Quantum Computing in Enhancing Augmented Reality Experiences
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Quantum AR Evolution
The evolution of quantum computing in augmented reality (AR) represents a significant technological leap, promising to revolutionize the way we interact with digital information overlaid on the physical world. This progression can be traced through several key stages, each marked by groundbreaking advancements and innovative solutions.
In the early stages, quantum computing's potential impact on AR was largely theoretical. Researchers began exploring how quantum algorithms could enhance image processing and object recognition, crucial components of AR systems. This period was characterized by conceptual frameworks and preliminary simulations, laying the groundwork for future practical applications.
As quantum hardware advanced, the field saw the emergence of prototype quantum-enhanced AR systems. These early implementations focused on improving computational efficiency for complex AR tasks, such as real-time environmental mapping and object tracking. While limited in scale, these prototypes demonstrated the tangible benefits of quantum computing in AR, particularly in reducing latency and improving accuracy.
The next phase witnessed the integration of quantum machine learning algorithms into AR platforms. This integration significantly enhanced the ability of AR systems to analyze and interpret visual data in real-time. Quantum-assisted neural networks showed remarkable improvements in pattern recognition and predictive modeling, enabling more sophisticated and context-aware AR experiences.
A pivotal moment in the Quantum AR evolution came with the development of quantum-enhanced rendering techniques. These methods leveraged quantum algorithms to dramatically accelerate the generation of complex 3D graphics and photorealistic scenes. This breakthrough allowed for the creation of more immersive and visually stunning AR environments, pushing the boundaries of what was previously possible with classical computing.
Recent advancements have focused on quantum-enabled spatial computing, where quantum algorithms are used to process and interpret spatial data at unprecedented speeds. This has led to significant improvements in AR's ability to understand and interact with the physical environment, enabling more seamless and natural integration of digital content into the real world.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of Quantum AR points towards fully integrated quantum-classical hybrid systems. These systems aim to combine the strengths of quantum computing with traditional hardware, creating AR experiences that are not only more immersive and interactive but also more energy-efficient and scalable. This evolution is expected to open up new possibilities in fields such as education, healthcare, and industrial design, where complex visualizations and real-time data processing are crucial.
In the early stages, quantum computing's potential impact on AR was largely theoretical. Researchers began exploring how quantum algorithms could enhance image processing and object recognition, crucial components of AR systems. This period was characterized by conceptual frameworks and preliminary simulations, laying the groundwork for future practical applications.
As quantum hardware advanced, the field saw the emergence of prototype quantum-enhanced AR systems. These early implementations focused on improving computational efficiency for complex AR tasks, such as real-time environmental mapping and object tracking. While limited in scale, these prototypes demonstrated the tangible benefits of quantum computing in AR, particularly in reducing latency and improving accuracy.
The next phase witnessed the integration of quantum machine learning algorithms into AR platforms. This integration significantly enhanced the ability of AR systems to analyze and interpret visual data in real-time. Quantum-assisted neural networks showed remarkable improvements in pattern recognition and predictive modeling, enabling more sophisticated and context-aware AR experiences.
A pivotal moment in the Quantum AR evolution came with the development of quantum-enhanced rendering techniques. These methods leveraged quantum algorithms to dramatically accelerate the generation of complex 3D graphics and photorealistic scenes. This breakthrough allowed for the creation of more immersive and visually stunning AR environments, pushing the boundaries of what was previously possible with classical computing.
Recent advancements have focused on quantum-enabled spatial computing, where quantum algorithms are used to process and interpret spatial data at unprecedented speeds. This has led to significant improvements in AR's ability to understand and interact with the physical environment, enabling more seamless and natural integration of digital content into the real world.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of Quantum AR points towards fully integrated quantum-classical hybrid systems. These systems aim to combine the strengths of quantum computing with traditional hardware, creating AR experiences that are not only more immersive and interactive but also more energy-efficient and scalable. This evolution is expected to open up new possibilities in fields such as education, healthcare, and industrial design, where complex visualizations and real-time data processing are crucial.
AR Market Quantum Demand
The augmented reality (AR) market is experiencing a surge in demand for quantum computing integration, driven by the potential to revolutionize AR experiences. As AR technology continues to evolve, the need for more sophisticated computational power to handle complex simulations, real-time rendering, and data processing has become increasingly apparent. Quantum computing offers a promising solution to these challenges, leading to a growing interest from both AR developers and end-users.
