HDPE's Role in Modernizing Irrigation Systems
HDPE in Irrigation: Background and Objectives
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) has emerged as a revolutionary material in modernizing irrigation systems, marking a significant shift from traditional methods. The evolution of irrigation technology has been driven by the need for more efficient water management, particularly in regions facing water scarcity and increasing agricultural demands. HDPE's introduction into this sector represents a critical milestone in addressing these challenges.
The development of HDPE for irrigation purposes can be traced back to the mid-20th century, coinciding with advancements in polymer science. Initially used in small-scale applications, HDPE's potential for large-scale irrigation systems became apparent as its properties were better understood and manufacturing processes improved. The material's durability, flexibility, and resistance to corrosion made it an ideal candidate for replacing conventional materials like concrete and metal in irrigation infrastructure.
As global concerns about water conservation and sustainable agriculture intensified, the adoption of HDPE in irrigation systems accelerated. This trend was further propelled by technological advancements in pipe manufacturing, allowing for the production of HDPE pipes with varying diameters and pressure ratings suitable for diverse irrigation needs. The material's ability to withstand high pressures and its low friction characteristics enabled the design of more efficient water distribution networks.
The primary objective of incorporating HDPE into irrigation systems is to enhance water use efficiency while reducing maintenance costs and environmental impact. HDPE pipes and fittings offer superior leak resistance, minimizing water loss during transportation. Their lightweight nature facilitates easier installation and reduces transportation costs, particularly in remote agricultural areas. Additionally, HDPE's resistance to chemical degradation and UV radiation extends the lifespan of irrigation infrastructure, contributing to long-term sustainability.
Another crucial goal is to improve the adaptability of irrigation systems to various terrains and climatic conditions. HDPE's flexibility allows for the creation of complex irrigation networks that can navigate challenging landscapes without compromising structural integrity. This adaptability is particularly valuable in precision agriculture, where targeted water delivery is essential for optimizing crop yields and conserving resources.
The integration of HDPE in irrigation also aims to support the broader objectives of smart farming and precision agriculture. The material's compatibility with modern sensing and control technologies enables the development of automated irrigation systems that can adjust water distribution based on real-time soil moisture data and crop requirements. This synergy between material science and digital technology represents a significant step towards more sustainable and efficient agricultural practices.
Market Analysis for HDPE Irrigation Systems
The global market for HDPE irrigation systems has been experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing need for efficient water management in agriculture. As water scarcity becomes a pressing issue worldwide, farmers and agricultural businesses are turning to advanced irrigation technologies to optimize water usage and improve crop yields. HDPE pipes and fittings have emerged as a preferred choice for modern irrigation systems due to their durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
The market size for HDPE irrigation systems is substantial and continues to expand. The agricultural sector represents the largest end-user segment, followed by landscaping and sports field applications. Geographically, North America and Europe currently hold significant market shares, but the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the rapid modernization of agricultural practices in countries like India and China, coupled with government initiatives to promote water-efficient irrigation methods.
Key factors driving the market include the rising global population, which necessitates increased food production, and the growing awareness of sustainable farming practices. Climate change and unpredictable weather patterns have also contributed to the adoption of more resilient and efficient irrigation systems. Additionally, the shift towards precision agriculture and smart farming techniques has created new opportunities for HDPE-based irrigation solutions integrated with IoT and automation technologies.
The market is characterized by a mix of established players and new entrants, with ongoing innovation in product design and manufacturing processes. Major companies are focusing on developing lightweight, UV-resistant, and easy-to-install HDPE pipes and fittings to meet the evolving needs of farmers and irrigation professionals. There is also a growing trend towards the use of recycled HDPE materials in irrigation systems, aligning with sustainability goals and circular economy principles.
Despite the positive outlook, the market faces challenges such as the high initial investment required for installing HDPE irrigation systems and the lack of awareness among small-scale farmers in developing regions. However, these challenges are being addressed through government subsidies, educational programs, and the development of more affordable solutions tailored to different farm sizes and crop types.
