Understanding the HDR10 vs Dolby Vision Regulatory Landscape
OCT 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HDR Technology Evolution and Objectives
High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology represents a significant advancement in visual display capabilities, evolving from the limitations of Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) to deliver enhanced contrast, brightness, and color accuracy. The journey began in the early 2000s with research into expanded luminance ranges, but commercial implementation only gained momentum around 2014 when the first HDR-capable displays entered the market.
The evolution of HDR technology has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, the focus was on increasing the peak brightness capabilities of displays from the traditional 100 nits to over 1,000 nits. This was followed by the development of wider color gamuts that could represent more colors than the conventional Rec.709 standard, leading to the adoption of the more expansive Rec.2020 color space.
HDR10, introduced in 2015, emerged as the first widely adopted HDR standard, utilizing static metadata to guide displays in rendering HDR content. Shortly thereafter, Dolby Vision was launched as a proprietary alternative, offering dynamic metadata capabilities that allow for frame-by-frame optimization of HDR parameters, potentially delivering superior visual experiences.
The primary objective of HDR technology development has been to create more immersive and realistic viewing experiences by more closely matching the capabilities of human vision. The human eye can perceive a much wider range of brightness and color than traditional displays could reproduce, and HDR aims to narrow this gap significantly.
In the context of HDR10 versus Dolby Vision, the technical objectives diverge in important ways. HDR10 prioritizes broad industry adoption through an open standard approach with minimal licensing requirements, while Dolby Vision focuses on maximizing visual quality through proprietary technology that requires licensing but offers enhanced capabilities.
The regulatory landscape surrounding these technologies reflects these different approaches. HDR10, as an open standard, has been widely adopted by manufacturers and content creators with minimal regulatory hurdles. Conversely, Dolby Vision's proprietary nature necessitates more complex licensing agreements and compliance with Dolby's technical specifications.
Looking forward, the evolution of HDR technology aims to address several challenges, including improving backward compatibility with SDR content, reducing the processing power required for HDR rendering, and developing more efficient compression methods for HDR content delivery. Additionally, there is ongoing work to harmonize HDR standards to reduce fragmentation in the market and simplify the consumer experience.
The evolution of HDR technology has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, the focus was on increasing the peak brightness capabilities of displays from the traditional 100 nits to over 1,000 nits. This was followed by the development of wider color gamuts that could represent more colors than the conventional Rec.709 standard, leading to the adoption of the more expansive Rec.2020 color space.
HDR10, introduced in 2015, emerged as the first widely adopted HDR standard, utilizing static metadata to guide displays in rendering HDR content. Shortly thereafter, Dolby Vision was launched as a proprietary alternative, offering dynamic metadata capabilities that allow for frame-by-frame optimization of HDR parameters, potentially delivering superior visual experiences.
The primary objective of HDR technology development has been to create more immersive and realistic viewing experiences by more closely matching the capabilities of human vision. The human eye can perceive a much wider range of brightness and color than traditional displays could reproduce, and HDR aims to narrow this gap significantly.
In the context of HDR10 versus Dolby Vision, the technical objectives diverge in important ways. HDR10 prioritizes broad industry adoption through an open standard approach with minimal licensing requirements, while Dolby Vision focuses on maximizing visual quality through proprietary technology that requires licensing but offers enhanced capabilities.
The regulatory landscape surrounding these technologies reflects these different approaches. HDR10, as an open standard, has been widely adopted by manufacturers and content creators with minimal regulatory hurdles. Conversely, Dolby Vision's proprietary nature necessitates more complex licensing agreements and compliance with Dolby's technical specifications.
Looking forward, the evolution of HDR technology aims to address several challenges, including improving backward compatibility with SDR content, reducing the processing power required for HDR rendering, and developing more efficient compression methods for HDR content delivery. Additionally, there is ongoing work to harmonize HDR standards to reduce fragmentation in the market and simplify the consumer experience.
