HDR10 vs Dolby Vision: A Study of Global Patent Portfolios
OCT 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HDR Technology Evolution and Objectives
High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology represents a significant advancement in visual display capabilities, evolving from the limitations of Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) to deliver enhanced contrast, brightness, and color accuracy. The journey began in the early 2000s with research into expanded luminance ranges, but gained substantial momentum around 2012 when the first commercial HDR displays emerged. This technological progression has been driven by the fundamental goal of creating more realistic and immersive viewing experiences that better approximate human visual perception.
The evolution of HDR technology has followed several distinct phases. Initially, research focused on expanding the theoretical foundations of dynamic range in digital imaging. This was followed by the development of prototype displays capable of higher brightness levels and contrast ratios. The standardization phase began around 2014-2015, leading to the establishment of HDR10 as an open standard, while Dolby Vision emerged as a proprietary alternative with more advanced capabilities.
A critical objective in HDR development has been achieving backward compatibility with existing SDR content while maximizing the visual impact of native HDR material. This has necessitated sophisticated tone-mapping algorithms and metadata systems to guide displays in rendering content appropriately across different viewing environments and device capabilities.
The technical objectives of modern HDR implementations include achieving peak brightness levels exceeding 1,000 nits (compared to SDR's typical 100 nits), supporting wider color gamuts (particularly Rec. 2020), and implementing dynamic metadata for scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame optimization. These advancements aim to reduce the gap between captured content and displayed imagery, preserving creative intent throughout the production and distribution chain.
The divergence between HDR10 and Dolby Vision represents different approaches to these objectives. HDR10 employs static metadata and a more standardized implementation path, while Dolby Vision utilizes dynamic metadata and offers potentially superior image quality at the cost of licensing requirements and greater processing demands.
Looking forward, the technical trajectory of HDR technology is moving toward even higher brightness capabilities (potentially exceeding 10,000 nits), more precise local dimming solutions, and more sophisticated metadata systems. The ultimate goal remains creating display technologies that can reproduce the full range of luminance and color that the human visual system can perceive, effectively eliminating the technical limitations of the display as a factor in the viewing experience.
The evolution of HDR technology has followed several distinct phases. Initially, research focused on expanding the theoretical foundations of dynamic range in digital imaging. This was followed by the development of prototype displays capable of higher brightness levels and contrast ratios. The standardization phase began around 2014-2015, leading to the establishment of HDR10 as an open standard, while Dolby Vision emerged as a proprietary alternative with more advanced capabilities.
A critical objective in HDR development has been achieving backward compatibility with existing SDR content while maximizing the visual impact of native HDR material. This has necessitated sophisticated tone-mapping algorithms and metadata systems to guide displays in rendering content appropriately across different viewing environments and device capabilities.
The technical objectives of modern HDR implementations include achieving peak brightness levels exceeding 1,000 nits (compared to SDR's typical 100 nits), supporting wider color gamuts (particularly Rec. 2020), and implementing dynamic metadata for scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame optimization. These advancements aim to reduce the gap between captured content and displayed imagery, preserving creative intent throughout the production and distribution chain.
The divergence between HDR10 and Dolby Vision represents different approaches to these objectives. HDR10 employs static metadata and a more standardized implementation path, while Dolby Vision utilizes dynamic metadata and offers potentially superior image quality at the cost of licensing requirements and greater processing demands.
Looking forward, the technical trajectory of HDR technology is moving toward even higher brightness capabilities (potentially exceeding 10,000 nits), more precise local dimming solutions, and more sophisticated metadata systems. The ultimate goal remains creating display technologies that can reproduce the full range of luminance and color that the human visual system can perceive, effectively eliminating the technical limitations of the display as a factor in the viewing experience.
Market Demand Analysis for Advanced Display Technologies
The global market for advanced display technologies has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for premium visual experiences across various platforms. High Dynamic Range (HDR) technologies, particularly HDR10 and Dolby Vision, have emerged as key differentiators in this competitive landscape, with both standards vying for market dominance through extensive patent portfolios.
Consumer electronics manufacturers report that devices supporting advanced HDR technologies command price premiums of 15-30% compared to standard displays, reflecting strong market willingness to pay for enhanced visual experiences. This premium pricing strategy has accelerated the adoption of HDR technologies across the display ecosystem, from content creation to distribution and consumption.
