The Market Dynamics of HDR10 vs Dolby Vision Technologies
OCT 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HDR Technology Evolution and Objectives
High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology represents a significant advancement in visual display capabilities, evolving from the limitations of Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) displays. The journey of HDR began in the early 2000s with research into expanded luminance ranges and color gamuts, but commercial implementation only gained momentum around 2014-2015. This evolution was driven by the increasing demand for more realistic and immersive viewing experiences across various platforms including cinema, home entertainment, and mobile devices.
The HDR landscape has developed into several competing formats, with HDR10 and Dolby Vision emerging as the primary contenders. HDR10, as an open standard, was introduced in 2015 and quickly adopted by manufacturers due to its royalty-free nature. Meanwhile, Dolby Vision, launched commercially in 2014, positioned itself as a premium proprietary solution offering enhanced capabilities through dynamic metadata and 12-bit color depth.
The technical objectives of HDR technology center around three key parameters: increased brightness (luminance), expanded color gamut, and enhanced contrast ratio. While SDR content typically maxes out at 100 nits of brightness, HDR content can reach peaks of 1,000-10,000 nits, allowing for significantly more detail in both bright highlights and dark shadows. This expanded dynamic range enables content creators to deliver visuals much closer to what the human eye can perceive in natural environments.
Color reproduction has also seen substantial improvement through the implementation of wider color spaces such as Rec. 2020, moving beyond the limitations of the traditional Rec. 709 standard used in HDTV. This expansion allows for the representation of approximately 75% of the visible color spectrum compared to about 35% in SDR, resulting in more vibrant and accurate color reproduction.
The ongoing evolution of HDR technology aims to address several challenges, including standardization across the ecosystem, backward compatibility with existing content and displays, and optimization for various viewing environments. The industry is working toward more efficient encoding methods that can deliver HDR content without substantially increasing bandwidth requirements, which is particularly important for streaming services and broadcast applications.
Looking forward, the technical roadmap for HDR includes further refinements in tone mapping algorithms, improved interoperability between different HDR formats, and the development of more affordable display technologies capable of meeting HDR specifications. The ultimate goal remains consistent: to narrow the gap between human visual perception and what can be reproduced on screens, creating increasingly realistic and immersive viewing experiences across all content delivery platforms.
The HDR landscape has developed into several competing formats, with HDR10 and Dolby Vision emerging as the primary contenders. HDR10, as an open standard, was introduced in 2015 and quickly adopted by manufacturers due to its royalty-free nature. Meanwhile, Dolby Vision, launched commercially in 2014, positioned itself as a premium proprietary solution offering enhanced capabilities through dynamic metadata and 12-bit color depth.
The technical objectives of HDR technology center around three key parameters: increased brightness (luminance), expanded color gamut, and enhanced contrast ratio. While SDR content typically maxes out at 100 nits of brightness, HDR content can reach peaks of 1,000-10,000 nits, allowing for significantly more detail in both bright highlights and dark shadows. This expanded dynamic range enables content creators to deliver visuals much closer to what the human eye can perceive in natural environments.
Color reproduction has also seen substantial improvement through the implementation of wider color spaces such as Rec. 2020, moving beyond the limitations of the traditional Rec. 709 standard used in HDTV. This expansion allows for the representation of approximately 75% of the visible color spectrum compared to about 35% in SDR, resulting in more vibrant and accurate color reproduction.
The ongoing evolution of HDR technology aims to address several challenges, including standardization across the ecosystem, backward compatibility with existing content and displays, and optimization for various viewing environments. The industry is working toward more efficient encoding methods that can deliver HDR content without substantially increasing bandwidth requirements, which is particularly important for streaming services and broadcast applications.
Looking forward, the technical roadmap for HDR includes further refinements in tone mapping algorithms, improved interoperability between different HDR formats, and the development of more affordable display technologies capable of meeting HDR specifications. The ultimate goal remains consistent: to narrow the gap between human visual perception and what can be reproduced on screens, creating increasingly realistic and immersive viewing experiences across all content delivery platforms.
Market Analysis of HDR Standards
The High Dynamic Range (HDR) display technology market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for enhanced visual experiences across various platforms. The global HDR market was valued at approximately $8.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $36.4 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 19.2% during the forecast period. This robust growth trajectory underscores the critical importance of HDR standards in shaping the future of visual content consumption.
