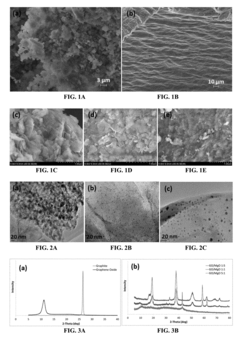
Graphene Oxide: Innovations for Pollution Reduction
Graphene Oxide Evolution and Objectives
Graphene oxide, a derivative of graphene, has emerged as a revolutionary material in the field of pollution reduction. Since its discovery in the early 2000s, researchers have been exploring its unique properties and potential applications in environmental remediation. The evolution of graphene oxide technology has been marked by significant advancements in synthesis methods, functionalization techniques, and integration into various pollution control systems.
Initially, graphene oxide was primarily studied for its electronic and mechanical properties. However, as environmental concerns grew, scientists began to investigate its potential for pollution reduction. The high surface area, abundant functional groups, and exceptional adsorption capabilities of graphene oxide made it an ideal candidate for removing contaminants from water and air.
The development of graphene oxide for pollution reduction has progressed through several key stages. Early research focused on understanding the material's structure and properties, followed by efforts to optimize synthesis methods for large-scale production. Subsequently, researchers explored various modification techniques to enhance the material's selectivity and efficiency in pollutant removal.
One of the primary objectives in graphene oxide research for pollution reduction is to develop cost-effective and scalable production methods. This includes improving the oxidation process of graphite and refining exfoliation techniques to produce high-quality graphene oxide sheets. Additionally, researchers aim to enhance the material's stability and recyclability to make it more suitable for long-term environmental applications.
Another crucial goal is to expand the range of pollutants that graphene oxide can effectively remove. While initial studies focused on heavy metal ions and organic dyes, current research aims to tackle more complex pollutants such as pharmaceutical residues, microplastics, and emerging contaminants. This involves tailoring the surface chemistry of graphene oxide to increase its affinity for specific target pollutants.
Researchers are also working towards integrating graphene oxide into existing water and air treatment systems. This includes developing composite materials that combine graphene oxide with other adsorbents or catalysts to create synergistic effects. The objective is to design multifunctional materials that can simultaneously remove various types of pollutants and potentially degrade them into harmless byproducts.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on developing environmentally friendly and sustainable approaches to graphene oxide production and application. This includes exploring bio-based precursors for synthesis, minimizing the use of harsh chemicals, and ensuring that the material itself does not pose any ecological risks when used in environmental remediation.
Market Demand for Pollution Reduction Solutions
The global market for pollution reduction solutions has been experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations worldwide. The demand for innovative technologies to address air, water, and soil pollution has created a substantial market opportunity for graphene oxide-based solutions. Industries across various sectors, including manufacturing, energy, transportation, and agriculture, are actively seeking advanced materials and technologies to mitigate their environmental impact and comply with evolving regulatory standards.
In the air pollution control segment, graphene oxide has shown promising applications in filtration systems and gas sensors. The market for air quality monitoring and purification technologies is projected to expand rapidly, with a particular focus on urban areas and industrial zones. Graphene oxide's exceptional adsorption properties and large surface area make it an attractive material for capturing particulate matter and harmful gases, addressing the growing concern over air quality in major cities worldwide.
Water treatment represents another significant market opportunity for graphene oxide-based solutions. With increasing water scarcity and contamination issues globally, there is a rising demand for efficient water purification technologies. Graphene oxide membranes have demonstrated superior performance in removing various pollutants, including heavy metals, organic compounds, and microplastics from water sources. The municipal water treatment sector, as well as industries such as mining, textiles, and pharmaceuticals, are potential adopters of these advanced filtration solutions.
Soil remediation is an emerging market segment where graphene oxide shows considerable potential. As awareness of soil pollution's impact on agriculture and ecosystem health grows, there is an increasing need for effective soil decontamination methods. Graphene oxide's ability to adsorb heavy metals and organic pollutants makes it a promising candidate for soil remediation applications, particularly in brownfield sites and areas affected by industrial activities.
The market demand for graphene oxide in pollution reduction is further bolstered by the global push towards sustainable development and circular economy principles. Industries are increasingly looking for materials that not only address pollution but also offer recyclability and reduced environmental footprint. Graphene oxide's potential for regeneration and reuse aligns well with these sustainability goals, making it an attractive option for companies seeking to improve their environmental performance.
As governments worldwide implement stricter environmental regulations and emission standards, the market for pollution reduction technologies is expected to expand further. This regulatory landscape creates a favorable environment for the adoption of innovative solutions like graphene oxide-based products. Additionally, growing consumer awareness and demand for eco-friendly products are driving companies to invest in cleaner technologies, further fueling the market for advanced pollution reduction solutions.
Graphene Oxide: Current State and Challenges
Graphene oxide (GO) has emerged as a promising material for pollution reduction, yet its current state and challenges present a complex landscape. The synthesis and large-scale production of high-quality GO remain significant hurdles. While various methods exist, including modified Hummers' method and chemical vapor deposition, achieving consistent quality and scalability simultaneously proves challenging. The oxidation process, crucial for GO production, often results in structural defects and variability in oxygen-containing functional groups, affecting its performance in pollution reduction applications.
