HDPE in Branding: Packaging Innovations
HDPE Packaging Evolution
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) packaging has undergone significant evolution since its introduction in the 1950s. Initially used primarily for milk bottles and household chemical containers, HDPE has expanded its application range to become a versatile material in the packaging industry.
The 1960s and 1970s saw the refinement of HDPE production processes, leading to improved material properties and cost-effectiveness. This period marked the beginning of HDPE's widespread adoption in various packaging applications, including food containers, personal care products, and industrial packaging.
In the 1980s and 1990s, advancements in blow molding and injection molding technologies enabled the production of more complex HDPE packaging shapes and designs. This era also witnessed the introduction of multi-layer HDPE packaging, enhancing barrier properties and expanding the material's use in sensitive product packaging.
The turn of the millennium brought increased focus on sustainability, driving innovations in HDPE recycling and the development of bio-based HDPE alternatives. Manufacturers began incorporating post-consumer recycled HDPE into new packaging, creating a more circular economy for plastic packaging.
Recent years have seen a surge in smart packaging solutions utilizing HDPE. Integration of RFID tags, QR codes, and other tracking technologies into HDPE packaging has improved supply chain management and enhanced consumer engagement. Additionally, advancements in material science have led to the development of HDPE packaging with improved barrier properties, extending product shelf life and reducing food waste.
The packaging industry has also witnessed innovations in HDPE surface treatments and printing technologies. These advancements have allowed for more sophisticated branding and design possibilities, elevating HDPE packaging from purely functional to a powerful marketing tool.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, the HDPE packaging industry is increasingly focusing on lightweight designs, recyclability, and the use of renewable resources. This has led to the development of mono-material HDPE packaging solutions that are easier to recycle and the exploration of chemical recycling technologies to further close the loop on HDPE packaging materials.
Looking ahead, the evolution of HDPE packaging is likely to continue along the lines of sustainability, functionality, and smart technology integration. Innovations in nanotechnology and material science promise to further enhance HDPE's properties, potentially leading to even more versatile and environmentally friendly packaging solutions in the future.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) in branding and packaging innovations has been steadily increasing in recent years. This growth is driven by several factors, including the material's versatility, durability, and recyclability. HDPE's unique properties make it an attractive choice for various packaging applications across multiple industries.
In the food and beverage sector, HDPE packaging has gained significant traction due to its excellent moisture barrier properties and resistance to chemicals. This makes it ideal for storing and transporting perishable goods, dairy products, and beverages. The demand for HDPE in this sector is expected to continue growing as consumers increasingly prioritize food safety and extended shelf life.
The personal care and cosmetics industry has also embraced HDPE packaging, particularly for products such as shampoos, lotions, and creams. The material's ability to withstand impact and its compatibility with a wide range of formulations have made it a preferred choice for many brands. As the global personal care market expands, the demand for HDPE packaging is projected to rise accordingly.
In the pharmaceutical sector, HDPE packaging is valued for its chemical resistance and ability to protect sensitive medications from external contaminants. With the increasing focus on healthcare and the growing pharmaceutical industry, the demand for HDPE in medical packaging is expected to see substantial growth in the coming years.
The e-commerce boom has further fueled the demand for HDPE packaging. As online shopping continues to gain popularity, there is a growing need for durable, lightweight packaging materials that can withstand the rigors of shipping and handling. HDPE's strength-to-weight ratio makes it an excellent choice for e-commerce packaging solutions.
Sustainability concerns are also driving market demand for HDPE packaging innovations. As consumers and regulators push for more environmentally friendly packaging options, brands are increasingly turning to recyclable materials like HDPE. The material's ability to be recycled multiple times without significant degradation in quality has made it a favored option for companies looking to improve their environmental footprint.
The automotive and industrial sectors are also contributing to the growing demand for HDPE packaging. The material's resistance to corrosion and chemicals makes it suitable for packaging automotive fluids, industrial chemicals, and other harsh substances. As these industries continue to expand, the demand for specialized HDPE packaging solutions is expected to increase.
