HDR10 vs Dolby Vision: Market Viability and Consumer Acceptance
OCT 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HDR Technology Evolution and Objectives
High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology represents a significant advancement in visual display capabilities, evolving from the limitations of Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) to deliver enhanced contrast, brightness, and color accuracy. The journey began in the early 2000s with research into expanded luminance ranges, but commercial implementation only gained momentum around 2014 when the first HDR-capable displays entered the market.
HDR technology aims to replicate the human visual experience more faithfully by expanding the range of luminance and color that can be displayed, creating more realistic and immersive viewing experiences. The primary objective is to bridge the gap between what the human eye can perceive in the natural world and what display technology can reproduce.
The evolution of HDR has been marked by several key technological milestones. Initially, displays were limited to 8-bit color depth, restricting the range of colors and brightness levels. The transition to 10-bit and eventually 12-bit color depth has been crucial in enabling the wider color gamuts and increased luminance ranges that define modern HDR implementations.
In the competitive landscape between HDR10 and Dolby Vision, distinct technological objectives have emerged. HDR10, as an open standard, focuses on providing a cost-effective, widely compatible HDR solution with static metadata. Its objective is mass market adoption through accessibility and compatibility with existing production workflows.
Dolby Vision, conversely, pursues technical excellence through dynamic metadata, 12-bit color depth, and scene-by-scene optimization. Its objective is to deliver the ultimate viewing experience, positioning itself as the premium HDR solution for discerning consumers and content creators.
The technical evolution continues with HDR10+ emerging as a response to Dolby Vision, incorporating dynamic metadata while maintaining the open standard approach of HDR10. This represents the ongoing refinement of HDR technology to balance quality with practical implementation considerations.
Looking forward, the technological objectives for HDR include increasing peak brightness capabilities, expanding color volume coverage, improving tone mapping algorithms, and enhancing metadata precision. Additionally, there is a push toward standardization to reduce market fragmentation and improve cross-platform compatibility, ensuring consumers can access HDR content regardless of their display technology.
The ultimate goal remains consistent: to deliver increasingly realistic visual experiences that more closely match human visual perception, while making this technology accessible across various price points and device categories.
HDR technology aims to replicate the human visual experience more faithfully by expanding the range of luminance and color that can be displayed, creating more realistic and immersive viewing experiences. The primary objective is to bridge the gap between what the human eye can perceive in the natural world and what display technology can reproduce.
The evolution of HDR has been marked by several key technological milestones. Initially, displays were limited to 8-bit color depth, restricting the range of colors and brightness levels. The transition to 10-bit and eventually 12-bit color depth has been crucial in enabling the wider color gamuts and increased luminance ranges that define modern HDR implementations.
In the competitive landscape between HDR10 and Dolby Vision, distinct technological objectives have emerged. HDR10, as an open standard, focuses on providing a cost-effective, widely compatible HDR solution with static metadata. Its objective is mass market adoption through accessibility and compatibility with existing production workflows.
Dolby Vision, conversely, pursues technical excellence through dynamic metadata, 12-bit color depth, and scene-by-scene optimization. Its objective is to deliver the ultimate viewing experience, positioning itself as the premium HDR solution for discerning consumers and content creators.
The technical evolution continues with HDR10+ emerging as a response to Dolby Vision, incorporating dynamic metadata while maintaining the open standard approach of HDR10. This represents the ongoing refinement of HDR technology to balance quality with practical implementation considerations.
Looking forward, the technological objectives for HDR include increasing peak brightness capabilities, expanding color volume coverage, improving tone mapping algorithms, and enhancing metadata precision. Additionally, there is a push toward standardization to reduce market fragmentation and improve cross-platform compatibility, ensuring consumers can access HDR content regardless of their display technology.
The ultimate goal remains consistent: to deliver increasingly realistic visual experiences that more closely match human visual perception, while making this technology accessible across various price points and device categories.
Consumer Demand Analysis for Premium Video Formats
The premium video format market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by consumer demand for enhanced viewing experiences. Market research indicates that global HDR TV shipments reached 177 million units in 2021, representing over 78% of total TV shipments. This rapid adoption demonstrates consumers' increasing preference for higher quality visual experiences, with HDR technology becoming a standard feature rather than a premium option in new television purchases.
