HDR10 vs Dolby Vision: Comparative Regulatory Framework
OCT 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HDR Technology Evolution and Objectives
High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology represents a significant advancement in visual display capabilities, evolving from the limitations of Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) to deliver enhanced contrast, brightness, and color accuracy. The journey began in the early 2000s with research into expanded luminance ranges, but commercial implementation only gained momentum around 2014 when the first HDR-capable displays entered the market.
The evolution of HDR technology has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, the focus was on increasing the peak brightness capabilities of displays from the traditional 100 nits to over 1,000 nits. This was followed by the development of wider color gamuts that could represent more colors than the conventional Rec.709 standard, moving toward the more comprehensive Rec.2020 color space.
HDR10, introduced in 2015, emerged as the first widely adopted HDR standard, utilizing static metadata to guide displays in rendering HDR content. This was soon followed by HDR10+, which incorporated dynamic metadata to optimize brightness levels on a scene-by-scene basis. Concurrently, Dolby Vision was developed as a proprietary format offering 12-bit color depth and dynamic metadata, positioning itself as a premium alternative to the open HDR10 standard.
The regulatory landscape surrounding these technologies has evolved in parallel, with organizations like the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE), and Consumer Technology Association (CTA) establishing technical specifications and standards. These frameworks have been crucial in ensuring interoperability across devices and content platforms.
The primary objective of HDR technology development has been to deliver a more immersive viewing experience that more closely resembles human visual perception. This includes achieving higher peak brightness, deeper blacks, more nuanced shadow details, and a broader spectrum of colors that can be displayed simultaneously.
In comparing HDR10 and Dolby Vision specifically, the regulatory frameworks differ significantly. HDR10, as an open standard, operates under less restrictive licensing terms, facilitating broader adoption across the industry. Conversely, Dolby Vision's proprietary nature means that manufacturers must adhere to Dolby's specific technical requirements and licensing agreements to implement the technology.
Looking forward, the technical objectives for HDR technology include increasing accessibility across more affordable display technologies, improving energy efficiency while maintaining performance, and developing more sophisticated tone mapping algorithms to better translate creative intent across various display capabilities.
The evolution of HDR technology has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, the focus was on increasing the peak brightness capabilities of displays from the traditional 100 nits to over 1,000 nits. This was followed by the development of wider color gamuts that could represent more colors than the conventional Rec.709 standard, moving toward the more comprehensive Rec.2020 color space.
HDR10, introduced in 2015, emerged as the first widely adopted HDR standard, utilizing static metadata to guide displays in rendering HDR content. This was soon followed by HDR10+, which incorporated dynamic metadata to optimize brightness levels on a scene-by-scene basis. Concurrently, Dolby Vision was developed as a proprietary format offering 12-bit color depth and dynamic metadata, positioning itself as a premium alternative to the open HDR10 standard.
The regulatory landscape surrounding these technologies has evolved in parallel, with organizations like the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE), and Consumer Technology Association (CTA) establishing technical specifications and standards. These frameworks have been crucial in ensuring interoperability across devices and content platforms.
The primary objective of HDR technology development has been to deliver a more immersive viewing experience that more closely resembles human visual perception. This includes achieving higher peak brightness, deeper blacks, more nuanced shadow details, and a broader spectrum of colors that can be displayed simultaneously.
In comparing HDR10 and Dolby Vision specifically, the regulatory frameworks differ significantly. HDR10, as an open standard, operates under less restrictive licensing terms, facilitating broader adoption across the industry. Conversely, Dolby Vision's proprietary nature means that manufacturers must adhere to Dolby's specific technical requirements and licensing agreements to implement the technology.
Looking forward, the technical objectives for HDR technology include increasing accessibility across more affordable display technologies, improving energy efficiency while maintaining performance, and developing more sophisticated tone mapping algorithms to better translate creative intent across various display capabilities.