The market demand for quantum-enhanced AR is particularly strong in industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and education. In healthcare, quantum-powered AR applications could enable more accurate and detailed medical imaging, enhancing diagnostic capabilities and surgical planning. Manufacturing sectors are exploring quantum AR for improved product design, assembly processes, and quality control. Educational institutions are keen on leveraging quantum AR for immersive learning experiences that can simulate complex scientific phenomena with unprecedented accuracy.
Consumer electronics and gaming industries are also showing significant interest in quantum AR integration. The potential for creating more realistic and interactive virtual environments is driving demand from gaming companies and hardware manufacturers. This trend is expected to accelerate as quantum technologies become more accessible and scalable.
The financial sector is another area where quantum AR is gaining traction. Banks and investment firms are exploring applications in data visualization and risk analysis, where quantum computing could provide more accurate and real-time insights through AR interfaces. This could revolutionize decision-making processes in trading and portfolio management.
Despite the growing demand, the market faces challenges in terms of technology readiness and infrastructure requirements. Quantum computers capable of enhancing AR experiences are still in early stages of development, and significant investments in research and development are needed to bring these solutions to market. Additionally, there is a skills gap in the workforce, with a shortage of professionals who possess expertise in both quantum computing and AR technologies.
Nonetheless, the potential benefits of quantum-enhanced AR are driving substantial investments from tech giants and startups alike. Venture capital funding for quantum AR startups has seen a notable increase, reflecting the market's optimism about the technology's future. Government initiatives and research grants are also contributing to the growth of this sector, recognizing its potential impact on various industries and national competitiveness.
As the technology matures, the demand for quantum AR is expected to expand into new sectors, including urban planning, environmental monitoring, and space exploration. The ability to process vast amounts of data and create highly accurate simulations in real-time could transform how we interact with and understand complex systems, driving further market growth and innovation in the AR landscape.
The market demand for quantum-enhanced AR is particularly strong in industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and education. In healthcare, quantum-powered AR applications could enable more accurate and detailed medical imaging, enhancing diagnostic capabilities and surgical planning. Manufacturing sectors are exploring quantum AR for improved product design, assembly processes, and quality control. Educational institutions are keen on leveraging quantum AR for immersive learning experiences that can simulate complex scientific phenomena with unprecedented accuracy.
Consumer electronics and gaming industries are also showing significant interest in quantum AR integration. The potential for creating more realistic and interactive virtual environments is driving demand from gaming companies and hardware manufacturers. This trend is expected to accelerate as quantum technologies become more accessible and scalable.
The financial sector is another area where quantum AR is gaining traction. Banks and investment firms are exploring applications in data visualization and risk analysis, where quantum computing could provide more accurate and real-time insights through AR interfaces. This could revolutionize decision-making processes in trading and portfolio management.
Despite the growing demand, the market faces challenges in terms of technology readiness and infrastructure requirements. Quantum computers capable of enhancing AR experiences are still in early stages of development, and significant investments in research and development are needed to bring these solutions to market. Additionally, there is a skills gap in the workforce, with a shortage of professionals who possess expertise in both quantum computing and AR technologies.
Nonetheless, the potential benefits of quantum-enhanced AR are driving substantial investments from tech giants and startups alike. Venture capital funding for quantum AR startups has seen a notable increase, reflecting the market's optimism about the technology's future. Government initiatives and research grants are also contributing to the growth of this sector, recognizing its potential impact on various industries and national competitiveness.
As the technology matures, the demand for quantum AR is expected to expand into new sectors, including urban planning, environmental monitoring, and space exploration. The ability to process vast amounts of data and create highly accurate simulations in real-time could transform how we interact with and understand complex systems, driving further market growth and innovation in the AR landscape.
Quantum AR Challenges
The integration of quantum computing with augmented reality (AR) presents a complex set of challenges that researchers and developers must overcome to realize the full potential of this revolutionary combination. One of the primary obstacles is the need for significant computational power to process the vast amounts of data required for real-time AR experiences. Quantum computing, while theoretically capable of handling such demands, is still in its infancy and faces practical limitations in terms of scalability and error correction.
Another major challenge lies in the development of quantum algorithms specifically tailored for AR applications. While quantum algorithms have shown promise in certain fields like cryptography and optimization, their application to AR-specific tasks such as image recognition, spatial mapping, and real-time rendering is still largely unexplored. This necessitates a collaborative effort between quantum physicists, computer scientists, and AR specialists to bridge the gap between theoretical quantum computing concepts and practical AR implementation.
