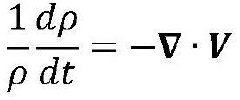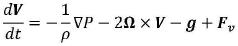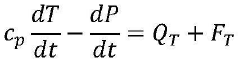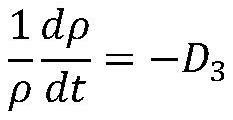Quantum Computing's Impact on Forecasting Natural Disasters
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Quantum Computing in Disaster Prediction: Background and Objectives
Quantum computing represents a revolutionary paradigm in computational technology, leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics to process information. In the context of forecasting natural disasters, this emerging field holds immense potential to transform our predictive capabilities. The background of quantum computing in disaster prediction is rooted in the limitations of classical computing systems when dealing with complex, multivariable environmental models.
Traditional forecasting methods often struggle with the vast amounts of data and intricate calculations required to accurately predict natural disasters. Quantum computing offers a solution by harnessing quantum superposition and entanglement, allowing for the simultaneous processing of multiple states and rapid computation of complex algorithms. This capability is particularly relevant in modeling chaotic systems like weather patterns and geological phenomena, which are inherently difficult to predict using conventional methods.
The evolution of quantum computing in this domain has been marked by significant milestones. Early theoretical work in the 1980s and 1990s laid the foundation for quantum algorithms that could potentially outperform classical ones in specific tasks. As quantum hardware has advanced, researchers have begun exploring practical applications in environmental modeling and disaster prediction.
The primary objective of integrating quantum computing into disaster forecasting is to enhance the accuracy, speed, and reliability of predictions. This involves developing quantum algorithms tailored to process and analyze vast datasets from various sources, including satellite imagery, seismic sensors, and atmospheric measurements. By improving the resolution and timeliness of forecasts, quantum-powered systems aim to provide earlier warnings for events such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and tsunamis.
Another crucial goal is to enable more comprehensive risk assessments by simulating complex scenarios that are computationally infeasible with classical systems. This could lead to better understanding of long-term climate trends and their impact on disaster frequency and severity. Additionally, quantum computing seeks to optimize resource allocation and emergency response strategies by rapidly evaluating multiple scenarios and outcomes.
The integration of quantum computing with machine learning and artificial intelligence presents another exciting frontier. Quantum machine learning algorithms have the potential to identify subtle patterns and correlations in historical disaster data that might elude classical analysis, potentially uncovering new predictive indicators.
As research progresses, the field aims to overcome current limitations in quantum hardware, such as error rates and qubit stability, to realize the full potential of quantum computing in disaster prediction. The ultimate vision is to create a global, quantum-enhanced early warning system that significantly reduces the human and economic toll of natural disasters through vastly improved forecasting capabilities.
Traditional forecasting methods often struggle with the vast amounts of data and intricate calculations required to accurately predict natural disasters. Quantum computing offers a solution by harnessing quantum superposition and entanglement, allowing for the simultaneous processing of multiple states and rapid computation of complex algorithms. This capability is particularly relevant in modeling chaotic systems like weather patterns and geological phenomena, which are inherently difficult to predict using conventional methods.
The evolution of quantum computing in this domain has been marked by significant milestones. Early theoretical work in the 1980s and 1990s laid the foundation for quantum algorithms that could potentially outperform classical ones in specific tasks. As quantum hardware has advanced, researchers have begun exploring practical applications in environmental modeling and disaster prediction.
The primary objective of integrating quantum computing into disaster forecasting is to enhance the accuracy, speed, and reliability of predictions. This involves developing quantum algorithms tailored to process and analyze vast datasets from various sources, including satellite imagery, seismic sensors, and atmospheric measurements. By improving the resolution and timeliness of forecasts, quantum-powered systems aim to provide earlier warnings for events such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and tsunamis.
Another crucial goal is to enable more comprehensive risk assessments by simulating complex scenarios that are computationally infeasible with classical systems. This could lead to better understanding of long-term climate trends and their impact on disaster frequency and severity. Additionally, quantum computing seeks to optimize resource allocation and emergency response strategies by rapidly evaluating multiple scenarios and outcomes.
The integration of quantum computing with machine learning and artificial intelligence presents another exciting frontier. Quantum machine learning algorithms have the potential to identify subtle patterns and correlations in historical disaster data that might elude classical analysis, potentially uncovering new predictive indicators.
As research progresses, the field aims to overcome current limitations in quantum hardware, such as error rates and qubit stability, to realize the full potential of quantum computing in disaster prediction. The ultimate vision is to create a global, quantum-enhanced early warning system that significantly reduces the human and economic toll of natural disasters through vastly improved forecasting capabilities.
Market Analysis for Quantum-Enhanced Disaster Forecasting
The market for quantum-enhanced disaster forecasting is poised for significant growth as the potential of quantum computing in predicting and mitigating natural disasters becomes increasingly apparent. This emerging sector sits at the intersection of quantum technology, environmental science, and disaster management, offering a promising avenue for addressing the growing challenges posed by climate change and extreme weather events.
Current market estimates suggest that the global disaster management market, which includes forecasting and early warning systems, is valued at approximately $107 billion and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% through 2025. While quantum-enhanced forecasting represents a small fraction of this market at present, it is anticipated to be a key driver of growth in the coming years.