Market Demand Analysis for HDR Content
The global market for HDR (High Dynamic Range) content has experienced exponential growth over the past five years, driven by increasing consumer demand for premium visual experiences. According to recent industry reports, the HDR content market was valued at approximately $13.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $51.4 billion by 2027, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 30.1%.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have responded to this demand by rapidly integrating HDR technology into their product lines. As of 2023, over 85% of premium televisions sold globally support at least one HDR format, with mid-range models increasingly incorporating this technology as a standard feature. This hardware penetration has created a robust ecosystem for HDR content delivery and consumption.
Streaming platforms have emerged as the primary drivers of HDR content adoption. Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, and Apple TV+ have all made significant investments in HDR content production and delivery infrastructure. Netflix alone reported that over 40% of its original content released in 2022 was available in HDR formats, with plans to increase this to 75% by 2025.
Market research indicates distinct regional variations in HDR content demand. North America currently leads consumption with approximately 42% market share, followed by Europe (27%), Asia-Pacific (23%), and rest of the world (8%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 35.7% annually, primarily driven by increasing adoption in China, Japan, and South Korea.
Content categories demonstrate varying levels of HDR adoption. Feature films and premium television series lead implementation with approximately 65% of new releases incorporating HDR technology. Sports broadcasting has seen accelerated adoption, growing from just 12% of premium events in 2020 to over 30% in 2023. Gaming represents another high-growth segment, with 55% of AAA game titles now supporting HDR rendering.
Consumer willingness to pay premium prices for HDR content has been validated across multiple studies. Surveys indicate that 68% of consumers recognize HDR as a valuable feature and 47% are willing to pay an additional 10-15% for HDR-enabled content services. This price elasticity has encouraged content providers to invest in HDR production capabilities despite the higher associated costs.
The competitive landscape between HDR10 and Dolby Vision has significant implications for market growth. While HDR10 enjoys broader hardware compatibility due to its open standard nature, Dolby Vision's superior technical capabilities have secured it strong positioning in premium content segments. Market analysis suggests that content available in both formats achieves 22% higher engagement metrics compared to SDR-only alternatives.
Consumer electronics manufacturers have responded to this demand by rapidly integrating HDR technology into their product lines. As of 2023, over 85% of premium televisions sold globally support at least one HDR format, with mid-range models increasingly incorporating this technology as a standard feature. This hardware penetration has created a robust ecosystem for HDR content delivery and consumption.
Streaming platforms have emerged as the primary drivers of HDR content adoption. Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, and Apple TV+ have all made significant investments in HDR content production and delivery infrastructure. Netflix alone reported that over 40% of its original content released in 2022 was available in HDR formats, with plans to increase this to 75% by 2025.
Market research indicates distinct regional variations in HDR content demand. North America currently leads consumption with approximately 42% market share, followed by Europe (27%), Asia-Pacific (23%), and rest of the world (8%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 35.7% annually, primarily driven by increasing adoption in China, Japan, and South Korea.
Content categories demonstrate varying levels of HDR adoption. Feature films and premium television series lead implementation with approximately 65% of new releases incorporating HDR technology. Sports broadcasting has seen accelerated adoption, growing from just 12% of premium events in 2020 to over 30% in 2023. Gaming represents another high-growth segment, with 55% of AAA game titles now supporting HDR rendering.
Consumer willingness to pay premium prices for HDR content has been validated across multiple studies. Surveys indicate that 68% of consumers recognize HDR as a valuable feature and 47% are willing to pay an additional 10-15% for HDR-enabled content services. This price elasticity has encouraged content providers to invest in HDR production capabilities despite the higher associated costs.
The competitive landscape between HDR10 and Dolby Vision has significant implications for market growth. While HDR10 enjoys broader hardware compatibility due to its open standard nature, Dolby Vision's superior technical capabilities have secured it strong positioning in premium content segments. Market analysis suggests that content available in both formats achieves 22% higher engagement metrics compared to SDR-only alternatives.
Current State and Challenges in HDR Standards
The global HDR (High Dynamic Range) standards landscape is currently dominated by two major technologies: HDR10 and Dolby Vision, each with distinct regulatory frameworks and market positions. HDR10, as an open standard, has achieved widespread adoption across the industry, supported by numerous device manufacturers and content creators without licensing fees. This has facilitated its integration into a broad range of consumer electronics and streaming platforms.
