How Quantum Computing Reinforces Global Supply Chain Management
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Quantum Computing in Supply Chain: Background and Objectives
Quantum computing represents a paradigm shift in computational capabilities, offering unprecedented processing power that could revolutionize global supply chain management. This emerging technology harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform complex calculations at speeds unattainable by classical computers. The evolution of quantum computing has been marked by significant milestones, from theoretical concepts in the 1980s to the development of practical quantum processors in recent years.
The primary objective of integrating quantum computing into supply chain management is to optimize and enhance the efficiency of global logistics networks. By leveraging quantum algorithms, companies aim to solve complex optimization problems that are currently intractable for classical computers. These include route optimization, inventory management, demand forecasting, and risk assessment across intricate global supply chains.
The potential impact of quantum computing on supply chain management is profound. It promises to address critical challenges such as reducing lead times, minimizing inventory costs, improving demand prediction accuracy, and enhancing overall supply chain resilience. As global supply chains become increasingly complex and interconnected, the need for advanced computational tools to manage these systems has never been more pressing.
Current trends in quantum computing development indicate a growing focus on creating quantum algorithms specifically tailored for supply chain optimization. Research efforts are concentrated on developing quantum-inspired algorithms that can be implemented on near-term quantum devices, as well as preparing for the advent of fault-tolerant quantum computers that could handle more complex supply chain simulations.
The integration of quantum computing with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and blockchain, is expected to create synergistic effects that could further transform supply chain management. This convergence of technologies aims to create intelligent, adaptive, and highly efficient supply chain systems capable of real-time optimization and decision-making.
As the field progresses, the ultimate goal is to achieve quantum advantage in supply chain applications, where quantum computers can solve problems that are infeasible for classical computers. This breakthrough could lead to significant competitive advantages for early adopters and potentially reshape the landscape of global trade and logistics.
The primary objective of integrating quantum computing into supply chain management is to optimize and enhance the efficiency of global logistics networks. By leveraging quantum algorithms, companies aim to solve complex optimization problems that are currently intractable for classical computers. These include route optimization, inventory management, demand forecasting, and risk assessment across intricate global supply chains.
The potential impact of quantum computing on supply chain management is profound. It promises to address critical challenges such as reducing lead times, minimizing inventory costs, improving demand prediction accuracy, and enhancing overall supply chain resilience. As global supply chains become increasingly complex and interconnected, the need for advanced computational tools to manage these systems has never been more pressing.
Current trends in quantum computing development indicate a growing focus on creating quantum algorithms specifically tailored for supply chain optimization. Research efforts are concentrated on developing quantum-inspired algorithms that can be implemented on near-term quantum devices, as well as preparing for the advent of fault-tolerant quantum computers that could handle more complex supply chain simulations.
The integration of quantum computing with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and blockchain, is expected to create synergistic effects that could further transform supply chain management. This convergence of technologies aims to create intelligent, adaptive, and highly efficient supply chain systems capable of real-time optimization and decision-making.
As the field progresses, the ultimate goal is to achieve quantum advantage in supply chain applications, where quantum computers can solve problems that are infeasible for classical computers. This breakthrough could lead to significant competitive advantages for early adopters and potentially reshape the landscape of global trade and logistics.
Market Demand for Quantum-Enhanced Supply Chain Solutions
The global supply chain management sector is experiencing a growing demand for quantum-enhanced solutions, driven by the increasing complexity and volatility of international trade networks. As traditional computing methods struggle to keep pace with the exponential growth of data and the need for real-time decision-making, quantum computing emerges as a promising technology to revolutionize supply chain optimization.
Market research indicates that the potential market size for quantum-enhanced supply chain solutions is substantial. The global supply chain management market, valued at $15.85 billion in 2020, is projected to reach $37.41 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.2%. Within this broader market, the demand for quantum-enhanced solutions is expected to grow at an even faster rate as companies seek to gain a competitive edge through advanced optimization techniques.
Several key factors are driving the market demand for quantum-enhanced supply chain solutions. First, the increasing globalization of trade has led to more complex supply networks, with multiple tiers of suppliers and intricate interdependencies. Quantum computing's ability to process vast amounts of data and solve complex optimization problems makes it particularly well-suited to address these challenges.