Currently, several HDR standards compete for market dominance, with HDR10 and Dolby Vision emerging as the primary contenders. HDR10, as an open standard, has achieved widespread adoption across the industry, supported by major manufacturers and content providers. According to industry reports, approximately 90% of HDR-capable displays support the HDR10 standard, making it the most ubiquitous HDR format in the market.
Dolby Vision, despite being a proprietary technology requiring licensing fees, has carved out a significant market share due to its superior technical capabilities. Market research indicates that Dolby Vision is supported by approximately 45% of premium HDR displays, with particularly strong penetration in the high-end television segment where consumers are willing to pay premium prices for enhanced visual experiences.
Regional adoption patterns reveal interesting market dynamics. North America leads in HDR technology adoption, accounting for 38% of the global market share, followed by Europe (27%) and Asia-Pacific (25%). The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and South Korea, is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 22.3% annually, driven by the presence of major display manufacturers and increasing consumer spending power.
Content availability serves as a critical driver for HDR standard adoption. Streaming platforms have emerged as the primary distribution channels for HDR content, with Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ collectively hosting over 5,000 hours of HDR content. Netflix reports that 32% of its premium subscribers regularly consume HDR content, with this percentage growing steadily year-over-year.
Consumer electronics manufacturers play a pivotal role in determining market dynamics through their implementation choices. Samsung, LG, and Sony collectively control 63% of the premium display market, with their technology choices significantly influencing standard adoption rates. Samsung has predominantly supported HDR10+, while LG has embraced both Dolby Vision and HDR10, reflecting the complex competitive landscape.
The gaming industry has emerged as a significant growth vector for HDR technology, with next-generation consoles and gaming PCs increasingly supporting various HDR standards. The gaming segment is projected to grow at 24.7% annually, potentially reshaping market dynamics as consumer preferences in this segment may differ from traditional content consumption patterns.
Currently, several HDR standards compete for market dominance, with HDR10 and Dolby Vision emerging as the primary contenders. HDR10, as an open standard, has achieved widespread adoption across the industry, supported by major manufacturers and content providers. According to industry reports, approximately 90% of HDR-capable displays support the HDR10 standard, making it the most ubiquitous HDR format in the market.
Dolby Vision, despite being a proprietary technology requiring licensing fees, has carved out a significant market share due to its superior technical capabilities. Market research indicates that Dolby Vision is supported by approximately 45% of premium HDR displays, with particularly strong penetration in the high-end television segment where consumers are willing to pay premium prices for enhanced visual experiences.
Regional adoption patterns reveal interesting market dynamics. North America leads in HDR technology adoption, accounting for 38% of the global market share, followed by Europe (27%) and Asia-Pacific (25%). The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and South Korea, is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 22.3% annually, driven by the presence of major display manufacturers and increasing consumer spending power.
Content availability serves as a critical driver for HDR standard adoption. Streaming platforms have emerged as the primary distribution channels for HDR content, with Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ collectively hosting over 5,000 hours of HDR content. Netflix reports that 32% of its premium subscribers regularly consume HDR content, with this percentage growing steadily year-over-year.
Consumer electronics manufacturers play a pivotal role in determining market dynamics through their implementation choices. Samsung, LG, and Sony collectively control 63% of the premium display market, with their technology choices significantly influencing standard adoption rates. Samsung has predominantly supported HDR10+, while LG has embraced both Dolby Vision and HDR10, reflecting the complex competitive landscape.
The gaming industry has emerged as a significant growth vector for HDR technology, with next-generation consoles and gaming PCs increasingly supporting various HDR standards. The gaming segment is projected to grow at 24.7% annually, potentially reshaping market dynamics as consumer preferences in this segment may differ from traditional content consumption patterns.
Current HDR Implementation Challenges
Despite the significant advancements in HDR technology, several critical implementation challenges persist in the current market landscape. The coexistence of HDR10 and Dolby Vision creates a fragmented ecosystem that complicates deployment across the content creation and delivery chain. Content creators face substantial technical hurdles when producing for multiple HDR formats simultaneously, requiring specialized equipment and expertise to ensure consistent visual quality across platforms.