The streaming media sector represents one of the most significant market drivers for HDR technology adoption. Major platforms including Netflix, Amazon Prime, Disney+, and Apple TV+ have all invested heavily in HDR content libraries, with Dolby Vision-enabled titles growing at approximately twice the rate of standard HDR10 content between 2019 and 2023. This content expansion directly correlates with increased consumer demand for compatible display devices.
Regional market analysis reveals varying adoption patterns, with North America and Western Europe leading in premium HDR technology penetration, while Asia-Pacific markets demonstrate the fastest growth rate, particularly in China and South Korea. These regional differences significantly influence patent filing strategies for both HDR10 and Dolby Vision technologies.
The gaming industry has emerged as another crucial market segment driving HDR technology demand. Next-generation gaming consoles and high-end PC graphics cards now universally support HDR rendering, with game developers increasingly optimizing content for these display capabilities. Market research indicates that gaming-specific displays with HDR capabilities grew by over 40% annually between 2020 and 2023.
Professional markets, including film production, broadcast, and digital signage, represent smaller but highly profitable segments for advanced HDR technologies. These professional applications often demand the highest technical specifications and are willing to pay substantial premiums for superior color accuracy and dynamic range capabilities.
Market forecasts project the global HDR display market to maintain double-digit growth rates through 2028, with particularly strong expansion in automotive displays, mobile devices, and virtual/augmented reality applications. This sustained growth trajectory has intensified patent competition between open standards like HDR10 and proprietary technologies like Dolby Vision, as both seek to secure technological advantages in emerging application areas.
Consumer electronics manufacturers report that devices supporting advanced HDR technologies command price premiums of 15-30% compared to standard displays, reflecting strong market willingness to pay for enhanced visual experiences. This premium pricing strategy has accelerated the adoption of HDR technologies across the display ecosystem, from content creation to distribution and consumption.
The streaming media sector represents one of the most significant market drivers for HDR technology adoption. Major platforms including Netflix, Amazon Prime, Disney+, and Apple TV+ have all invested heavily in HDR content libraries, with Dolby Vision-enabled titles growing at approximately twice the rate of standard HDR10 content between 2019 and 2023. This content expansion directly correlates with increased consumer demand for compatible display devices.
Regional market analysis reveals varying adoption patterns, with North America and Western Europe leading in premium HDR technology penetration, while Asia-Pacific markets demonstrate the fastest growth rate, particularly in China and South Korea. These regional differences significantly influence patent filing strategies for both HDR10 and Dolby Vision technologies.
The gaming industry has emerged as another crucial market segment driving HDR technology demand. Next-generation gaming consoles and high-end PC graphics cards now universally support HDR rendering, with game developers increasingly optimizing content for these display capabilities. Market research indicates that gaming-specific displays with HDR capabilities grew by over 40% annually between 2020 and 2023.
Professional markets, including film production, broadcast, and digital signage, represent smaller but highly profitable segments for advanced HDR technologies. These professional applications often demand the highest technical specifications and are willing to pay substantial premiums for superior color accuracy and dynamic range capabilities.
Market forecasts project the global HDR display market to maintain double-digit growth rates through 2028, with particularly strong expansion in automotive displays, mobile devices, and virtual/augmented reality applications. This sustained growth trajectory has intensified patent competition between open standards like HDR10 and proprietary technologies like Dolby Vision, as both seek to secure technological advantages in emerging application areas.
Current HDR Standards Landscape and Technical Barriers
The High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology landscape currently features several competing standards, each with distinct technical specifications and market positioning. HDR10, as an open standard, has achieved widespread adoption across the industry due to its royalty-free nature and relatively straightforward implementation requirements. It supports 10-bit color depth and static metadata, allowing content creators to set brightness parameters once for an entire piece of content.
In contrast, Dolby Vision represents a proprietary solution offering 12-bit color depth and dynamic metadata capabilities, enabling frame-by-frame optimization of brightness levels. This technical advantage comes with licensing costs and more complex implementation requirements, creating a significant barrier to universal adoption despite its superior technical specifications.
