Regulatory and Patent Landscape of HDR10 vs Dolby Vision
OCT 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HDR Technology Evolution and Objectives
High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology represents a significant advancement in visual display capabilities, evolving from the limitations of Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) to deliver enhanced contrast, brightness, and color accuracy. The journey of HDR began in the early 2000s with research into expanded luminance ranges, but gained substantial momentum around 2012 when display manufacturers started exploring technologies capable of reproducing wider brightness spectrums.
The evolution of HDR technology can be traced through several key developmental phases. Initially, the focus was on increasing peak brightness capabilities of displays, moving from traditional 100 nits to 1,000+ nits. This was followed by advancements in color gamut expansion, transitioning from the limited Rec.709 color space to the more comprehensive Rec.2020 standard, enabling a significantly broader range of displayable colors.
HDR10, introduced in 2015, emerged as the first widely adopted HDR standard, utilizing static metadata to guide display rendering. This was quickly followed by HDR10+, which incorporated dynamic metadata to optimize scene-by-scene brightness levels. Concurrently, Dolby Vision was developed as a proprietary alternative, offering enhanced capabilities through dynamic metadata and support for up to 12-bit color depth.
The primary objective of HDR technology development has been to create more immersive and realistic viewing experiences by more accurately reproducing the full range of light and color that exists in the natural world. This includes capturing the nuances of extremely bright highlights and deep shadows within the same frame, something previously impossible with SDR technology.
From a regulatory perspective, HDR standards have evolved within a complex ecosystem of industry consortiums, international standardization bodies, and proprietary interests. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has played a crucial role in establishing recommendations like BT.2100, which provides specifications for HDR implementation in broadcasting.
The patent landscape surrounding HDR technologies reveals a competitive environment dominated by key players like Dolby Laboratories, Samsung, and other major display manufacturers. Dolby Vision's proprietary nature is protected by an extensive patent portfolio covering various aspects of dynamic metadata processing and display optimization, while HDR10, as an open standard, operates under different intellectual property conditions.
Current technological objectives in the HDR space include improving backward compatibility with legacy displays, reducing computational overhead for real-time HDR processing, and developing more efficient compression techniques for HDR content delivery. Additionally, there is significant focus on standardizing HDR implementation across diverse display technologies, from traditional LCD and OLED to emerging microLED and quantum dot displays.
The evolution of HDR technology can be traced through several key developmental phases. Initially, the focus was on increasing peak brightness capabilities of displays, moving from traditional 100 nits to 1,000+ nits. This was followed by advancements in color gamut expansion, transitioning from the limited Rec.709 color space to the more comprehensive Rec.2020 standard, enabling a significantly broader range of displayable colors.
HDR10, introduced in 2015, emerged as the first widely adopted HDR standard, utilizing static metadata to guide display rendering. This was quickly followed by HDR10+, which incorporated dynamic metadata to optimize scene-by-scene brightness levels. Concurrently, Dolby Vision was developed as a proprietary alternative, offering enhanced capabilities through dynamic metadata and support for up to 12-bit color depth.
The primary objective of HDR technology development has been to create more immersive and realistic viewing experiences by more accurately reproducing the full range of light and color that exists in the natural world. This includes capturing the nuances of extremely bright highlights and deep shadows within the same frame, something previously impossible with SDR technology.
From a regulatory perspective, HDR standards have evolved within a complex ecosystem of industry consortiums, international standardization bodies, and proprietary interests. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has played a crucial role in establishing recommendations like BT.2100, which provides specifications for HDR implementation in broadcasting.
The patent landscape surrounding HDR technologies reveals a competitive environment dominated by key players like Dolby Laboratories, Samsung, and other major display manufacturers. Dolby Vision's proprietary nature is protected by an extensive patent portfolio covering various aspects of dynamic metadata processing and display optimization, while HDR10, as an open standard, operates under different intellectual property conditions.
Current technological objectives in the HDR space include improving backward compatibility with legacy displays, reducing computational overhead for real-time HDR processing, and developing more efficient compression techniques for HDR content delivery. Additionally, there is significant focus on standardizing HDR implementation across diverse display technologies, from traditional LCD and OLED to emerging microLED and quantum dot displays.