In contrast, Dolby Vision operates under a proprietary licensing model, requiring manufacturers and content producers to pay fees for implementation. Despite this commercial barrier, Dolby Vision has secured significant market share due to its technical advantages in dynamic metadata processing and scene-by-scene optimization capabilities.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have approached HDR standards with varying degrees of formality. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has established Recommendation BT.2100, which encompasses both HDR10 (based on the Perceptual Quantizer or PQ system) and Hybrid Log-Gamma (HLG), but does not explicitly include Dolby Vision specifications. This creates a regulatory gap where Dolby Vision exists somewhat outside the formal international standardization framework.
The Consumer Technology Association (CTA) in North America has developed certification programs for HDR compatibility, including both HDR10 and Dolby Vision, providing consumers with clarity regarding device capabilities. However, these certifications focus primarily on technical specifications rather than content delivery regulations.
A significant challenge in the current HDR standards landscape is the fragmentation of implementation requirements across different regions. The European Broadcasting Union (EBU) has established guidelines that differ slightly from those in North America and Asia, creating compliance complexities for global manufacturers and content distributors.
Content creators face additional challenges with the lack of unified mastering standards across platforms. While HDR10 content follows relatively standardized production workflows, Dolby Vision requires specialized tools and processes, creating inefficiencies in content production pipelines that must support multiple HDR formats simultaneously.
The regulatory framework for HDR technologies also faces challenges regarding consumer protection and transparency. There is currently limited standardization in how HDR performance metrics are communicated to consumers, leading to potential confusion in the marketplace about the actual capabilities of HDR-labeled devices.
As streaming platforms increasingly become the primary distribution channel for HDR content, the absence of consistent quality control regulations across different territories presents another significant challenge, with varying requirements for minimum bitrates, color accuracy, and dynamic range implementation.
In contrast, Dolby Vision operates under a proprietary licensing model, requiring manufacturers and content producers to pay fees for implementation. Despite this commercial barrier, Dolby Vision has secured significant market share due to its technical advantages in dynamic metadata processing and scene-by-scene optimization capabilities.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have approached HDR standards with varying degrees of formality. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has established Recommendation BT.2100, which encompasses both HDR10 (based on the Perceptual Quantizer or PQ system) and Hybrid Log-Gamma (HLG), but does not explicitly include Dolby Vision specifications. This creates a regulatory gap where Dolby Vision exists somewhat outside the formal international standardization framework.
The Consumer Technology Association (CTA) in North America has developed certification programs for HDR compatibility, including both HDR10 and Dolby Vision, providing consumers with clarity regarding device capabilities. However, these certifications focus primarily on technical specifications rather than content delivery regulations.
A significant challenge in the current HDR standards landscape is the fragmentation of implementation requirements across different regions. The European Broadcasting Union (EBU) has established guidelines that differ slightly from those in North America and Asia, creating compliance complexities for global manufacturers and content distributors.
Content creators face additional challenges with the lack of unified mastering standards across platforms. While HDR10 content follows relatively standardized production workflows, Dolby Vision requires specialized tools and processes, creating inefficiencies in content production pipelines that must support multiple HDR formats simultaneously.
The regulatory framework for HDR technologies also faces challenges regarding consumer protection and transparency. There is currently limited standardization in how HDR performance metrics are communicated to consumers, leading to potential confusion in the marketplace about the actual capabilities of HDR-labeled devices.
As streaming platforms increasingly become the primary distribution channel for HDR content, the absence of consistent quality control regulations across different territories presents another significant challenge, with varying requirements for minimum bitrates, color accuracy, and dynamic range implementation.
Technical Implementation Approaches
01 HDR10 and Dolby Vision standards implementation
Implementation of High Dynamic Range (HDR10) and Dolby Vision technologies in display devices requires adherence to specific technical standards. These standards define parameters for color gamut, brightness levels, and contrast ratios that manufacturers must follow to ensure compatibility and optimal performance. The implementation involves specialized hardware and software components that process and render HDR content according to these specifications.- HDR10 and Dolby Vision standards implementation: Implementation of HDR10 and Dolby Vision standards in display technologies requires specific technical frameworks to ensure proper rendering of high dynamic range content. These standards define parameters for brightness, color gamut, and contrast that exceed traditional display capabilities. The implementation involves hardware and software components that must work together to process and display HDR metadata correctly, ensuring compatibility across different devices and content sources.