HDR10+ emerged as Samsung's response to Dolby Vision, offering dynamic metadata functionality while maintaining an open standard approach. However, it faces challenges in gaining widespread content support compared to its competitors. HLG (Hybrid Log-Gamma), developed by BBC and NHK, offers backward compatibility with SDR displays but lacks the peak brightness capabilities of other standards.
The fragmented standards landscape creates substantial technical barriers for content creators, device manufacturers, and consumers alike. Content producers must often create multiple masters to support different HDR formats, significantly increasing production costs and workflow complexity. This fragmentation has slowed the overall market penetration of HDR technology.
Device manufacturers face the challenge of implementing multiple HDR decoders to ensure compatibility across standards, increasing hardware costs and development complexity. Many opt to support only HDR10 as the baseline standard, limiting the consumer experience for content available in premium formats like Dolby Vision.
Patent-related barriers further complicate the landscape. Dolby's extensive patent portfolio around dynamic metadata implementation creates significant entry barriers for competitors and implementers. Analysis of global patent filings reveals concentrated ownership patterns, with Dolby holding dominant positions in key markets including the United States, Europe, and Japan.
Technical interoperability remains a critical challenge, as content optimized for one HDR standard may not display optimally on devices supporting different standards. The absence of a universal conversion mechanism between HDR formats creates inconsistent viewing experiences across different display technologies and ecosystems.
Standardization efforts through organizations like SMPTE, ITU, and CTA continue to evolve, but competing commercial interests have thus far prevented convergence toward a unified HDR standard, creating ongoing market uncertainty and slowing broader technology adoption.
In contrast, Dolby Vision represents a proprietary solution offering 12-bit color depth and dynamic metadata capabilities, enabling frame-by-frame optimization of brightness levels. This technical advantage comes with licensing costs and more complex implementation requirements, creating a significant barrier to universal adoption despite its superior technical specifications.
HDR10+ emerged as Samsung's response to Dolby Vision, offering dynamic metadata functionality while maintaining an open standard approach. However, it faces challenges in gaining widespread content support compared to its competitors. HLG (Hybrid Log-Gamma), developed by BBC and NHK, offers backward compatibility with SDR displays but lacks the peak brightness capabilities of other standards.
The fragmented standards landscape creates substantial technical barriers for content creators, device manufacturers, and consumers alike. Content producers must often create multiple masters to support different HDR formats, significantly increasing production costs and workflow complexity. This fragmentation has slowed the overall market penetration of HDR technology.
Device manufacturers face the challenge of implementing multiple HDR decoders to ensure compatibility across standards, increasing hardware costs and development complexity. Many opt to support only HDR10 as the baseline standard, limiting the consumer experience for content available in premium formats like Dolby Vision.
Patent-related barriers further complicate the landscape. Dolby's extensive patent portfolio around dynamic metadata implementation creates significant entry barriers for competitors and implementers. Analysis of global patent filings reveals concentrated ownership patterns, with Dolby holding dominant positions in key markets including the United States, Europe, and Japan.
Technical interoperability remains a critical challenge, as content optimized for one HDR standard may not display optimally on devices supporting different standards. The absence of a universal conversion mechanism between HDR formats creates inconsistent viewing experiences across different display technologies and ecosystems.
Standardization efforts through organizations like SMPTE, ITU, and CTA continue to evolve, but competing commercial interests have thus far prevented convergence toward a unified HDR standard, creating ongoing market uncertainty and slowing broader technology adoption.
Technical Comparison of HDR10 and Dolby Vision Implementations
01 HDR10 display technology patents
High Dynamic Range (HDR10) technology patents cover methods for displaying content with enhanced contrast and color depth. These patents include techniques for processing HDR metadata, color mapping algorithms, and display calibration methods that enable screens to show a wider range of brightness levels and more vivid colors than standard displays. The technology allows for more realistic image reproduction by preserving details in both very bright and very dark areas of the image.- HDR10 and Dolby Vision display technology patents: Patents related to High Dynamic Range (HDR10) and Dolby Vision display technologies, which enhance the visual experience by providing greater contrast, brightness, and color accuracy. These technologies enable displays to show a wider range of colors and brightness levels, creating more realistic and immersive viewing experiences. The patents cover various aspects of HDR implementation, including signal processing, color mapping, and display calibration techniques.
