Quantum Computing in Enhancing Human-Computer Interaction Systems
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Quantum HCI Evolution
The evolution of quantum computing in human-computer interaction (HCI) systems represents a significant paradigm shift in the way we interact with technology. This journey began with the recognition of quantum computing's potential to revolutionize computational power and its implications for user interfaces and interaction modalities.
In the early stages, researchers focused on understanding how quantum principles could be applied to enhance traditional HCI systems. This led to the development of quantum-inspired algorithms for gesture recognition, voice processing, and pattern matching, which showed promising improvements in accuracy and speed compared to classical methods.
As quantum hardware became more accessible, the field saw a surge in experimental applications. Quantum sensors, for instance, enabled ultra-precise motion tracking and haptic feedback systems, pushing the boundaries of virtual and augmented reality experiences. These advancements allowed for more immersive and responsive user interfaces, reducing latency and increasing the fidelity of user interactions.
The integration of quantum machine learning algorithms into HCI systems marked another significant milestone. These algorithms demonstrated superior performance in natural language processing, context awareness, and user behavior prediction. This led to the development of more intuitive and adaptive user interfaces that could anticipate user needs and preferences with unprecedented accuracy.
Quantum cryptography also played a crucial role in enhancing the security aspects of HCI systems. The implementation of quantum key distribution protocols ensured unbreakable encryption for user data and communications, addressing growing concerns about privacy and data protection in interactive systems.
Recent years have seen the emergence of quantum-enhanced brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). By leveraging quantum sensors and algorithms, these systems have achieved remarkable improvements in signal detection and interpretation, opening new possibilities for direct neural control of devices and applications.
The ongoing research in quantum error correction and fault-tolerant quantum computing promises to bring even more stability and reliability to quantum-enhanced HCI systems. This is expected to pave the way for large-scale deployment of quantum technologies in everyday computing devices, further transforming the landscape of human-computer interaction.
As we look to the future, the convergence of quantum computing with other emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things is set to redefine the boundaries of HCI. This synergy is likely to result in highly personalized, context-aware, and seamlessly integrated interaction experiences that adapt in real-time to user needs and environmental conditions.
In the early stages, researchers focused on understanding how quantum principles could be applied to enhance traditional HCI systems. This led to the development of quantum-inspired algorithms for gesture recognition, voice processing, and pattern matching, which showed promising improvements in accuracy and speed compared to classical methods.
As quantum hardware became more accessible, the field saw a surge in experimental applications. Quantum sensors, for instance, enabled ultra-precise motion tracking and haptic feedback systems, pushing the boundaries of virtual and augmented reality experiences. These advancements allowed for more immersive and responsive user interfaces, reducing latency and increasing the fidelity of user interactions.
The integration of quantum machine learning algorithms into HCI systems marked another significant milestone. These algorithms demonstrated superior performance in natural language processing, context awareness, and user behavior prediction. This led to the development of more intuitive and adaptive user interfaces that could anticipate user needs and preferences with unprecedented accuracy.
Quantum cryptography also played a crucial role in enhancing the security aspects of HCI systems. The implementation of quantum key distribution protocols ensured unbreakable encryption for user data and communications, addressing growing concerns about privacy and data protection in interactive systems.
Recent years have seen the emergence of quantum-enhanced brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). By leveraging quantum sensors and algorithms, these systems have achieved remarkable improvements in signal detection and interpretation, opening new possibilities for direct neural control of devices and applications.
The ongoing research in quantum error correction and fault-tolerant quantum computing promises to bring even more stability and reliability to quantum-enhanced HCI systems. This is expected to pave the way for large-scale deployment of quantum technologies in everyday computing devices, further transforming the landscape of human-computer interaction.
As we look to the future, the convergence of quantum computing with other emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things is set to redefine the boundaries of HCI. This synergy is likely to result in highly personalized, context-aware, and seamlessly integrated interaction experiences that adapt in real-time to user needs and environmental conditions.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for quantum computing in enhancing human-computer interaction (HCI) systems is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing complexity of data processing and the need for more intuitive and efficient user interfaces. As traditional computing approaches reach their limits in handling complex HCI tasks, quantum computing offers promising solutions to overcome these challenges.
In the field of natural language processing, a key component of HCI systems, quantum algorithms show potential for dramatically improving language understanding and generation. This capability is particularly valuable for virtual assistants, chatbots, and voice-controlled interfaces, where more natural and context-aware interactions are highly sought after. The market for these applications is expanding rapidly across various sectors, including customer service, healthcare, and smart home technologies.