Looking ahead, the HDPE irrigation systems market is poised for continued growth, with technological advancements and increasing water stress driving adoption. The integration of HDPE pipes with smart irrigation controllers, sensors, and mobile applications is expected to further enhance the appeal of these systems, offering precise water delivery and real-time monitoring capabilities. As the agricultural sector continues to evolve, HDPE irrigation systems are likely to play a crucial role in shaping the future of sustainable and efficient farming practices worldwide.
HDPE Irrigation Technology: Current State and Challenges
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) has emerged as a game-changing material in modern irrigation systems, offering significant advantages over traditional materials. However, the current state of HDPE irrigation technology also presents several challenges that need to be addressed for its widespread adoption and optimal performance.
One of the primary advantages of HDPE in irrigation systems is its durability and longevity. HDPE pipes can last up to 50 years or more, significantly reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance. This longevity translates to cost savings and improved system reliability over time. Additionally, HDPE's flexibility allows for easier installation, particularly in challenging terrains, and its resistance to corrosion and chemical degradation makes it suitable for various water qualities and soil conditions.
Despite these benefits, the implementation of HDPE in irrigation systems faces several technical challenges. One significant issue is the potential for biofilm formation inside HDPE pipes. Biofilms can reduce water flow, decrease water quality, and potentially harbor harmful microorganisms. Research is ongoing to develop surface treatments or additives that can mitigate biofilm formation without compromising the material's other beneficial properties.
Another challenge lies in the joining of HDPE pipes. While heat fusion is a reliable method for creating leak-free joints, it requires specialized equipment and skilled operators. This can increase installation costs and complexity, particularly in remote agricultural areas. Developing more user-friendly and cost-effective joining methods remains an area of active research and development.
The thermal expansion of HDPE is also a concern in irrigation systems. Temperature fluctuations can cause HDPE pipes to expand and contract, potentially leading to stress on joints and fittings. Proper design and installation techniques are crucial to accommodate this thermal movement and prevent leaks or structural failures.
Furthermore, the recycling and end-of-life management of HDPE irrigation systems present both opportunities and challenges. While HDPE is recyclable, the collection and processing of used irrigation pipes from widespread agricultural areas can be logistically complex and economically challenging. Developing efficient recycling systems and promoting circular economy principles in the agricultural sector is an ongoing effort.
Lastly, the integration of smart technologies with HDPE irrigation systems is an emerging field with great potential but also technical hurdles. Incorporating sensors, IoT devices, and automation systems into HDPE-based irrigation networks requires careful consideration of material compatibility, long-term durability, and data transmission capabilities in agricultural environments.
Current HDPE Irrigation Solutions
01 Composition and properties of HDPE
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer with a high strength-to-density ratio. It is characterized by its long linear chains with minimal branching, resulting in higher tensile strength, stiffness, and chemical resistance compared to other polyethylene types. HDPE's properties make it suitable for various applications, including packaging, pipes, and automotive parts.- Composition and properties of HDPE: High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer with a high strength-to-density ratio. It is characterized by its long linear chains with minimal branching, resulting in higher tensile strength, stiffness, and chemical resistance compared to other polyethylene types. HDPE's properties make it suitable for various applications in packaging, construction, and automotive industries.
- HDPE blends and composites: HDPE can be blended with other materials or reinforced with fillers to enhance its properties. These blends and composites can improve mechanical strength, thermal stability, or specific functional characteristics. Common additives include other polymers, natural fibers, or inorganic particles, resulting in materials with tailored properties for specific applications.
- HDPE processing techniques: Various processing techniques are used to manufacture HDPE products, including injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding. These methods allow for the production of a wide range of items, from bottles and containers to pipes and automotive parts. Advanced processing techniques can improve the material's performance or enable the creation of complex shapes and structures.
- Recycling and sustainability of HDPE: HDPE is widely recycled due to its thermoplastic nature, allowing it to be melted and reformed multiple times. Recycling processes for HDPE include mechanical recycling, chemical recycling, and the development of upcycling techniques. These methods aim to reduce environmental impact and promote circular economy principles in plastic use.