- Regulatory compliance for HDR technologies: HDR technologies like HDR10 and Dolby Vision must comply with various regulatory frameworks across different jurisdictions. These regulations cover aspects such as power consumption, electromagnetic compatibility, and content protection mechanisms. Manufacturers need to ensure their HDR-capable devices meet these requirements before market introduction, which may include certification processes and conformity assessments to established standards.
- Content protection and digital rights management: HDR10 and Dolby Vision technologies incorporate sophisticated content protection and digital rights management systems to prevent unauthorized copying and distribution of premium content. These protection mechanisms are essential components of the regulatory framework governing high-quality video distribution. The systems include encryption protocols, authentication methods, and secure playback pathways that maintain content integrity while ensuring only authorized devices can decode and display protected HDR content.
- Certification and interoperability standards: Certification programs and interoperability standards ensure that devices supporting HDR10 and Dolby Vision can properly communicate and display content as intended. These standards define testing methodologies, performance benchmarks, and compatibility requirements that manufacturers must meet. The certification process validates that displays, content creation tools, and distribution systems work seamlessly together, providing consumers with consistent HDR experiences across different brands and platforms.
- Display technology adaptations for HDR standards: Implementing HDR10 and Dolby Vision requires specific adaptations to display technologies to handle the expanded brightness range and color volume. These adaptations include enhanced backlighting systems, improved color processing algorithms, and specialized tone mapping techniques. Display manufacturers must develop hardware and software solutions that can accurately reproduce the intended visual experience while adhering to the technical specifications of these HDR standards.
02 Regulatory compliance for HDR technologies
HDR technologies like HDR10 and Dolby Vision must comply with various regulatory frameworks across different jurisdictions. These regulations cover aspects such as electromagnetic compatibility, power consumption standards, and content protection mechanisms. Manufacturers need to ensure their HDR-enabled devices meet these regulatory requirements before they can be marketed and sold in specific regions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Content protection and digital rights management
HDR10 and Dolby Vision technologies incorporate sophisticated content protection and digital rights management systems to prevent unauthorized copying and distribution of premium content. These protection mechanisms include encryption protocols, authentication systems, and secure content delivery pathways that ensure only authorized devices can decode and display protected HDR content.Expand Specific Solutions04 Certification processes for display devices
Display devices supporting HDR10 and Dolby Vision must undergo specific certification processes to verify their compliance with technical specifications and performance standards. These certification procedures involve testing color accuracy, peak brightness capabilities, contrast performance, and content processing capabilities. Certified devices are authorized to use official HDR10 or Dolby Vision logos, providing consumers with assurance of compatibility and quality.Expand Specific Solutions05 Interoperability and backward compatibility frameworks
Regulatory frameworks for HDR technologies address interoperability between different HDR formats and backward compatibility with standard dynamic range content. These frameworks establish guidelines for content conversion, metadata handling, and display adaptation to ensure seamless operation across various devices and content sources. The specifications enable devices to properly interpret and display content regardless of whether it was mastered in HDR10, Dolby Vision, or standard formats.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in HDR Ecosystem
The HDR10 vs Dolby Vision regulatory framework landscape is currently in a mature growth phase, with the global HDR market expected to reach $36.7 billion by 2027. Dolby Laboratories maintains a proprietary advantage with Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata approach, while HDR10, supported by Samsung, Sony, and Philips, offers an open-standard alternative. The ecosystem shows technological divergence with companies like V-Nova and Novatek developing complementary technologies. Major consumer electronics manufacturers including Apple, OPPO, and Skyworth have strategically aligned with either or both standards, creating a competitive environment where content providers must navigate licensing requirements and technical specifications across platforms.
Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp.