Quantum computing also holds promise for enhancing computer vision and image recognition systems, which are crucial for augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications. As the AR/VR market continues to grow, estimated to reach $209.2 billion by 2022, the demand for more sophisticated and responsive visual processing capabilities is increasing. Quantum algorithms could potentially enable real-time, high-fidelity image analysis and generation, significantly improving user experiences in gaming, training simulations, and immersive environments.
In the realm of user behavior prediction and personalization, quantum machine learning algorithms offer the potential for more accurate and efficient analysis of large-scale user data. This capability is particularly valuable for e-commerce platforms, content recommendation systems, and personalized user interfaces. As businesses increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making, the demand for quantum-enhanced HCI systems that can provide deeper insights and more tailored user experiences is growing.
The healthcare sector represents another significant market for quantum-enhanced HCI systems. Quantum computing could revolutionize medical imaging analysis, drug discovery processes, and personalized treatment planning. The ability to process and interpret complex medical data more efficiently could lead to improved diagnostic tools and more intuitive interfaces for healthcare professionals.
However, it's important to note that the market for quantum-enhanced HCI systems is still in its early stages. While there is considerable interest and investment in this field, practical applications are limited by the current state of quantum hardware and the need for further development of quantum algorithms specifically tailored for HCI tasks. As these technologies mature, we can expect to see a surge in demand across various industries seeking to leverage quantum computing to create more powerful, intuitive, and responsive human-computer interaction systems.
In the field of natural language processing, a key component of HCI systems, quantum algorithms show potential for dramatically improving language understanding and generation. This capability is particularly valuable for virtual assistants, chatbots, and voice-controlled interfaces, where more natural and context-aware interactions are highly sought after. The market for these applications is expanding rapidly across various sectors, including customer service, healthcare, and smart home technologies.
Quantum computing also holds promise for enhancing computer vision and image recognition systems, which are crucial for augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applications. As the AR/VR market continues to grow, estimated to reach $209.2 billion by 2022, the demand for more sophisticated and responsive visual processing capabilities is increasing. Quantum algorithms could potentially enable real-time, high-fidelity image analysis and generation, significantly improving user experiences in gaming, training simulations, and immersive environments.
In the realm of user behavior prediction and personalization, quantum machine learning algorithms offer the potential for more accurate and efficient analysis of large-scale user data. This capability is particularly valuable for e-commerce platforms, content recommendation systems, and personalized user interfaces. As businesses increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making, the demand for quantum-enhanced HCI systems that can provide deeper insights and more tailored user experiences is growing.
The healthcare sector represents another significant market for quantum-enhanced HCI systems. Quantum computing could revolutionize medical imaging analysis, drug discovery processes, and personalized treatment planning. The ability to process and interpret complex medical data more efficiently could lead to improved diagnostic tools and more intuitive interfaces for healthcare professionals.
However, it's important to note that the market for quantum-enhanced HCI systems is still in its early stages. While there is considerable interest and investment in this field, practical applications are limited by the current state of quantum hardware and the need for further development of quantum algorithms specifically tailored for HCI tasks. As these technologies mature, we can expect to see a surge in demand across various industries seeking to leverage quantum computing to create more powerful, intuitive, and responsive human-computer interaction systems.
Quantum HCI Challenges
The integration of quantum computing into human-computer interaction (HCI) systems presents a unique set of challenges that researchers and developers must address. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of quantum systems and their inherent probabilistic nature, which can make it difficult to create intuitive and user-friendly interfaces. Traditional HCI paradigms may not be directly applicable to quantum systems, necessitating the development of new interaction models and metaphors.
Another significant challenge lies in the representation and visualization of quantum information. Quantum states and operations often involve complex mathematical concepts that are not easily translatable into visual or tactile representations. This creates a barrier for users who may not have a deep understanding of quantum mechanics, limiting the accessibility of quantum-enhanced HCI systems to a broader audience.
The issue of quantum decoherence poses a substantial hurdle in maintaining the stability and reliability of quantum-enhanced HCI systems. Quantum states are extremely sensitive to environmental disturbances, which can lead to errors and loss of information. Designing interfaces that can effectively mitigate or compensate for these effects while maintaining real-time responsiveness is a formidable task.
Scalability presents another major challenge. As quantum systems grow in complexity and capability, ensuring that HCI remains efficient and effective becomes increasingly difficult. This is particularly evident in the design of control systems for large-scale quantum computers, where the sheer number of qubits and operations can overwhelm traditional interface designs.
The integration of classical and quantum components in hybrid systems introduces additional complexities. Bridging the gap between classical user inputs and quantum processing, and then translating quantum outputs back into classical forms that users can interpret, requires sophisticated interface design and data translation mechanisms.