Market Demand Analysis for Premium Video Standards
The premium video standards market has witnessed substantial growth driven by consumer demand for enhanced viewing experiences. As display technologies advance, HDR (High Dynamic Range) formats like HDR10 and Dolby Vision have emerged as leading standards that significantly improve picture quality through expanded brightness, contrast, and color gamut capabilities.
Market research indicates the global HDR TV market is experiencing robust annual growth rates between 15-20%, with premium content platforms increasingly adopting these advanced standards as differentiating features. Consumer willingness to pay premium prices for enhanced viewing experiences has created a lucrative ecosystem spanning hardware manufacturers, content creators, and streaming services.
The demand for premium video standards is particularly strong in regions with high disposable income and advanced digital infrastructure, with North America and Western Europe leading adoption rates, followed by rapidly growing markets in Asia-Pacific, particularly Japan, South Korea, and China. Market penetration correlates strongly with broadband infrastructure quality and streaming service availability.
Content availability represents a critical market driver, with major streaming platforms investing heavily in HDR content production. Netflix, Amazon Prime, Disney+, and Apple TV+ have all expanded their HDR libraries significantly, with many new productions being mastered in both HDR10 and Dolby Vision formats to maximize compatibility and viewing quality.
Hardware adoption trends show accelerating integration of HDR capabilities across the display ecosystem. Premium television manufacturers have widely adopted HDR10 as a baseline standard, while Dolby Vision implementation continues to expand in higher-end models. The gaming console market has embraced HDR technology, with both PlayStation and Xbox platforms supporting various HDR standards, further driving consumer awareness and demand.
Consumer research reveals increasing recognition of HDR as a desirable feature, though confusion between competing standards remains prevalent. While technical enthusiasts demonstrate preference for Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata capabilities, mainstream consumers primarily respond to visual demonstrations rather than technical specifications, suggesting marketing emphasis should focus on experiential benefits rather than technical differentiation.
Industry forecasts project continued market expansion as HDR technology becomes standardized across mid-range devices, with premium formats serving as key differentiators in higher-end segments. The regulatory landscape increasingly recognizes HDR standards in broadcast specifications, further legitimizing and accelerating market adoption across traditional and streaming content delivery channels.
Market research indicates the global HDR TV market is experiencing robust annual growth rates between 15-20%, with premium content platforms increasingly adopting these advanced standards as differentiating features. Consumer willingness to pay premium prices for enhanced viewing experiences has created a lucrative ecosystem spanning hardware manufacturers, content creators, and streaming services.
The demand for premium video standards is particularly strong in regions with high disposable income and advanced digital infrastructure, with North America and Western Europe leading adoption rates, followed by rapidly growing markets in Asia-Pacific, particularly Japan, South Korea, and China. Market penetration correlates strongly with broadband infrastructure quality and streaming service availability.
Content availability represents a critical market driver, with major streaming platforms investing heavily in HDR content production. Netflix, Amazon Prime, Disney+, and Apple TV+ have all expanded their HDR libraries significantly, with many new productions being mastered in both HDR10 and Dolby Vision formats to maximize compatibility and viewing quality.
Hardware adoption trends show accelerating integration of HDR capabilities across the display ecosystem. Premium television manufacturers have widely adopted HDR10 as a baseline standard, while Dolby Vision implementation continues to expand in higher-end models. The gaming console market has embraced HDR technology, with both PlayStation and Xbox platforms supporting various HDR standards, further driving consumer awareness and demand.
Consumer research reveals increasing recognition of HDR as a desirable feature, though confusion between competing standards remains prevalent. While technical enthusiasts demonstrate preference for Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata capabilities, mainstream consumers primarily respond to visual demonstrations rather than technical specifications, suggesting marketing emphasis should focus on experiential benefits rather than technical differentiation.
Industry forecasts project continued market expansion as HDR technology becomes standardized across mid-range devices, with premium formats serving as key differentiators in higher-end segments. The regulatory landscape increasingly recognizes HDR standards in broadcast specifications, further legitimizing and accelerating market adoption across traditional and streaming content delivery channels.