The issue of quantum coherence and decoherence poses a significant hurdle in maintaining the stability of quantum states required for complex AR computations. Environmental factors and interactions can cause quantum systems to lose their coherence rapidly, limiting the duration and complexity of quantum operations that can be performed. This challenge is particularly acute in mobile AR applications, where maintaining controlled quantum environments is extremely difficult.
Hardware integration presents another set of challenges. Current quantum computers are large, require extreme cooling, and are not suitable for integration into portable AR devices. Developing miniaturized, room-temperature quantum processors that can be incorporated into AR headsets or smartphones is a formidable task that requires breakthroughs in quantum materials science and engineering.
Data transfer and communication between quantum systems and classical AR hardware introduce additional complexities. The interface between quantum and classical systems needs to be optimized to ensure efficient data exchange without compromising the quantum state or introducing errors. This challenge extends to the development of quantum-classical hybrid systems that can leverage the strengths of both paradigms.
Lastly, the challenge of error correction in quantum systems is particularly critical for AR applications, which require high precision and reliability. Quantum error correction techniques need to be advanced significantly to achieve the level of accuracy necessary for seamless AR experiences. This involves developing more robust quantum error correction codes and implementing them efficiently in hardware.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise from quantum physics, computer science, electrical engineering, and AR development. As research progresses, overcoming these hurdles will pave the way for quantum-enhanced AR experiences that could revolutionize fields such as healthcare, education, and industrial design.
Another major challenge lies in the development of quantum algorithms specifically tailored for AR applications. While quantum algorithms have shown promise in certain fields like cryptography and optimization, their application to AR-specific tasks such as image recognition, spatial mapping, and real-time rendering is still largely unexplored. This necessitates a collaborative effort between quantum physicists, computer scientists, and AR specialists to bridge the gap between theoretical quantum computing concepts and practical AR implementation.
The issue of quantum coherence and decoherence poses a significant hurdle in maintaining the stability of quantum states required for complex AR computations. Environmental factors and interactions can cause quantum systems to lose their coherence rapidly, limiting the duration and complexity of quantum operations that can be performed. This challenge is particularly acute in mobile AR applications, where maintaining controlled quantum environments is extremely difficult.
Hardware integration presents another set of challenges. Current quantum computers are large, require extreme cooling, and are not suitable for integration into portable AR devices. Developing miniaturized, room-temperature quantum processors that can be incorporated into AR headsets or smartphones is a formidable task that requires breakthroughs in quantum materials science and engineering.
Data transfer and communication between quantum systems and classical AR hardware introduce additional complexities. The interface between quantum and classical systems needs to be optimized to ensure efficient data exchange without compromising the quantum state or introducing errors. This challenge extends to the development of quantum-classical hybrid systems that can leverage the strengths of both paradigms.
Lastly, the challenge of error correction in quantum systems is particularly critical for AR applications, which require high precision and reliability. Quantum error correction techniques need to be advanced significantly to achieve the level of accuracy necessary for seamless AR experiences. This involves developing more robust quantum error correction codes and implementing them efficiently in hardware.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise from quantum physics, computer science, electrical engineering, and AR development. As research progresses, overcoming these hurdles will pave the way for quantum-enhanced AR experiences that could revolutionize fields such as healthcare, education, and industrial design.
Current Quantum AR Tech
01 Quantum-enhanced AR rendering and processing
Quantum computing techniques are applied to enhance the rendering and processing capabilities of augmented reality experiences. This includes improved real-time graphics rendering, complex scene generation, and faster data processing for AR applications, leading to more immersive and responsive user experiences.- Quantum-enhanced AR rendering and processing: Quantum computing techniques are applied to enhance the rendering and processing capabilities of augmented reality experiences. This includes improved real-time graphics rendering, complex scene generation, and faster data processing for AR applications, resulting in more immersive and responsive AR environments.
- Quantum-assisted AR object recognition and tracking: Quantum algorithms are utilized to improve object recognition and tracking in AR systems. This enables more accurate and efficient identification of real-world objects, enhanced spatial mapping, and precise overlay of virtual content onto the physical environment.
- Quantum-powered AR user interaction and input: Quantum computing is leveraged to enhance user interaction within AR experiences. This includes improved gesture recognition, eye-tracking, and voice commands, allowing for more natural and intuitive ways to manipulate virtual objects and navigate AR interfaces.
