What Technical Parameters Define HDR10 vs Dolby Vision Enhancements
OCT 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HDR Technology Evolution and Objectives
High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology has evolved significantly since its inception, transforming from a theoretical concept to a mainstream feature in modern display technologies. The journey began in the early 2000s with research into expanded luminance ranges beyond standard dynamic range (SDR) capabilities. By 2012, the first commercial implementations emerged, though these early versions offered limited brightness ranges compared to today's standards.
The evolution accelerated around 2014-2015 when the HDR10 standard was established as an open format, providing a foundation for wider industry adoption. This standard introduced key parameters including 10-bit color depth, BT.2020 color gamut, and static metadata for scene-by-scene optimization. Shortly thereafter, Dolby Vision emerged as a proprietary alternative, pushing technical boundaries with 12-bit color depth and dynamic metadata capabilities that adjust brightness levels on a frame-by-frame basis.
The technical progression of HDR technology has been driven by the pursuit of more realistic visual experiences that better approximate human visual perception. Traditional SDR content typically maxes out at around 100 nits of brightness, whereas modern HDR displays can reach peaks of 1,000-4,000 nits, dramatically expanding the visible contrast ratio and enabling more nuanced representation of both bright highlights and shadow details.
Industry objectives for HDR technology have centered around several key areas. First is the enhancement of viewer experience through more lifelike imagery with greater depth and dimensionality. Second is the establishment of standardized implementations that ensure content creators' artistic intent is preserved across different display devices. Third is backward compatibility with existing infrastructure to facilitate broader market adoption.
The divergence between HDR10 and Dolby Vision represents different philosophical approaches to these objectives. HDR10, as an open standard, prioritizes accessibility and widespread implementation, while Dolby Vision emphasizes premium performance through more sophisticated metadata handling and greater color precision. This dichotomy has shaped the market's evolution, with HDR10 gaining broader hardware support while Dolby Vision positions itself as a premium offering.
Current technical objectives in the field include increasing maximum brightness capabilities, expanding color volume representation, improving tone mapping algorithms for various viewing environments, and developing more efficient metadata structures. Additionally, there is growing focus on optimizing HDR content for a wider range of devices, from professional-grade monitors to mobile screens, each with different technical capabilities and viewing conditions.
The evolution accelerated around 2014-2015 when the HDR10 standard was established as an open format, providing a foundation for wider industry adoption. This standard introduced key parameters including 10-bit color depth, BT.2020 color gamut, and static metadata for scene-by-scene optimization. Shortly thereafter, Dolby Vision emerged as a proprietary alternative, pushing technical boundaries with 12-bit color depth and dynamic metadata capabilities that adjust brightness levels on a frame-by-frame basis.
The technical progression of HDR technology has been driven by the pursuit of more realistic visual experiences that better approximate human visual perception. Traditional SDR content typically maxes out at around 100 nits of brightness, whereas modern HDR displays can reach peaks of 1,000-4,000 nits, dramatically expanding the visible contrast ratio and enabling more nuanced representation of both bright highlights and shadow details.
Industry objectives for HDR technology have centered around several key areas. First is the enhancement of viewer experience through more lifelike imagery with greater depth and dimensionality. Second is the establishment of standardized implementations that ensure content creators' artistic intent is preserved across different display devices. Third is backward compatibility with existing infrastructure to facilitate broader market adoption.
The divergence between HDR10 and Dolby Vision represents different philosophical approaches to these objectives. HDR10, as an open standard, prioritizes accessibility and widespread implementation, while Dolby Vision emphasizes premium performance through more sophisticated metadata handling and greater color precision. This dichotomy has shaped the market's evolution, with HDR10 gaining broader hardware support while Dolby Vision positions itself as a premium offering.
Current technical objectives in the field include increasing maximum brightness capabilities, expanding color volume representation, improving tone mapping algorithms for various viewing environments, and developing more efficient metadata structures. Additionally, there is growing focus on optimizing HDR content for a wider range of devices, from professional-grade monitors to mobile screens, each with different technical capabilities and viewing conditions.
Market Demand for Premium HDR Content
The demand for premium HDR content has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, driven by the increasing adoption of HDR-capable displays and streaming services. Market research indicates that consumers are increasingly prioritizing visual quality in their entertainment choices, with HDR technology becoming a significant differentiator in purchasing decisions for both content subscriptions and display hardware.