Market Demand Analysis for Premium HDR Formats
The global market for premium HDR formats has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for superior visual experiences across various entertainment platforms. HDR10 and Dolby Vision have emerged as the leading technologies in this space, with distinct market positioning and adoption rates across different regions and industry segments.
Consumer electronics retailers report that HDR-capable displays now account for over 70% of premium television sales, with a growing percentage of consumers specifically requesting Dolby Vision compatibility when making purchasing decisions. This trend is particularly pronounced in North America and Western Europe, where home theater enthusiasts demonstrate strong brand awareness regarding HDR format differences.
Content streaming platforms have become major drivers of HDR format adoption, with Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, and Apple TV+ all offering extensive libraries of HDR content. Market research indicates that subscribers are increasingly using HDR support as a criterion when selecting streaming services, creating competitive pressure for platforms to expand their HDR offerings. The availability of premium HDR content has grown by approximately 200% annually since 2018.
The cinema and professional content creation sectors represent another significant market segment. Major film studios have widely adopted HDR mastering workflows, with Dolby Vision gaining particular traction in theatrical releases. The post-production industry has responded with substantial investments in HDR-capable equipment and expertise, creating a specialized market segment for professional HDR tools and services.
Regional market analysis reveals varying adoption patterns, with North American and East Asian markets leading in consumer HDR display penetration. European markets show strong growth trajectories, while emerging markets demonstrate increasing interest as HDR-capable devices become more affordable. The gaming industry has become a particularly dynamic growth sector for premium HDR formats, with next-generation consoles and gaming PCs supporting advanced HDR rendering.
Market forecasts project continued strong growth for premium HDR formats through 2027, with compound annual growth rates exceeding general consumer electronics industry averages. The market is increasingly segmented between mass-market implementations (primarily HDR10) and premium experiences (often Dolby Vision), creating distinct price tiers and consumer segments.
Consumer research indicates that while general awareness of HDR technology has increased significantly, detailed understanding of format differences remains limited to enthusiast segments. This suggests potential for market education initiatives to drive further adoption of premium formats like Dolby Vision, particularly as price premiums for compatible devices continue to decrease.
Consumer electronics retailers report that HDR-capable displays now account for over 70% of premium television sales, with a growing percentage of consumers specifically requesting Dolby Vision compatibility when making purchasing decisions. This trend is particularly pronounced in North America and Western Europe, where home theater enthusiasts demonstrate strong brand awareness regarding HDR format differences.
Content streaming platforms have become major drivers of HDR format adoption, with Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, and Apple TV+ all offering extensive libraries of HDR content. Market research indicates that subscribers are increasingly using HDR support as a criterion when selecting streaming services, creating competitive pressure for platforms to expand their HDR offerings. The availability of premium HDR content has grown by approximately 200% annually since 2018.
The cinema and professional content creation sectors represent another significant market segment. Major film studios have widely adopted HDR mastering workflows, with Dolby Vision gaining particular traction in theatrical releases. The post-production industry has responded with substantial investments in HDR-capable equipment and expertise, creating a specialized market segment for professional HDR tools and services.
Regional market analysis reveals varying adoption patterns, with North American and East Asian markets leading in consumer HDR display penetration. European markets show strong growth trajectories, while emerging markets demonstrate increasing interest as HDR-capable devices become more affordable. The gaming industry has become a particularly dynamic growth sector for premium HDR formats, with next-generation consoles and gaming PCs supporting advanced HDR rendering.
Market forecasts project continued strong growth for premium HDR formats through 2027, with compound annual growth rates exceeding general consumer electronics industry averages. The market is increasingly segmented between mass-market implementations (primarily HDR10) and premium experiences (often Dolby Vision), creating distinct price tiers and consumer segments.
Consumer research indicates that while general awareness of HDR technology has increased significantly, detailed understanding of format differences remains limited to enthusiast segments. This suggests potential for market education initiatives to drive further adoption of premium formats like Dolby Vision, particularly as price premiums for compatible devices continue to decrease.