Ethical considerations also come into play when developing quantum-enhanced HCI systems. The potential for quantum computers to process vast amounts of personal data raises concerns about privacy and security. Designing interfaces that protect user information while leveraging the power of quantum computing is a critical challenge that must be addressed.
Lastly, the lack of standardization in quantum computing hardware and software platforms creates difficulties in developing consistent and portable HCI solutions. This fragmentation can hinder the widespread adoption of quantum-enhanced interfaces and slow down innovation in the field.
Another significant challenge lies in the representation and visualization of quantum information. Quantum states and operations often involve complex mathematical concepts that are not easily translatable into visual or tactile representations. This creates a barrier for users who may not have a deep understanding of quantum mechanics, limiting the accessibility of quantum-enhanced HCI systems to a broader audience.
The issue of quantum decoherence poses a substantial hurdle in maintaining the stability and reliability of quantum-enhanced HCI systems. Quantum states are extremely sensitive to environmental disturbances, which can lead to errors and loss of information. Designing interfaces that can effectively mitigate or compensate for these effects while maintaining real-time responsiveness is a formidable task.
Scalability presents another major challenge. As quantum systems grow in complexity and capability, ensuring that HCI remains efficient and effective becomes increasingly difficult. This is particularly evident in the design of control systems for large-scale quantum computers, where the sheer number of qubits and operations can overwhelm traditional interface designs.
The integration of classical and quantum components in hybrid systems introduces additional complexities. Bridging the gap between classical user inputs and quantum processing, and then translating quantum outputs back into classical forms that users can interpret, requires sophisticated interface design and data translation mechanisms.
Ethical considerations also come into play when developing quantum-enhanced HCI systems. The potential for quantum computers to process vast amounts of personal data raises concerns about privacy and security. Designing interfaces that protect user information while leveraging the power of quantum computing is a critical challenge that must be addressed.
Lastly, the lack of standardization in quantum computing hardware and software platforms creates difficulties in developing consistent and portable HCI solutions. This fragmentation can hinder the widespread adoption of quantum-enhanced interfaces and slow down innovation in the field.
Current Quantum HCI
01 Quantum-enhanced user interfaces
Quantum computing is being integrated into human-computer interaction systems to create more intuitive and responsive user interfaces. These interfaces leverage quantum properties like superposition and entanglement to process complex user inputs and generate more natural, context-aware responses. This approach aims to enhance the overall user experience by providing more accurate and personalized interactions.- Quantum-enhanced user interfaces: This approach focuses on developing user interfaces that leverage quantum computing capabilities to enhance human-computer interaction. These interfaces may utilize quantum algorithms to process and display complex information more efficiently, enabling more intuitive and responsive interactions between users and quantum systems.
- Quantum-classical hybrid interaction systems: These systems combine classical computing elements with quantum components to create more effective human-computer interaction platforms. By integrating quantum processing capabilities with traditional interface designs, these hybrid systems aim to bridge the gap between quantum computing complexities and user-friendly interactions.
- Quantum-inspired visualization techniques: This approach involves developing novel visualization methods inspired by quantum principles to represent complex quantum data and processes. These techniques aim to make quantum concepts more accessible and understandable to users, facilitating better interaction with quantum computing systems.
- Quantum error correction in HCI systems: This focuses on implementing quantum error correction techniques in human-computer interaction systems to improve the reliability and accuracy of quantum-based interfaces. By mitigating errors inherent in quantum systems, these methods aim to enhance the stability and usability of quantum HCI platforms.
- Quantum-enhanced natural language processing for HCI: This approach utilizes quantum computing algorithms to enhance natural language processing capabilities in human-computer interaction systems. By leveraging quantum techniques, these systems aim to improve language understanding, translation, and generation, leading to more natural and efficient communication between users and quantum computers.