Consumer electronics retailers report that HDR compatibility ranks among the top five features consumers look for when purchasing new televisions, with premium HDR formats like Dolby Vision often commanding price premiums of 15-20% over standard HDR10 models. This trend reflects growing consumer awareness and appreciation of enhanced dynamic range and color accuracy in visual content.
Content streaming platforms have responded to this demand by expanding their HDR libraries. Major services including Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, and Apple TV+ have all increased their HDR content offerings, with many new releases now available in both HDR10 and Dolby Vision formats. Industry data shows that HDR-enabled titles typically receive higher viewer engagement metrics, with average viewing times approximately 27% longer than for standard dynamic range content.
The film and television production industry has similarly embraced HDR technology, with most major studios now incorporating HDR mastering into their standard production workflows. This shift represents a significant investment in technical infrastructure and expertise, indicating strong confidence in continued market demand for premium visual experiences.
Market segmentation analysis reveals particularly strong demand for HDR content in several key categories. Premium episodic content, blockbuster films, nature documentaries, and sports broadcasts show the highest consumer preference for HDR formats. Gaming represents another rapidly growing segment, with next-generation consoles and PC graphics hardware supporting various HDR standards to meet player expectations for visual fidelity.
Regional analysis indicates that North America and East Asia lead in HDR content consumption, correlating with higher penetration rates of compatible display technology. However, emerging markets are showing accelerated adoption curves as HDR-capable devices become more affordable and streaming infrastructure improves.
Industry forecasts project continued growth in the premium HDR content market, with compound annual growth rates expected to remain in double digits through 2027. This growth trajectory is supported by ongoing technological advancements in both HDR10 and Dolby Vision standards, as well as decreasing production costs that enable broader implementation across content categories.
Consumer electronics retailers report that HDR compatibility ranks among the top five features consumers look for when purchasing new televisions, with premium HDR formats like Dolby Vision often commanding price premiums of 15-20% over standard HDR10 models. This trend reflects growing consumer awareness and appreciation of enhanced dynamic range and color accuracy in visual content.
Content streaming platforms have responded to this demand by expanding their HDR libraries. Major services including Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, and Apple TV+ have all increased their HDR content offerings, with many new releases now available in both HDR10 and Dolby Vision formats. Industry data shows that HDR-enabled titles typically receive higher viewer engagement metrics, with average viewing times approximately 27% longer than for standard dynamic range content.
The film and television production industry has similarly embraced HDR technology, with most major studios now incorporating HDR mastering into their standard production workflows. This shift represents a significant investment in technical infrastructure and expertise, indicating strong confidence in continued market demand for premium visual experiences.
Market segmentation analysis reveals particularly strong demand for HDR content in several key categories. Premium episodic content, blockbuster films, nature documentaries, and sports broadcasts show the highest consumer preference for HDR formats. Gaming represents another rapidly growing segment, with next-generation consoles and PC graphics hardware supporting various HDR standards to meet player expectations for visual fidelity.
Regional analysis indicates that North America and East Asia lead in HDR content consumption, correlating with higher penetration rates of compatible display technology. However, emerging markets are showing accelerated adoption curves as HDR-capable devices become more affordable and streaming infrastructure improves.
Industry forecasts project continued growth in the premium HDR content market, with compound annual growth rates expected to remain in double digits through 2027. This growth trajectory is supported by ongoing technological advancements in both HDR10 and Dolby Vision standards, as well as decreasing production costs that enable broader implementation across content categories.
Current HDR Standards and Technical Limitations
The High Dynamic Range (HDR) landscape is currently dominated by several competing standards, each with distinct technical specifications and limitations. HDR10, as the baseline open standard, supports 10-bit color depth allowing for approximately 1.07 billion colors and peak brightness levels of 1,000 nits. While widely adopted due to its non-proprietary nature, HDR10 employs static metadata that applies the same brightness parameters throughout an entire piece of content, limiting its ability to optimize scene-by-scene or frame-by-frame.
HDR10+ addresses some limitations of its predecessor by incorporating dynamic metadata, enabling brightness adjustments on a scene-by-scene basis. However, its market penetration remains limited compared to other standards, with inconsistent implementation across display manufacturers and content providers.
Dolby Vision represents the premium tier of current HDR technology, supporting 12-bit color depth (68.7 billion colors) and brightness capabilities up to 10,000 nits, though current consumer displays typically max out at 4,000 nits. Its dynamic metadata allows frame-by-frame optimization, resulting in more precise image rendering. The proprietary nature of Dolby Vision, however, requires licensing fees that increase production costs and limit widespread adoption.