HDR10 vs Dolby Vision: Technical Challenges
HDR10 and Dolby Vision represent two competing standards in the High Dynamic Range (HDR) video technology landscape, each presenting distinct technical challenges for implementation and adoption. The fundamental technical hurdle for both technologies lies in the accurate representation of expanded luminance ranges and wider color gamuts across diverse display hardware.
HDR10 utilizes static metadata that remains constant throughout content playback, creating significant limitations in scene-by-scene optimization. This static approach struggles with mixed-brightness content, where dark scenes may appear too bright or bright scenes too dim. Additionally, HDR10's reliance on 10-bit color depth creates potential banding issues in gradients, particularly noticeable in scenes with subtle color transitions.
Dolby Vision employs dynamic metadata that adjusts parameters frame-by-frame, requiring substantially more complex processing capabilities. This increased computational demand presents challenges for lower-end devices and creates higher implementation costs for manufacturers. The proprietary nature of Dolby Vision also necessitates licensing fees, creating economic barriers to widespread adoption, particularly in budget consumer electronics.
Content mastering presents another significant challenge. HDR10 content requires mastering at a fixed peak brightness (typically 1000 nits), which doesn't adapt well to displays with different capabilities. Conversely, Dolby Vision's dynamic approach requires more sophisticated mastering workflows and specialized equipment, increasing production costs and complexity.
Backward compatibility issues persist for both standards. Legacy displays lacking HDR capabilities may exhibit washed-out colors or improper brightness levels when attempting to display HDR content. While both standards include tone-mapping algorithms to address this, the results often compromise the creator's artistic intent.
Bandwidth and storage requirements present additional hurdles. The enhanced color information and metadata in both HDR formats increase bitrate requirements for streaming and file sizes for storage. This is particularly problematic for streaming services operating in regions with bandwidth limitations and for consumer devices with restricted storage capacity.
Standardization and fragmentation issues further complicate the landscape. The coexistence of multiple HDR formats (including HDR10+ and HLG alongside HDR10 and Dolby Vision) creates confusion for consumers and increases implementation costs for manufacturers who must support multiple standards. This fragmentation slows industry-wide adoption and complicates content distribution strategies.
HDR10 utilizes static metadata that remains constant throughout content playback, creating significant limitations in scene-by-scene optimization. This static approach struggles with mixed-brightness content, where dark scenes may appear too bright or bright scenes too dim. Additionally, HDR10's reliance on 10-bit color depth creates potential banding issues in gradients, particularly noticeable in scenes with subtle color transitions.
Dolby Vision employs dynamic metadata that adjusts parameters frame-by-frame, requiring substantially more complex processing capabilities. This increased computational demand presents challenges for lower-end devices and creates higher implementation costs for manufacturers. The proprietary nature of Dolby Vision also necessitates licensing fees, creating economic barriers to widespread adoption, particularly in budget consumer electronics.
Content mastering presents another significant challenge. HDR10 content requires mastering at a fixed peak brightness (typically 1000 nits), which doesn't adapt well to displays with different capabilities. Conversely, Dolby Vision's dynamic approach requires more sophisticated mastering workflows and specialized equipment, increasing production costs and complexity.
Backward compatibility issues persist for both standards. Legacy displays lacking HDR capabilities may exhibit washed-out colors or improper brightness levels when attempting to display HDR content. While both standards include tone-mapping algorithms to address this, the results often compromise the creator's artistic intent.
Bandwidth and storage requirements present additional hurdles. The enhanced color information and metadata in both HDR formats increase bitrate requirements for streaming and file sizes for storage. This is particularly problematic for streaming services operating in regions with bandwidth limitations and for consumer devices with restricted storage capacity.