Overall, the market demand for HDPE in branding and packaging innovations is robust and diverse. The material's versatility, coupled with increasing consumer awareness of sustainability issues, is likely to drive continued growth in this sector. As brands seek to differentiate themselves and meet evolving consumer preferences, innovative HDPE packaging solutions will play a crucial role in product development and marketing strategies across various industries.
Technical Challenges
The adoption of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) in packaging innovations faces several technical challenges that need to be addressed for its successful implementation in branding strategies. One of the primary obstacles is the material's limited barrier properties, particularly its permeability to gases and moisture. This characteristic can compromise the shelf life and quality of certain products, especially in the food and beverage industry where maintaining freshness is crucial.
Another significant challenge lies in the printing and decoration processes for HDPE packaging. The low surface energy of HDPE makes it difficult for inks and adhesives to adhere properly, often resulting in poor print quality or labels that peel off easily. This issue directly impacts the visual appeal and brand representation on the packaging, which is a critical aspect of product marketing and consumer engagement.
The recyclability of HDPE, while generally considered an advantage, presents its own set of challenges in the context of innovative packaging designs. Complex multi-layer structures or the addition of certain additives, often used to enhance performance or aesthetics, can complicate the recycling process. This creates a tension between achieving desired packaging properties and maintaining environmental sustainability, a growing concern for both consumers and brands.
Furthermore, the mechanical properties of HDPE can be a limiting factor in certain packaging applications. While it offers good impact resistance and flexibility, it may not provide sufficient rigidity or strength for some product types without significant thickness, potentially leading to increased material usage and costs.
The processing of HDPE for innovative packaging designs also presents technical hurdles. Achieving consistent wall thickness in blow molding processes, especially for complex shapes, can be challenging. This can lead to variations in packaging quality and performance, affecting both the functional and aesthetic aspects of the final product.
Lastly, the development of bio-based or biodegradable alternatives to traditional HDPE is an ongoing challenge. While there is increasing demand for more environmentally friendly packaging solutions, creating bio-based materials that match the performance, cost-effectiveness, and processability of conventional HDPE remains a significant technical hurdle.
Addressing these challenges requires ongoing research and development efforts, collaboration between material scientists, packaging engineers, and brand strategists, as well as investment in new technologies and processing methods. The successful resolution of these technical issues will be crucial in fully leveraging HDPE's potential for innovative and sustainable packaging solutions in branding strategies.
Current HDPE Solutions
01 Composition and properties of HDPE for packaging
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is widely used in packaging due to its excellent properties. It offers high strength-to-density ratio, chemical resistance, and durability. HDPE packaging materials can be formulated with various additives to enhance specific properties such as UV resistance, impact strength, and barrier properties. The composition and processing conditions of HDPE can be optimized to achieve desired characteristics for different packaging applications.- Composition and properties of HDPE for packaging: High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a versatile material used in packaging due to its excellent properties. It offers high strength-to-density ratio, chemical resistance, and durability. HDPE can be modified with additives to enhance specific characteristics such as UV resistance, impact strength, and processability, making it suitable for various packaging applications.
- Manufacturing processes for HDPE packaging: Various manufacturing processes are employed to produce HDPE packaging, including blow molding, injection molding, and extrusion. These processes can be optimized to improve the quality and efficiency of HDPE packaging production. Advanced techniques such as multi-layer co-extrusion and in-mold labeling are used to create specialized HDPE packaging with enhanced properties.
- Recycling and sustainability of HDPE packaging: HDPE packaging is recyclable, and efforts are being made to improve its sustainability. This includes developing recycling processes that maintain the material's properties, incorporating recycled HDPE into new packaging, and designing packaging for easier recycling. Innovations in this area focus on reducing environmental impact while maintaining the performance of HDPE packaging.
- Specialized HDPE packaging solutions: HDPE is used to create specialized packaging solutions for various industries. This includes barrier packaging for food and pharmaceuticals, tamper-evident containers, and packaging with specific shapes or features for improved functionality. Innovations in this area focus on tailoring HDPE packaging to meet specific industry requirements and consumer needs.