02 Quantum-assisted natural language processing
Quantum algorithms are being applied to natural language processing tasks in human-computer interaction systems. This integration allows for more efficient processing of large language datasets, improved language understanding, and enhanced translation capabilities. The quantum approach enables the system to handle complex linguistic structures and nuances more effectively than classical computing methods.Expand Specific Solutions03 Quantum-based gesture and motion recognition
Quantum computing techniques are being utilized to enhance gesture and motion recognition in human-computer interaction systems. These systems use quantum algorithms to process and analyze complex motion data more efficiently, enabling more accurate and responsive gesture-based interfaces. This approach allows for more natural and intuitive interactions between users and computers.Expand Specific Solutions04 Quantum-enhanced biometric authentication
Quantum computing is being applied to improve biometric authentication methods in human-computer interaction systems. This includes enhancing the security and accuracy of fingerprint, facial recognition, and other biometric identification techniques. Quantum algorithms allow for more complex pattern matching and data analysis, resulting in more reliable and secure user authentication processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quantum-powered adaptive learning interfaces
Human-computer interaction systems are incorporating quantum computing to create more adaptive and personalized learning interfaces. These systems use quantum algorithms to analyze user behavior, preferences, and learning patterns in real-time, allowing for dynamic adjustments to the interface and content presentation. This approach aims to optimize the learning experience and improve knowledge retention for individual users.