Standardization and fragmentation issues further complicate the landscape. The coexistence of multiple HDR formats (including HDR10+ and HLG alongside HDR10 and Dolby Vision) creates confusion for consumers and increases implementation costs for manufacturers who must support multiple standards. This fragmentation slows industry-wide adoption and complicates content distribution strategies.
Current HDR Implementation Solutions
01 HDR10 and Dolby Vision licensing and certification requirements
High Dynamic Range (HDR) technologies like HDR10 and Dolby Vision require specific licensing agreements and certification processes for manufacturers. Companies must comply with technical specifications and undergo testing to ensure their devices properly support these formats. The certification process involves verification of display capabilities, color accuracy, and brightness levels to maintain consistent quality across different devices implementing these standards.- HDR10 and Dolby Vision licensing and certification requirements: High Dynamic Range (HDR) technologies like HDR10 and Dolby Vision require specific licensing agreements and certification processes for manufacturers. Companies must comply with technical specifications and undergo testing to ensure their devices properly support these formats. The certification process involves verification of display capabilities, color accuracy, and brightness levels to maintain consistent quality across different devices implementing these technologies.
- Technical standards compliance for HDR display technologies: Manufacturers must adhere to specific technical standards when implementing HDR10 and Dolby Vision in their displays. These standards govern aspects such as color gamut, bit depth, brightness levels, and metadata handling. Compliance with these technical specifications ensures interoperability between content and display devices while maintaining the intended visual experience across different platforms and manufacturers.
- Content protection and digital rights management for HDR formats: HDR10 and Dolby Vision implementations must incorporate specific content protection mechanisms and digital rights management systems. These security measures protect premium HDR content from unauthorized copying or distribution while ensuring that only certified devices can decode and display the content. The regulatory framework includes encryption standards, authentication protocols, and secure playback pathways that content providers and device manufacturers must implement.
- International market access requirements for HDR-enabled devices: Different regions have varying regulatory requirements for HDR-enabled devices entering their markets. These include electromagnetic compatibility standards, energy efficiency regulations, and specific technical certifications. Manufacturers must navigate these regional differences to ensure their HDR10 and Dolby Vision products can be legally sold in global markets, which may involve obtaining region-specific approvals and adapting to local technical standards.
- Consumer protection regulations related to HDR performance claims: Regulatory bodies have established guidelines regarding how manufacturers can advertise and market HDR capabilities in their products. These regulations aim to protect consumers from misleading claims about HDR performance. Manufacturers must accurately represent their products' capabilities regarding peak brightness, contrast ratios, and color reproduction. Some jurisdictions require specific testing methodologies to verify performance claims before products can be marketed as HDR10 or Dolby Vision compatible.
02 Technical standards compliance for HDR content delivery
Implementation of HDR10 and Dolby Vision must adhere to established technical standards for content delivery across various platforms. These standards govern aspects such as metadata handling, color space mapping, and brightness levels. Regulatory frameworks ensure interoperability between content creation tools, distribution platforms, and display devices, allowing for consistent HDR experiences regardless of the hardware or software being used.Expand Specific Solutions03 International regulatory frameworks for HDR technologies
Different regions have established varying regulatory requirements for HDR technologies, including HDR10 and Dolby Vision. These frameworks address aspects such as energy consumption standards, electromagnetic compatibility, and consumer protection measures. Manufacturers must navigate these international regulations when deploying HDR-capable devices across global markets, ensuring compliance with regional certification bodies and standards organizations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Intellectual property protection for HDR display technologies
HDR technologies are protected by extensive intellectual property rights, with Dolby Vision and HDR10 covered by different patent portfolios. Companies implementing these technologies must navigate the patent landscape to ensure proper licensing and avoid infringement issues. The regulatory landscape includes patent pools, cross-licensing agreements, and standard-essential patents that impact how manufacturers can implement these HDR formats in their products.Expand Specific Solutions05 Consumer protection regulations for HDR display marketing
Regulatory bodies have established guidelines for marketing claims related to HDR technologies to protect consumers. These regulations govern how manufacturers can advertise HDR capabilities, including brightness levels, color gamut coverage, and format support. Companies must ensure their marketing materials accurately represent the actual HDR performance of their products, with some regions requiring specific testing and verification before making HDR-related claims.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in HDR Ecosystem
The HDR10 vs Dolby Vision regulatory landscape represents a maturing market within the premium display technology sector, currently in a growth phase with increasing adoption across consumer electronics. The market is characterized by a duopoly between open-standard HDR10 (supported by Samsung, Apple, Roku) and proprietary Dolby Vision (licensed by Dolby Laboratories). Key technology players include content ecosystem companies (Philips, MediaTek, Realtek) providing hardware solutions, while device manufacturers (Xiaomi, TCL, Skyworth) implement these standards in their products. The competitive dynamics are evolving as manufacturers balance licensing costs against premium features, with Dolby Vision commanding higher licensing fees but offering superior technical capabilities through dynamic metadata and greater color depth compared to HDR10's static approach.
Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp.
Technical Solution: Dolby Laboratories has developed Dolby Vision as a proprietary HDR format that offers dynamic metadata capabilities, allowing frame-by-frame optimization of brightness, contrast, and color. Their technology supports up to 12-bit color depth (providing 68 billion colors) and peak brightness levels of up to 10,000 nits, significantly exceeding HDR10's static metadata approach. Dolby Vision implements a sophisticated content mapping technology that optimizes content for each specific display's capabilities, ensuring consistent visual experience across different devices. The company maintains strict certification requirements for manufacturers, requiring hardware-level implementation and quality control testing to ensure compliance with their standards. Dolby has also developed an ecosystem approach, working with content creators to ensure end-to-end implementation from production to display.
Strengths: Superior technical capabilities with dynamic metadata; better color accuracy and brightness control; established partnerships with major studios and OEMs; comprehensive certification program ensuring quality. Weaknesses: Higher licensing costs compared to open standards; requires dedicated hardware implementation; more complex implementation process for manufacturers; market penetration limited by cost barriers.
Koninklijke Philips NV
Technical Solution: Philips has been instrumental in the development of HDR10 as an open standard for High Dynamic Range content. Their approach focuses on implementing static metadata that applies consistent HDR parameters throughout an entire piece of content. Philips, along with other industry partners, helped establish the HDR10 specification which supports 10-bit color depth (over 1 billion colors) and peak brightness levels of 1,000 nits. The company has also developed HDR10+, an enhanced version that adds dynamic metadata capabilities while maintaining an open licensing model. Philips has integrated these technologies across their display product lines and works with the UHD Alliance to promote standardization. Their P5 processing engine specifically optimizes HDR content rendering on their displays, with algorithms designed to maximize the visual impact of HDR10 content while maintaining compatibility with various content sources.
Strengths: Pioneer in open HDR standards development; broad industry support for HDR10; lower implementation costs for manufacturers; widespread adoption across the industry. Weaknesses: HDR10's static metadata provides less precise image optimization compared to dynamic solutions; limited peak brightness specifications; requires additional technology (HDR10+) to match some competing features.
Core Patents and Technical Specifications
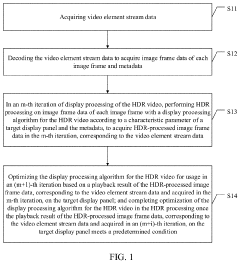
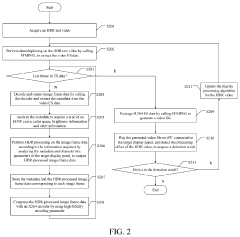
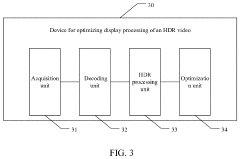
Method and apparatus for optimizing HDR video display processing, and storage medium and terminal
PatentActiveUS20230298305A1
Innovation
- A method that couples decoding and display processing by extracting metadata and image frame data from HDR videos, performing HDR processing on each frame with a display processing algorithm, and optimizing the algorithm based on playback results until predetermined conditions are met, thereby reducing the development cycle and improving efficiency.