Hardware compatibility remains a significant obstacle, as many existing displays lack the necessary specifications to fully realize HDR's potential. While newer premium televisions support both formats, the majority of mid-range and budget displays only accommodate HDR10, creating market segmentation. This hardware limitation extends to production equipment, where the cost of Dolby Vision-compatible cameras, monitors, and editing systems represents a substantial investment barrier for smaller studios.
Bandwidth constraints continue to challenge streaming platforms implementing HDR content delivery. The additional data requirements for HDR streams—particularly Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata—necessitate robust internet connections that many consumers still lack. Content providers must balance visual quality against accessibility, often resulting in compromised implementations that fail to showcase HDR's full capabilities.
Standardization issues further complicate the landscape, with inconsistent implementation of HDR specifications across device manufacturers. The absence of universal certification standards leads to varying interpretations of HDR performance metrics, creating consumer confusion and inconsistent viewing experiences. This problem is particularly acute in the mobile device market, where HDR implementation varies dramatically between manufacturers.
Technical knowledge gaps among content creators represent another significant challenge. Many production teams lack comprehensive understanding of HDR color science, resulting in suboptimal content that fails to leverage the format's expanded capabilities. The learning curve for mastering HDR content is steep, requiring specialized training that many smaller production houses cannot afford.
Consumer education remains inadequate, with many viewers unaware of the differences between HDR formats or how to optimize their viewing experience. This knowledge gap leads to underutilization of HDR capabilities and diminished perceived value of premium content offerings. Retailers and manufacturers have struggled to effectively communicate HDR benefits in ways that resonate with average consumers.
Workflow integration challenges persist throughout the production pipeline, as existing tools and processes designed for SDR content require significant modification to accommodate HDR requirements. The complexity of managing multiple delivery formats increases production time and costs, creating efficiency bottlenecks that slow industry adoption.
Hardware compatibility remains a significant obstacle, as many existing displays lack the necessary specifications to fully realize HDR's potential. While newer premium televisions support both formats, the majority of mid-range and budget displays only accommodate HDR10, creating market segmentation. This hardware limitation extends to production equipment, where the cost of Dolby Vision-compatible cameras, monitors, and editing systems represents a substantial investment barrier for smaller studios.
Bandwidth constraints continue to challenge streaming platforms implementing HDR content delivery. The additional data requirements for HDR streams—particularly Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata—necessitate robust internet connections that many consumers still lack. Content providers must balance visual quality against accessibility, often resulting in compromised implementations that fail to showcase HDR's full capabilities.
Standardization issues further complicate the landscape, with inconsistent implementation of HDR specifications across device manufacturers. The absence of universal certification standards leads to varying interpretations of HDR performance metrics, creating consumer confusion and inconsistent viewing experiences. This problem is particularly acute in the mobile device market, where HDR implementation varies dramatically between manufacturers.
Technical knowledge gaps among content creators represent another significant challenge. Many production teams lack comprehensive understanding of HDR color science, resulting in suboptimal content that fails to leverage the format's expanded capabilities. The learning curve for mastering HDR content is steep, requiring specialized training that many smaller production houses cannot afford.
Consumer education remains inadequate, with many viewers unaware of the differences between HDR formats or how to optimize their viewing experience. This knowledge gap leads to underutilization of HDR capabilities and diminished perceived value of premium content offerings. Retailers and manufacturers have struggled to effectively communicate HDR benefits in ways that resonate with average consumers.
Workflow integration challenges persist throughout the production pipeline, as existing tools and processes designed for SDR content require significant modification to accommodate HDR requirements. The complexity of managing multiple delivery formats increases production time and costs, creating efficiency bottlenecks that slow industry adoption.
Technical Comparison of HDR10 and Dolby Vision
01 HDR10 and Dolby Vision display technologies
High Dynamic Range (HDR10) and Dolby Vision are advanced display technologies that enhance visual content by providing greater brightness, contrast, and color accuracy. These technologies enable displays to show more realistic images with deeper blacks, brighter highlights, and a wider color gamut. The implementation of these technologies in various display devices has significantly improved the viewing experience for consumers.- HDR10 and Dolby Vision display technologies: High Dynamic Range (HDR10) and Dolby Vision are advanced display technologies that enhance visual content by providing greater brightness, contrast, and color accuracy. These technologies enable displays to show more realistic images with deeper blacks, brighter highlights, and a wider color gamut. The implementation of these technologies in various display devices has significantly improved the viewing experience for consumers.