The characterization and standardization of GO also pose considerable challenges. The lack of universally accepted standards for GO quality assessment hinders comparisons between different research outcomes and industrial applications. This inconsistency in characterization methods and reporting standards impedes the translation of laboratory successes to real-world environmental solutions.
In terms of environmental applications, GO shows great potential in water purification, air filtration, and soil remediation. However, the stability and long-term performance of GO-based materials in complex environmental matrices remain concerns. The potential for GO to aggregate or re-stack in aqueous environments can reduce its effective surface area and adsorption capacity over time. Additionally, the potential release of GO into the environment during its application raises questions about its eco-toxicological impacts, which are not yet fully understood.
The cost-effectiveness of GO-based pollution reduction technologies is another critical challenge. While GO demonstrates superior performance in many pollution reduction scenarios, the current production costs and scalability issues limit its widespread adoption. Bridging the gap between laboratory-scale successes and economically viable large-scale applications remains a significant hurdle for the industry.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding GO and its applications in environmental remediation is still evolving. The lack of clear guidelines and regulations regarding the use and disposal of GO-based materials in environmental applications creates uncertainty for both researchers and industry stakeholders. This regulatory ambiguity can potentially slow down the development and implementation of GO-based pollution reduction technologies.
Current Graphene Oxide Pollution Reduction Methods
01 Removal and treatment of graphene oxide pollution
Various methods and systems have been developed to remove and treat graphene oxide pollution from water and other environments. These techniques may include adsorption, filtration, and chemical treatments to effectively eliminate graphene oxide contaminants and mitigate their environmental impact.- Removal and treatment of graphene oxide pollution: Various methods and technologies have been developed to remove and treat graphene oxide pollution from water and other environments. These include advanced filtration systems, chemical treatments, and novel adsorption materials designed specifically for graphene oxide removal. Such techniques aim to mitigate the potential environmental and health risks associated with graphene oxide contamination.
- Detection and monitoring of graphene oxide in the environment: Innovative sensors and detection methods have been created to identify and quantify graphene oxide in various environmental matrices. These technologies enable more accurate monitoring of graphene oxide pollution levels in water, soil, and air, facilitating better environmental management and risk assessment strategies.
- Modification of graphene oxide for reduced environmental impact: Research has focused on modifying graphene oxide to reduce its potential environmental toxicity while maintaining its beneficial properties. This includes developing eco-friendly synthesis methods, surface functionalization techniques, and biodegradable graphene oxide derivatives that minimize long-term environmental persistence and associated pollution risks.
- Recycling and recovery of graphene oxide from waste: Methods for recycling and recovering graphene oxide from industrial waste and contaminated environments have been developed. These processes aim to reduce pollution by reusing graphene oxide in various applications, thereby minimizing its release into the environment and promoting a more circular economy approach to graphene-based materials.
- Prevention of graphene oxide release during manufacturing and use: Strategies and technologies have been invented to prevent the release of graphene oxide during its manufacturing, handling, and application processes. These include improved containment systems, safer production methods, and the development of more stable graphene oxide formulations that reduce the risk of environmental contamination at the source.
02 Detection and monitoring of graphene oxide pollution
Advanced sensors and detection methods have been invented to identify and monitor graphene oxide pollution in various media. These technologies enable accurate measurement of graphene oxide concentrations and help in assessing the extent of contamination in different environmental settings.Expand Specific Solutions03 Prevention of graphene oxide release into the environment
Innovative approaches have been developed to prevent the release of graphene oxide into the environment during manufacturing and handling processes. These methods focus on containment, safe disposal, and minimizing the risk of graphene oxide pollution at its source.Expand Specific Solutions04 Eco-friendly production of graphene oxide
Research has led to the development of environmentally friendly methods for producing graphene oxide, aiming to reduce the potential for pollution. These green synthesis techniques minimize the use of harmful chemicals and reduce waste generation during the manufacturing process.Expand Specific Solutions05 Remediation of graphene oxide-contaminated ecosystems
Strategies have been devised for the remediation of ecosystems contaminated with graphene oxide. These approaches involve the use of specialized materials, biological agents, or physical processes to restore affected environments and mitigate the long-term impacts of graphene oxide pollution on flora and fauna.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Graphene Oxide Research
The field of Graphene Oxide for pollution reduction is in a dynamic growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global market for graphene-based products is expanding rapidly, driven by environmental concerns and stringent regulations. The technology's maturity varies across applications, with some areas more developed than others. Key players like The University of Manchester, a pioneer in graphene research, and Toray Advanced Materials Research Laboratories are pushing the boundaries of innovation. Companies such as The Sixth Element (Changzhou) Materials Technology Co., Ltd. and Hubei Highland Graphene Technology Co., Ltd. are commercializing graphene oxide solutions for pollution reduction. Academic institutions, including Peking University and Rice University, are contributing significantly to fundamental research, while industry collaborations with entities like the Taiwan Textile Research Institute are accelerating practical applications.