Second, the rise of e-commerce and the expectation of faster delivery times have put pressure on companies to optimize their logistics and inventory management. Quantum algorithms can potentially solve routing and scheduling problems more efficiently than classical methods, leading to significant cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
Third, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the need for more resilient and adaptive supply chains. Quantum computing can help companies model and simulate various scenarios, enabling them to better prepare for disruptions and quickly adjust their strategies in response to changing conditions.
Furthermore, the increasing focus on sustainability and environmental impact has created a demand for solutions that can optimize supply chains for both economic and ecological factors. Quantum computing's ability to handle multi-objective optimization problems makes it an attractive option for companies looking to balance profitability with environmental responsibility.
Industry analysts predict that early adopters of quantum-enhanced supply chain solutions will gain significant competitive advantages. As a result, there is growing interest from major logistics companies, manufacturers, and retailers in exploring and investing in quantum technologies. This trend is expected to accelerate as quantum hardware becomes more powerful and accessible, and as quantum algorithms for supply chain optimization continue to improve.
However, it is important to note that the market for quantum-enhanced supply chain solutions is still in its early stages. While the potential benefits are significant, there are challenges to overcome, including the need for more robust quantum hardware, the development of industry-specific quantum algorithms, and the integration of quantum solutions with existing supply chain management systems.
Market research indicates that the potential market size for quantum-enhanced supply chain solutions is substantial. The global supply chain management market, valued at $15.85 billion in 2020, is projected to reach $37.41 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.2%. Within this broader market, the demand for quantum-enhanced solutions is expected to grow at an even faster rate as companies seek to gain a competitive edge through advanced optimization techniques.
Several key factors are driving the market demand for quantum-enhanced supply chain solutions. First, the increasing globalization of trade has led to more complex supply networks, with multiple tiers of suppliers and intricate interdependencies. Quantum computing's ability to process vast amounts of data and solve complex optimization problems makes it particularly well-suited to address these challenges.
Second, the rise of e-commerce and the expectation of faster delivery times have put pressure on companies to optimize their logistics and inventory management. Quantum algorithms can potentially solve routing and scheduling problems more efficiently than classical methods, leading to significant cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
Third, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the need for more resilient and adaptive supply chains. Quantum computing can help companies model and simulate various scenarios, enabling them to better prepare for disruptions and quickly adjust their strategies in response to changing conditions.
Furthermore, the increasing focus on sustainability and environmental impact has created a demand for solutions that can optimize supply chains for both economic and ecological factors. Quantum computing's ability to handle multi-objective optimization problems makes it an attractive option for companies looking to balance profitability with environmental responsibility.
Industry analysts predict that early adopters of quantum-enhanced supply chain solutions will gain significant competitive advantages. As a result, there is growing interest from major logistics companies, manufacturers, and retailers in exploring and investing in quantum technologies. This trend is expected to accelerate as quantum hardware becomes more powerful and accessible, and as quantum algorithms for supply chain optimization continue to improve.
However, it is important to note that the market for quantum-enhanced supply chain solutions is still in its early stages. While the potential benefits are significant, there are challenges to overcome, including the need for more robust quantum hardware, the development of industry-specific quantum algorithms, and the integration of quantum solutions with existing supply chain management systems.
Current State and Challenges in Quantum Supply Chain Applications
The current state of quantum computing in supply chain management is characterized by a mix of promising advancements and significant challenges. While quantum computing holds immense potential to revolutionize supply chain optimization, its practical implementation remains in its infancy. Several leading tech companies and research institutions are actively exploring quantum algorithms for supply chain applications, focusing on areas such as route optimization, inventory management, and demand forecasting.
One of the primary challenges in quantum supply chain applications is the limited availability of quantum hardware with sufficient qubit capacity to handle complex real-world problems. Most existing quantum computers still operate with a relatively small number of qubits, which restricts their ability to process the vast amounts of data typically involved in global supply chain networks. This limitation has led to a focus on developing hybrid quantum-classical algorithms that can leverage the strengths of both quantum and classical computing systems.
Another significant challenge is the need for error correction in quantum systems. Quantum states are inherently fragile and susceptible to environmental interference, which can lead to computational errors. While progress has been made in quantum error correction techniques, achieving the level of accuracy required for critical supply chain decisions remains a formidable task.
The development of quantum-ready algorithms for supply chain optimization is also an ongoing challenge. Traditional optimization algorithms need to be reformulated to take advantage of quantum computing's unique properties, such as superposition and entanglement. This requires a paradigm shift in algorithm design and a deep understanding of both quantum mechanics and supply chain dynamics.