- Digital rights management for HDR content: Patents covering digital rights management (DRM) systems specifically designed for HDR content protection. These technologies ensure that premium HDR content, including HDR10 and Dolby Vision formats, is securely distributed and accessed only by authorized users or devices. The patents include encryption methods, authentication protocols, and license management systems tailored for high-value HDR content in streaming and broadcast environments.
- Licensing and royalty management for HDR technologies: Patents related to systems and methods for managing licensing agreements and royalty payments for HDR technologies like HDR10 and Dolby Vision. These patents cover platforms that track usage of patented HDR technologies, calculate royalty obligations, and facilitate licensing transactions between technology providers and implementers. The systems help streamline the complex licensing ecosystem surrounding premium video technologies.
- Content adaptation for HDR formats: Patents covering technologies for converting, optimizing, and adapting content between different HDR formats, including conversions between HDR10 and Dolby Vision, as well as from SDR to HDR. These patents address challenges in preserving creative intent while transforming content between different dynamic range and color gamut specifications. The technologies include tone mapping algorithms, metadata processing, and content-aware adaptation techniques.
- Business methods for HDR technology commercialization: Patents related to business methods and commercial strategies for monetizing HDR technologies in the marketplace. These patents cover approaches for valuing intellectual property related to HDR10 and Dolby Vision, creating patent portfolios, establishing licensing programs, and developing business models for technology deployment across the display and content ecosystem. The patents address the commercial aspects of bringing advanced HDR technologies to market.
02 Dolby Vision licensing and patent management
Patents related to Dolby Vision licensing frameworks cover business methods for managing intellectual property rights, royalty collection systems, and compliance verification mechanisms. These patents describe methods for tracking usage of the proprietary HDR technology across different devices and content platforms, ensuring proper implementation of the technology specifications, and facilitating licensing agreements between Dolby and manufacturers or content creators.Expand Specific Solutions03 Content protection for HDR technologies
Patents covering content protection methods for HDR video streams include encryption techniques, digital rights management systems, and secure transmission protocols specifically designed for high-value HDR content. These technologies ensure that premium HDR content cannot be illegally copied or distributed while maintaining the quality and integrity of the enhanced visual experience. The patents cover both hardware and software implementations of security measures across the content delivery chain.Expand Specific Solutions04 HDR content creation and processing workflows
Patents related to HDR content creation cover the entire workflow from capture to delivery, including color grading tools, tone mapping algorithms, and format conversion methods. These patents describe techniques for processing raw camera data into HDR formats, preserving creative intent across different display capabilities, and optimizing content for various HDR standards. The technologies enable content creators to take full advantage of the expanded dynamic range and color gamut available in modern displays.Expand Specific Solutions05 Cross-platform HDR implementation technologies
Patents covering cross-platform HDR implementation focus on ensuring compatibility across different devices and standards. These technologies include adaptive processing methods that optimize HDR content for various display capabilities, backward compatibility solutions for SDR displays, and conversion algorithms between different HDR formats. The patents describe methods for maintaining consistent visual experiences across televisions, mobile devices, and computer monitors with varying HDR capabilities.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in HDR Technology Ecosystem
The HDR10 vs Dolby Vision patent landscape reflects a maturing high dynamic range display technology market with significant growth potential. The competitive field is dominated by established media technology leaders like Dolby Laboratories, which pioneered Dolby Vision, alongside major electronics manufacturers including Samsung, Sony, and LG who have invested in HDR10 development. Technology giants Microsoft, Apple, and Google are also building substantial patent portfolios in this space. The market is characterized by intense competition between the royalty-free HDR10 standard and the premium Dolby Vision format, with semiconductor companies like MediaTek and NVIDIA developing supporting hardware solutions. Asian manufacturers, particularly from China and South Korea, are rapidly expanding their patent holdings to secure positions in this strategically important display technology ecosystem.
Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp.