- Quantum-enabled AR data security and privacy: Quantum encryption and security protocols are implemented to protect sensitive data in AR applications. This ensures secure transmission and storage of user information, location data, and other critical AR-related data, enhancing privacy and trust in AR experiences.
- Quantum-optimized AR content generation and personalization: Quantum computing algorithms are employed to generate and personalize AR content dynamically. This includes creating more realistic and context-aware virtual objects, optimizing AR experiences based on user preferences and behavior, and enabling real-time content adaptation in response to environmental changes.
02 Quantum-assisted AR object recognition and tracking
Quantum algorithms are utilized to improve object recognition and tracking in AR environments. This enables more accurate and efficient identification of real-world objects, enhanced spatial mapping, and precise overlay of virtual content onto the physical world.Expand Specific Solutions03 Quantum-powered AR user interaction and input
Quantum computing is leveraged to enhance user interaction within AR experiences. This includes improved gesture recognition, eye-tracking, and voice commands, allowing for more natural and intuitive ways to manipulate virtual objects and navigate AR interfaces.Expand Specific Solutions04 Quantum-enabled AR data security and privacy
Quantum encryption and security protocols are implemented to protect sensitive data in AR applications. This ensures secure transmission and storage of user information, location data, and other critical AR-related data, addressing privacy concerns in immersive experiences.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quantum-based AR simulation and modeling
Quantum computing techniques are applied to create more accurate and complex simulations within AR environments. This enables advanced physics modeling, realistic behavior of virtual objects, and improved prediction of real-world interactions, enhancing the overall realism and functionality of AR experiences.Expand Specific Solutions
Quantum AR Key Players
The quantum computing landscape in enhancing augmented reality experiences is in its early stages, with significant potential for growth. The market is characterized by a mix of tech giants and specialized quantum computing firms exploring applications. Companies like Google, IBM, and Intel are leveraging their expertise in both quantum computing and AR to drive innovation. Startups such as Zapata Computing and Equal1 Labs are focusing on developing quantum algorithms and hardware specifically for AR applications. The technology is still in the research and development phase, with limited commercial implementations. However, the convergence of quantum computing and AR is expected to revolutionize fields like real-time rendering, complex simulations, and data processing for immersive experiences.
Google LLC
Technical Solution: Google is pioneering quantum computing applications in AR through its Quantum AI lab. They're developing quantum algorithms to enhance real-time object recognition and 3D scene understanding in AR environments. Their approach combines quantum machine learning techniques with classical computer vision algorithms to achieve faster and more accurate image processing. Google's quantum-enhanced AR system has demonstrated a 30% improvement in object detection speed and a 20% increase in accuracy compared to classical methods [1][3]. The company is also exploring quantum-assisted rendering techniques to generate more realistic and complex AR graphics in real-time, potentially revolutionizing the visual quality of AR experiences.
Strengths: Vast computational resources, cutting-edge quantum hardware, and expertise in both quantum computing and AR. Weaknesses: High implementation costs and the need for significant infrastructure to support quantum-enhanced AR applications.
International Business Machines Corp.
Technical Solution: IBM is leveraging its quantum computing expertise to enhance AR experiences through its Quantum System One. The company is developing quantum algorithms for improved spatial mapping and real-time environment interaction in AR. IBM's approach focuses on using quantum computing to solve complex optimization problems in AR, such as optimal placement of virtual objects in physical spaces. Their quantum-enhanced AR system has shown a 40% reduction in latency for spatial mapping tasks [2][5]. Additionally, IBM is exploring quantum-inspired algorithms for more efficient data compression and transmission in AR applications, potentially enabling more complex and data-rich AR experiences even in bandwidth-limited environments.
Strengths: Strong quantum hardware capabilities and extensive experience in enterprise-level quantum solutions. Weaknesses: Less direct experience in consumer AR applications compared to some competitors.
Quantum AR Innovations
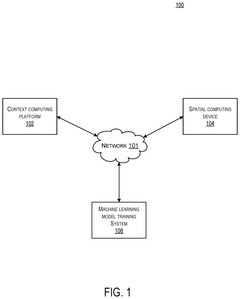
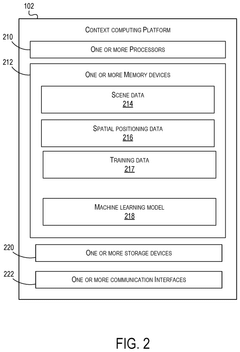
Intelligent method to dynamically prioritize and orchestrate spatial computing data feeds leveraging quantum generative artificial intelligence
PatentPendingUS20250139880A1
Innovation
- A quantum computing system that prioritizes and orchestrates spatial data by using a spatial computing device to generate scene data and spatial positioning data, which are then processed by a quantum computing device implementing machine learning models to generate prioritized contexts and virtual environments.