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The quantum computing landscape in enhancing human-computer interaction systems is rapidly evolving, with the industry currently in its early growth stage. The market size is expanding, driven by increasing investments and technological advancements. While still in its nascent phase, the technology's maturity is progressing, with key players like Google, IBM, and Intel leading research and development efforts. Emerging companies such as Zapata Computing and IonQ are also making significant contributions. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of tech giants and specialized quantum computing startups, each focusing on different aspects of quantum-enhanced HCI systems. As the field advances, we can expect increased collaboration between academia and industry, with institutions like the University of Maryland and Caltech playing crucial roles in pushing the boundaries of quantum computing applications in human-computer interaction.
Google LLC
Technical Solution: Google's approach to quantum computing in enhancing human-computer interaction systems focuses on developing Sycamore, a 53-qubit quantum processor. This processor has demonstrated quantum supremacy by performing a specific task in 200 seconds that would take a classical supercomputer 10,000 years[1]. Google is also working on error correction techniques and developing quantum algorithms that could potentially revolutionize natural language processing and computer vision, key components of HCI systems. Their Quantum AI lab is exploring the integration of quantum computing with machine learning to enhance user experience and interaction modalities[2][3].
Strengths: Advanced quantum hardware, strong research team, and integration with existing AI technologies. Weaknesses: Still in early stages of practical application for HCI systems, and facing challenges in scaling up qubit count while maintaining coherence.
International Business Machines Corp.
Technical Solution: IBM's quantum computing strategy for enhancing HCI systems revolves around their IBM Q System One, the first integrated quantum computing system for commercial use. They are developing quantum algorithms that could potentially enhance natural language processing, sentiment analysis, and pattern recognition in HCI applications. IBM's Qiskit, an open-source quantum computing software development framework, allows researchers to experiment with quantum algorithms for HCI tasks[4]. Their recent breakthrough in error mitigation techniques, such as quantum error correction and dynamic circuits, aims to improve the reliability and performance of quantum systems in real-world HCI applications[5].
Strengths: Extensive experience in quantum hardware and software development, strong industry partnerships. Weaknesses: Quantum systems still require extremely low temperatures, limiting widespread adoption in consumer HCI devices.
Quantum HCI Patents
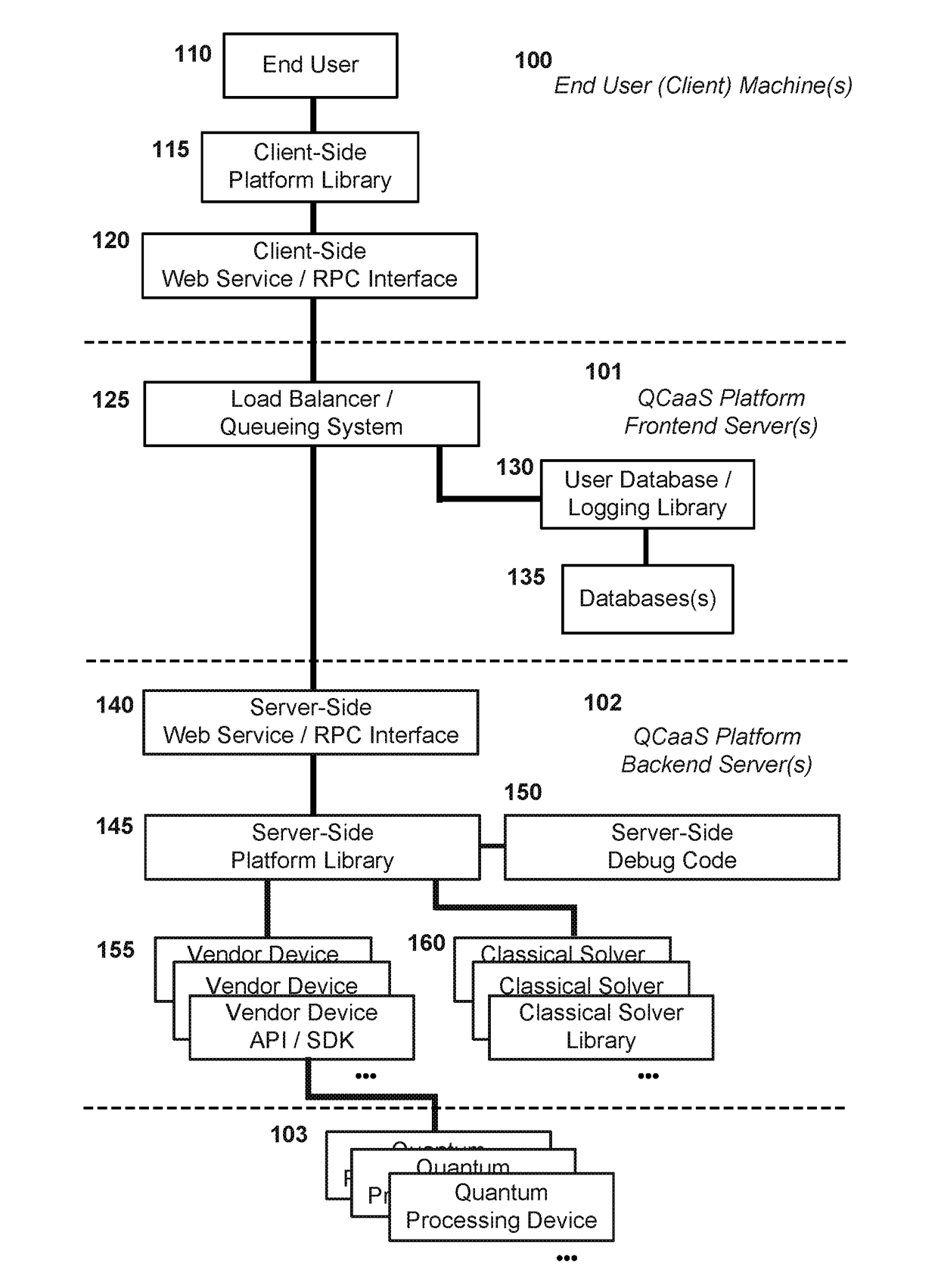
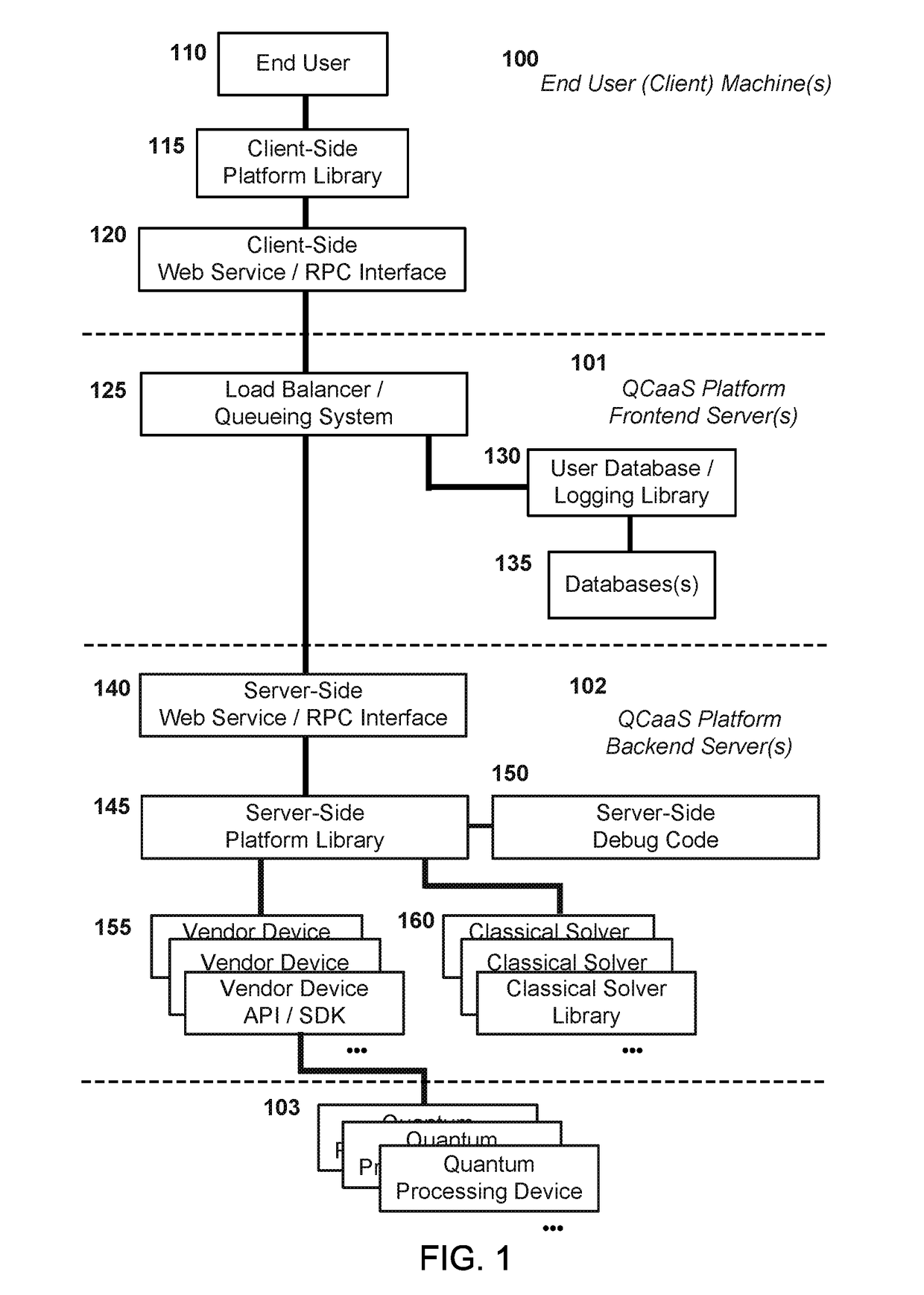
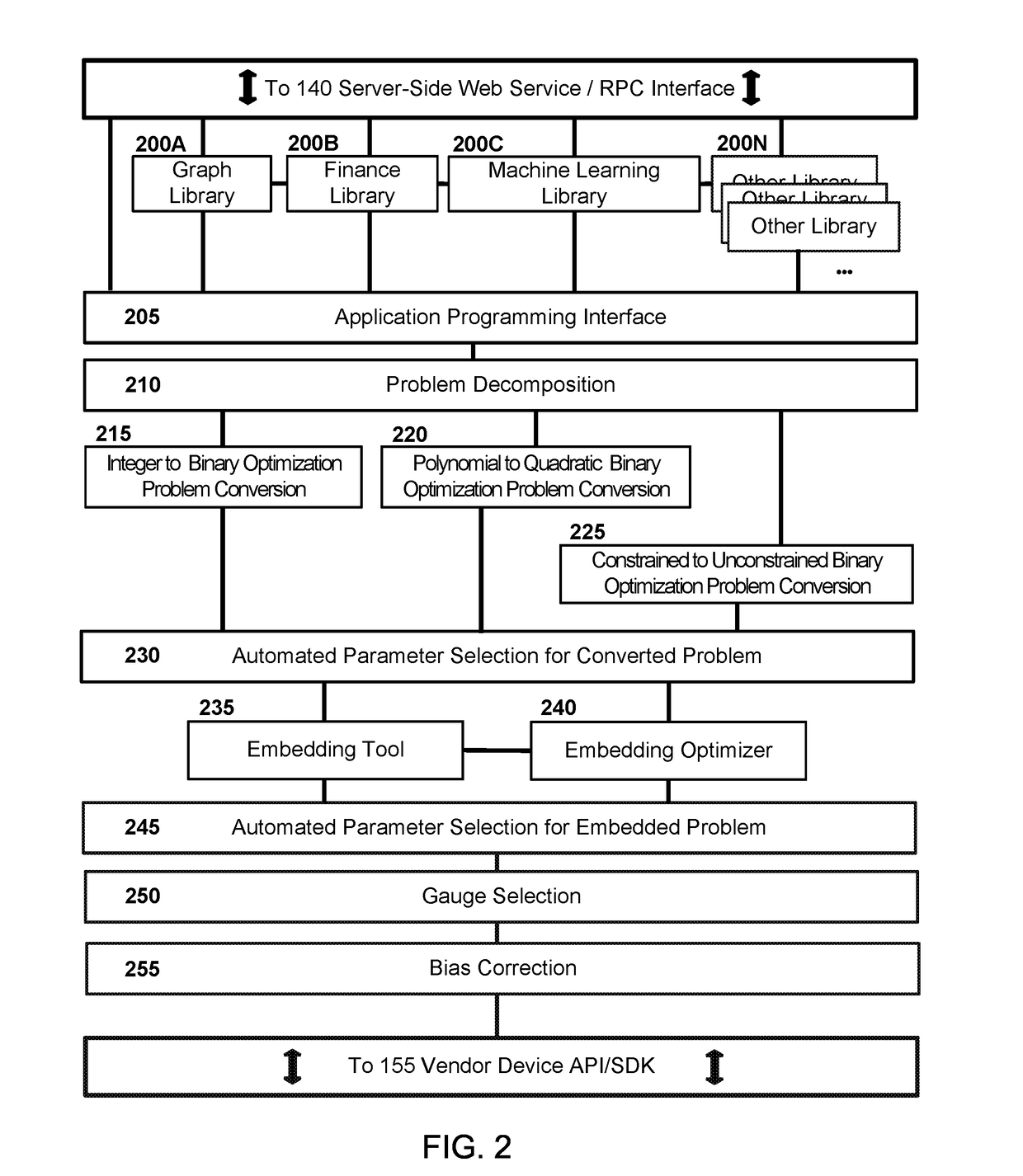
Quantum Computing as a Service
PatentActiveUS20170223094A1
Innovation
- A quantum computing as a service (QCaaS) platform that provides cross-platform compatibility and reduces programmer burden by offering a service for development, testing, and execution of quantum software, utilizing a server-side and client-side platform library with domain-specific modules and algorithms to prepare and execute computational problems on quantum processing devices.