Current State and Challenges in HDR Implementation
The implementation of High Dynamic Range (HDR) technologies has seen significant advancement in recent years, with HDR10 and Dolby Vision emerging as the two dominant standards in the market. Currently, HDR10 enjoys broader adoption due to its open standard nature and royalty-free implementation, making it the baseline HDR format supported by most 4K UHD displays and content platforms. The standard supports 10-bit color depth and static metadata, allowing for enhanced brightness levels up to 1,000 nits and wider color gamut compared to traditional SDR content.
In contrast, Dolby Vision represents a more advanced implementation with 12-bit color depth, dynamic metadata capabilities, and theoretical brightness peaks of up to 10,000 nits. This proprietary technology enables frame-by-frame optimization of content, resulting in potentially superior image quality. However, its closed ecosystem and licensing requirements have limited its adoption compared to HDR10.
The current HDR landscape faces several significant technical challenges. Content creation remains complex and expensive, requiring specialized equipment and expertise to properly capture, grade, and master HDR content. This has created a bottleneck in the availability of native HDR content, particularly for smaller production companies and content creators.
Interoperability issues persist across the ecosystem, with inconsistent implementation of HDR standards across different display manufacturers. This results in varying visual experiences for consumers depending on their specific hardware configuration. The lack of standardized calibration methods further exacerbates this problem, making it difficult to ensure consistent content presentation across different viewing environments.
Bandwidth limitations present another substantial challenge, particularly for streaming services and broadcast applications. HDR content typically requires higher bitrates to preserve the enhanced visual information, creating distribution challenges in regions with limited internet infrastructure or for consumers with data caps.
From a regulatory perspective, there is a notable absence of unified global standards governing HDR implementation. Different regions have established varying requirements for HDR certification and labeling, creating confusion in the marketplace and complicating international content distribution. The European Broadcasting Union and SMPTE have attempted to establish technical guidelines, but comprehensive regulatory frameworks remain underdeveloped.
Patent complexities further complicate the HDR landscape. While HDR10 operates as an open standard, certain underlying technologies may still be subject to patent claims. Dolby Vision's proprietary nature involves a more clearly defined but restrictive licensing structure. This patent environment creates uncertainty for manufacturers and content creators navigating the HDR ecosystem, potentially inhibiting innovation and broader adoption.
In contrast, Dolby Vision represents a more advanced implementation with 12-bit color depth, dynamic metadata capabilities, and theoretical brightness peaks of up to 10,000 nits. This proprietary technology enables frame-by-frame optimization of content, resulting in potentially superior image quality. However, its closed ecosystem and licensing requirements have limited its adoption compared to HDR10.
The current HDR landscape faces several significant technical challenges. Content creation remains complex and expensive, requiring specialized equipment and expertise to properly capture, grade, and master HDR content. This has created a bottleneck in the availability of native HDR content, particularly for smaller production companies and content creators.
Interoperability issues persist across the ecosystem, with inconsistent implementation of HDR standards across different display manufacturers. This results in varying visual experiences for consumers depending on their specific hardware configuration. The lack of standardized calibration methods further exacerbates this problem, making it difficult to ensure consistent content presentation across different viewing environments.
Bandwidth limitations present another substantial challenge, particularly for streaming services and broadcast applications. HDR content typically requires higher bitrates to preserve the enhanced visual information, creating distribution challenges in regions with limited internet infrastructure or for consumers with data caps.
From a regulatory perspective, there is a notable absence of unified global standards governing HDR implementation. Different regions have established varying requirements for HDR certification and labeling, creating confusion in the marketplace and complicating international content distribution. The European Broadcasting Union and SMPTE have attempted to establish technical guidelines, but comprehensive regulatory frameworks remain underdeveloped.
Patent complexities further complicate the HDR landscape. While HDR10 operates as an open standard, certain underlying technologies may still be subject to patent claims. Dolby Vision's proprietary nature involves a more clearly defined but restrictive licensing structure. This patent environment creates uncertainty for manufacturers and content creators navigating the HDR ecosystem, potentially inhibiting innovation and broader adoption.