Toray Advanced Materials Research Laboratories (China) Co. Ltd
The Sixth Element (Changzhou) Materials Technology Co., Ltd.
Core Innovations in Graphene Oxide Applications
- Development of graphene oxide/magnesium oxide nanocomposites with varying weight ratios (10:1 to 1:10) that settle in aqueous solutions, allowing for efficient removal of organic molecules through sonication and subsequent separation without the need for a magnetic field.
- A non-hazardous, in-air reduction process using a catalytic amount of ceric ammonium sulfate hydrated salt at controlled temperatures (50-150°C) to achieve rapid (10-minute) production of high-quality reduced graphene oxide with increased surface area, suitable for diverse applications such as wastewater treatment and energy harvesting.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of graphene oxide (GO) for pollution reduction reveals both promising benefits and potential risks. GO's unique properties, including its large surface area and high adsorption capacity, make it an effective material for removing various pollutants from water and air. Studies have shown that GO can efficiently adsorb heavy metals, organic compounds, and even microplastics from contaminated water sources. In air purification applications, GO-based filters have demonstrated superior performance in capturing particulate matter and harmful gases.
However, the widespread use of GO in environmental remediation raises concerns about its potential ecological effects. The small size of GO nanoparticles allows them to easily disperse in aquatic environments, potentially affecting aquatic organisms. Research has indicated that GO can accumulate in the gills and digestive tracts of fish, leading to oxidative stress and potential long-term health effects. Additionally, the interaction between GO and other pollutants in the environment may result in unforeseen consequences, such as the formation of more toxic compounds or the alteration of pollutant bioavailability.
The production and disposal of GO-based materials also warrant careful consideration. The synthesis of GO often involves the use of strong oxidizing agents and acids, which can generate hazardous waste if not properly managed. Furthermore, the end-of-life disposal of GO-containing products poses challenges, as the long-term environmental fate of these nanomaterials remains uncertain.
Despite these concerns, the potential benefits of GO in pollution reduction are significant. When properly engineered and applied, GO-based technologies can offer more efficient and cost-effective solutions for environmental remediation compared to conventional methods. To maximize the positive impact while minimizing risks, ongoing research focuses on developing eco-friendly synthesis methods, improving the stability and recyclability of GO-based materials, and investigating the long-term environmental behavior of GO.
As the field advances, comprehensive life cycle assessments and rigorous environmental monitoring will be crucial to fully understand and mitigate the potential negative impacts of GO applications in pollution reduction. Balancing the remarkable pollution reduction capabilities of GO with responsible development and implementation will be key to harnessing its full potential for environmental protection.
Scalability and Cost Analysis
The scalability and cost analysis of graphene oxide (GO) for pollution reduction applications is crucial for its widespread adoption and commercial viability. Current production methods for GO, such as the modified Hummers method, face challenges in scaling up to industrial levels while maintaining cost-effectiveness. The primary bottleneck lies in the complex and time-consuming oxidation process, which requires careful control of reaction conditions and extensive purification steps.
Large-scale production of GO is currently limited by several factors. The use of strong oxidizing agents and acids in the synthesis process poses safety concerns and necessitates specialized equipment, increasing production costs. Additionally, the exfoliation and purification stages are energy-intensive and time-consuming, further impacting scalability. These challenges have led to relatively high production costs, estimated at $50-100 per gram for high-quality GO, which hinders its widespread application in pollution reduction technologies.
However, recent advancements in GO production methods show promise for improved scalability and cost reduction. Electrochemical exfoliation techniques have emerged as a potential solution, offering a more environmentally friendly and scalable approach. This method can produce GO at a fraction of the cost of traditional methods, with some estimates suggesting production costs as low as $1-5 per gram. Furthermore, continuous flow reactors and microwave-assisted synthesis have demonstrated potential for increasing production rates while maintaining product quality.
The economic viability of GO-based pollution reduction solutions depends not only on production costs but also on the performance and longevity of the materials in real-world applications. While initial material costs may be higher than conventional alternatives, the superior adsorption capacity and potential for regeneration of GO-based materials could lead to long-term cost savings. For instance, in water treatment applications, GO membranes have shown exceptional flux rates and contaminant removal efficiencies, potentially reducing operational costs and extending filter lifetimes.
To further improve scalability and reduce costs, research efforts are focusing on developing more efficient oxidation processes, optimizing exfoliation techniques, and exploring alternative precursor materials. The use of renewable carbon sources and waste materials as graphene precursors could significantly reduce raw material costs. Additionally, the integration of GO production with existing industrial processes could lead to synergies and cost reductions through shared infrastructure and waste heat utilization.
As production scales up and technologies mature, economies of scale are expected to drive down costs further. Industry projections suggest that large-scale GO production could reach costs as low as $0.1-1 per gram within the next decade, making it increasingly competitive for pollution reduction applications. However, achieving this level of cost-effectiveness will require continued investment in research and development, as well as the establishment of robust supply chains and manufacturing infrastructure.