Technical Solution: Dolby Vision represents Dolby's proprietary HDR technology that offers dynamic metadata capabilities, allowing frame-by-frame optimization of brightness, contrast, and color. The technology supports up to 12-bit color depth (68.7 billion colors), peak brightness of up to 10,000 nits, and implements a sophisticated content mapping technology that ensures consistent viewing experience across different display capabilities. From a regulatory perspective, Dolby maintains strict certification requirements for both content creation tools and consumer displays. Manufacturers must license Dolby Vision technology and pass rigorous compliance testing to receive certification. The regulatory framework includes mandatory implementation of Dolby's proprietary algorithms for tone mapping and color volume transformation, ensuring consistent quality across certified devices. Dolby Vision also maintains backward compatibility with HDR10 through a dual-layer approach, where base layer conforms to HDR10 standards while enhancement layer carries Dolby Vision-specific data.
Strengths: Superior technical capabilities with dynamic metadata allowing scene-by-scene optimization; comprehensive ecosystem spanning content creation to display; strict quality control through certification process. Weaknesses: Proprietary technology requiring licensing fees; more complex implementation requirements for manufacturers; higher computational demands for real-time processing.
Koninklijke Philips NV
Technical Solution: Philips, as one of the founding members of the HDR10 standard, has developed an open-standard approach to HDR implementation. Their HDR10 technology solution utilizes static metadata based on the SMPTE ST 2084 standard (PQ curve) and SMPTE ST 2086 (static metadata). The regulatory framework is notably different from Dolby Vision, as HDR10 operates as an open standard without licensing fees for the core technology. Philips has focused on ensuring HDR10 compatibility across a wide range of devices through standardized implementation guidelines rather than strict certification processes. Their approach includes support for 10-bit color depth (over 1 billion colors) and peak brightness targets of 1,000 nits. Philips has also contributed to the development of HDR10+, an enhanced version that adds dynamic metadata capabilities while maintaining the open standard philosophy. From a regulatory perspective, Philips advocates for minimal barriers to adoption, with compliance based on adherence to published technical specifications rather than proprietary certification processes.
Strengths: Open standard approach with no licensing fees for core technology; widely adopted across the industry; simpler implementation requirements for manufacturers. Weaknesses: Limited to 10-bit color depth compared to Dolby Vision's 12-bit; static metadata provides less optimization capability for varying content; less consistent quality control across implementations.
Core Patents and Innovations
Enhancement decoder for video signals with multi-level enhancement and coding format adjustment
PatentWO2020074898A1
Innovation
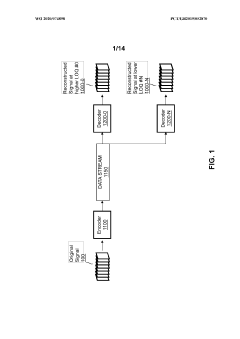
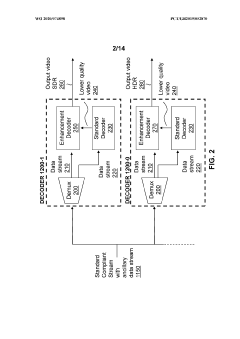
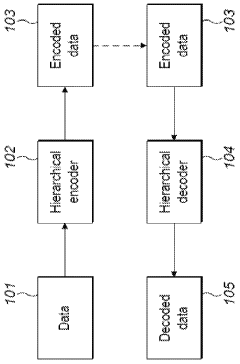
- A hierarchical coding scheme that allows for the encoding and decoding of HDR-type signals to be compatible with both HDR and SDR displays, using an enhancement decoder that includes an interface for receiving video streams, de-multiplexing enhancement data, and a coding format adjustment module to convert between different bit lengths and resolutions, ensuring backwards compatibility and flexibility in signal processing.