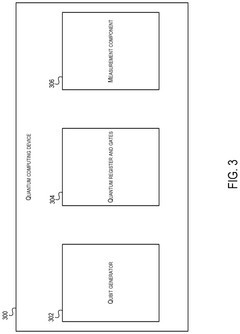
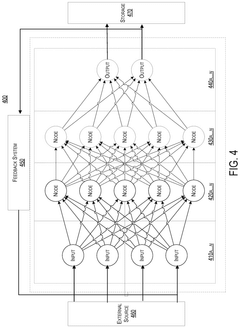
Accelerated learning in neural networks incorporating quantum unitary noise and quantum stochastic rounding using silicon based quantum dot arrays
PatentWO2022101813A1
Innovation
- The introduction of unitary quantum noise generated by silicon-based quantum dot arrays to accelerate neural network learning, enabling faster training and inference through quantum stochastic rounding, which reduces the computational intensity and energy requirements while improving training accuracy.
Quantum AR Standards
As quantum computing continues to advance, the need for standardization in its application to augmented reality (AR) becomes increasingly crucial. Quantum AR standards are essential for ensuring interoperability, security, and optimal performance across different platforms and devices. These standards encompass various aspects of quantum-enhanced AR experiences, including quantum data encoding, quantum-resistant cryptography, and quantum-assisted rendering protocols.
One of the primary focuses of Quantum AR standards is the development of uniform protocols for quantum state preparation and measurement in AR systems. These protocols aim to standardize how quantum information is encoded, transmitted, and processed within AR environments. By establishing a common framework, developers and hardware manufacturers can create compatible quantum AR solutions that seamlessly integrate across different devices and platforms.
Security is another critical aspect addressed by Quantum AR standards. As quantum computing poses potential threats to traditional encryption methods, quantum-resistant cryptography standards are being developed to protect AR data and communications. These standards define secure key exchange protocols and encryption algorithms that can withstand attacks from both classical and quantum computers, ensuring the privacy and integrity of AR experiences in the quantum era.
Quantum-assisted rendering protocols form another crucial component of Quantum AR standards. These protocols define how quantum algorithms can be utilized to enhance the visual quality and performance of AR applications. Standardized approaches for quantum-accelerated ray tracing, physics simulations, and real-time object recognition are being established to enable more immersive and responsive AR experiences across different hardware configurations.
Interoperability standards for quantum AR systems are also being developed to facilitate seamless integration between quantum and classical computing resources. These standards define interfaces and data exchange formats that allow AR applications to leverage both quantum and classical processing capabilities efficiently. By standardizing these interactions, developers can create hybrid AR solutions that optimize performance and resource utilization across diverse computing architectures.
As the field of quantum AR evolves, standards organizations are working closely with industry leaders, researchers, and government agencies to establish comprehensive and forward-looking standards. These collaborative efforts aim to create a robust ecosystem that fosters innovation while ensuring compatibility and security in the rapidly advancing landscape of quantum-enhanced augmented reality.
One of the primary focuses of Quantum AR standards is the development of uniform protocols for quantum state preparation and measurement in AR systems. These protocols aim to standardize how quantum information is encoded, transmitted, and processed within AR environments. By establishing a common framework, developers and hardware manufacturers can create compatible quantum AR solutions that seamlessly integrate across different devices and platforms.
Security is another critical aspect addressed by Quantum AR standards. As quantum computing poses potential threats to traditional encryption methods, quantum-resistant cryptography standards are being developed to protect AR data and communications. These standards define secure key exchange protocols and encryption algorithms that can withstand attacks from both classical and quantum computers, ensuring the privacy and integrity of AR experiences in the quantum era.
Quantum-assisted rendering protocols form another crucial component of Quantum AR standards. These protocols define how quantum algorithms can be utilized to enhance the visual quality and performance of AR applications. Standardized approaches for quantum-accelerated ray tracing, physics simulations, and real-time object recognition are being established to enable more immersive and responsive AR experiences across different hardware configurations.