Despite these challenges, several promising quantum applications for supply chain management are emerging. Quantum annealing, a specialized form of quantum computing, has shown potential in solving combinatorial optimization problems relevant to logistics and distribution. Additionally, quantum machine learning algorithms are being explored for improved demand forecasting and pattern recognition in supply chain data.
The integration of quantum computing with existing supply chain management systems poses another hurdle. Most current supply chain software and infrastructure are not designed to interface with quantum systems, necessitating the development of new middleware and APIs to bridge this gap. This integration challenge extends to the workforce as well, with a shortage of professionals who possess both quantum computing expertise and supply chain management knowledge.
As the field progresses, addressing these challenges will be crucial for realizing the full potential of quantum computing in reinforcing global supply chain management. Continued research, investment, and collaboration between quantum physicists, computer scientists, and supply chain experts will be essential in overcoming these obstacles and paving the way for quantum-enhanced supply chain solutions.
One of the primary challenges in quantum supply chain applications is the limited availability of quantum hardware with sufficient qubit capacity to handle complex real-world problems. Most existing quantum computers still operate with a relatively small number of qubits, which restricts their ability to process the vast amounts of data typically involved in global supply chain networks. This limitation has led to a focus on developing hybrid quantum-classical algorithms that can leverage the strengths of both quantum and classical computing systems.
Another significant challenge is the need for error correction in quantum systems. Quantum states are inherently fragile and susceptible to environmental interference, which can lead to computational errors. While progress has been made in quantum error correction techniques, achieving the level of accuracy required for critical supply chain decisions remains a formidable task.
The development of quantum-ready algorithms for supply chain optimization is also an ongoing challenge. Traditional optimization algorithms need to be reformulated to take advantage of quantum computing's unique properties, such as superposition and entanglement. This requires a paradigm shift in algorithm design and a deep understanding of both quantum mechanics and supply chain dynamics.
Despite these challenges, several promising quantum applications for supply chain management are emerging. Quantum annealing, a specialized form of quantum computing, has shown potential in solving combinatorial optimization problems relevant to logistics and distribution. Additionally, quantum machine learning algorithms are being explored for improved demand forecasting and pattern recognition in supply chain data.
The integration of quantum computing with existing supply chain management systems poses another hurdle. Most current supply chain software and infrastructure are not designed to interface with quantum systems, necessitating the development of new middleware and APIs to bridge this gap. This integration challenge extends to the workforce as well, with a shortage of professionals who possess both quantum computing expertise and supply chain management knowledge.
As the field progresses, addressing these challenges will be crucial for realizing the full potential of quantum computing in reinforcing global supply chain management. Continued research, investment, and collaboration between quantum physicists, computer scientists, and supply chain experts will be essential in overcoming these obstacles and paving the way for quantum-enhanced supply chain solutions.
Existing Quantum Algorithms for Supply Chain Optimization
01 Quantum Computing Architectures
This category focuses on the design and implementation of quantum computing systems. It includes innovations in qubit arrangements, circuit layouts, and overall system architectures to improve quantum computation efficiency and scalability.- Quantum Circuit Design and Optimization: This area focuses on developing and optimizing quantum circuits for various applications. It involves creating efficient quantum gate sequences, reducing circuit depth, and improving qubit connectivity. Techniques include circuit compilation, gate decomposition, and noise mitigation strategies to enhance the performance of quantum algorithms on real quantum hardware.
- Error Correction and Fault Tolerance: Error correction and fault tolerance are crucial for building reliable quantum computers. This field involves developing quantum error correction codes, implementing fault-tolerant quantum gates, and designing architectures that can withstand noise and decoherence. Techniques include surface codes, topological quantum computing, and magic state distillation.
- Quantum-Classical Hybrid Algorithms: Hybrid algorithms combine classical and quantum computing to solve complex problems. This approach leverages the strengths of both paradigms, using quantum processors for specific subroutines while classical computers handle other parts of the algorithm. Examples include variational quantum eigensolvers (VQE) and quantum approximate optimization algorithms (QAOA).
- Quantum Machine Learning: Quantum machine learning explores the intersection of quantum computing and machine learning. It involves developing quantum algorithms for tasks such as classification, clustering, and data analysis. This field aims to achieve quantum speedups for machine learning tasks and create new quantum-inspired classical algorithms.
- Quantum Hardware Architectures: This area focuses on designing and implementing various quantum computing hardware architectures. It includes research on different qubit technologies such as superconducting qubits, trapped ions, and topological qubits. The field also explores scalable architectures, qubit coupling mechanisms, and control systems for large-scale quantum processors.