- HDPE applications in various industries: HDPE finds applications across numerous industries due to its versatile properties. It is commonly used in packaging for food and beverages, household products, and chemicals. In construction, HDPE is utilized for pipes, geomembranes, and insulation. The material also plays a role in automotive components, medical devices, and consumer goods, showcasing its adaptability to different product requirements.
02 HDPE blends and composites
HDPE can be blended with other materials or reinforced with fillers to enhance its properties. These blends and composites can improve mechanical strength, thermal stability, or specific functional characteristics. Examples include HDPE blended with other polymers, reinforced with natural fibers, or combined with nanoparticles to create materials with tailored properties for specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 HDPE processing techniques
Various processing techniques are used to manufacture HDPE products, including injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, and rotational molding. Each technique offers specific advantages and is suited for different product types. Innovations in processing methods focus on improving efficiency, reducing cycle times, and enhancing the quality of the final products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Recycling and sustainability of HDPE
HDPE is recyclable and efforts are being made to improve its recycling processes and increase the use of recycled HDPE in various applications. This includes developing better sorting and cleaning technologies, as well as finding new uses for recycled HDPE to promote a circular economy and reduce environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions05 HDPE applications in specific industries
HDPE finds applications in various industries due to its versatile properties. It is used in packaging for food and beverages, chemical storage containers, pipes for water and gas distribution, automotive components, and construction materials. Ongoing research focuses on expanding HDPE's use in specialized applications such as medical devices, 3D printing, and advanced composite materials.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HDPE Irrigation Industry
The HDPE irrigation systems market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing water scarcity and the need for efficient agricultural practices. The market size is expanding globally, with significant potential in developing regions. Technologically, HDPE pipes for irrigation are mature, but innovations continue in areas such as smart irrigation systems and enhanced durability. Companies like Dow Global Technologies LLC and Basell Polyolefine GmbH are leading in material development, while Jiangsu Huayuan Water Saving Co., Ltd. and Prinsco, Inc. focus on application-specific solutions. Academic institutions such as China University of Mining & Technology and the University of South Carolina contribute to ongoing research and development, indicating a dynamic and competitive landscape with opportunities for further technological advancements.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Jiangsu Huayuan Water Saving Co., Ltd.
Innovations in HDPE for Irrigation
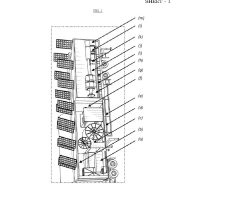
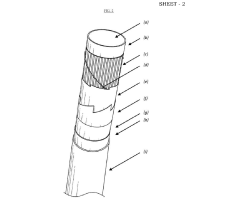
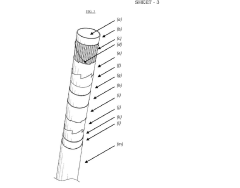
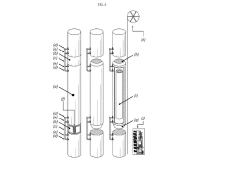
- The development of HDPE/PP laminated woven fabric lay-flat tubes with a lay-flat connector and lock ring system, which are lightweight, flexible, and easy to install, eliminating the need for joints and reducing the complexity of transportation and installation.
- The development of a tubular composite structure (TCS) comprising multiple layers of sealing, reinforcement, sensing, and protection materials, with optional interspatial annular cylinders, which can be manufactured on-site using a mobile factory to provide a flexible, durable, and efficient solution for pipeline renewal and storage.
Environmental Impact of HDPE in Irrigation
The environmental impact of HDPE in irrigation systems is a critical consideration as the agricultural sector seeks to modernize and improve water efficiency. HDPE pipes have emerged as a preferred material for irrigation infrastructure due to their durability, flexibility, and resistance to corrosion. However, their widespread adoption necessitates a thorough examination of their environmental footprint.
One of the primary environmental benefits of HDPE in irrigation is its potential to reduce water waste. The smooth interior surface of HDPE pipes minimizes friction, allowing for more efficient water flow and reducing energy consumption in pumping systems. This efficiency can lead to significant water savings, particularly in large-scale agricultural operations. Additionally, the leak-resistant nature of HDPE pipes helps prevent water loss through seepage, further conserving this precious resource.