Technical Solution: Dolby Laboratories has pioneered Dolby Vision as a proprietary HDR format that offers dynamic metadata capabilities, allowing frame-by-frame optimization of brightness, contrast, and color. Their technical approach involves a 12-bit color depth system capable of displaying up to 10,000 nits of peak brightness, significantly exceeding HDR10's static 10-bit implementation limited to 1,000 nits. Dolby Vision employs perceptual quantization (PQ) curve for electro-optical transfer functions and incorporates dynamic tone mapping that adjusts content to the specific display capabilities of each device. The company holds over 200 patents specifically related to HDR technologies, with approximately 100 directly addressing Dolby Vision implementations across content creation, distribution, and playback ecosystems. Their patent portfolio covers core technologies including dynamic metadata processing, color volume mapping, and display management systems that enable consistent visual experiences across different display technologies.
Strengths: Comprehensive end-to-end ecosystem control; superior technical specifications with 12-bit color depth and higher brightness capabilities; dynamic metadata allowing content optimization for each display. Weaknesses: Licensing fees create barriers to adoption; proprietary nature limits interoperability; requires dedicated hardware implementation increasing manufacturing costs.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has developed HDR10+ as an extension of the HDR10 standard, incorporating dynamic metadata capabilities while maintaining an open, royalty-free licensing model. Their technical approach focuses on frame-by-frame brightness adjustments through dynamic tone mapping, achieving visual quality comparable to Dolby Vision without the associated licensing costs. Samsung's patent portfolio in this space includes innovations in tone mapping algorithms, display calibration technologies, and content mastering tools. The company has implemented specialized image processing engines in their display products that can analyze and optimize HDR content in real-time, adjusting brightness, contrast, and color saturation based on scene characteristics and ambient lighting conditions. Samsung has secured approximately 150 patents related to HDR technologies, with significant focus on enhancing the capabilities of HDR10 through dynamic metadata implementations while maintaining backward compatibility with existing HDR10 content and distribution infrastructure.
Strengths: Royalty-free licensing model promotes wider adoption; backward compatibility with HDR10 content; strong hardware integration across their extensive product ecosystem. Weaknesses: Less established than Dolby Vision in professional content creation workflows; slightly lower technical specifications with 10-bit color depth versus Dolby's 12-bit; more limited industry partnerships compared to Dolby's extensive Hollywood connections.
Critical Patent Analysis in HDR Display Technologies
Enhancement decoder for video signals with multi-level enhancement and coding format adjustment
PatentWO2020074898A1
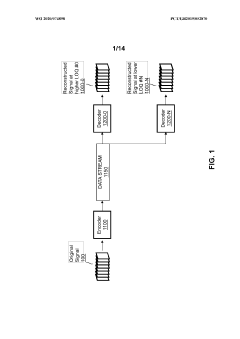
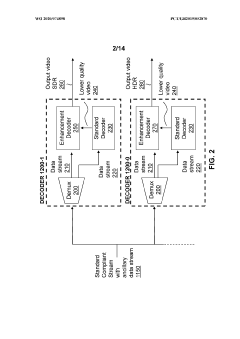
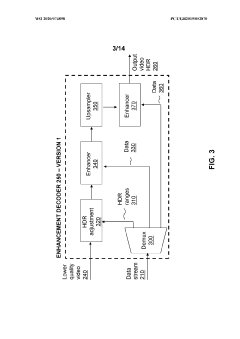
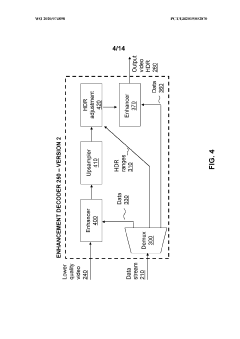
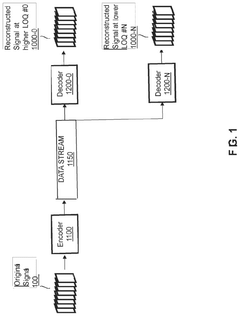
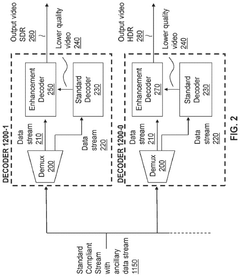
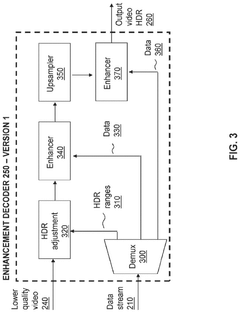
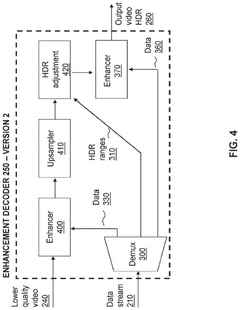
Innovation
- A hierarchical coding scheme that allows for the encoding and decoding of HDR-type signals to be compatible with both HDR and SDR displays, using an enhancement decoder that includes an interface for receiving video streams, de-multiplexing enhancement data, and a coding format adjustment module to convert between different bit lengths and resolutions, ensuring backwards compatibility and flexibility in signal processing.