Hybrid Log-Gamma (HLG), developed by BBC and NHK, offers backward compatibility with SDR displays but sacrifices some of the peak brightness capabilities found in other HDR formats. Its primary advantage lies in broadcast applications, though it lacks the dynamic range optimization of Dolby Vision.
Technical limitations persist across all current HDR standards. Content mastering inconsistencies create significant variability in viewer experience, as content produced on reference monitors often appears differently on consumer displays. The "tone mapping" process—how displays adapt HDR content to their specific capabilities—remains inconsistently implemented across manufacturers.
Bandwidth constraints continue to impact streaming quality, with compression artifacts particularly noticeable in dark scenes or gradients. Most streaming platforms must balance HDR quality against data transmission limitations, often resulting in compromised image quality.
Display technology limitations further complicate HDR implementation. LED/LCD displays struggle with blooming effects and limited contrast ratios, while OLED panels excel in contrast but face brightness limitations and potential burn-in issues. Mini-LED and QD-OLED technologies attempt to address these shortcomings but introduce their own technical challenges and cost considerations.
The fragmented HDR ecosystem creates compatibility issues across the content delivery chain, with consumers often confused by inconsistent labeling and performance across different viewing platforms and devices.
HDR10+ addresses some limitations of its predecessor by incorporating dynamic metadata, enabling brightness adjustments on a scene-by-scene basis. However, its market penetration remains limited compared to other standards, with inconsistent implementation across display manufacturers and content providers.
Dolby Vision represents the premium tier of current HDR technology, supporting 12-bit color depth (68.7 billion colors) and brightness capabilities up to 10,000 nits, though current consumer displays typically max out at 4,000 nits. Its dynamic metadata allows frame-by-frame optimization, resulting in more precise image rendering. The proprietary nature of Dolby Vision, however, requires licensing fees that increase production costs and limit widespread adoption.
Hybrid Log-Gamma (HLG), developed by BBC and NHK, offers backward compatibility with SDR displays but sacrifices some of the peak brightness capabilities found in other HDR formats. Its primary advantage lies in broadcast applications, though it lacks the dynamic range optimization of Dolby Vision.
Technical limitations persist across all current HDR standards. Content mastering inconsistencies create significant variability in viewer experience, as content produced on reference monitors often appears differently on consumer displays. The "tone mapping" process—how displays adapt HDR content to their specific capabilities—remains inconsistently implemented across manufacturers.
Bandwidth constraints continue to impact streaming quality, with compression artifacts particularly noticeable in dark scenes or gradients. Most streaming platforms must balance HDR quality against data transmission limitations, often resulting in compromised image quality.
Display technology limitations further complicate HDR implementation. LED/LCD displays struggle with blooming effects and limited contrast ratios, while OLED panels excel in contrast but face brightness limitations and potential burn-in issues. Mini-LED and QD-OLED technologies attempt to address these shortcomings but introduce their own technical challenges and cost considerations.
The fragmented HDR ecosystem creates compatibility issues across the content delivery chain, with consumers often confused by inconsistent labeling and performance across different viewing platforms and devices.
Technical Comparison of HDR10 vs Dolby Vision
01 HDR10 Technical Parameters and Standards
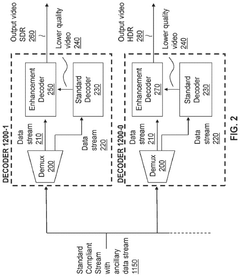
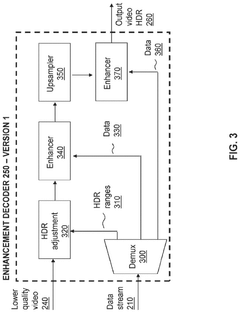
HDR10 is an open standard for high dynamic range displays that specifies key technical parameters including 10-bit color depth, wider color gamut using Rec.2020 color space, and peak brightness levels up to 1,000 nits. It uses static metadata that remains constant throughout content playback and employs the PQ (Perceptual Quantizer) EOTF (Electro-Optical Transfer Function) for brightness mapping. HDR10 supports a maximum resolution of 4K and 8K with frame rates up to 60fps, making it widely adopted across various display technologies.- HDR10 Technical Parameters and Standards: HDR10 is an open standard for high dynamic range displays that specifies technical parameters including 10-bit color depth, wider color gamut using Rec.2020 color space, and peak brightness levels up to 1,000 nits. It utilizes static metadata that remains constant throughout content playback and employs the PQ (Perceptual Quantizer) EOTF (Electro-Optical Transfer Function) for brightness mapping. HDR10 supports up to 4K resolution and is widely adopted across various display manufacturers.