Technical Comparison of HDR10 and Dolby Vision
01 HDR10 and Dolby Vision display technologies
High Dynamic Range (HDR10) and Dolby Vision are advanced display technologies that enhance visual content by providing greater brightness, contrast, and color accuracy. These technologies enable displays to show a wider range of colors and luminance levels, resulting in more realistic and immersive viewing experiences. The implementation of these technologies in various display devices allows for better representation of content as intended by creators.- HDR10 and Dolby Vision display technologies: High Dynamic Range (HDR10) and Dolby Vision are advanced display technologies that enhance video content by providing greater brightness, contrast, and color accuracy. These technologies enable displays to show more realistic images with deeper blacks, brighter highlights, and a wider color gamut. The implementation of these standards in various display devices allows for superior visual experiences compared to standard dynamic range content.
- Signal processing for HDR content: Signal processing techniques are essential for handling HDR content, including both HDR10 and Dolby Vision formats. These techniques involve specialized algorithms for tone mapping, color space conversion, and dynamic range adaptation. The processing systems enable compatibility between different HDR formats and ensure optimal display of content across various devices with different capabilities.
- Content creation and encoding for HDR formats: Creating and encoding content for HDR10 and Dolby Vision requires specific workflows and tools. This includes specialized cameras, color grading systems, and encoding algorithms that can capture, process, and preserve the expanded dynamic range and color information. The encoding methods must efficiently handle the increased data requirements while maintaining compatibility with distribution channels.
- Display device optimization for HDR content: Display devices require specific optimizations to properly render HDR10 and Dolby Vision content. These optimizations include enhanced backlighting systems, improved panel technologies, and specialized processing chips. The display hardware must be capable of reproducing the wider brightness range and color gamut that HDR formats provide, while maintaining energy efficiency and thermal management.
- Content delivery and playback systems for HDR: Content delivery and playback systems for HDR10 and Dolby Vision require specialized infrastructure to maintain the integrity of the high dynamic range data throughout the distribution chain. This includes transmission protocols, streaming technologies, and playback devices that can properly interpret and display the enhanced content. These systems must also handle backward compatibility with standard dynamic range displays and content.
02 Signal processing for HDR content
Signal processing techniques are essential for handling HDR content, including both HDR10 and Dolby Vision formats. These techniques involve specialized algorithms for tone mapping, color space conversion, and dynamic range adaptation. The processing systems enable compatibility between different HDR formats and ensure optimal display of content across various devices with different capabilities, maintaining the visual quality intended by content creators.Expand Specific Solutions03 Content creation and mastering for HDR formats
Creating and mastering content for HDR10 and Dolby Vision requires specialized workflows and tools. This includes camera systems capable of capturing high dynamic range, color grading equipment that can process the expanded color and brightness information, and mastering techniques that preserve the enhanced visual data. These processes ensure that the final content takes full advantage of the capabilities offered by HDR display technologies.Expand Specific Solutions04 Compatibility and conversion between HDR formats
Systems and methods for ensuring compatibility between different HDR formats, particularly HDR10 and Dolby Vision, are crucial for content distribution. These include conversion algorithms that translate between formats while preserving as much of the original visual information as possible. Such technologies enable content to be displayed optimally across a wide range of devices with varying HDR capabilities, ensuring consistent viewing experiences regardless of the display technology.Expand Specific Solutions05 Hardware implementation for HDR processing
Hardware designs specifically optimized for processing HDR10 and Dolby Vision content include specialized circuits, processors, and display components. These hardware implementations focus on efficiently handling the increased data requirements of HDR content while maintaining power efficiency. The hardware solutions range from dedicated chips in consumer electronics to specialized display panels capable of reproducing the expanded brightness and color ranges required for HDR content.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in HDR Technology
The HDR10 vs Dolby Vision competitive landscape is currently in a mature growth phase, with the global HDR market expected to reach $85 billion by 2027. Dolby Laboratories maintains a proprietary advantage with Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata approach, while HDR10 offers an open-standard alternative supported by a broader coalition including Samsung, Sony, and Microsoft. The ecosystem reflects a strategic divide between proprietary excellence and open accessibility. Key technology players like NVIDIA, Intel, and Google are integrating both standards, while content providers like NBCUniversal influence adoption rates. Display manufacturers including BOE Technology, Sharp, and Samsung Display are critical for hardware implementation, creating a complex ecosystem balancing innovation with market accessibility.
Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp.
Technical Solution: Dolby Vision represents Dolby's proprietary HDR technology that offers dynamic metadata capabilities, allowing frame-by-frame optimization of brightness, contrast, and color. The technology supports up to 12-bit color depth, providing a potential palette of 68.7 billion colors, and can deliver brightness levels up to 10,000 nits[1]. Dolby Vision's patent portfolio encompasses over 3,000 patents related to imaging technologies. The technology implements a dual-layer approach: a base HDR10 layer for backward compatibility and an enhancement layer containing dynamic metadata. This architecture ensures content can be displayed on non-Dolby Vision screens while providing enhanced quality on supported displays[2]. Dolby maintains strict certification requirements for hardware manufacturers, requiring specific technical specifications and quality standards to be met before granting Dolby Vision certification, creating a controlled ecosystem that ensures consistent quality across implementations[3].
Strengths: Superior technical capabilities with dynamic metadata allowing scene-by-scene optimization; established licensing model with widespread industry adoption; comprehensive patent protection. Weaknesses: Higher licensing costs compared to open standards; stricter hardware requirements increasing implementation costs; closed ecosystem requiring certification.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has been instrumental in developing HDR10+, an enhanced version of the open HDR10 standard that adds dynamic metadata capabilities to compete with Dolby Vision. Samsung's approach focuses on royalty-free implementation while still delivering advanced HDR capabilities. The HDR10+ technology allows for dynamic tone mapping that optimizes brightness, contrast, and color on a scene-by-scene or frame-by-frame basis, supporting up to 4,000 nits peak brightness and 10-bit color depth[4]. Samsung has established the HDR10+ Technologies LLC, a joint venture with 20th Century Fox and Panasonic, to license and promote the technology. Their patent strategy centers on essential improvements to the base HDR10 standard while maintaining an open ecosystem approach. Samsung has secured numerous patents related to HDR metadata processing, display calibration, and content mastering workflows that support their implementation[5]. The company has also developed certification programs for HDR10+ to ensure quality standards across different manufacturers.
Strengths: Royalty-free licensing model making it attractive for manufacturers; dynamic metadata capabilities similar to Dolby Vision; strong industry partnerships expanding ecosystem adoption. Weaknesses: Less comprehensive technical specifications than Dolby Vision; more recent market entry resulting in smaller content library; less rigorous certification requirements potentially leading to inconsistent implementations.
Critical Patents and IP Analysis in HDR Space
Colour conversion within a hierarchical coding scheme
PatentActiveUS12120305B2
Innovation
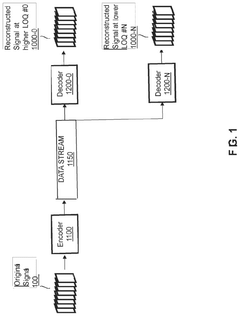
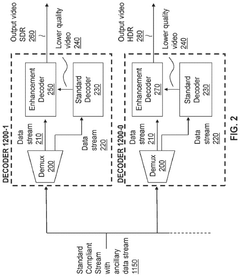
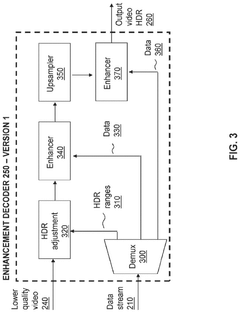
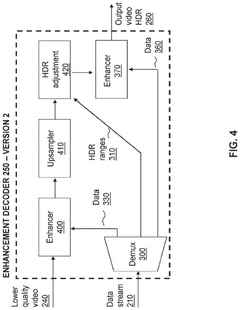
- A hierarchical coding scheme that allows for the encoding and decoding of HDR-type signals in a way that enables compatibility with both HDR and SDR displays, using a method that involves converting input signals between color spaces, down-sampling, and adding ancillary data for reconstruction, thereby providing backwards compatibility and reduced bandwidth requirements.