Consumer awareness of premium video formats shows interesting patterns across different demographics. Surveys reveal that approximately 67% of consumers under 35 years old recognize HDR as a desirable feature when purchasing new displays, while awareness drops to 42% among consumers over 55. Dolby Vision awareness lags behind HDR10, with recognition rates of 38% and 59% respectively across all age groups, indicating a significant knowledge gap despite Dolby's strong brand presence in audio technologies.
Purchase intention data reveals that while consumers express interest in premium video formats, this doesn't always translate to purchasing decisions. When presented with price premiums for Dolby Vision-capable devices (typically 15-25% higher than HDR10-only devices), only 31% of consumers maintained their preference for the more expensive option. This price sensitivity is particularly pronounced in mid-range product segments.
Content availability significantly influences format adoption. Streaming platforms report that viewers with HDR-capable devices spend 27% more time watching HDR content when available, suggesting strong engagement once consumers experience the technology. Netflix and Amazon Prime Video have expanded their HDR libraries by over 200% in the past two years, with both platforms supporting both formats but showing a slight preference for HDR10+ and Dolby Vision for their original productions.
Regional variations in premium format adoption are substantial. North American and Western European markets show higher willingness to pay for premium formats (44% and 39% respectively), while emerging markets in Asia-Pacific demonstrate faster growth rates but lower absolute adoption. China represents a unique case with strong domestic manufacturer support for HDR10+ creating different market dynamics compared to Dolby Vision's stronger position in Western markets.
Consumer satisfaction metrics reveal that once experienced, both formats generate positive responses, with Dolby Vision scoring marginally higher in blind tests (8.4/10 versus 7.9/10 for HDR10). However, when brand information is revealed, Dolby Vision's perceived quality advantage increases significantly, demonstrating the power of Dolby's brand equity in influencing consumer perception of visual quality.
Consumer awareness of premium video formats shows interesting patterns across different demographics. Surveys reveal that approximately 67% of consumers under 35 years old recognize HDR as a desirable feature when purchasing new displays, while awareness drops to 42% among consumers over 55. Dolby Vision awareness lags behind HDR10, with recognition rates of 38% and 59% respectively across all age groups, indicating a significant knowledge gap despite Dolby's strong brand presence in audio technologies.
Purchase intention data reveals that while consumers express interest in premium video formats, this doesn't always translate to purchasing decisions. When presented with price premiums for Dolby Vision-capable devices (typically 15-25% higher than HDR10-only devices), only 31% of consumers maintained their preference for the more expensive option. This price sensitivity is particularly pronounced in mid-range product segments.
Content availability significantly influences format adoption. Streaming platforms report that viewers with HDR-capable devices spend 27% more time watching HDR content when available, suggesting strong engagement once consumers experience the technology. Netflix and Amazon Prime Video have expanded their HDR libraries by over 200% in the past two years, with both platforms supporting both formats but showing a slight preference for HDR10+ and Dolby Vision for their original productions.
Regional variations in premium format adoption are substantial. North American and Western European markets show higher willingness to pay for premium formats (44% and 39% respectively), while emerging markets in Asia-Pacific demonstrate faster growth rates but lower absolute adoption. China represents a unique case with strong domestic manufacturer support for HDR10+ creating different market dynamics compared to Dolby Vision's stronger position in Western markets.
Consumer satisfaction metrics reveal that once experienced, both formats generate positive responses, with Dolby Vision scoring marginally higher in blind tests (8.4/10 versus 7.9/10 for HDR10). However, when brand information is revealed, Dolby Vision's perceived quality advantage increases significantly, demonstrating the power of Dolby's brand equity in influencing consumer perception of visual quality.
HDR Standards Landscape and Technical Barriers
The High Dynamic Range (HDR) video technology landscape is currently dominated by several competing standards, with HDR10 and Dolby Vision emerging as the primary contenders. HDR10, as an open standard, has gained widespread adoption across the industry due to its royalty-free nature and relatively straightforward implementation requirements. Meanwhile, Dolby Vision offers superior technical capabilities with dynamic metadata that allows frame-by-frame optimization, albeit at higher licensing costs and more complex implementation requirements.
