drill bit market demand. As easily accessible mineral deposits become depleted, mining companies are forced to explore deeper and in more challenging geological conditions. This has created a need for more robust and efficient drill bits that can maintain performance in harsh environments, further boosting the demand for 4140 steel-based drill bits.
In the construction industry, the growing trend towards urbanization and infrastructure development has led to an increased demand for drilling equipment, including drill bits. The use of 4140 steel in drill bit manufacturing for construction applications has gained traction due to its ability to handle diverse soil and rock conditions encountered in foundation work, tunneling, and other construction projects.
The manufacturing sector also contributes to the drill bit market demand, particularly in industries requiring precision drilling operations, such as aerospace, automotive, and machinery production. The superior mechanical properties of 4140 steel make it an attractive option for manufacturing drill bits used in these high-precision applications.
As environmental concerns and regulations become more stringent, there is a growing emphasis on developing drill bits that can improve drilling efficiency and reduce environmental impact. This trend has further fueled the demand for advanced materials like 4140 steel, which can contribute to longer bit life, reduced drilling time, and improved overall drilling performance.
4140 Steel Challenges
The application of 4140 steel in drill bit manufacturing faces several significant challenges that impact its performance and durability in harsh drilling environments. One of the primary issues is the material's susceptibility to hydrogen embrittlement, particularly in sour gas wells or environments with high hydrogen sulfide concentrations. This phenomenon can lead to premature failure of drill bit components, reducing their operational lifespan and increasing the risk of costly downtime.
Another challenge lies in achieving the optimal balance between hardness and toughness. While 4140 steel can be heat-treated to attain high hardness levels, this often comes at the expense of toughness. In drill bit applications, where both wear resistance and impact strength are crucial, finding the right compromise between these properties is essential but challenging. Inadequate toughness can result in chipping or fracturing of cutting elements under the high-stress conditions encountered during drilling operations.
The heat treatment process itself presents additional complexities. Achieving consistent and uniform properties throughout the drill bit components, especially in larger or complex geometries, can be difficult. Variations in cooling rates during quenching can lead to residual stresses and potential distortions, affecting the dimensional accuracy and performance of the finished product. Moreover, the heat treatment parameters must be carefully controlled to avoid the formation of undesirable microstructures that could compromise the steel's mechanical properties.
Corrosion resistance is another area of concern for 4140 steel in drill bit applications. While the material offers moderate corrosion resistance, it may not be sufficient for all drilling environments, particularly those involving corrosive fluids or high temperatures. This limitation can lead to accelerated wear and degradation of drill bit components, reducing their effectiveness and lifespan.
The machining of 4140 steel for drill bit components also presents challenges. The material's high strength and hardness after heat treatment can make it difficult to machine with precision, potentially leading to increased production costs and longer manufacturing times. This issue is particularly pronounced when creating complex geometries or features required for advanced drill bit designs.
Lastly, the weight of 4140 steel components can be a limiting factor in certain drilling applications where lighter materials are preferred to reduce overall drill string weight. This challenge becomes more significant as drilling depths increase and weight considerations become more critical for efficient operations.
Another challenge lies in achieving the optimal balance between hardness and toughness. While 4140 steel can be heat-treated to attain high hardness levels, this often comes at the expense of toughness. In drill bit applications, where both wear resistance and impact strength are crucial, finding the right compromise between these properties is essential but challenging. Inadequate toughness can result in chipping or fracturing of cutting elements under the high-stress conditions encountered during drilling operations.
The heat treatment process itself presents additional complexities. Achieving consistent and uniform properties throughout the drill bit components, especially in larger or complex geometries, can be difficult. Variations in cooling rates during quenching can lead to residual stresses and potential distortions, affecting the dimensional accuracy and performance of the finished product. Moreover, the heat treatment parameters must be carefully controlled to avoid the formation of undesirable microstructures that could compromise the steel's mechanical properties.
Corrosion resistance is another area of concern for 4140 steel in drill bit applications. While the material offers moderate corrosion resistance, it may not be sufficient for all drilling environments, particularly those involving corrosive fluids or high temperatures. This limitation can lead to accelerated wear and degradation of drill bit components, reducing their effectiveness and lifespan.
The machining of 4140 steel for drill bit components also presents challenges. The material's high strength and hardness after heat treatment can make it difficult to machine with precision, potentially leading to increased production costs and longer manufacturing times. This issue is particularly pronounced when creating complex geometries or features required for advanced drill bit designs.
Lastly, the weight of 4140 steel components can be a limiting factor in certain drilling applications where lighter materials are preferred to reduce overall drill string weight. This challenge becomes more significant as drilling depths increase and weight considerations become more critical for efficient operations.