The longevity of HDPE pipes also contributes to their environmental profile. With a lifespan of up to 100 years, HDPE irrigation systems require less frequent replacement compared to traditional materials like concrete or metal. This durability translates to reduced material consumption and waste generation over time. Furthermore, HDPE is recyclable, allowing for the potential reuse of materials at the end of the system's life cycle.
However, the production of HDPE does raise environmental concerns. The manufacturing process relies on fossil fuel-derived raw materials and energy-intensive processes, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. The carbon footprint of HDPE production must be weighed against the long-term environmental benefits of its use in irrigation systems. Efforts to incorporate recycled content and improve manufacturing efficiency are ongoing to mitigate these impacts.
The chemical stability of HDPE is a double-edged sword from an environmental perspective. While it prevents leaching of harmful substances into soil and water, it also means that HDPE does not biodegrade naturally. Proper disposal and recycling practices are crucial to prevent HDPE irrigation components from contributing to plastic pollution in agricultural landscapes.
In terms of soil health, HDPE irrigation systems can have both positive and negative effects. The precision of water delivery through HDPE pipes can help maintain optimal soil moisture levels, reducing erosion and nutrient leaching. However, the extensive underground network of pipes may disrupt soil structure and microbial communities during installation and maintenance.
As the agricultural sector grapples with climate change and water scarcity, the role of HDPE in irrigation systems continues to evolve. Ongoing research focuses on improving the environmental performance of HDPE through advanced recycling technologies, bio-based alternatives, and optimized system designs. These efforts aim to enhance the sustainability of HDPE irrigation systems while maintaining their technical and economic advantages.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of HDPE Irrigation Systems
The implementation of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) irrigation systems presents a compelling case for modernizing agricultural practices, with significant cost-benefit implications. Initial investment in HDPE systems is typically higher than traditional irrigation methods, primarily due to material costs and installation requirements. However, this upfront expenditure is offset by long-term savings and increased efficiency.
HDPE pipes offer superior durability and longevity compared to conventional materials, with an expected lifespan of 50 years or more under normal operating conditions. This extended service life significantly reduces replacement and maintenance costs over time. The smooth interior surface of HDPE pipes minimizes friction losses, allowing for more efficient water delivery and reduced pumping costs. Studies have shown that HDPE systems can achieve energy savings of up to 30% compared to steel or concrete alternatives.
Water conservation is a key benefit of HDPE irrigation systems. The leak-resistant nature of HDPE pipes, coupled with precise control mechanisms, can reduce water losses by up to 40% compared to traditional open canal systems. This not only conserves a precious resource but also translates to substantial cost savings on water bills for farmers and irrigation districts.
The flexibility of HDPE pipes allows for easier installation in challenging terrains, reducing labor costs and minimizing soil disturbance. This adaptability also facilitates the implementation of advanced irrigation techniques such as drip irrigation and micro-sprinklers, which can further enhance water use efficiency and crop yields.
From an operational perspective, HDPE systems require less frequent maintenance and repairs due to their resistance to corrosion, chemical degradation, and root intrusion. This translates to reduced downtime and lower ongoing maintenance costs. Additionally, the lightweight nature of HDPE pipes simplifies transportation and handling, potentially lowering installation and repair costs.
Environmental benefits, while harder to quantify in monetary terms, contribute significantly to the overall value proposition of HDPE irrigation systems. Reduced water usage and energy consumption lead to a smaller carbon footprint, aligning with sustainability goals and potentially qualifying for environmental incentives or certifications.
In terms of crop productivity, the improved water distribution and control offered by HDPE systems can lead to increased yields and crop quality. Studies have reported yield increases of 10-25% in various crops when transitioning to modern HDPE-based irrigation methods. This productivity boost directly impacts the farmer's bottom line and can offset the initial investment costs within a few growing seasons.
While the cost-benefit analysis of HDPE irrigation systems is overwhelmingly positive in the long term, it's important to consider regional variations in water costs, energy prices, and agricultural practices. The payback period for the initial investment can vary but typically ranges from 3 to 7 years, depending on the scale of implementation and local conditions.