- Market adoption and integration in consumer electronics: The adoption of HDR10 and Dolby Vision technologies in consumer electronics has been growing rapidly. Television manufacturers, streaming platforms, and content creators are increasingly integrating these technologies into their products and services. This market trend is driven by consumer demand for higher quality visual experiences and the competitive advantage these technologies provide to manufacturers in the premium segment of the market.
- Content delivery and distribution systems: The distribution of HDR10 and Dolby Vision content requires specialized delivery systems and infrastructure. Streaming platforms, broadcast networks, and physical media manufacturers have developed methods to encode, transmit, and decode HDR content efficiently. These systems ensure that the enhanced visual quality reaches end-users without degradation, while managing bandwidth constraints and compatibility with various playback devices.
- Licensing and intellectual property landscape: The HDR10 and Dolby Vision technologies are protected by various patents and intellectual property rights. Dolby Vision, as a proprietary technology, operates under a licensing model that impacts market dynamics and adoption rates. Meanwhile, HDR10 has more open standards. The licensing structures, royalty fees, and intellectual property strategies significantly influence the competitive landscape and business models in this market.
- Competitive technologies and market differentiation: Beyond HDR10 and Dolby Vision, other competing HDR technologies exist in the market, creating a complex competitive landscape. Manufacturers and content providers often differentiate their offerings through exclusive support for specific HDR formats or by implementing unique enhancements to these technologies. This competition drives innovation and affects market segmentation, with different technologies targeting various price points and use cases.
02 Content delivery and distribution systems
The market dynamics of HDR10 and Dolby Vision technologies are heavily influenced by content delivery and distribution systems. These systems include streaming platforms, broadcast networks, and physical media that support high dynamic range content. The adoption of these technologies by content providers and the development of efficient delivery methods are crucial factors in the market growth of HDR technologies.Expand Specific Solutions03 Licensing and intellectual property strategies
The market for HDR10 and Dolby Vision technologies is significantly shaped by licensing models and intellectual property strategies. Dolby Vision operates on a proprietary licensing model, while HDR10 is more openly available. These different approaches affect adoption rates, implementation costs, and market penetration across various device manufacturers and content creators, ultimately influencing the competitive landscape of the HDR technology market.Expand Specific Solutions04 Consumer adoption and market trends
Consumer adoption patterns and market trends play a crucial role in the HDR10 and Dolby Vision technologies market. Factors such as consumer awareness, perceived value, price sensitivity, and compatibility with existing devices influence the rate of adoption. Market trends indicate a growing demand for premium viewing experiences, with consumers increasingly seeking devices that support these advanced display technologies.Expand Specific Solutions05 Technical integration and compatibility solutions
Technical integration challenges and compatibility solutions are significant aspects of the HDR10 and Dolby Vision market dynamics. These include methods for backward compatibility with SDR content, solutions for devices supporting multiple HDR formats, and integration with various display technologies. The development of efficient conversion algorithms and universal standards affects the seamless implementation of these technologies across the consumer electronics ecosystem.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in HDR Ecosystem
The HDR10 vs Dolby Vision market is currently in a growth phase, with the global HDR technology market expanding rapidly as consumer demand for enhanced visual experiences increases. Dolby Laboratories maintains a dominant position with its premium Dolby Vision technology, while Samsung leads the open-standard HDR10+ alliance. Other significant players include major electronics manufacturers like Huawei, OPPO, TCL, and Skyworth, who are implementing these technologies across their product lines. The ecosystem is further enriched by specialized companies like V-Nova International providing complementary compression technologies. While HDR10 enjoys broader adoption due to its royalty-free nature, Dolby Vision's superior technical capabilities are gaining traction among premium content providers and high-end device manufacturers, creating a two-tier market structure.
Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp.