The technical barriers between these standards create significant challenges for content creators, device manufacturers, and consumers alike. Content producers must decide which format(s) to master in, often resulting in multiple workflows that increase production costs and complexity. For device manufacturers, supporting multiple HDR formats requires additional hardware capabilities, software development, and licensing negotiations, which can impact product pricing and market positioning.
A critical technical barrier lies in the backward compatibility domain. While Dolby Vision content can include a base layer compatible with HDR10 displays, the reverse is not possible. This asymmetry creates market fragmentation and potential consumer confusion. Additionally, the implementation of dynamic metadata in Dolby Vision requires more sophisticated processing capabilities in both content creation tools and playback devices.
Bandwidth and storage requirements present another significant challenge. HDR content generally demands higher bitrates than standard dynamic range (SDR) content, with Dolby Vision typically requiring approximately 10-15% more bandwidth than HDR10 due to its additional metadata layer. This has implications for streaming services, broadcast infrastructure, and physical media capacity.
The certification process also creates barriers to market entry. Dolby Vision implementation requires rigorous certification from Dolby Laboratories, while HDR10 has less stringent requirements. This disparity affects time-to-market considerations and development cycles for new products and services.
Technical limitations in display technology further complicate the landscape. Many consumer displays cannot fully realize the theoretical capabilities of either HDR10 or Dolby Vision, with limitations in peak brightness, contrast ratios, and color gamut coverage. The varying capabilities across different price points create inconsistent viewing experiences that undermine consumer confidence in HDR technology as a whole.
Standardization efforts continue to evolve, with HDR10+ emerging as an enhanced open standard that incorporates dynamic metadata similar to Dolby Vision. However, this further fragments the market and creates additional compatibility challenges for the ecosystem. The lack of a unified industry approach to HDR implementation remains one of the most significant barriers to widespread consumer adoption and market growth.
The technical barriers between these standards create significant challenges for content creators, device manufacturers, and consumers alike. Content producers must decide which format(s) to master in, often resulting in multiple workflows that increase production costs and complexity. For device manufacturers, supporting multiple HDR formats requires additional hardware capabilities, software development, and licensing negotiations, which can impact product pricing and market positioning.
A critical technical barrier lies in the backward compatibility domain. While Dolby Vision content can include a base layer compatible with HDR10 displays, the reverse is not possible. This asymmetry creates market fragmentation and potential consumer confusion. Additionally, the implementation of dynamic metadata in Dolby Vision requires more sophisticated processing capabilities in both content creation tools and playback devices.
Bandwidth and storage requirements present another significant challenge. HDR content generally demands higher bitrates than standard dynamic range (SDR) content, with Dolby Vision typically requiring approximately 10-15% more bandwidth than HDR10 due to its additional metadata layer. This has implications for streaming services, broadcast infrastructure, and physical media capacity.
The certification process also creates barriers to market entry. Dolby Vision implementation requires rigorous certification from Dolby Laboratories, while HDR10 has less stringent requirements. This disparity affects time-to-market considerations and development cycles for new products and services.
Technical limitations in display technology further complicate the landscape. Many consumer displays cannot fully realize the theoretical capabilities of either HDR10 or Dolby Vision, with limitations in peak brightness, contrast ratios, and color gamut coverage. The varying capabilities across different price points create inconsistent viewing experiences that undermine consumer confidence in HDR technology as a whole.
Standardization efforts continue to evolve, with HDR10+ emerging as an enhanced open standard that incorporates dynamic metadata similar to Dolby Vision. However, this further fragments the market and creates additional compatibility challenges for the ecosystem. The lack of a unified industry approach to HDR implementation remains one of the most significant barriers to widespread consumer adoption and market growth.
Current HDR10 and Dolby Vision Implementation Approaches
01 Market adoption and consumer preferences for HDR technologies
The market adoption of HDR10 and Dolby Vision technologies is influenced by consumer preferences and viewing experiences. Research indicates that consumers are increasingly valuing enhanced visual quality in displays, with HDR technologies offering improved contrast, brightness, and color accuracy. Market studies show varying levels of consumer awareness and willingness to pay premium prices for these advanced display technologies, with adoption rates differing across geographic regions and demographic segments.- Market adoption and consumer preferences for HDR technologies: The adoption of HDR10 and Dolby Vision in the consumer market depends on various factors including consumer preferences, perceived value, and compatibility with existing devices. Market research indicates that consumers are increasingly valuing enhanced visual experiences, with HDR technologies gaining traction in premium content delivery platforms. The acceptance rate varies across different demographic segments, with early adopters and tech-enthusiasts showing higher willingness to invest in HDR-capable devices.