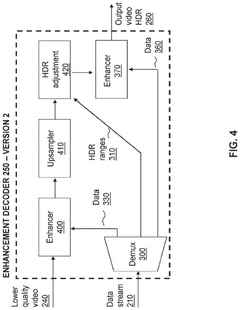
- Dolby Vision Technical Specifications: Dolby Vision is a proprietary HDR format that offers enhanced capabilities compared to standard HDR10. It supports 12-bit color depth, providing up to 68 billion colors, and can achieve brightness levels up to 10,000 nits. A key distinguishing feature is its use of dynamic metadata that can adjust brightness, color, and contrast on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis. This allows for more precise image optimization throughout content playback, resulting in more accurate representation of the creator's intent across different display capabilities.
- Color Processing and Management in HDR Systems: Advanced color processing is essential for HDR display technologies to accurately reproduce the expanded color gamut and dynamic range. This includes sophisticated color mapping algorithms that transform content between different color spaces while preserving artistic intent. HDR systems implement color volume mapping to adapt content to the specific capabilities of different displays. These technologies utilize complex tone mapping operations to maintain color accuracy across varying brightness levels, ensuring consistent color representation even when adapting content for displays with different peak luminance capabilities.
- Display Hardware Requirements for HDR Implementation: Implementing HDR technologies requires specific hardware capabilities in display devices. These include local dimming technologies that allow for precise control of backlight zones to achieve higher contrast ratios. Quantum dot technology or advanced OLED panels are often used to achieve the wider color gamut necessary for HDR content. Display processors need sufficient computational power to handle the complex tone mapping and color transformation algorithms. Additionally, displays must support the appropriate HDMI specifications (typically HDMI 2.0a or later) to receive HDR metadata and content properly.
- Content Creation and Mastering for HDR Formats: Creating content for HDR display technologies involves specialized mastering processes. Content creators use reference monitors capable of displaying the full HDR specification to ensure accurate representation. The mastering process includes setting appropriate metadata parameters such as MaxCLL (Maximum Content Light Level) and MaxFALL (Maximum Frame Average Light Level) that guide displays in rendering content correctly. For Dolby Vision, this includes creating dynamic metadata throughout the content. HDR grading tools allow colorists to take advantage of the expanded dynamic range and color volume while maintaining creative intent across different display capabilities.
02 Dolby Vision Technical Specifications
Dolby Vision is a proprietary HDR format that offers enhanced capabilities compared to standard HDR10. It supports 12-bit color depth, providing up to 68 billion colors, and can achieve brightness levels up to 10,000 nits. A key distinguishing feature is its use of dynamic metadata that can adjust HDR parameters on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis, resulting in more optimized image quality. Dolby Vision also incorporates advanced color mapping algorithms and supports backward compatibility with HDR10 content.Expand Specific Solutions03 Color Processing and Management in HDR Systems
Advanced color processing is essential for HDR display technologies to accurately reproduce the expanded color gamut and dynamic range. This includes sophisticated color mapping algorithms that transform content to match the capabilities of specific displays while preserving creative intent. HDR systems implement color volume mapping to handle the translation between different color spaces and dynamic ranges. Wide color gamut processing enables the representation of previously unachievable colors in standard displays, while maintaining color accuracy across different viewing environments and display technologies.Expand Specific Solutions04 HDR Signal Processing and Content Delivery
HDR signal processing involves specialized techniques for encoding, transmitting, and decoding high dynamic range content. This includes efficient compression methods to handle the increased data requirements of HDR content while maintaining quality. Content delivery systems must manage the metadata that accompanies HDR signals, ensuring proper interpretation by compatible displays. Adaptive tone mapping algorithms are employed to optimize content for different display capabilities, and format conversion systems enable interoperability between various HDR standards. These processing techniques ensure consistent quality across different viewing platforms.Expand Specific Solutions05 Display Hardware Requirements for HDR Implementation
Implementing HDR technologies requires specific hardware capabilities in display devices. This includes panels capable of higher peak brightness and deeper black levels to achieve the expanded dynamic range. Local dimming technologies with multiple zones or per-pixel control (as in OLED) are essential for contrast management. Display processors must handle the complex tone mapping and color volume transformations required by HDR content. Additionally, HDR-capable displays need enhanced thermal management systems to handle the increased power requirements when displaying bright HDR content, particularly in smaller form factors like mobile devices.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in HDR Technology
The HDR10 vs Dolby Vision enhancement landscape is currently in a mature growth phase, with the global HDR market expected to reach $36.7 billion by 2028. Dolby Laboratories leads with its proprietary Dolby Vision technology offering dynamic metadata and 12-bit color depth, while Samsung champions the open-source HDR10+ standard. Other significant players include Netflix supporting both formats, and consumer electronics manufacturers like OPPO, TCL, and Skyworth implementing these technologies in their displays. MediaTek and V-Nova contribute through codec development, while content providers drive adoption through expanding HDR libraries. The competition centers on technical superiority versus accessibility, with Dolby Vision offering premium features at licensing costs, while HDR10 provides a more accessible but technically limited alternative.
Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp.
Technical Solution: Dolby Vision represents Dolby's premium HDR technology that builds upon and enhances the HDR10 standard. While HDR10 uses static metadata that remains constant throughout content, Dolby Vision implements dynamic metadata that can adjust brightness, contrast, and color settings on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis. Technically, Dolby Vision supports up to 12-bit color depth (compared to HDR10's 10-bit), allowing for a theoretical 68.7 billion colors versus HDR10's 1.07 billion. Dolby Vision can achieve peak brightness levels of up to 10,000 nits (though current displays typically max out around 4,000 nits), while HDR10 typically targets 1,000 nits. Additionally, Dolby Vision incorporates proprietary color mapping algorithms that optimize content for specific display capabilities, ensuring consistent visual experience across different devices through its certified ecosystem approach.
Strengths: Superior dynamic range with frame-by-frame optimization; wider color gamut with 12-bit color depth; better cross-device consistency through certification program; backward compatibility with HDR10. Weaknesses: Requires licensing fees for manufacturers; higher processing requirements; limited content availability compared to standard formats; requires compatible hardware throughout the viewing chain.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has developed HDR10+ as its answer to Dolby Vision, building upon the HDR10 standard. HDR10+ incorporates dynamic metadata similar to Dolby Vision but maintains the 10-bit color depth of HDR10. The technical implementation allows for brightness adjustments up to 4,000 nits and uses scene-by-scene or shot-by-shot dynamic metadata to optimize picture quality. Samsung's approach focuses on an open, royalty-free standard that maintains compatibility with existing HDR10 infrastructure while adding dynamic tone mapping. Their technology includes an adaptive mapping algorithm that optimizes content based on the specific display capabilities of Samsung devices, particularly their QLED TV lineup. The metadata structure in HDR10+ uses SMPTE ST 2094-40 format for dynamic data transmission, allowing for more precise control over how content is displayed while maintaining broader industry compatibility.
Strengths: Royalty-free standard encouraging wider adoption; backward compatibility with HDR10 content; dynamic metadata improves picture quality over standard HDR10; strong ecosystem support from Samsung's display technologies. Weaknesses: Less color depth than Dolby Vision (10-bit vs 12-bit); more limited peak brightness capabilities; less consistent cross-device performance without strict certification; smaller content library compared to Dolby Vision.
Core Patents and Innovations in HDR Technology
Colour conversion within a hierarchical coding scheme
PatentActiveUS12120305B2
Innovation
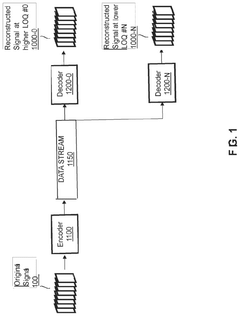
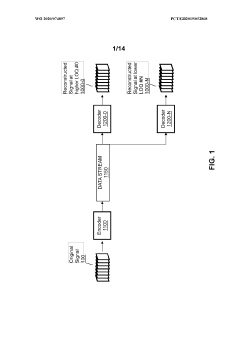
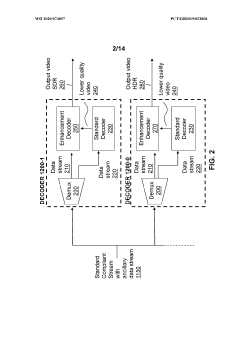
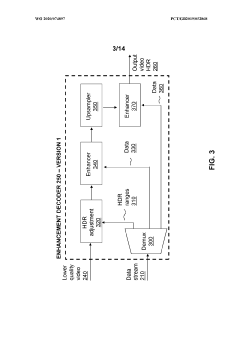
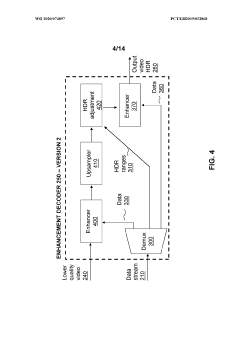
- A hierarchical coding scheme that allows for the encoding and decoding of HDR-type signals in a way that enables compatibility with both HDR and SDR displays, using a method that involves converting input signals between color spaces, down-sampling, and adding ancillary data for reconstruction, thereby providing backwards compatibility and reduced bandwidth requirements.