Current 4140 Solutions
01 Composition and properties of 4140 steel
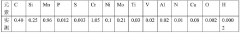
4140 steel is a medium carbon, low alloy steel known for its high strength, toughness, and wear resistance. It typically contains chromium and molybdenum as key alloying elements, which contribute to its improved hardenability and mechanical properties. This steel grade is widely used in various industrial applications due to its balanced combination of strength and ductility.- Composition and properties of 4140 steel: 4140 steel is a medium carbon, low alloy steel known for its high strength, toughness, and wear resistance. It typically contains chromium and molybdenum as key alloying elements, which contribute to its improved hardenability and mechanical properties. This steel grade is widely used in various industrial applications due to its balanced combination of strength and ductility.
- Heat treatment processes for 4140 steel: Various heat treatment processes can be applied to 4140 steel to enhance its mechanical properties. These may include quenching and tempering, normalizing, and annealing. The specific heat treatment parameters can be adjusted to achieve desired hardness, strength, and toughness levels, making 4140 steel suitable for a wide range of applications in different industries.
- Applications of 4140 steel in oil and gas industry: 4140 steel is commonly used in the oil and gas industry for various components and equipment. Its high strength and resistance to wear and corrosion make it suitable for applications such as drill collars, tool joints, and other downhole tools. The material's properties contribute to improved performance and durability in challenging drilling environments.
- Manufacturing processes for 4140 steel components: Various manufacturing processes can be employed to produce components from 4140 steel. These may include forging, machining, and casting. The choice of manufacturing method depends on the specific requirements of the final product, such as shape complexity, dimensional accuracy, and surface finish. Advanced manufacturing techniques can be used to optimize the production of 4140 steel parts for different applications.
- Surface treatments and coatings for 4140 steel: Various surface treatments and coatings can be applied to 4140 steel components to enhance their performance and durability. These treatments may include nitriding, carburizing, or the application of protective coatings. Such processes can improve the steel's wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and fatigue strength, extending the service life of components made from 4140 steel in demanding applications.
02 Heat treatment processes for 4140 steel
Various heat treatment processes can be applied to 4140 steel to enhance its mechanical properties. These may include quenching and tempering, normalizing, and annealing. The specific heat treatment process chosen depends on the desired final properties and application requirements. Proper heat treatment can significantly improve the steel's strength, hardness, and toughness.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications of 4140 steel in oil and gas industry
4140 steel is commonly used in the oil and gas industry due to its excellent mechanical properties and resistance to harsh environments. It is often employed in the manufacturing of drilling equipment, wellhead components, and other downhole tools. The steel's high strength-to-weight ratio and good fatigue resistance make it suitable for these demanding applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Machining and fabrication of 4140 steel
4140 steel can be machined and fabricated using various techniques, including turning, milling, drilling, and welding. However, due to its high strength and hardness, especially after heat treatment, special considerations may be required during machining processes. Proper tooling, cutting speeds, and cooling methods are essential for efficient and accurate fabrication of 4140 steel components.Expand Specific Solutions05 Surface treatments and coatings for 4140 steel
To further enhance the performance and durability of 4140 steel components, various surface treatments and coatings can be applied. These may include nitriding, carburizing, or the application of wear-resistant coatings. Such treatments can improve the steel's surface hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance, extending the service life of components made from 4140 steel.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The application of 4140 steel in drill bit manufacturing is in a mature stage of industry development, with a significant global market size driven by ongoing demand in oil and gas exploration. The technology is well-established, with major players like Schlumberger, Baker Hughes, and Smith International dominating the field. These companies have extensive experience and advanced capabilities in drill bit design and manufacturing. Emerging players such as Ulterra Drilling Technologies and Varel International are also contributing to innovation in the sector. The market is characterized by continuous improvements in material properties and bit designs to enhance drilling efficiency and durability in challenging environments.
Schlumberger Technologies, Inc.
Technical Solution: Schlumberger has developed advanced manufacturing techniques for 4140 steel drill bits, incorporating precision heat treatment and surface hardening processes. Their method involves controlled quenching and tempering to achieve optimal hardness and toughness balance. They utilize computer-aided design and simulation to optimize bit geometry for specific drilling conditions[1]. Schlumberger's bits feature proprietary cutter placement patterns and hydraulic designs to enhance drilling efficiency and bit life in various formations[2]. The company has also implemented advanced coating technologies to improve wear resistance and reduce friction during drilling operations[3].
Strengths: Industry-leading R&D capabilities, global presence, and extensive field testing. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to some competitors, potential over-engineering for simpler applications.
Baker Hughes Co.