- Technical implementation and compatibility challenges: The implementation of HDR10 and Dolby Vision faces technical challenges related to compatibility with existing display technologies and content delivery systems. These challenges include ensuring backward compatibility with SDR content, managing bandwidth requirements for streaming HDR content, and addressing variations in display capabilities across different devices. Solutions involve adaptive streaming technologies, efficient metadata handling, and scalable encoding methods to ensure optimal viewing experiences across diverse hardware configurations.
- Content ecosystem and distribution strategies: The viability of HDR10 and Dolby Vision depends significantly on the availability of compatible content and effective distribution strategies. Content creators and distributors are developing strategies to leverage these technologies to enhance viewer engagement. This includes partnerships between streaming platforms, content producers, and device manufacturers to create integrated ecosystems that deliver HDR content seamlessly to consumers. The growth of exclusive HDR content is becoming a key differentiator in competitive streaming markets.
- Economic factors and pricing strategies: Economic considerations play a crucial role in the market viability of HDR technologies. Pricing strategies for HDR-capable devices and premium content services influence consumer adoption rates. Manufacturers and content providers are exploring various business models, including tiered pricing for HDR content, bundling strategies with other premium features, and gradual price reduction of HDR-capable displays to increase market penetration. The perceived value-to-cost ratio is a key determinant in consumer purchasing decisions regarding HDR technology.
- Regional market differences and regulatory considerations: The acceptance and implementation of HDR technologies vary significantly across different regions due to varying consumer preferences, economic conditions, and regulatory frameworks. Some regions show faster adoption rates due to higher disposable incomes and greater technological infrastructure. Regulatory considerations, including standards for energy efficiency, content protection, and accessibility requirements, also influence how HDR technologies are implemented and marketed in different regions. Companies are developing region-specific strategies to address these variations.
02 Technical implementation and compatibility challenges
The implementation of HDR10 and Dolby Vision faces technical challenges related to compatibility across different devices and platforms. These challenges include standardization issues, hardware requirements, and software integration complexities. The varying technical specifications between HDR10 (which is an open standard) and Dolby Vision (which is proprietary) create interoperability concerns that affect market adoption and consumer acceptance. Solutions addressing these technical barriers are critical for widespread implementation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Content availability and distribution strategies
The availability of content optimized for HDR10 and Dolby Vision significantly impacts their market viability. Distribution strategies across streaming platforms, physical media, and broadcast channels influence consumer adoption rates. Research shows that consumers are more likely to invest in HDR-capable devices when there is abundant high-quality content available. Content creators and distributors are developing various approaches to leverage these technologies while managing production costs and technical requirements.Expand Specific Solutions04 Economic factors and pricing strategies
Economic considerations play a crucial role in the market viability of HDR10 and Dolby Vision technologies. Pricing strategies for HDR-enabled devices, licensing costs for manufacturers, and consumer willingness to pay premium prices affect adoption rates. Market research indicates price sensitivity varies across consumer segments, with early adopters showing greater willingness to invest in premium HDR experiences. Manufacturers are employing various pricing approaches to balance technology implementation costs with consumer affordability expectations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration with emerging display technologies
The integration of HDR10 and Dolby Vision with other emerging display technologies affects their long-term market viability. These HDR formats are being incorporated into various display technologies including OLED, QLED, and microLED displays. Consumer acceptance is influenced by how these HDR standards enhance overall viewing experiences when combined with other innovations. Research indicates that the synergistic effects of multiple display technologies can drive consumer interest and market growth for premium visual experiences.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in HDR Ecosystem
The HDR10 vs Dolby Vision market landscape is currently in a mature growth phase, with the global HDR content market exceeding $25 billion and growing at 15% annually. While HDR10 enjoys broader adoption due to its open-source nature, Dolby Vision is gaining momentum through premium positioning. Technologically, Dolby Laboratories leads with its proprietary dynamic metadata solution, while Samsung champions the open HDR10+ standard. Other significant players include LG, Sony, and Panasonic offering compatible displays, with content support from major streaming platforms. Technology maturity varies, with Dolby Vision offering superior technical capabilities through dynamic scene-by-scene optimization, though at higher licensing costs compared to the royalty-free HDR10 standard.
Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp.
Technical Solution: Dolby Vision represents Dolby's premium HDR solution that delivers dynamic metadata on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis. This technology enables precise control of brightness, contrast, and color across compatible displays, supporting up to 12-bit color depth (68.7 billion colors) and peak brightness levels of up to 10,000 nits. Dolby Vision's technical approach involves dynamic metadata that allows content creators to specify exactly how each scene should be displayed, preserving creative intent across different display capabilities. The technology includes an advanced color mapping algorithm that optimizes content for each specific display model, ensuring consistent quality across various hardware. Dolby has also developed an end-to-end ecosystem including content creation tools, distribution specifications, and certification programs for consumer electronics manufacturers to ensure seamless implementation across the media delivery chain.
Strengths: Superior technical capabilities with dynamic metadata allowing frame-by-frame optimization; comprehensive ecosystem spanning content creation to display; better preservation of creative intent across different displays. Weaknesses: Higher licensing costs for manufacturers; requires dedicated hardware support; more complex implementation compared to open standards like HDR10.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has been a primary driver behind HDR10 and HDR10+ technologies as alternatives to Dolby Vision. Samsung's approach focuses on HDR10+ which adds dynamic metadata to the static metadata foundation of HDR10, allowing for scene-by-scene brightness adjustments. Their technical implementation utilizes a more open licensing model compared to Dolby Vision, while still delivering enhanced picture quality. Samsung's HDR technology supports 10-bit color depth (over 1 billion colors) and brightness levels up to 4,000 nits. The company has developed specialized quantum dot display technology (QLED) specifically optimized for HDR content reproduction, enhancing color volume and brightness capabilities. Samsung has also created an adaptive tone-mapping algorithm that analyzes content characteristics to optimize HDR presentation based on ambient lighting conditions and display capabilities, improving viewing experiences across various environments.
Strengths: More open ecosystem with lower licensing costs; widespread adoption across multiple manufacturers; strong hardware integration with Samsung's display technologies. Weaknesses: Technical specifications slightly below Dolby Vision (10-bit vs 12-bit color depth); less granular metadata control; consumer awareness of HDR10+ lags behind Dolby Vision branding.
Technical Deep Dive: HDR10 vs Dolby Vision Patents
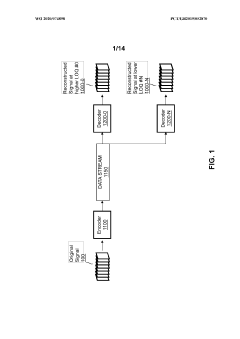
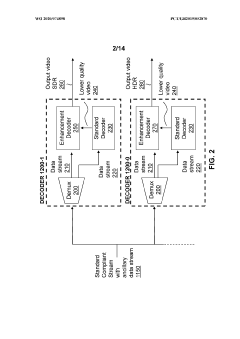
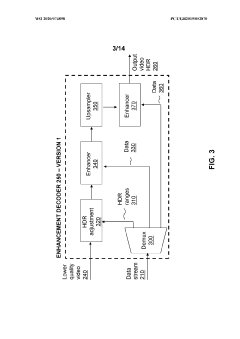
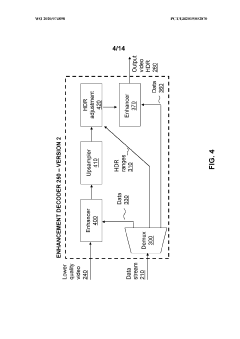
Enhancement decoder for video signals with multi-level enhancement and coding format adjustment
PatentWO2020074898A1
Innovation
- A hierarchical coding scheme that allows for the encoding and decoding of HDR-type signals to be compatible with both HDR and SDR displays, using an enhancement decoder that includes an interface for receiving video streams, de-multiplexing enhancement data, and a coding format adjustment module to convert between different bit lengths and resolutions, ensuring backwards compatibility and flexibility in signal processing.