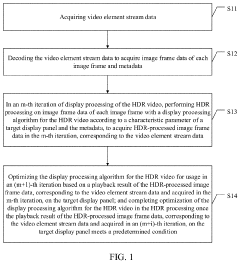
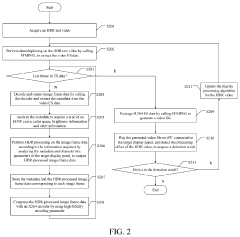
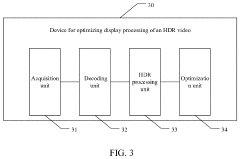
Method and apparatus for optimizing HDR video display processing, and storage medium and terminal
PatentActiveUS20230298305A1
Innovation
- A method that couples decoding and display processing by extracting metadata and image frame data from HDR videos, performing HDR processing on each frame with a display processing algorithm, and optimizing the algorithm based on playback results until predetermined conditions are met, thereby reducing the development cycle and improving efficiency.
Licensing Models and Cost Implications
The licensing models for HDR10 and Dolby Vision represent significantly different approaches to market penetration and revenue generation in the high dynamic range video technology space. HDR10, as an open standard developed by the Consumer Technology Association, operates under a royalty-free licensing model. This approach has facilitated widespread adoption across the industry, allowing manufacturers to implement the technology without incurring additional licensing costs. The absence of licensing fees has positioned HDR10 as the baseline HDR standard in the market, with nearly universal support across display devices, content creation tools, and distribution platforms.
In contrast, Dolby Vision employs a proprietary licensing model that requires manufacturers to pay royalties for implementation in their products. The licensing structure typically includes both fixed fees for certification and per-unit royalties that vary based on the device type and market segment. For television manufacturers, these costs can range from $2-3 per unit, while professional equipment may command higher licensing fees. Content creators must also license Dolby Vision tools for production and mastering, adding another layer of cost to the ecosystem.
The financial implications of these divergent licensing approaches extend throughout the value chain. For hardware manufacturers, the decision to support Dolby Vision represents a strategic calculation weighing increased production costs against potential market differentiation. Premium device manufacturers often absorb these costs to position their products in higher market segments, while budget-oriented manufacturers typically limit their offerings to HDR10 compatibility.
Content distributors face similar considerations, with streaming platforms evaluating whether the enhanced visual experience of Dolby Vision justifies the additional encoding, storage, and licensing expenses. Major platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ have opted to support both standards, offering Dolby Vision for premium content while maintaining HDR10 compatibility for broader accessibility.
The long-term cost implications also differ substantially. HDR10's open standard approach provides stability and predictability in implementation costs, while Dolby Vision's licensing model may evolve over time based on market conditions and Dolby's corporate strategy. This uncertainty represents an additional factor for ecosystem participants to consider when making technology adoption decisions.
These contrasting licensing approaches have shaped the competitive landscape, with HDR10 achieving broader market penetration while Dolby Vision has established itself as a premium offering with enhanced technical capabilities. The coexistence of these models illustrates the tension between open standards and proprietary technologies in the digital media ecosystem, with each approach offering distinct advantages and limitations for different market participants.
In contrast, Dolby Vision employs a proprietary licensing model that requires manufacturers to pay royalties for implementation in their products. The licensing structure typically includes both fixed fees for certification and per-unit royalties that vary based on the device type and market segment. For television manufacturers, these costs can range from $2-3 per unit, while professional equipment may command higher licensing fees. Content creators must also license Dolby Vision tools for production and mastering, adding another layer of cost to the ecosystem.
The financial implications of these divergent licensing approaches extend throughout the value chain. For hardware manufacturers, the decision to support Dolby Vision represents a strategic calculation weighing increased production costs against potential market differentiation. Premium device manufacturers often absorb these costs to position their products in higher market segments, while budget-oriented manufacturers typically limit their offerings to HDR10 compatibility.
Content distributors face similar considerations, with streaming platforms evaluating whether the enhanced visual experience of Dolby Vision justifies the additional encoding, storage, and licensing expenses. Major platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ have opted to support both standards, offering Dolby Vision for premium content while maintaining HDR10 compatibility for broader accessibility.
The long-term cost implications also differ substantially. HDR10's open standard approach provides stability and predictability in implementation costs, while Dolby Vision's licensing model may evolve over time based on market conditions and Dolby's corporate strategy. This uncertainty represents an additional factor for ecosystem participants to consider when making technology adoption decisions.