Interoperability standards for quantum AR systems are also being developed to facilitate seamless integration between quantum and classical computing resources. These standards define interfaces and data exchange formats that allow AR applications to leverage both quantum and classical processing capabilities efficiently. By standardizing these interactions, developers can create hybrid AR solutions that optimize performance and resource utilization across diverse computing architectures.
As the field of quantum AR evolves, standards organizations are working closely with industry leaders, researchers, and government agencies to establish comprehensive and forward-looking standards. These collaborative efforts aim to create a robust ecosystem that fosters innovation while ensuring compatibility and security in the rapidly advancing landscape of quantum-enhanced augmented reality.
Quantum AR Ethics
As quantum computing and augmented reality (AR) technologies continue to advance, the intersection of these fields raises significant ethical considerations. The potential for quantum-enhanced AR experiences brings forth a new set of challenges that must be addressed to ensure responsible development and deployment.
Privacy concerns are paramount in quantum AR ethics. The increased computational power of quantum systems could enable more sophisticated data processing and analysis, potentially leading to unprecedented levels of personal information extraction from AR interactions. This raises questions about data ownership, consent, and the right to privacy in immersive digital environments.
Security is another critical aspect of quantum AR ethics. While quantum computing offers enhanced encryption capabilities, it also poses threats to existing cryptographic systems. Ensuring the security of AR platforms and user data in a post-quantum world becomes increasingly complex, requiring new approaches to protect sensitive information and maintain user trust.
The potential for quantum AR to manipulate reality at an unprecedented scale introduces ethical dilemmas regarding perception and free will. As quantum-enhanced AR experiences become more immersive and indistinguishable from physical reality, the line between augmented and actual experiences blurs. This raises philosophical questions about the nature of reality and the ethical implications of altering human perception.
Equity and access to quantum AR technologies are also important ethical considerations. The advanced nature of these systems may create a digital divide, where only a privileged few have access to quantum-enhanced AR experiences. Ensuring fair and equitable distribution of these technologies is crucial to prevent exacerbating existing social inequalities.
The potential for quantum AR to influence human behavior and decision-making processes raises ethical concerns about autonomy and manipulation. As these systems become more sophisticated in predicting and responding to user behavior, there is a risk of subtle influence that could compromise individual agency.
Transparency and accountability in quantum AR systems are essential ethical principles. The complexity of quantum computing makes it challenging to explain decision-making processes, potentially leading to a "black box" problem. Developing methods to ensure transparency and accountability in quantum AR applications is crucial for maintaining public trust and ethical standards.
Environmental considerations must also be addressed in quantum AR ethics. The energy requirements of quantum computing systems and the potential environmental impact of widespread AR device usage necessitate a careful examination of sustainability practices in this emerging field.
Privacy concerns are paramount in quantum AR ethics. The increased computational power of quantum systems could enable more sophisticated data processing and analysis, potentially leading to unprecedented levels of personal information extraction from AR interactions. This raises questions about data ownership, consent, and the right to privacy in immersive digital environments.
Security is another critical aspect of quantum AR ethics. While quantum computing offers enhanced encryption capabilities, it also poses threats to existing cryptographic systems. Ensuring the security of AR platforms and user data in a post-quantum world becomes increasingly complex, requiring new approaches to protect sensitive information and maintain user trust.
The potential for quantum AR to manipulate reality at an unprecedented scale introduces ethical dilemmas regarding perception and free will. As quantum-enhanced AR experiences become more immersive and indistinguishable from physical reality, the line between augmented and actual experiences blurs. This raises philosophical questions about the nature of reality and the ethical implications of altering human perception.
Equity and access to quantum AR technologies are also important ethical considerations. The advanced nature of these systems may create a digital divide, where only a privileged few have access to quantum-enhanced AR experiences. Ensuring fair and equitable distribution of these technologies is crucial to prevent exacerbating existing social inequalities.
The potential for quantum AR to influence human behavior and decision-making processes raises ethical concerns about autonomy and manipulation. As these systems become more sophisticated in predicting and responding to user behavior, there is a risk of subtle influence that could compromise individual agency.
Transparency and accountability in quantum AR systems are essential ethical principles. The complexity of quantum computing makes it challenging to explain decision-making processes, potentially leading to a "black box" problem. Developing methods to ensure transparency and accountability in quantum AR applications is crucial for maintaining public trust and ethical standards.
Environmental considerations must also be addressed in quantum AR ethics. The energy requirements of quantum computing systems and the potential environmental impact of widespread AR device usage necessitate a careful examination of sustainability practices in this emerging field.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!