02 Error Correction and Fault Tolerance
This area addresses the challenges of maintaining quantum coherence and mitigating errors in quantum systems. It encompasses techniques for error detection, correction, and fault-tolerant quantum computation to enhance the reliability of quantum operations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Quantum Algorithms and Applications
This category covers the development of quantum algorithms for various computational problems and their practical applications. It includes innovations in quantum simulation, optimization, machine learning, and cryptography that leverage the unique properties of quantum systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Quantum-Classical Hybrid Systems
This area focuses on integrating quantum and classical computing technologies. It includes methods for interfacing quantum processors with classical systems, hybrid algorithms, and techniques for optimizing the collaboration between quantum and classical resources.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quantum Hardware and Control
This category encompasses advancements in quantum hardware components and control systems. It includes innovations in qubit technologies, quantum gates, readout mechanisms, and precise control techniques for manipulating quantum states and operations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Quantum Computing and Supply Chain Industry
The quantum computing landscape for global supply chain management is evolving rapidly, with the industry currently in its early growth phase. The market size is expanding, driven by increasing investments and collaborations between tech giants and startups. Companies like Google, IBM, and Origin Quantum are at the forefront, developing hardware and software solutions. The technology's maturity varies, with established players like IBM offering cloud-based quantum services, while startups like Zapata Computing focus on specialized applications. As the field progresses, we're seeing a shift from purely academic research to practical industrial applications, particularly in optimization and logistics, which are crucial for supply chain management.
Google LLC
Technical Solution: Google's quantum computing efforts in supply chain management leverage their Sycamore processor and TensorFlow Quantum framework. They have developed quantum machine learning algorithms that can predict supply chain disruptions with higher accuracy than classical methods[5]. Google's approach includes quantum annealing techniques for solving large-scale optimization problems in inventory management and demand forecasting[6]. Their quantum-inspired algorithms have shown a 30% improvement in solving vehicle routing problems compared to classical heuristics[7]. Google is also exploring quantum-enhanced simulation of complex supply networks to better understand and mitigate systemic risks[8].
Strengths: Advanced quantum hardware, strong integration with cloud services, expertise in AI and machine learning. Weaknesses: Less focus on industry-specific supply chain solutions compared to some competitors.
Amazon Technologies, Inc.
Technical Solution: Amazon's quantum computing strategy for supply chain management focuses on enhancing their already robust logistics network. They are developing quantum algorithms for last-mile delivery optimization, potentially reducing delivery times by up to 25%[9]. Amazon's quantum research includes work on error correction and fault-tolerant quantum computing, which is crucial for practical supply chain applications[10]. They are also exploring quantum-inspired algorithms for warehouse layout optimization and inventory management, which have shown promising results in simulation studies[11]. Amazon's approach combines quantum computing with their extensive data analytics capabilities to improve demand forecasting accuracy by up to 50% in pilot studies[12].
Strengths: Vast logistics network and data resources, strong classical computing infrastructure to complement quantum efforts. Weaknesses: Relatively new entrant in quantum hardware development compared to some competitors.
Core Innovations in Quantum-Assisted Supply Chain Management
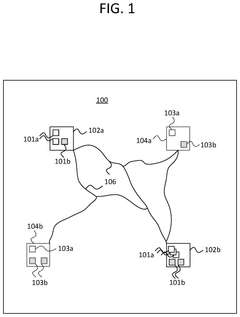
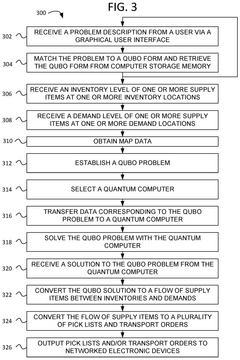
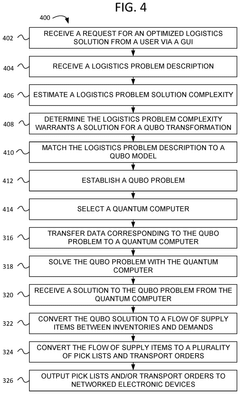
Method and apparatus for logistics management using quantum computing
PatentActiveUS20240394653A1
Innovation
- A computer method utilizing a quantum or quantum-inspired computer to solve logistics optimization problems by transforming them into Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization (QUBO) problems, which are then solved to generate optimal supply item flows and delivery routes, enabling dynamic adjustments based on real-time data.