Quantum computer performance enhancement
PatentActiveUS20230315516A1
Innovation
- A system comprising a monitoring job component, a modeler component, and a calibration agent that executes monitoring jobs, determines system state parameter values, and develops a calibration strategy to optimize qubit performance by scheduling calibration tasks based on input data and system state parameters, using artificial intelligence for efficient calibration.
Quantum Ethics in HCI
As quantum computing continues to advance, its integration with human-computer interaction (HCI) systems raises significant ethical considerations. The potential for quantum-enhanced HCI to revolutionize user experiences and capabilities also brings forth complex moral dilemmas that must be carefully addressed.
One primary ethical concern is the issue of privacy and data security. Quantum computing's ability to process vast amounts of data at unprecedented speeds could potentially compromise existing encryption methods, putting user information at risk. This necessitates the development of quantum-resistant cryptography and robust data protection measures to safeguard user privacy in quantum-enhanced HCI systems.
Another critical ethical consideration is the potential for quantum-enhanced HCI to exacerbate existing societal inequalities. As these advanced systems become more prevalent, there is a risk of creating a technological divide between those who have access to quantum-enhanced interfaces and those who do not. This disparity could lead to significant advantages in areas such as education, employment, and healthcare for privileged groups, further widening the gap in society.
The ethical implications of quantum-enhanced decision-making algorithms in HCI systems also warrant careful examination. While these algorithms may offer unprecedented accuracy and efficiency, they raise questions about transparency, accountability, and the potential for bias. Ensuring that quantum-enhanced HCI systems make fair and unbiased decisions is crucial to maintain trust and prevent discrimination.
Furthermore, the potential for quantum-enhanced HCI to manipulate human cognition and behavior presents ethical challenges. As these systems become more sophisticated in understanding and responding to human emotions and thought patterns, there is a need to establish clear boundaries to prevent undue influence or manipulation of users.
The ethical use of quantum-enhanced HCI in sensitive applications, such as healthcare and national security, requires careful consideration. While these systems may offer significant benefits, they also pose risks related to data misuse, privacy breaches, and potential harm if not properly regulated and monitored.
Addressing these ethical concerns requires a multidisciplinary approach involving technologists, ethicists, policymakers, and end-users. Developing ethical guidelines and regulatory frameworks specific to quantum-enhanced HCI is essential to ensure responsible development and deployment of these technologies. This includes establishing principles for transparency, accountability, and user consent in quantum-enhanced HCI systems.
One primary ethical concern is the issue of privacy and data security. Quantum computing's ability to process vast amounts of data at unprecedented speeds could potentially compromise existing encryption methods, putting user information at risk. This necessitates the development of quantum-resistant cryptography and robust data protection measures to safeguard user privacy in quantum-enhanced HCI systems.
Another critical ethical consideration is the potential for quantum-enhanced HCI to exacerbate existing societal inequalities. As these advanced systems become more prevalent, there is a risk of creating a technological divide between those who have access to quantum-enhanced interfaces and those who do not. This disparity could lead to significant advantages in areas such as education, employment, and healthcare for privileged groups, further widening the gap in society.
The ethical implications of quantum-enhanced decision-making algorithms in HCI systems also warrant careful examination. While these algorithms may offer unprecedented accuracy and efficiency, they raise questions about transparency, accountability, and the potential for bias. Ensuring that quantum-enhanced HCI systems make fair and unbiased decisions is crucial to maintain trust and prevent discrimination.