Technical Solution: Dolby Laboratories has developed Dolby Vision as a premium HDR format that offers 12-bit color depth (versus HDR10's 10-bit), dynamic metadata for scene-by-scene optimization, and up to 10,000 nits of peak brightness. The technology employs frame-by-frame analysis to optimize content display based on the capabilities of each specific display device. Dolby Vision's implementation includes a sophisticated content mapping algorithm that preserves creative intent across various display capabilities. The technology has been widely adopted in premium content ecosystems, with major streaming platforms like Netflix, Disney+, and Apple TV+ offering Dolby Vision content. Dolby maintains strict certification requirements for hardware manufacturers, ensuring consistent quality across Dolby Vision-enabled devices.
Strengths: Superior technical specifications with 12-bit color depth and dynamic metadata; Strong industry partnerships with content creators and device manufacturers; Consistent quality control through certification process. Weaknesses: Higher licensing costs compared to open standards like HDR10; Requires dedicated hardware support; More complex implementation for content creators and device manufacturers.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has been a primary driving force behind HDR10 and its evolution to HDR10+. As a founding member of the HDR10+ Alliance alongside 20th Century Fox and Panasonic, Samsung developed HDR10+ as a royalty-free alternative to Dolby Vision. The technology incorporates dynamic metadata similar to Dolby Vision but maintains an open standard approach. Samsung's implementation focuses on optimizing brightness, contrast, and color accuracy through scene-by-scene adjustments. Their QLED display technology is specifically engineered to maximize HDR10/HDR10+ performance, with some models capable of peak brightness exceeding 2,000 nits. Samsung has also developed adaptive tone mapping algorithms that analyze content characteristics to optimize HDR presentation based on ambient lighting conditions and display capabilities.
Strengths: Royalty-free licensing model promotes wider adoption; Strong hardware integration with Samsung's display technologies; Open standard approach encourages industry participation. Weaknesses: Technical specifications slightly behind Dolby Vision (10-bit vs 12-bit color depth); Less consistent implementation across different manufacturers; More limited content ecosystem compared to Dolby Vision.
Patent Analysis of HDR Technologies
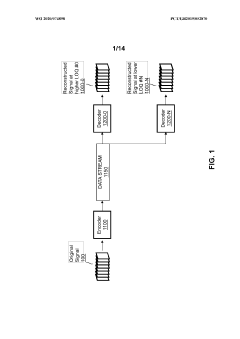
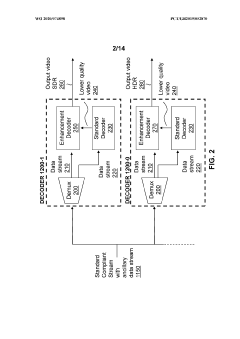
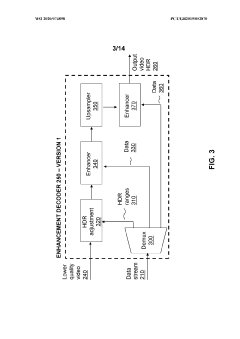
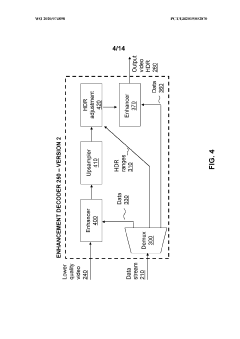
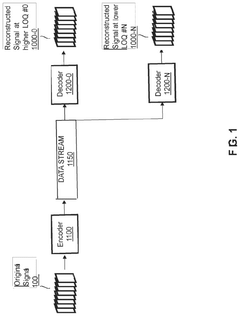
Enhancement decoder for video signals with multi-level enhancement and coding format adjustment
PatentWO2020074898A1
Innovation
- A hierarchical coding scheme that allows for the encoding and decoding of HDR-type signals to be compatible with both HDR and SDR displays, using an enhancement decoder that includes an interface for receiving video streams, de-multiplexing enhancement data, and a coding format adjustment module to convert between different bit lengths and resolutions, ensuring backwards compatibility and flexibility in signal processing.