These contrasting licensing approaches have shaped the competitive landscape, with HDR10 achieving broader market penetration while Dolby Vision has established itself as a premium offering with enhanced technical capabilities. The coexistence of these models illustrates the tension between open standards and proprietary technologies in the digital media ecosystem, with each approach offering distinct advantages and limitations for different market participants.
Global Regulatory Framework for Video Standards
The global regulatory landscape for video standards has evolved significantly with the emergence of High Dynamic Range (HDR) technologies like HDR10 and Dolby Vision. These standards are subject to varying regulatory frameworks across different regions, creating a complex environment for manufacturers, content creators, and distributors.
In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has established guidelines for digital television transmission that accommodate HDR formats, though without explicitly mandating specific HDR standards. The Consumer Technology Association (CTA) has developed voluntary standards that recognize both HDR10 and Dolby Vision as acceptable HDR formats for consumer electronics.
The European Union, through the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), has incorporated HDR standards into its digital video broadcasting (DVB) specifications. The EU has taken a technology-neutral approach, allowing both HDR10 (as an open standard) and proprietary solutions like Dolby Vision to operate within the market, provided they meet baseline technical requirements.
In Asia, regulatory approaches vary significantly. Japan's Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications has endorsed both formats through its 4K/8K broadcast standards. China's National Radio and Television Administration has shown preference for open standards like HDR10, while still permitting Dolby Vision in consumer electronics and streaming platforms.
International standards bodies play a crucial role in harmonizing these regional frameworks. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has published Recommendation ITU-R BT.2100, which defines HDR parameters that underpin both HDR10 and Dolby Vision implementations. Similarly, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) have developed standards that accommodate both HDR formats.
Content delivery regulations also impact HDR implementation. Streaming platforms must navigate different regulatory requirements across territories, with some regions mandating accessibility features that must work alongside HDR content. Broadcast regulations in many countries are still catching up to HDR technology, creating temporary regulatory gaps.
Energy efficiency regulations present another regulatory dimension. The European Union's EcoDesign Directive and similar programs in other regions impose power consumption limits on displays, which can influence HDR implementation decisions as HDR content typically requires higher brightness levels and potentially increased power consumption.
The regulatory landscape continues to evolve, with standards bodies increasingly recognizing the importance of interoperability between different HDR formats to prevent market fragmentation and ensure consumer access to high-quality content regardless of their chosen display technology.
In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has established guidelines for digital television transmission that accommodate HDR formats, though without explicitly mandating specific HDR standards. The Consumer Technology Association (CTA) has developed voluntary standards that recognize both HDR10 and Dolby Vision as acceptable HDR formats for consumer electronics.
The European Union, through the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), has incorporated HDR standards into its digital video broadcasting (DVB) specifications. The EU has taken a technology-neutral approach, allowing both HDR10 (as an open standard) and proprietary solutions like Dolby Vision to operate within the market, provided they meet baseline technical requirements.
In Asia, regulatory approaches vary significantly. Japan's Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications has endorsed both formats through its 4K/8K broadcast standards. China's National Radio and Television Administration has shown preference for open standards like HDR10, while still permitting Dolby Vision in consumer electronics and streaming platforms.
International standards bodies play a crucial role in harmonizing these regional frameworks. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has published Recommendation ITU-R BT.2100, which defines HDR parameters that underpin both HDR10 and Dolby Vision implementations. Similarly, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) have developed standards that accommodate both HDR formats.
Content delivery regulations also impact HDR implementation. Streaming platforms must navigate different regulatory requirements across territories, with some regions mandating accessibility features that must work alongside HDR content. Broadcast regulations in many countries are still catching up to HDR technology, creating temporary regulatory gaps.
Energy efficiency regulations present another regulatory dimension. The European Union's EcoDesign Directive and similar programs in other regions impose power consumption limits on displays, which can influence HDR implementation decisions as HDR content typically requires higher brightness levels and potentially increased power consumption.
The regulatory landscape continues to evolve, with standards bodies increasingly recognizing the importance of interoperability between different HDR formats to prevent market fragmentation and ensure consumer access to high-quality content regardless of their chosen display technology.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!