- Surface treatment and decoration of HDPE packaging: Various surface treatment and decoration techniques are applied to HDPE packaging to improve its appearance and functionality. These include surface activation for better printability, application of coatings for enhanced barrier properties, and advanced printing technologies for high-quality graphics. Innovations in this area aim to expand the aesthetic and functional capabilities of HDPE packaging.
02 HDPE packaging manufacturing techniques
Various manufacturing techniques are employed to produce HDPE packaging. These include blow molding, injection molding, and extrusion. Each method offers specific advantages for different types of packaging products. Advanced manufacturing processes can improve the quality, consistency, and efficiency of HDPE packaging production. Innovations in manufacturing techniques focus on reducing material usage, improving barrier properties, and enhancing the overall performance of HDPE packaging.Expand Specific Solutions03 Recycling and sustainability of HDPE packaging
HDPE packaging is recyclable, making it an environmentally friendly option. Efforts are being made to improve the recycling processes for HDPE packaging, including better sorting techniques and methods to maintain material quality through multiple recycling cycles. Innovations in this area focus on developing more sustainable HDPE packaging solutions, such as incorporating recycled content, reducing material usage, and improving end-of-life recyclability.Expand Specific Solutions04 HDPE packaging for specific applications
HDPE packaging is used in various industries, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. Specialized HDPE packaging solutions are developed to meet the specific requirements of different products and industries. This includes designing packaging with enhanced barrier properties, tamper-evident features, and compatibility with specific contents. Innovations focus on tailoring HDPE packaging to meet regulatory requirements and improve product protection and shelf life.Expand Specific Solutions05 Surface treatment and modification of HDPE packaging
Surface treatments and modifications can enhance the properties of HDPE packaging. These techniques include plasma treatment, corona treatment, and the application of coatings or laminates. Such modifications can improve printability, adhesion, barrier properties, and aesthetics of HDPE packaging. Innovations in this area focus on developing new surface modification techniques and environmentally friendly treatments that do not compromise the recyclability of HDPE packaging.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The HDPE packaging innovation market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for sustainable and high-performance packaging solutions. The market size is expanding rapidly, with major players like Dow Global Technologies, DuPont de Nemours, and NOVA Chemicals leading technological advancements. The technology maturity varies, with established companies like Borealis AG and Chevron Phillips Chemical Co. LP focusing on enhancing HDPE properties for branding applications. Emerging players such as Huangshan Novel Co., Ltd. and Jiangsu University of Technology are contributing to regional market growth. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of global petrochemical giants and specialized packaging innovators, with companies like Unilever and Nestlé driving demand for advanced HDPE packaging solutions in the consumer goods sector.
Borealis AG
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Breakthrough Technologies
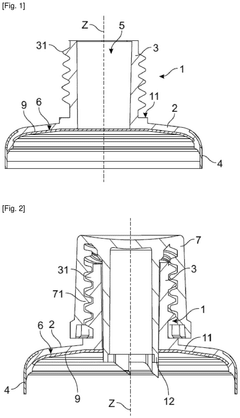
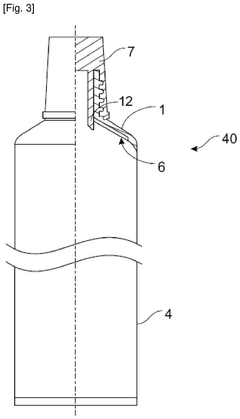
- The use of dual core HDPE material with colored layers, where three-dimensional advertising imagery is engraved and assembled into outdoor furniture segments, providing durability and visibility through computer-controlled engraving and ultraviolet inhibitors, and allowing for removable and replaceable segments.
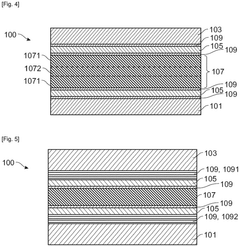
- A multi-layer insert made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) with polymeric barrier layers, specifically designed to be easily positioned and centered due to color differentiation from the tube head, providing enhanced barrier properties and resistance to deformation.
Sustainability Factors
Sustainability has become a critical factor in the development and adoption of HDPE packaging innovations. As consumers and regulators increasingly prioritize environmental concerns, the packaging industry is under pressure to develop more sustainable solutions. HDPE, despite being a plastic material, offers several advantages in terms of sustainability when compared to alternative packaging materials.