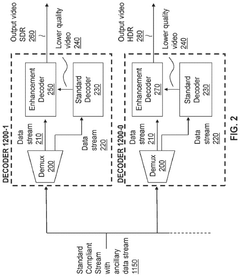
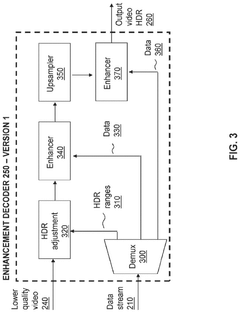
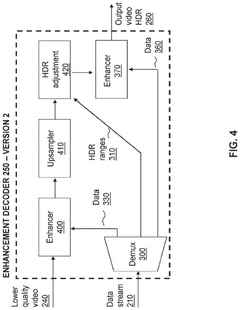
Colour conversion within a hierarchical coding scheme
PatentActiveUS12120305B2
Innovation
- A hierarchical coding scheme that allows for the encoding and decoding of HDR-type signals in a way that enables compatibility with both HDR and SDR displays, using a method that involves converting input signals between color spaces, down-sampling, and adding ancillary data for reconstruction, thereby providing backwards compatibility and reduced bandwidth requirements.
Content Creation Pipeline for HDR Formats
The content creation workflow for HDR formats represents a critical component in the adoption and market success of competing HDR technologies. Both HDR10 and Dolby Vision require specific production pipelines that significantly impact their market positioning and industry adoption rates.
For HDR10, the content creation process follows a relatively standardized approach. Content creators capture footage using cameras capable of wide dynamic range, then grade this content to a peak brightness of 1,000 nits using static metadata that remains consistent throughout the entire content. This simplicity offers production efficiency but limits creative flexibility, as brightness parameters cannot be adjusted on a scene-by-scene basis.
Dolby Vision, conversely, implements a more sophisticated pipeline requiring specialized tools and expertise. Its dynamic metadata capability allows brightness and color adjustments for individual scenes, enabling more precise creative control. The Dolby Vision creation process typically involves a two-layer workflow: a base HDR10 layer for compatibility, plus an enhancement layer containing frame-by-frame metadata instructions.
Production costs represent a significant market differentiator between these technologies. HDR10 content creation requires minimal additional investment beyond standard HDR equipment, making it accessible to smaller studios and content producers. Dolby Vision production demands licensed encoding tools, certified monitors, and often specialized colorists, increasing production costs by an estimated 10-15% compared to standard HDR workflows.
Time-to-market considerations also influence technology adoption. HDR10 content can be produced more rapidly due to its streamlined workflow, while Dolby Vision's additional quality control and metadata generation steps extend production timelines by approximately 20-30%, according to industry estimates.
The distribution ecosystem further shapes market dynamics. Major streaming platforms have developed varying approaches: Netflix and Amazon Prime support both formats but have different certification requirements for content creators. Disney+ has heavily invested in Dolby Vision, while YouTube primarily supports HDR10 and its derivative HDR10+.
Content availability trends show HDR10 maintaining a significant lead in total available content (estimated at 70% of all HDR content), though Dolby Vision is growing rapidly in premium entertainment categories where its enhanced visual quality justifies the additional production investment.
For HDR10, the content creation process follows a relatively standardized approach. Content creators capture footage using cameras capable of wide dynamic range, then grade this content to a peak brightness of 1,000 nits using static metadata that remains consistent throughout the entire content. This simplicity offers production efficiency but limits creative flexibility, as brightness parameters cannot be adjusted on a scene-by-scene basis.
Dolby Vision, conversely, implements a more sophisticated pipeline requiring specialized tools and expertise. Its dynamic metadata capability allows brightness and color adjustments for individual scenes, enabling more precise creative control. The Dolby Vision creation process typically involves a two-layer workflow: a base HDR10 layer for compatibility, plus an enhancement layer containing frame-by-frame metadata instructions.
Production costs represent a significant market differentiator between these technologies. HDR10 content creation requires minimal additional investment beyond standard HDR equipment, making it accessible to smaller studios and content producers. Dolby Vision production demands licensed encoding tools, certified monitors, and often specialized colorists, increasing production costs by an estimated 10-15% compared to standard HDR workflows.
Time-to-market considerations also influence technology adoption. HDR10 content can be produced more rapidly due to its streamlined workflow, while Dolby Vision's additional quality control and metadata generation steps extend production timelines by approximately 20-30%, according to industry estimates.
The distribution ecosystem further shapes market dynamics. Major streaming platforms have developed varying approaches: Netflix and Amazon Prime support both formats but have different certification requirements for content creators. Disney+ has heavily invested in Dolby Vision, while YouTube primarily supports HDR10 and its derivative HDR10+.