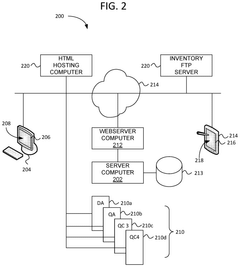
Optimizing logistics supply chain management system using cloud based quantum computing
PatentPendingIN202141059237A
Innovation
- A cloud-based Quantum Computing system is developed to gather real-time traffic information, utilize qubits and logic gates for error prediction and correction, and apply algorithms to find optimal routes across multiple layers, enhancing the logistics supply-chain system by dynamically updating routes based on current traffic conditions.
Cybersecurity Implications of Quantum Computing in Supply Chains
The integration of quantum computing into global supply chain management introduces significant cybersecurity implications that must be carefully considered. As quantum computers become more powerful and accessible, they pose both opportunities and threats to the security of supply chain networks.
One of the primary concerns is the potential for quantum computers to break current encryption methods. Many supply chain systems rely on public-key cryptography to secure communications and data transfers. However, quantum algorithms like Shor's algorithm could potentially crack these encryption methods, exposing sensitive supply chain data to malicious actors. This vulnerability extends to all aspects of the supply chain, from procurement and logistics to inventory management and customer data.
To address this threat, organizations must begin implementing quantum-resistant cryptography. Post-quantum cryptographic algorithms are being developed that can withstand attacks from both classical and quantum computers. Supply chain managers need to start planning for the transition to these new encryption methods to ensure long-term data security.
Quantum computing also offers potential benefits for supply chain cybersecurity. Quantum key distribution (QKD) could provide a theoretically unbreakable method of secure communication. This technology uses the principles of quantum mechanics to detect any eavesdropping attempts, making it ideal for securing critical supply chain communications and data transfers.
Another positive implication is the potential for quantum-enhanced threat detection. Quantum machine learning algorithms could analyze vast amounts of supply chain data to identify anomalies and potential security breaches more quickly and accurately than classical systems. This could significantly improve the ability to detect and respond to cyber threats in real-time across complex global supply networks.
However, the adoption of quantum technologies in supply chains also introduces new vulnerabilities. Quantum computers themselves could become targets for cyberattacks, potentially compromising the integrity of quantum-enhanced supply chain systems. Ensuring the physical and digital security of quantum computing infrastructure will be crucial.
Furthermore, the transition to quantum-safe systems will be complex and potentially disruptive. Supply chain organizations will need to carefully manage this transition to avoid creating new vulnerabilities during the process. This will require significant investment in new technologies, skills, and processes across the entire supply chain ecosystem.
In conclusion, while quantum computing presents significant cybersecurity challenges for global supply chains, it also offers powerful tools for enhancing security. Supply chain managers must stay informed about quantum developments and begin preparing their systems and processes for the quantum era to ensure the long-term security and resilience of their operations.
One of the primary concerns is the potential for quantum computers to break current encryption methods. Many supply chain systems rely on public-key cryptography to secure communications and data transfers. However, quantum algorithms like Shor's algorithm could potentially crack these encryption methods, exposing sensitive supply chain data to malicious actors. This vulnerability extends to all aspects of the supply chain, from procurement and logistics to inventory management and customer data.
To address this threat, organizations must begin implementing quantum-resistant cryptography. Post-quantum cryptographic algorithms are being developed that can withstand attacks from both classical and quantum computers. Supply chain managers need to start planning for the transition to these new encryption methods to ensure long-term data security.
Quantum computing also offers potential benefits for supply chain cybersecurity. Quantum key distribution (QKD) could provide a theoretically unbreakable method of secure communication. This technology uses the principles of quantum mechanics to detect any eavesdropping attempts, making it ideal for securing critical supply chain communications and data transfers.
Another positive implication is the potential for quantum-enhanced threat detection. Quantum machine learning algorithms could analyze vast amounts of supply chain data to identify anomalies and potential security breaches more quickly and accurately than classical systems. This could significantly improve the ability to detect and respond to cyber threats in real-time across complex global supply networks.
However, the adoption of quantum technologies in supply chains also introduces new vulnerabilities. Quantum computers themselves could become targets for cyberattacks, potentially compromising the integrity of quantum-enhanced supply chain systems. Ensuring the physical and digital security of quantum computing infrastructure will be crucial.