Signal processing with overlay regions
PatentWO2023187307A1
Innovation
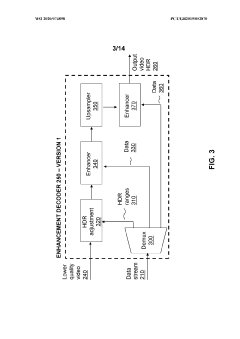
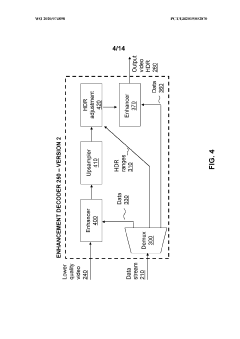
- A hierarchical coding scheme that uses residual data to efficiently encode and decode signals, allowing for the overlay of HDR content onto SDR content by generating residuals indicative of differences between HDR and SDR signals, which are then encoded using a method like LCEVC, enabling flexible and efficient distribution across various devices.
Licensing Models Comparison
The licensing models of HDR10 and Dolby Vision represent fundamentally different approaches to technology commercialization in the display industry, with significant implications for manufacturers, content creators, and consumers alike.
HDR10 operates under an open-source licensing framework, requiring no royalty payments for implementation. This royalty-free model has facilitated widespread adoption across the industry, allowing manufacturers to incorporate HDR10 capabilities into their products without incurring additional licensing costs. The technology specifications are managed by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA), which maintains the standard while ensuring it remains freely accessible to all market participants.
In contrast, Dolby Vision employs a proprietary licensing model that requires manufacturers to pay royalties for implementation in their devices. This closed ecosystem approach involves a multi-tiered fee structure: device manufacturers pay per-unit royalties, content creators must license encoding tools, and distribution platforms need licenses for delivery infrastructure. Dolby Laboratories maintains strict certification requirements, ensuring that all Dolby Vision-enabled products meet specific performance standards before receiving authorization to use the technology.
The financial implications of these divergent models are substantial. For large-scale manufacturers, Dolby Vision licensing can represent a significant cost factor, estimated between $2-3 per device, while HDR10 implementation involves only the engineering costs without additional licensing fees. This cost differential has influenced market penetration patterns, with HDR10 achieving broader implementation across price segments while Dolby Vision remains more prevalent in premium product categories.
From a compliance perspective, HDR10 implementers must adhere to the technical specifications but face minimal regulatory oversight beyond standard industry certifications. Dolby Vision licensees, however, must navigate a more complex compliance landscape, including regular quality assurance testing, firmware update requirements, and potential audits by Dolby Laboratories to ensure ongoing adherence to technical specifications.
The competitive dynamics created by these contrasting licensing approaches have shaped the market evolution of HDR technologies. HDR10's open model has fostered innovation through collaborative development, while Dolby Vision's proprietary approach has enabled more controlled quality assurance and feature integration. These different strategies represent classic technology commercialization paradigms: open standards promoting widespread adoption versus proprietary systems emphasizing quality control and revenue generation through intellectual property.
HDR10 operates under an open-source licensing framework, requiring no royalty payments for implementation. This royalty-free model has facilitated widespread adoption across the industry, allowing manufacturers to incorporate HDR10 capabilities into their products without incurring additional licensing costs. The technology specifications are managed by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA), which maintains the standard while ensuring it remains freely accessible to all market participants.
In contrast, Dolby Vision employs a proprietary licensing model that requires manufacturers to pay royalties for implementation in their devices. This closed ecosystem approach involves a multi-tiered fee structure: device manufacturers pay per-unit royalties, content creators must license encoding tools, and distribution platforms need licenses for delivery infrastructure. Dolby Laboratories maintains strict certification requirements, ensuring that all Dolby Vision-enabled products meet specific performance standards before receiving authorization to use the technology.
The financial implications of these divergent models are substantial. For large-scale manufacturers, Dolby Vision licensing can represent a significant cost factor, estimated between $2-3 per device, while HDR10 implementation involves only the engineering costs without additional licensing fees. This cost differential has influenced market penetration patterns, with HDR10 achieving broader implementation across price segments while Dolby Vision remains more prevalent in premium product categories.
From a compliance perspective, HDR10 implementers must adhere to the technical specifications but face minimal regulatory oversight beyond standard industry certifications. Dolby Vision licensees, however, must navigate a more complex compliance landscape, including regular quality assurance testing, firmware update requirements, and potential audits by Dolby Laboratories to ensure ongoing adherence to technical specifications.