Content availability trends show HDR10 maintaining a significant lead in total available content (estimated at 70% of all HDR content), though Dolby Vision is growing rapidly in premium entertainment categories where its enhanced visual quality justifies the additional production investment.
Consumer Adoption Trends and Barriers
The adoption of HDR technologies among consumers has shown distinct patterns between HDR10 and Dolby Vision. Consumer awareness of HDR technology has grown significantly since 2016, with approximately 65% of TV buyers now considering HDR capabilities as an important purchasing factor. However, this awareness does not translate equally across different HDR formats.
HDR10, being an open standard with no licensing fees for manufacturers, has achieved broader market penetration. Approximately 85% of HDR-capable TVs support HDR10, making it the de facto baseline standard. This widespread availability has created a network effect that reinforces its position as the most commonly encountered HDR format for average consumers.
Dolby Vision, despite its technical advantages, faces several adoption barriers. The primary obstacle is the licensing cost imposed on manufacturers, which typically increases the retail price of Dolby Vision-enabled devices by 10-15%. This price premium creates a significant barrier for price-sensitive market segments, particularly in emerging economies where cost considerations often outweigh performance benefits.
Consumer understanding represents another substantial barrier. Market research indicates that only 27% of consumers can accurately explain the difference between HDR10 and Dolby Vision. This knowledge gap undermines consumers' willingness to pay premium prices for Dolby Vision technology when they cannot clearly articulate its benefits over the more ubiquitous HDR10.
Content availability also shapes adoption patterns significantly. While streaming platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ have embraced Dolby Vision for their original productions, the overall content library featuring Dolby Vision remains smaller than HDR10-compatible content. This content disparity reduces the perceived value proposition for consumers considering Dolby Vision-enabled devices.
Device ecosystem compatibility further influences consumer adoption. HDR10's broader compatibility with various devices creates fewer friction points in the consumer experience. Conversely, Dolby Vision's stricter implementation requirements can lead to compatibility issues across different manufacturers' ecosystems, creating potential frustration points for consumers.
Regional variations in adoption are also notable, with North American and Western European markets showing higher Dolby Vision adoption rates (approximately 35% of premium TV sales) compared to Asian markets (around 22%), excluding Japan where proprietary HDR standards have gained significant traction. These regional differences reflect varying consumer preferences, pricing sensitivities, and content availability across global markets.
HDR10, being an open standard with no licensing fees for manufacturers, has achieved broader market penetration. Approximately 85% of HDR-capable TVs support HDR10, making it the de facto baseline standard. This widespread availability has created a network effect that reinforces its position as the most commonly encountered HDR format for average consumers.
Dolby Vision, despite its technical advantages, faces several adoption barriers. The primary obstacle is the licensing cost imposed on manufacturers, which typically increases the retail price of Dolby Vision-enabled devices by 10-15%. This price premium creates a significant barrier for price-sensitive market segments, particularly in emerging economies where cost considerations often outweigh performance benefits.
Consumer understanding represents another substantial barrier. Market research indicates that only 27% of consumers can accurately explain the difference between HDR10 and Dolby Vision. This knowledge gap undermines consumers' willingness to pay premium prices for Dolby Vision technology when they cannot clearly articulate its benefits over the more ubiquitous HDR10.
Content availability also shapes adoption patterns significantly. While streaming platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ have embraced Dolby Vision for their original productions, the overall content library featuring Dolby Vision remains smaller than HDR10-compatible content. This content disparity reduces the perceived value proposition for consumers considering Dolby Vision-enabled devices.
Device ecosystem compatibility further influences consumer adoption. HDR10's broader compatibility with various devices creates fewer friction points in the consumer experience. Conversely, Dolby Vision's stricter implementation requirements can lead to compatibility issues across different manufacturers' ecosystems, creating potential frustration points for consumers.
Regional variations in adoption are also notable, with North American and Western European markets showing higher Dolby Vision adoption rates (approximately 35% of premium TV sales) compared to Asian markets (around 22%), excluding Japan where proprietary HDR standards have gained significant traction. These regional differences reflect varying consumer preferences, pricing sensitivities, and content availability across global markets.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!