One of the key sustainability factors of HDPE packaging is its recyclability. HDPE is widely accepted in recycling programs and can be easily reprocessed into new products. This characteristic significantly reduces the environmental impact of HDPE packaging by promoting a circular economy and minimizing waste. Additionally, the recycling process for HDPE requires less energy compared to the production of virgin material, further enhancing its sustainability profile.
The durability and lightweight nature of HDPE packaging also contribute to its sustainability. HDPE's strength-to-weight ratio allows for the creation of thin-walled containers that use less material while maintaining structural integrity. This reduction in material usage not only conserves resources but also decreases transportation-related emissions due to lighter loads.
HDPE's chemical resistance and barrier properties play a crucial role in extending product shelf life, particularly for food and beverage packaging. By effectively protecting contents from external factors, HDPE packaging helps reduce food waste, which is a significant environmental concern. The extended shelf life also contributes to more efficient logistics and reduced energy consumption in the supply chain.
Recent innovations in HDPE packaging have focused on incorporating recycled content and developing bio-based alternatives. Many companies are now producing HDPE packaging with a percentage of post-consumer recycled (PCR) content, reducing the demand for virgin plastic. Simultaneously, research into bio-based HDPE derived from renewable resources like sugarcane is gaining traction, offering a potential pathway to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
The sustainability of HDPE packaging is further enhanced by ongoing efforts to optimize its production processes. Manufacturers are implementing energy-efficient technologies and exploring cleaner energy sources to reduce the carbon footprint associated with HDPE production. Additionally, advancements in packaging design are focusing on minimizing material usage while maintaining or improving functionality.
However, challenges remain in fully realizing the sustainability potential of HDPE packaging. Improving collection and recycling infrastructure, increasing consumer awareness about proper disposal, and developing more efficient recycling technologies are crucial areas that require continued attention and investment. The packaging industry must also address concerns about microplastic pollution and work towards closed-loop recycling systems to maximize the environmental benefits of HDPE packaging.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance plays a crucial role in the adoption and implementation of HDPE packaging innovations in branding. As the use of HDPE in packaging continues to evolve, manufacturers and brands must navigate a complex landscape of regulations to ensure their products meet safety standards and environmental requirements.
One of the primary regulatory considerations for HDPE packaging is food contact safety. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates materials used in food packaging, including HDPE. Manufacturers must ensure that their HDPE packaging complies with FDA regulations, particularly 21 CFR 177.1520, which outlines the specifications for olefin polymers used in food contact applications. Similarly, in the European Union, HDPE packaging must adhere to Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 on materials and articles intended to come into contact with food.
Environmental regulations also significantly impact HDPE packaging innovations. Many countries and regions have implemented or are in the process of implementing extended producer responsibility (EPR) laws, which hold manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their packaging. These regulations often require companies to establish collection and recycling systems for their HDPE packaging or contribute to existing recycling infrastructure.
The push for sustainability has led to increased scrutiny of single-use plastics, including HDPE packaging. Some jurisdictions have introduced bans or restrictions on certain single-use plastic items, which may affect HDPE packaging designs. For instance, the EU Single-Use Plastics Directive aims to reduce the impact of specific plastic products on the environment, potentially influencing the use of HDPE in certain applications.
Labeling requirements present another regulatory challenge for HDPE packaging innovations. Many countries mandate specific labeling for plastic packaging, including resin identification codes and recycling instructions. In the United States, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) regulates environmental marketing claims, including those related to recyclability and recycled content in packaging.
As the circular economy gains traction, regulations promoting the use of recycled content in packaging are becoming more prevalent. For example, the EU's Circular Economy Action Plan sets targets for recycled content in plastic packaging, which will impact HDPE packaging design and production. Manufacturers must ensure that their recycled HDPE meets food safety standards when used in food contact applications.
Chemical regulations, such as the EU's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) and various global initiatives to reduce hazardous substances, also affect HDPE packaging innovations. Manufacturers must carefully consider the additives and colorants used in their HDPE formulations to ensure compliance with these regulations.