Colour conversion within a hierarchical coding scheme
PatentActiveUS12120305B2
Innovation
- A hierarchical coding scheme that allows for the encoding and decoding of HDR-type signals in a way that enables compatibility with both HDR and SDR displays, using a method that involves converting input signals between color spaces, down-sampling, and adding ancillary data for reconstruction, thereby providing backwards compatibility and reduced bandwidth requirements.
Licensing Models and IP Monetization Strategies
The licensing landscape for HDR technologies presents a stark contrast between HDR10 and Dolby Vision approaches, reflecting fundamentally different IP monetization strategies. HDR10, as an open standard, operates on a royalty-free basis, allowing manufacturers to implement the technology without direct licensing costs. This approach has facilitated rapid market adoption across various device categories and price points, creating a broad ecosystem of compatible content and devices.
In contrast, Dolby Vision employs a proprietary licensing model requiring manufacturers to pay royalties for implementation. Dolby's fee structure typically includes both fixed certification costs and per-unit royalties, estimated between $2-3 per device. This premium pricing strategy positions Dolby Vision as a high-end solution while generating substantial recurring revenue streams for Dolby Laboratories.
The patent portfolios underpinning these technologies reveal strategic differences in IP development and protection. HDR10's patent landscape features contributions from multiple stakeholders including Samsung, LG, and industry consortia, with patents primarily focused on core HDR implementation techniques. These patents are often licensed through patent pools or cross-licensing agreements that maintain the royalty-free nature of the standard.
Dolby Vision's patent portfolio is more centralized and comprehensive, covering not only fundamental HDR technologies but also specialized algorithms for dynamic metadata processing, display management, and content creation workflows. This extensive patent coverage creates significant barriers to entry for potential competitors and strengthens Dolby's negotiating position with implementers.
Recent market developments indicate evolving monetization strategies, with Dolby expanding its revenue model beyond hardware licensing to include content creation tools and professional services. Meanwhile, HDR10+ (Samsung's enhanced version of HDR10) has introduced a minimal licensing fee structure that represents a middle ground between the two approaches, charging administrative fees rather than per-unit royalties.
For content creators and distributors, these licensing models create different cost structures and market considerations. While Dolby Vision implementation requires higher upfront investment in both technology licensing and specialized production workflows, it potentially offers premium positioning and enhanced consumer experiences that may command higher content prices or subscription rates.
In contrast, Dolby Vision employs a proprietary licensing model requiring manufacturers to pay royalties for implementation. Dolby's fee structure typically includes both fixed certification costs and per-unit royalties, estimated between $2-3 per device. This premium pricing strategy positions Dolby Vision as a high-end solution while generating substantial recurring revenue streams for Dolby Laboratories.
The patent portfolios underpinning these technologies reveal strategic differences in IP development and protection. HDR10's patent landscape features contributions from multiple stakeholders including Samsung, LG, and industry consortia, with patents primarily focused on core HDR implementation techniques. These patents are often licensed through patent pools or cross-licensing agreements that maintain the royalty-free nature of the standard.
Dolby Vision's patent portfolio is more centralized and comprehensive, covering not only fundamental HDR technologies but also specialized algorithms for dynamic metadata processing, display management, and content creation workflows. This extensive patent coverage creates significant barriers to entry for potential competitors and strengthens Dolby's negotiating position with implementers.