Dynamic range support within a multi-layer hierarchical coding scheme
PatentWO2020074897A1
Innovation
- A method for encoding and decoding that converts HDR signals to Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) and back, allowing for flexible streaming of HDR information and mitigating codec inaccuracies and artefacts, while ensuring backwards compatibility and reducing bandwidth requirements through hierarchical coding schemes.
Content Creation Pipeline for HDR Formats
The HDR content creation pipeline represents a complex workflow that differs significantly between HDR10 and Dolby Vision formats. Content creators begin with high-quality source material, typically captured on cameras capable of wide dynamic range and color gamut. For HDR10 production, creators work with a relatively straightforward pipeline where content is mastered to a peak brightness of 1000 nits and uses static metadata that remains constant throughout the content.
In contrast, Dolby Vision requires a more sophisticated approach, utilizing a dual-layer encoding system. Content creators must generate both a base HDR10 layer and an enhancement layer containing dynamic metadata and additional color information. This process typically involves specialized color grading tools like Dolby Vision Content Creation Tools that allow frame-by-frame optimization of brightness, contrast, and color.
The color grading process represents a critical divergence point between formats. HDR10 content is graded once for optimal viewing on reference monitors, with colorists making static decisions that must work across the entire content. Dolby Vision enables a more nuanced approach where colorists can create dynamic "trim passes" that adjust parameters throughout the content, optimizing for dramatic shifts in brightness or color requirements between scenes.
Metadata generation also differs substantially between formats. HDR10 employs simple static metadata including MaxCLL (Maximum Content Light Level) and MaxFALL (Maximum Frame Average Light Level) values that describe the overall content characteristics. Dolby Vision generates comprehensive dynamic metadata containing scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame instructions for display optimization, including precise mapping information for different display capabilities.
Quality control procedures vary as well, with Dolby Vision requiring certification of the entire production chain. Content must be verified on Dolby-certified monitors, and the final deliverables undergo validation through Dolby's quality control tools. HDR10 quality control is less standardized, though still requires verification on reference HDR displays to ensure proper implementation of the format specifications.
Distribution preparation represents the final stage, where HDR10 content is packaged with its static metadata in formats compatible with standard delivery channels. Dolby Vision content requires additional processing to ensure the enhancement layer and base layer are properly synchronized and packaged according to Dolby specifications, often resulting in slightly larger file sizes but with the benefit of greater display adaptability.
In contrast, Dolby Vision requires a more sophisticated approach, utilizing a dual-layer encoding system. Content creators must generate both a base HDR10 layer and an enhancement layer containing dynamic metadata and additional color information. This process typically involves specialized color grading tools like Dolby Vision Content Creation Tools that allow frame-by-frame optimization of brightness, contrast, and color.
The color grading process represents a critical divergence point between formats. HDR10 content is graded once for optimal viewing on reference monitors, with colorists making static decisions that must work across the entire content. Dolby Vision enables a more nuanced approach where colorists can create dynamic "trim passes" that adjust parameters throughout the content, optimizing for dramatic shifts in brightness or color requirements between scenes.
Metadata generation also differs substantially between formats. HDR10 employs simple static metadata including MaxCLL (Maximum Content Light Level) and MaxFALL (Maximum Frame Average Light Level) values that describe the overall content characteristics. Dolby Vision generates comprehensive dynamic metadata containing scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame instructions for display optimization, including precise mapping information for different display capabilities.