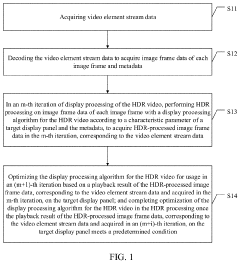
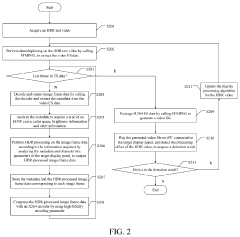
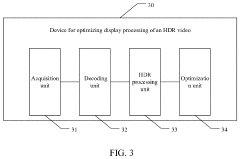
Method and apparatus for optimizing HDR video display processing, and storage medium and terminal
PatentActiveUS20230298305A1
Innovation
- A method that couples decoding and display processing by extracting metadata and image frame data from HDR videos, performing HDR processing on each frame with a display processing algorithm, and optimizing the algorithm based on playback results until predetermined conditions are met, thereby reducing the development cycle and improving efficiency.
Content Creation and Distribution Infrastructure
The content creation and distribution infrastructure for HDR technologies represents a critical component in the market competition between HDR10 and Dolby Vision. Currently, HDR10 benefits from a more accessible production pipeline, requiring less specialized equipment and technical expertise. Content creators can implement HDR10 using standard color grading tools with relatively minimal additional investment, making it an attractive option for studios with budget constraints.
In contrast, Dolby Vision demands a more sophisticated production workflow. It requires specialized monitors, color grading systems, and trained colorists who understand the nuances of dynamic metadata implementation. This higher barrier to entry has limited Dolby Vision content creation primarily to major studios and premium productions, though this landscape is gradually evolving as tools become more accessible.
From a distribution perspective, HDR10 content delivery has been streamlined across multiple platforms. Its static metadata approach requires less bandwidth and processing power, facilitating easier integration with existing broadcast and streaming infrastructures. Most content delivery networks have established protocols for HDR10 distribution, creating a relatively frictionless pipeline from creation to consumer.
Dolby Vision's distribution infrastructure presents more complexity due to its dynamic metadata requirements. Streaming platforms must implement specific encoding and decoding capabilities to properly handle the frame-by-frame metadata. However, major streaming services including Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+ have invested heavily in Dolby Vision infrastructure, recognizing its premium positioning and technical advantages.
The physical media landscape shows similar patterns, with HDR10 being universally supported across all Ultra HD Blu-ray discs, while Dolby Vision appears on select premium titles. This differential availability reinforces Dolby Vision's position as a premium offering rather than a universal standard.
Content availability statistics reveal the infrastructure gap: approximately 80% of HDR content is available in HDR10 format, while only about 30% offers Dolby Vision support. This disparity directly impacts consumer adoption rates and reinforces HDR10's position as the de facto standard despite Dolby Vision's technical superiority.
The infrastructure challenge extends to live broadcast implementations, where HDR10 has made significant inroads for sports and special events, while Dolby Vision live broadcast remains limited to experimental and showcase implementations due to the additional complexity of real-time dynamic metadata processing.
In contrast, Dolby Vision demands a more sophisticated production workflow. It requires specialized monitors, color grading systems, and trained colorists who understand the nuances of dynamic metadata implementation. This higher barrier to entry has limited Dolby Vision content creation primarily to major studios and premium productions, though this landscape is gradually evolving as tools become more accessible.
From a distribution perspective, HDR10 content delivery has been streamlined across multiple platforms. Its static metadata approach requires less bandwidth and processing power, facilitating easier integration with existing broadcast and streaming infrastructures. Most content delivery networks have established protocols for HDR10 distribution, creating a relatively frictionless pipeline from creation to consumer.
Dolby Vision's distribution infrastructure presents more complexity due to its dynamic metadata requirements. Streaming platforms must implement specific encoding and decoding capabilities to properly handle the frame-by-frame metadata. However, major streaming services including Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+ have invested heavily in Dolby Vision infrastructure, recognizing its premium positioning and technical advantages.
The physical media landscape shows similar patterns, with HDR10 being universally supported across all Ultra HD Blu-ray discs, while Dolby Vision appears on select premium titles. This differential availability reinforces Dolby Vision's position as a premium offering rather than a universal standard.
Content availability statistics reveal the infrastructure gap: approximately 80% of HDR content is available in HDR10 format, while only about 30% offers Dolby Vision support. This disparity directly impacts consumer adoption rates and reinforces HDR10's position as the de facto standard despite Dolby Vision's technical superiority.