Recent market developments indicate evolving monetization strategies, with Dolby expanding its revenue model beyond hardware licensing to include content creation tools and professional services. Meanwhile, HDR10+ (Samsung's enhanced version of HDR10) has introduced a minimal licensing fee structure that represents a middle ground between the two approaches, charging administrative fees rather than per-unit royalties.
For content creators and distributors, these licensing models create different cost structures and market considerations. While Dolby Vision implementation requires higher upfront investment in both technology licensing and specialized production workflows, it potentially offers premium positioning and enhanced consumer experiences that may command higher content prices or subscription rates.
Global Regulatory Framework for Display Standards
The global regulatory landscape for display standards has evolved significantly with the emergence of High Dynamic Range (HDR) technologies. Different regions have established varying frameworks to govern the implementation and certification of HDR technologies, particularly HDR10 and Dolby Vision.
In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has not mandated specific HDR standards but recognizes both HDR10 and Dolby Vision as acceptable formats for broadcast and streaming services. The Consumer Technology Association (CTA) has developed certification programs for HDR-compatible devices, with distinct requirements for HDR10 and Dolby Vision compliance.
The European Union, through the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), has incorporated HDR standards into its Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) specifications. The EU has adopted a technology-neutral approach, allowing both HDR10 and Dolby Vision, but requires clear consumer information about supported formats on product packaging and marketing materials.
In Asia, regulatory approaches vary significantly. Japan's Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications has endorsed both formats while focusing on compatibility with its Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) 3.0 standard. China's National Radio and Television Administration has shown preference for HDR10+ and its own domestic standards, creating a more fragmented regulatory environment for Dolby Vision implementation.
International standards bodies play a crucial role in harmonizing these regional frameworks. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has published Recommendation BT.2100, which defines technical parameters for HDR systems including both HDR10 and Dolby Vision. Similarly, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed testing methodologies for HDR display performance verification.
Content regulation adds another layer of complexity. Many countries require proper labeling of HDR content, with specific guidelines for indicating whether content meets HDR10 or Dolby Vision specifications. Streaming platforms must navigate these varying requirements across different jurisdictions, often implementing region-specific delivery protocols.
Patent licensing regulations also impact the global HDR landscape. While HDR10 operates under a royalty-free model in most jurisdictions, Dolby Vision requires licensing fees that are subject to different regulatory scrutiny across regions. Some countries have implemented price controls or mandatory licensing provisions to ensure market accessibility.
The regulatory framework continues to evolve as HDR technology advances, with ongoing efforts to standardize certification processes and ensure interoperability between different HDR formats and display technologies across global markets.
In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has not mandated specific HDR standards but recognizes both HDR10 and Dolby Vision as acceptable formats for broadcast and streaming services. The Consumer Technology Association (CTA) has developed certification programs for HDR-compatible devices, with distinct requirements for HDR10 and Dolby Vision compliance.
The European Union, through the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), has incorporated HDR standards into its Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) specifications. The EU has adopted a technology-neutral approach, allowing both HDR10 and Dolby Vision, but requires clear consumer information about supported formats on product packaging and marketing materials.
In Asia, regulatory approaches vary significantly. Japan's Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications has endorsed both formats while focusing on compatibility with its Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) 3.0 standard. China's National Radio and Television Administration has shown preference for HDR10+ and its own domestic standards, creating a more fragmented regulatory environment for Dolby Vision implementation.
International standards bodies play a crucial role in harmonizing these regional frameworks. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has published Recommendation BT.2100, which defines technical parameters for HDR systems including both HDR10 and Dolby Vision. Similarly, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed testing methodologies for HDR display performance verification.
Content regulation adds another layer of complexity. Many countries require proper labeling of HDR content, with specific guidelines for indicating whether content meets HDR10 or Dolby Vision specifications. Streaming platforms must navigate these varying requirements across different jurisdictions, often implementing region-specific delivery protocols.
Patent licensing regulations also impact the global HDR landscape. While HDR10 operates under a royalty-free model in most jurisdictions, Dolby Vision requires licensing fees that are subject to different regulatory scrutiny across regions. Some countries have implemented price controls or mandatory licensing provisions to ensure market accessibility.
The regulatory framework continues to evolve as HDR technology advances, with ongoing efforts to standardize certification processes and ensure interoperability between different HDR formats and display technologies across global markets.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!