Furthermore, the transition to quantum-safe systems will be complex and potentially disruptive. Supply chain organizations will need to carefully manage this transition to avoid creating new vulnerabilities during the process. This will require significant investment in new technologies, skills, and processes across the entire supply chain ecosystem.
In conclusion, while quantum computing presents significant cybersecurity challenges for global supply chains, it also offers powerful tools for enhancing security. Supply chain managers must stay informed about quantum developments and begin preparing their systems and processes for the quantum era to ensure the long-term security and resilience of their operations.
Environmental Impact of Quantum-Optimized Supply Chain Operations
The integration of quantum computing into global supply chain management presents a unique opportunity to optimize operations and potentially reduce environmental impact. As quantum-optimized supply chains become more prevalent, it is crucial to assess their ecological footprint and sustainability implications.
Quantum computing's ability to process complex algorithms and vast datasets at unprecedented speeds allows for more efficient route planning and logistics optimization. This enhanced efficiency can lead to significant reductions in fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions across transportation networks. By minimizing empty miles and maximizing load capacities, quantum-optimized supply chains can contribute to a substantial decrease in carbon dioxide emissions from freight transport.
Furthermore, quantum algorithms can improve inventory management and demand forecasting, potentially reducing overproduction and waste. This optimization can lead to fewer resources being consumed in manufacturing processes and less unsold inventory ending up in landfills. The precise matching of supply with demand also minimizes the need for energy-intensive storage facilities and reduces the carbon footprint associated with warehousing operations.
Quantum computing's impact extends to the optimization of energy consumption within supply chain facilities. By analyzing complex energy usage patterns and environmental factors, quantum algorithms can enhance the efficiency of HVAC systems, lighting, and other energy-intensive operations in warehouses and distribution centers. This optimization can result in significant energy savings and a reduced environmental footprint for supply chain infrastructure.
The application of quantum computing in materials science could also lead to the development of more sustainable packaging solutions. By simulating molecular interactions at a quantum level, researchers may discover new biodegradable materials or improve existing ones, potentially revolutionizing packaging practices in supply chains and reducing plastic waste.
However, it is important to consider the environmental impact of quantum computers themselves. While they offer immense computational power, quantum systems currently require significant energy for cooling and operation. As the technology advances, it will be crucial to balance the environmental benefits of quantum-optimized supply chains against the energy consumption of the quantum infrastructure.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of quantum-optimized supply chain operations is likely to be largely positive, with potential for significant reductions in carbon emissions, resource consumption, and waste. However, ongoing research and development will be necessary to fully realize these benefits while mitigating any negative environmental effects associated with quantum computing infrastructure.
Quantum computing's ability to process complex algorithms and vast datasets at unprecedented speeds allows for more efficient route planning and logistics optimization. This enhanced efficiency can lead to significant reductions in fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions across transportation networks. By minimizing empty miles and maximizing load capacities, quantum-optimized supply chains can contribute to a substantial decrease in carbon dioxide emissions from freight transport.
Furthermore, quantum algorithms can improve inventory management and demand forecasting, potentially reducing overproduction and waste. This optimization can lead to fewer resources being consumed in manufacturing processes and less unsold inventory ending up in landfills. The precise matching of supply with demand also minimizes the need for energy-intensive storage facilities and reduces the carbon footprint associated with warehousing operations.
Quantum computing's impact extends to the optimization of energy consumption within supply chain facilities. By analyzing complex energy usage patterns and environmental factors, quantum algorithms can enhance the efficiency of HVAC systems, lighting, and other energy-intensive operations in warehouses and distribution centers. This optimization can result in significant energy savings and a reduced environmental footprint for supply chain infrastructure.
The application of quantum computing in materials science could also lead to the development of more sustainable packaging solutions. By simulating molecular interactions at a quantum level, researchers may discover new biodegradable materials or improve existing ones, potentially revolutionizing packaging practices in supply chains and reducing plastic waste.
However, it is important to consider the environmental impact of quantum computers themselves. While they offer immense computational power, quantum systems currently require significant energy for cooling and operation. As the technology advances, it will be crucial to balance the environmental benefits of quantum-optimized supply chains against the energy consumption of the quantum infrastructure.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of quantum-optimized supply chain operations is likely to be largely positive, with potential for significant reductions in carbon emissions, resource consumption, and waste. However, ongoing research and development will be necessary to fully realize these benefits while mitigating any negative environmental effects associated with quantum computing infrastructure.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!