The infrastructure challenge extends to live broadcast implementations, where HDR10 has made significant inroads for sports and special events, while Dolby Vision live broadcast remains limited to experimental and showcase implementations due to the additional complexity of real-time dynamic metadata processing.
Device Compatibility and Adoption Challenges
The compatibility landscape for HDR10 and Dolby Vision technologies presents significant challenges for market adoption. HDR10, being an open standard, enjoys broader implementation across devices, with support from major manufacturers including Samsung, Sony, LG, and TCL. This widespread compatibility stems from its royalty-free nature, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious manufacturers and consumers alike.
In contrast, Dolby Vision requires specific hardware implementation and licensing fees, creating a more restricted ecosystem. While premium devices from brands like LG, Sony, and Vizio incorporate Dolby Vision, many mid-range and entry-level products exclude this technology due to cost considerations. This bifurcation creates a fragmented market where consumers must carefully verify device compatibility before purchase.
Content delivery platforms face similar adoption challenges. Streaming services must maintain multiple HDR formats to ensure compatibility across the device spectrum. Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ support both formats, but smaller platforms often prioritize HDR10 due to its universal compatibility. This creates inconsistent viewing experiences as consumers move between different services and devices.
The gaming industry presents additional compatibility hurdles. While next-generation consoles like Xbox Series X support both formats, PlayStation 5 only supports HDR10, creating format disparities across gaming platforms. This inconsistency extends to gaming monitors and televisions, where manufacturers must decide which standards to implement based on target demographics and price points.
Legacy device integration represents another significant challenge. Older televisions and media players lack HDR capabilities entirely, creating a substantial installed base that cannot access either format without hardware replacement. Even among HDR-capable devices, firmware update limitations may prevent adoption of newer format refinements, creating technical obsolescence that frustrates consumers.
Mobile device compatibility further complicates the landscape. While premium smartphones increasingly support HDR content, implementation varies significantly across manufacturers and price points. Apple devices support Dolby Vision, while many Android devices prioritize HDR10 or HDR10+, creating platform-specific viewing experiences that fragment the mobile content ecosystem.
These compatibility challenges collectively slow market adoption rates for both technologies, with consumers often confused by technical specifications and uncertain about future-proofing their purchases. The resulting hesitation impacts content creation decisions, as producers must weigh the benefits of enhanced visual quality against the limited reach of more advanced HDR implementations.
In contrast, Dolby Vision requires specific hardware implementation and licensing fees, creating a more restricted ecosystem. While premium devices from brands like LG, Sony, and Vizio incorporate Dolby Vision, many mid-range and entry-level products exclude this technology due to cost considerations. This bifurcation creates a fragmented market where consumers must carefully verify device compatibility before purchase.
Content delivery platforms face similar adoption challenges. Streaming services must maintain multiple HDR formats to ensure compatibility across the device spectrum. Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ support both formats, but smaller platforms often prioritize HDR10 due to its universal compatibility. This creates inconsistent viewing experiences as consumers move between different services and devices.
The gaming industry presents additional compatibility hurdles. While next-generation consoles like Xbox Series X support both formats, PlayStation 5 only supports HDR10, creating format disparities across gaming platforms. This inconsistency extends to gaming monitors and televisions, where manufacturers must decide which standards to implement based on target demographics and price points.
Legacy device integration represents another significant challenge. Older televisions and media players lack HDR capabilities entirely, creating a substantial installed base that cannot access either format without hardware replacement. Even among HDR-capable devices, firmware update limitations may prevent adoption of newer format refinements, creating technical obsolescence that frustrates consumers.
Mobile device compatibility further complicates the landscape. While premium smartphones increasingly support HDR content, implementation varies significantly across manufacturers and price points. Apple devices support Dolby Vision, while many Android devices prioritize HDR10 or HDR10+, creating platform-specific viewing experiences that fragment the mobile content ecosystem.
These compatibility challenges collectively slow market adoption rates for both technologies, with consumers often confused by technical specifications and uncertain about future-proofing their purchases. The resulting hesitation impacts content creation decisions, as producers must weigh the benefits of enhanced visual quality against the limited reach of more advanced HDR implementations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!