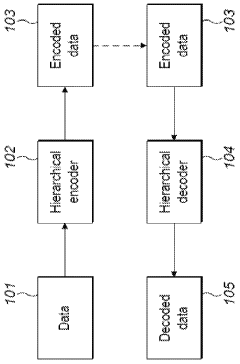
Signal processing with overlay regions
PatentWO2023187307A1
Innovation
- A hierarchical coding scheme that uses residual data to efficiently encode and decode signals, allowing for the overlay of HDR content onto SDR content by generating residuals indicative of differences between HDR and SDR signals, which are then encoded using a method like LCEVC, enabling flexible and efficient distribution across various devices.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance Requirements
The regulatory landscape governing HDR technologies, particularly HDR10 and Dolby Vision, is complex and multifaceted, involving standards bodies, industry consortiums, and governmental regulations across different jurisdictions. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has established the BT.2100 recommendation, which provides the foundation for HDR implementation including both the HDR10 and Dolby Vision formats. This recommendation outlines technical parameters such as color gamut, bit depth, and transfer functions that compliant devices must adhere to.
In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has integrated HDR standards into its broader digital television regulations, requiring manufacturers to clearly label HDR capabilities on consumer electronics. The Consumer Technology Association (CTA) has developed certification programs for HDR technologies, with distinct requirements for HDR10 and Dolby Vision compliance. Manufacturers seeking to implement either technology must undergo testing procedures to ensure their products meet these specifications.
The European Union approaches HDR regulation through the Digital Single Market strategy, with the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) providing technical guidelines. The EU's Ecodesign Directive also impacts HDR implementation by setting energy efficiency requirements for displays, which manufacturers must balance with HDR performance capabilities. Additionally, the EU mandates clear consumer information regarding HDR functionality through labeling directives.
For Dolby Vision specifically, implementers must navigate Dolby Laboratories' licensing framework, which includes technical compliance requirements and royalty structures. This creates a more controlled ecosystem compared to HDR10, which operates as an open standard with fewer direct licensing costs but still requires adherence to technical specifications maintained by the Ultra HD Alliance.
Content creators face distinct regulatory considerations, including metadata requirements that differ significantly between formats. HDR10 utilizes static metadata conforming to SMPTE ST 2086, while Dolby Vision implements dynamic metadata following proprietary specifications that require specialized production workflows to maintain regulatory compliance.
The regulatory landscape continues to evolve with the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) working to harmonize HDR standards globally. Their joint technical committee is developing frameworks that may eventually create more unified compliance requirements across different HDR technologies, potentially reducing the current fragmentation between HDR10 and Dolby Vision implementation requirements.
In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has integrated HDR standards into its broader digital television regulations, requiring manufacturers to clearly label HDR capabilities on consumer electronics. The Consumer Technology Association (CTA) has developed certification programs for HDR technologies, with distinct requirements for HDR10 and Dolby Vision compliance. Manufacturers seeking to implement either technology must undergo testing procedures to ensure their products meet these specifications.
The European Union approaches HDR regulation through the Digital Single Market strategy, with the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) providing technical guidelines. The EU's Ecodesign Directive also impacts HDR implementation by setting energy efficiency requirements for displays, which manufacturers must balance with HDR performance capabilities. Additionally, the EU mandates clear consumer information regarding HDR functionality through labeling directives.
For Dolby Vision specifically, implementers must navigate Dolby Laboratories' licensing framework, which includes technical compliance requirements and royalty structures. This creates a more controlled ecosystem compared to HDR10, which operates as an open standard with fewer direct licensing costs but still requires adherence to technical specifications maintained by the Ultra HD Alliance.