Furthermore, the potential for quantum-enhanced HCI to manipulate human cognition and behavior presents ethical challenges. As these systems become more sophisticated in understanding and responding to human emotions and thought patterns, there is a need to establish clear boundaries to prevent undue influence or manipulation of users.
The ethical use of quantum-enhanced HCI in sensitive applications, such as healthcare and national security, requires careful consideration. While these systems may offer significant benefits, they also pose risks related to data misuse, privacy breaches, and potential harm if not properly regulated and monitored.
Addressing these ethical concerns requires a multidisciplinary approach involving technologists, ethicists, policymakers, and end-users. Developing ethical guidelines and regulatory frameworks specific to quantum-enhanced HCI is essential to ensure responsible development and deployment of these technologies. This includes establishing principles for transparency, accountability, and user consent in quantum-enhanced HCI systems.
Quantum HCI Standards
The development of quantum computing has sparked interest in establishing standards for quantum human-computer interaction (HCI) systems. These standards aim to ensure consistency, interoperability, and user-friendliness across quantum HCI applications. As quantum technologies advance, it becomes crucial to define guidelines that bridge the gap between classical and quantum computing paradigms in user interfaces.
One key aspect of quantum HCI standards is the representation of quantum states and operations. Standardized visual representations of qubits, quantum gates, and measurement outcomes are essential for creating intuitive interfaces that allow users to interact with quantum systems effectively. These standards should consider both expert users familiar with quantum mechanics and novice users who may be exploring quantum computing for the first time.
Quantum HCI standards also need to address the unique challenges posed by quantum systems, such as the probabilistic nature of quantum measurements and the concept of superposition. Guidelines for presenting quantum simulation results and visualizing complex quantum states in a comprehensible manner are crucial for enabling users to interpret and analyze quantum data effectively.
Interoperability is another critical consideration in quantum HCI standards. As various quantum hardware platforms and software frameworks emerge, it is essential to establish protocols for data exchange and communication between different quantum systems and classical interfaces. This includes standardizing file formats for quantum circuits, measurement results, and quantum state descriptions.
Security and privacy considerations are paramount in quantum HCI standards, given the potential of quantum computing to break certain classical encryption methods. Guidelines for secure user authentication, data protection, and privacy-preserving quantum computations must be integrated into the standards to ensure the responsible development and deployment of quantum HCI systems.
Accessibility is a crucial aspect of quantum HCI standards, ensuring that quantum computing interfaces are usable by individuals with diverse abilities and backgrounds. This includes guidelines for creating adaptive interfaces, providing alternative input methods, and designing quantum visualizations that accommodate various perceptual abilities.
As quantum computing continues to evolve, quantum HCI standards must remain flexible and adaptable to accommodate new discoveries and technological advancements. Regular review and updates to these standards will be necessary to keep pace with the rapidly changing landscape of quantum technologies and ensure that human-computer interaction in the quantum domain remains effective, efficient, and user-centric.
One key aspect of quantum HCI standards is the representation of quantum states and operations. Standardized visual representations of qubits, quantum gates, and measurement outcomes are essential for creating intuitive interfaces that allow users to interact with quantum systems effectively. These standards should consider both expert users familiar with quantum mechanics and novice users who may be exploring quantum computing for the first time.
Quantum HCI standards also need to address the unique challenges posed by quantum systems, such as the probabilistic nature of quantum measurements and the concept of superposition. Guidelines for presenting quantum simulation results and visualizing complex quantum states in a comprehensible manner are crucial for enabling users to interpret and analyze quantum data effectively.
Interoperability is another critical consideration in quantum HCI standards. As various quantum hardware platforms and software frameworks emerge, it is essential to establish protocols for data exchange and communication between different quantum systems and classical interfaces. This includes standardizing file formats for quantum circuits, measurement results, and quantum state descriptions.
Security and privacy considerations are paramount in quantum HCI standards, given the potential of quantum computing to break certain classical encryption methods. Guidelines for secure user authentication, data protection, and privacy-preserving quantum computations must be integrated into the standards to ensure the responsible development and deployment of quantum HCI systems.
Accessibility is a crucial aspect of quantum HCI standards, ensuring that quantum computing interfaces are usable by individuals with diverse abilities and backgrounds. This includes guidelines for creating adaptive interfaces, providing alternative input methods, and designing quantum visualizations that accommodate various perceptual abilities.
As quantum computing continues to evolve, quantum HCI standards must remain flexible and adaptable to accommodate new discoveries and technological advancements. Regular review and updates to these standards will be necessary to keep pace with the rapidly changing landscape of quantum technologies and ensure that human-computer interaction in the quantum domain remains effective, efficient, and user-centric.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!