The competitive dynamics created by these contrasting licensing approaches have shaped the market evolution of HDR technologies. HDR10's open model has fostered innovation through collaborative development, while Dolby Vision's proprietary approach has enabled more controlled quality assurance and feature integration. These different strategies represent classic technology commercialization paradigms: open standards promoting widespread adoption versus proprietary systems emphasizing quality control and revenue generation through intellectual property.
Global Adoption and Compliance Requirements
The global regulatory landscape for HDR technologies reveals significant variations in adoption patterns and compliance requirements across different regions. In North America, HDR10 has achieved widespread adoption due to its open-source nature and compatibility with existing broadcast infrastructure. The FCC has established baseline requirements for HDR content delivery but has not mandated specific format adoption, allowing market forces to determine technology preferences. Meanwhile, Dolby Vision has gained traction through strategic partnerships with major streaming platforms and premium content providers.
The European Union has implemented more structured regulatory frameworks through the Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) consortium, which has endorsed both HDR10 and Dolby Vision as acceptable HDR formats. The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) has published technical specifications that manufacturers must adhere to when implementing either technology. Notably, the EU's energy efficiency regulations have indirectly influenced HDR technology adoption by requiring display manufacturers to optimize power consumption while maintaining high dynamic range performance.
In the Asia-Pacific region, adoption patterns show significant diversity. Japan's NHK has developed its own Hybrid Log-Gamma (HLG) format alongside supporting HDR10, while China has implemented national standards that favor HDR10+ and domestic adaptations. South Korea has emerged as a strong proponent of Dolby Vision, particularly through Samsung's integration of the technology in premium displays.
Compliance requirements across these regions present varying challenges for manufacturers. Device certification processes differ substantially, with Dolby Vision requiring specific licensing and certification procedures that manufacturers must complete before implementing the technology. This includes rigorous testing against Dolby's proprietary standards and payment of associated licensing fees. In contrast, HDR10 implementation requires adherence to the open HDR10 specification but lacks a centralized certification authority.
Content creators face additional compliance considerations, including metadata formatting requirements that differ between the two technologies. Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata approach necessitates specialized production workflows and quality control processes that exceed those required for static metadata HDR10 content. These differences have significant implications for global content distribution strategies, as content providers must navigate multiple technical specifications to ensure compatibility across markets.
The regulatory frameworks continue to evolve as standardization bodies work toward greater interoperability between HDR formats. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) are developing unified standards that may eventually reduce fragmentation in global HDR implementation requirements.
The European Union has implemented more structured regulatory frameworks through the Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) consortium, which has endorsed both HDR10 and Dolby Vision as acceptable HDR formats. The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) has published technical specifications that manufacturers must adhere to when implementing either technology. Notably, the EU's energy efficiency regulations have indirectly influenced HDR technology adoption by requiring display manufacturers to optimize power consumption while maintaining high dynamic range performance.
In the Asia-Pacific region, adoption patterns show significant diversity. Japan's NHK has developed its own Hybrid Log-Gamma (HLG) format alongside supporting HDR10, while China has implemented national standards that favor HDR10+ and domestic adaptations. South Korea has emerged as a strong proponent of Dolby Vision, particularly through Samsung's integration of the technology in premium displays.
Compliance requirements across these regions present varying challenges for manufacturers. Device certification processes differ substantially, with Dolby Vision requiring specific licensing and certification procedures that manufacturers must complete before implementing the technology. This includes rigorous testing against Dolby's proprietary standards and payment of associated licensing fees. In contrast, HDR10 implementation requires adherence to the open HDR10 specification but lacks a centralized certification authority.
Content creators face additional compliance considerations, including metadata formatting requirements that differ between the two technologies. Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata approach necessitates specialized production workflows and quality control processes that exceed those required for static metadata HDR10 content. These differences have significant implications for global content distribution strategies, as content providers must navigate multiple technical specifications to ensure compatibility across markets.
The regulatory frameworks continue to evolve as standardization bodies work toward greater interoperability between HDR formats. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) are developing unified standards that may eventually reduce fragmentation in global HDR implementation requirements.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!