Quality control procedures vary as well, with Dolby Vision requiring certification of the entire production chain. Content must be verified on Dolby-certified monitors, and the final deliverables undergo validation through Dolby's quality control tools. HDR10 quality control is less standardized, though still requires verification on reference HDR displays to ensure proper implementation of the format specifications.
Distribution preparation represents the final stage, where HDR10 content is packaged with its static metadata in formats compatible with standard delivery channels. Dolby Vision content requires additional processing to ensure the enhancement layer and base layer are properly synchronized and packaged according to Dolby specifications, often resulting in slightly larger file sizes but with the benefit of greater display adaptability.
Display Hardware Requirements and Compatibility
The implementation of HDR technologies requires specific hardware capabilities that vary between HDR10 and Dolby Vision standards. For HDR10 compatibility, displays must support a minimum of 10-bit color depth, enabling the representation of over 1 billion colors compared to the 16.7 million colors in standard 8-bit displays. Additionally, HDR10 displays need to achieve a peak brightness of at least 1,000 nits, though many consumer-grade displays typically operate between 400-600 nits.
In contrast, Dolby Vision imposes more stringent hardware requirements. While also demanding 10-bit color depth as a baseline, Dolby Vision's technical specifications recommend 12-bit color processing capability, potentially representing up to 68.7 billion colors. Furthermore, Dolby Vision-certified displays must support peak brightness levels of up to 4,000 nits, though current consumer displays rarely exceed 2,000 nits.
Both technologies necessitate wide color gamut support, with HDR10 requiring at least 90% coverage of the DCI-P3 color space, while Dolby Vision aims for complete BT.2020 color space coverage. This requirement translates to specialized panel technologies, with OLED, quantum dot-enhanced LCD (QLED), and mini-LED displays being the most common implementations capable of meeting these specifications.
The hardware distinction extends to processing capabilities as well. Dolby Vision requires more sophisticated image processing hardware to handle its dynamic metadata, necessitating dedicated chips or enhanced processing units. This requirement often increases manufacturing costs and energy consumption compared to HDR10-only displays.
Backward compatibility presents another hardware consideration. Most Dolby Vision-capable displays can automatically process HDR10 content, but the reverse is not true. HDR10 displays cannot interpret Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata, resulting in either fallback to HDR10 mode or inability to display the content properly.
For content creators and professional environments, additional hardware requirements emerge. Reference monitors for Dolby Vision mastering must meet stricter calibration standards and typically cost significantly more than HDR10-capable professional displays. This cost differential extends throughout the production chain, affecting cameras, processing equipment, and storage systems.
The refresh cycle of display technology also impacts compatibility. With HDR standards evolving rapidly, hardware obsolescence becomes a concern, particularly for Dolby Vision implementations that may require firmware updates to support new profile versions or enhanced features.
In contrast, Dolby Vision imposes more stringent hardware requirements. While also demanding 10-bit color depth as a baseline, Dolby Vision's technical specifications recommend 12-bit color processing capability, potentially representing up to 68.7 billion colors. Furthermore, Dolby Vision-certified displays must support peak brightness levels of up to 4,000 nits, though current consumer displays rarely exceed 2,000 nits.
Both technologies necessitate wide color gamut support, with HDR10 requiring at least 90% coverage of the DCI-P3 color space, while Dolby Vision aims for complete BT.2020 color space coverage. This requirement translates to specialized panel technologies, with OLED, quantum dot-enhanced LCD (QLED), and mini-LED displays being the most common implementations capable of meeting these specifications.
The hardware distinction extends to processing capabilities as well. Dolby Vision requires more sophisticated image processing hardware to handle its dynamic metadata, necessitating dedicated chips or enhanced processing units. This requirement often increases manufacturing costs and energy consumption compared to HDR10-only displays.
Backward compatibility presents another hardware consideration. Most Dolby Vision-capable displays can automatically process HDR10 content, but the reverse is not true. HDR10 displays cannot interpret Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata, resulting in either fallback to HDR10 mode or inability to display the content properly.
For content creators and professional environments, additional hardware requirements emerge. Reference monitors for Dolby Vision mastering must meet stricter calibration standards and typically cost significantly more than HDR10-capable professional displays. This cost differential extends throughout the production chain, affecting cameras, processing equipment, and storage systems.
The refresh cycle of display technology also impacts compatibility. With HDR standards evolving rapidly, hardware obsolescence becomes a concern, particularly for Dolby Vision implementations that may require firmware updates to support new profile versions or enhanced features.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!