Technical Solution: Baker Hughes employs a multi-stage heat treatment process for 4140 steel drill bits, focusing on achieving a fine-grained martensitic structure. Their manufacturing technique includes precise control of carbon diffusion during austenitization, followed by carefully timed quenching and tempering cycles[4]. The company has developed proprietary alloying modifications to enhance the base 4140 steel properties, improving both hardness and impact resistance. Baker Hughes utilizes advanced CNC machining and EDM techniques to create complex bit geometries with tight tolerances[5]. They have also implemented innovative hardfacing applications to critical wear areas, extending bit life in abrasive formations[6].
Strengths: Comprehensive manufacturing capabilities, strong focus on customization for specific drilling environments. Weaknesses: Potentially longer lead times for highly customized bits, higher initial investment costs.
4140 Steel Innovations
100-150mm alloy structural steel 4140 thick plate and production technique thereof
PatentActiveCN103725966A
Innovation
- KR hot metal pretreatment, converter smelting, argon blowing treatment, LF refining, VD refining, die casting, steel ingot slow cooling, steel ingot cleaning, heating, controlled rolling, stack cooling, heat treatment and slow cooling are used to strictly control the content of harmful elements in steel. And the rolling process, through multi-stage rolling and heat treatment, ensures that the internal residual stress of the steel plate is minimized and the performance indicators meet the standards.
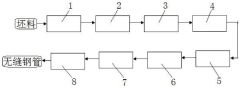
4140 medium-thick-wall seamless steel pipe and production method
PatentActiveCN113862556A
Innovation
- Using the optimized 4140 composition and the new Diesel hot rolling unit rolling combined with water quenching instead of oil quenching, medium-thick wall seamless products are produced through converter smelting, continuous casting, annealing, heating, rolling, water quenching, tempering and straightening processes. steel pipe.
Material Sustainability
The sustainability of 4140 steel in drill bit manufacturing is a critical consideration for the industry's long-term viability and environmental impact. This alloy steel, known for its high strength and wear resistance, offers several advantages in terms of material sustainability.
4140 steel's durability and resistance to wear contribute significantly to the longevity of drill bits, reducing the frequency of replacements and, consequently, the overall material consumption. This extended lifespan not only conserves resources but also minimizes waste generation in the manufacturing process. The steel's ability to withstand harsh drilling conditions without rapid degradation ensures that fewer drill bits are discarded, aligning with sustainable manufacturing practices.
The recyclability of 4140 steel further enhances its sustainability profile. At the end of a drill bit's useful life, the steel can be reclaimed and recycled, reducing the demand for virgin materials and the associated environmental impacts of mining and processing. This closed-loop approach to material usage aligns with circular economy principles, promoting resource efficiency and waste reduction.
From an energy perspective, the heat treatment processes required for 4140 steel, while energy-intensive, result in a product that offers superior performance and longevity. This trade-off between initial energy investment and long-term durability often leads to net energy savings over the product's lifecycle. Manufacturers are continually optimizing heat treatment processes to reduce energy consumption without compromising the steel's properties.
The alloying elements in 4140 steel, primarily chromium and molybdenum, are carefully selected to impart specific properties. While the extraction of these elements has environmental implications, their judicious use in 4140 steel results in a material that outperforms many alternatives in drill bit applications. This performance advantage translates to more efficient drilling operations, potentially reducing overall energy consumption and environmental impact in the oil and gas industry.
Advancements in manufacturing technologies are further improving the sustainability of 4140 steel drill bits. Precision machining and near-net-shape forming techniques minimize material waste during production. Additionally, surface treatments and coatings can enhance the steel's already impressive wear resistance, further extending the operational life of drill bits and reducing the frequency of replacements.
As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, research is ongoing to optimize the composition and processing of 4140 steel to enhance its environmental profile without compromising performance. This includes exploring ways to reduce the carbon footprint of steel production and investigating bio-based or recycled alternatives for certain alloying elements.
4140 steel's durability and resistance to wear contribute significantly to the longevity of drill bits, reducing the frequency of replacements and, consequently, the overall material consumption. This extended lifespan not only conserves resources but also minimizes waste generation in the manufacturing process. The steel's ability to withstand harsh drilling conditions without rapid degradation ensures that fewer drill bits are discarded, aligning with sustainable manufacturing practices.
The recyclability of 4140 steel further enhances its sustainability profile. At the end of a drill bit's useful life, the steel can be reclaimed and recycled, reducing the demand for virgin materials and the associated environmental impacts of mining and processing. This closed-loop approach to material usage aligns with circular economy principles, promoting resource efficiency and waste reduction.
From an energy perspective, the heat treatment processes required for 4140 steel, while energy-intensive, result in a product that offers superior performance and longevity. This trade-off between initial energy investment and long-term durability often leads to net energy savings over the product's lifecycle. Manufacturers are continually optimizing heat treatment processes to reduce energy consumption without compromising the steel's properties.