Content creators face distinct regulatory considerations, including metadata requirements that differ significantly between formats. HDR10 utilizes static metadata conforming to SMPTE ST 2086, while Dolby Vision implements dynamic metadata following proprietary specifications that require specialized production workflows to maintain regulatory compliance.
The regulatory landscape continues to evolve with the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) working to harmonize HDR standards globally. Their joint technical committee is developing frameworks that may eventually create more unified compliance requirements across different HDR technologies, potentially reducing the current fragmentation between HDR10 and Dolby Vision implementation requirements.
Content Creation Pipeline Considerations
Content creation for HDR10 and Dolby Vision requires distinct workflows that significantly impact production decisions. The HDR10 pipeline utilizes static metadata applied uniformly across an entire piece of content, simplifying the production process but limiting creative flexibility. This approach requires less specialized equipment and post-production resources, making it more accessible for smaller studios and content creators working with budget constraints.
Dolby Vision, conversely, employs a more complex pipeline that incorporates dynamic metadata capable of adjusting brightness, color, and contrast on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis. This sophisticated approach necessitates specialized cameras, monitors, and post-production tools certified by Dolby Laboratories. Content creators must also undergo specific training to properly implement Dolby Vision standards, representing a significant investment in both equipment and human resources.
The mastering process differs substantially between these formats. HDR10 content typically requires a single master that adheres to the HDR10 specification with a maximum brightness of 1,000 nits. Dolby Vision mastering involves creating a high-quality master at up to 4,000 nits, from which various versions can be derived to accommodate different display capabilities.
Content distribution considerations also impact the creation pipeline. HDR10 content can be more easily distributed across various platforms due to its open standard nature and widespread adoption. Dolby Vision content requires additional licensing and certification steps before distribution, adding complexity to the release workflow.
For content creators, the decision between HDR10 and Dolby Vision often involves balancing quality aspirations against practical constraints. Major studios and premium content producers typically opt for Dolby Vision to deliver the highest possible visual experience, while simultaneously creating HDR10 versions for broader compatibility. Independent filmmakers and smaller production houses may choose HDR10 exclusively due to its more straightforward implementation and lower resource requirements.
The regulatory landscape further complicates these pipeline considerations, as different regions may have varying requirements for HDR content delivery. Some markets mandate support for specific formats, influencing how content must be prepared during the creation phase to ensure compliance with local regulations while maintaining artistic integrity.
Dolby Vision, conversely, employs a more complex pipeline that incorporates dynamic metadata capable of adjusting brightness, color, and contrast on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis. This sophisticated approach necessitates specialized cameras, monitors, and post-production tools certified by Dolby Laboratories. Content creators must also undergo specific training to properly implement Dolby Vision standards, representing a significant investment in both equipment and human resources.
The mastering process differs substantially between these formats. HDR10 content typically requires a single master that adheres to the HDR10 specification with a maximum brightness of 1,000 nits. Dolby Vision mastering involves creating a high-quality master at up to 4,000 nits, from which various versions can be derived to accommodate different display capabilities.
Content distribution considerations also impact the creation pipeline. HDR10 content can be more easily distributed across various platforms due to its open standard nature and widespread adoption. Dolby Vision content requires additional licensing and certification steps before distribution, adding complexity to the release workflow.
For content creators, the decision between HDR10 and Dolby Vision often involves balancing quality aspirations against practical constraints. Major studios and premium content producers typically opt for Dolby Vision to deliver the highest possible visual experience, while simultaneously creating HDR10 versions for broader compatibility. Independent filmmakers and smaller production houses may choose HDR10 exclusively due to its more straightforward implementation and lower resource requirements.
The regulatory landscape further complicates these pipeline considerations, as different regions may have varying requirements for HDR content delivery. Some markets mandate support for specific formats, influencing how content must be prepared during the creation phase to ensure compliance with local regulations while maintaining artistic integrity.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!