The alloying elements in 4140 steel, primarily chromium and molybdenum, are carefully selected to impart specific properties. While the extraction of these elements has environmental implications, their judicious use in 4140 steel results in a material that outperforms many alternatives in drill bit applications. This performance advantage translates to more efficient drilling operations, potentially reducing overall energy consumption and environmental impact in the oil and gas industry.
Advancements in manufacturing technologies are further improving the sustainability of 4140 steel drill bits. Precision machining and near-net-shape forming techniques minimize material waste during production. Additionally, surface treatments and coatings can enhance the steel's already impressive wear resistance, further extending the operational life of drill bits and reducing the frequency of replacements.
As the industry moves towards more sustainable practices, research is ongoing to optimize the composition and processing of 4140 steel to enhance its environmental profile without compromising performance. This includes exploring ways to reduce the carbon footprint of steel production and investigating bio-based or recycled alternatives for certain alloying elements.
Regulatory Compliance
The application of 4140 steel in drill bit manufacturing is subject to various regulatory compliance requirements to ensure safety, quality, and environmental standards are met. These regulations primarily focus on material composition, manufacturing processes, and performance standards.
ASTM International, formerly known as the American Society for Testing and Materials, provides several standards relevant to 4140 steel and its use in drill bits. ASTM A29/A29M specifies the standard specification for general requirements for steel bars, carbon and alloy, hot-wrought, which includes 4140 steel. This standard outlines the chemical composition, mechanical properties, and testing methods required for compliance.
The American Petroleum Institute (API) also plays a crucial role in setting standards for drill bit manufacturing. API Specification 7-1 covers the requirements for rotary drill stem elements, including drill bits. It provides guidelines for material selection, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures that manufacturers must adhere to when producing drill bits using 4140 steel.
In terms of environmental compliance, manufacturers must consider regulations such as the European Union's Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. This regulation aims to protect human health and the environment from the risks posed by chemicals. Manufacturers using 4140 steel in drill bit production must ensure that the material and any associated processes comply with REACH requirements.
Occupational safety regulations also apply to the manufacturing process. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States sets standards for workplace safety, including those related to metalworking and machining operations involved in drill bit production. Manufacturers must comply with OSHA regulations to ensure worker safety during the production of drill bits using 4140 steel.
Quality management systems are another aspect of regulatory compliance. ISO 9001:2015 provides a framework for quality management that many drill bit manufacturers adopt to ensure consistent product quality and customer satisfaction. This standard helps companies implement processes that meet both regulatory requirements and customer expectations.
Furthermore, specific industry standards may apply depending on the intended use of the drill bits. For example, drill bits used in the oil and gas industry may need to comply with additional standards set by organizations such as the International Association of Drilling Contractors (IADC) or the Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE).
Compliance with these regulations and standards is essential for manufacturers using 4140 steel in drill bit production. It not only ensures legal and ethical operation but also contributes to product reliability, safety, and market acceptance. Manufacturers must stay informed about updates to these regulations and standards to maintain compliance and remain competitive in the industry.
ASTM International, formerly known as the American Society for Testing and Materials, provides several standards relevant to 4140 steel and its use in drill bits. ASTM A29/A29M specifies the standard specification for general requirements for steel bars, carbon and alloy, hot-wrought, which includes 4140 steel. This standard outlines the chemical composition, mechanical properties, and testing methods required for compliance.
The American Petroleum Institute (API) also plays a crucial role in setting standards for drill bit manufacturing. API Specification 7-1 covers the requirements for rotary drill stem elements, including drill bits. It provides guidelines for material selection, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures that manufacturers must adhere to when producing drill bits using 4140 steel.
In terms of environmental compliance, manufacturers must consider regulations such as the European Union's Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. This regulation aims to protect human health and the environment from the risks posed by chemicals. Manufacturers using 4140 steel in drill bit production must ensure that the material and any associated processes comply with REACH requirements.
Occupational safety regulations also apply to the manufacturing process. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States sets standards for workplace safety, including those related to metalworking and machining operations involved in drill bit production. Manufacturers must comply with OSHA regulations to ensure worker safety during the production of drill bits using 4140 steel.
Quality management systems are another aspect of regulatory compliance. ISO 9001:2015 provides a framework for quality management that many drill bit manufacturers adopt to ensure consistent product quality and customer satisfaction. This standard helps companies implement processes that meet both regulatory requirements and customer expectations.
Furthermore, specific industry standards may apply depending on the intended use of the drill bits. For example, drill bits used in the oil and gas industry may need to comply with additional standards set by organizations such as the International Association of Drilling Contractors (IADC) or the Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE).
Compliance with these regulations and standards is essential for manufacturers using 4140 steel in drill bit production. It not only ensures legal and ethical operation but also contributes to product reliability, safety, and market acceptance. Manufacturers must stay informed about updates to these regulations and standards to maintain compliance and remain competitive in the industry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!