The demand for more accurate and timely disaster predictions is being fueled by the increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters worldwide. In 2020 alone, natural disasters caused economic losses of $210 billion globally, highlighting the urgent need for improved forecasting capabilities. Quantum computing's potential to process vast amounts of complex climate data and run sophisticated simulations could significantly enhance the accuracy and lead time of disaster predictions, potentially saving lives and reducing economic losses.
Key market segments that are likely to benefit from quantum-enhanced disaster forecasting include government agencies responsible for emergency management, insurance companies seeking to better assess and price risk, and industries highly vulnerable to natural disasters such as agriculture, energy, and transportation. The public sector is expected to be the primary driver of initial market growth, with governments worldwide investing in quantum technologies to bolster their disaster preparedness capabilities.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently leading in quantum computing research and development, positioning them at the forefront of the quantum-enhanced disaster forecasting market. However, Asia-Pacific countries, particularly China and Japan, are making significant investments in quantum technologies and are expected to be major players in this market as it matures.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces several challenges. The high cost of quantum computing infrastructure, the scarcity of skilled personnel, and the need for further technological advancements to achieve practical quantum advantage in disaster forecasting are significant barriers to widespread adoption. Additionally, the market must navigate complex regulatory landscapes and address concerns about data privacy and security.
As the technology progresses and becomes more accessible, we can expect to see a gradual integration of quantum-enhanced forecasting into existing disaster management systems. This integration will likely drive the development of new products and services, creating opportunities for both established players in the quantum computing and disaster management sectors, as well as innovative startups focusing on niche applications of quantum technologies in environmental monitoring and prediction.
Current market estimates suggest that the global disaster management market, which includes forecasting and early warning systems, is valued at approximately $107 billion and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.3% through 2025. While quantum-enhanced forecasting represents a small fraction of this market at present, it is anticipated to be a key driver of growth in the coming years.
The demand for more accurate and timely disaster predictions is being fueled by the increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters worldwide. In 2020 alone, natural disasters caused economic losses of $210 billion globally, highlighting the urgent need for improved forecasting capabilities. Quantum computing's potential to process vast amounts of complex climate data and run sophisticated simulations could significantly enhance the accuracy and lead time of disaster predictions, potentially saving lives and reducing economic losses.
Key market segments that are likely to benefit from quantum-enhanced disaster forecasting include government agencies responsible for emergency management, insurance companies seeking to better assess and price risk, and industries highly vulnerable to natural disasters such as agriculture, energy, and transportation. The public sector is expected to be the primary driver of initial market growth, with governments worldwide investing in quantum technologies to bolster their disaster preparedness capabilities.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently leading in quantum computing research and development, positioning them at the forefront of the quantum-enhanced disaster forecasting market. However, Asia-Pacific countries, particularly China and Japan, are making significant investments in quantum technologies and are expected to be major players in this market as it matures.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces several challenges. The high cost of quantum computing infrastructure, the scarcity of skilled personnel, and the need for further technological advancements to achieve practical quantum advantage in disaster forecasting are significant barriers to widespread adoption. Additionally, the market must navigate complex regulatory landscapes and address concerns about data privacy and security.
As the technology progresses and becomes more accessible, we can expect to see a gradual integration of quantum-enhanced forecasting into existing disaster management systems. This integration will likely drive the development of new products and services, creating opportunities for both established players in the quantum computing and disaster management sectors, as well as innovative startups focusing on niche applications of quantum technologies in environmental monitoring and prediction.
Current Challenges in Quantum-Based Natural Disaster Prediction
The integration of quantum computing into natural disaster prediction presents significant challenges that researchers and technologists are actively working to overcome. One of the primary obstacles is the current limitation in quantum hardware capabilities. While quantum computers have shown promise in solving complex problems, they are still in their infancy when it comes to practical applications in disaster forecasting. The quantum systems available today lack the stability and scale required to process the vast amounts of data involved in climate and weather modeling.
Another major challenge lies in the development of quantum algorithms specifically tailored for natural disaster prediction. Traditional forecasting models rely heavily on classical computing methods, and translating these into quantum-compatible algorithms is a complex task. Researchers are grappling with the need to reformulate existing prediction models to harness the unique properties of quantum systems, such as superposition and entanglement, effectively.
Data integration and management pose additional hurdles in quantum-based disaster prediction. The sheer volume and variety of data sources involved in forecasting natural disasters, including satellite imagery, weather station readings, and historical climate data, require sophisticated quantum data handling techniques that are still in early stages of development. Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of quantum computations when dealing with such diverse and extensive datasets remains a significant challenge.
The issue of error correction in quantum systems is particularly critical for disaster prediction applications. Quantum bits (qubits) are highly sensitive to environmental disturbances, leading to decoherence and errors in computations. Developing robust error correction methods is essential to ensure the reliability of quantum-based predictions, especially given the high stakes involved in natural disaster forecasting.
Furthermore, the interdisciplinary nature of quantum-based disaster prediction demands collaboration between quantum physicists, climate scientists, and disaster management experts. Bridging the knowledge gap between these fields and fostering effective communication and cooperation is a ongoing challenge that impacts the progress of quantum applications in this domain.
Lastly, the high cost and technical complexity of quantum computing systems present barriers to widespread adoption in disaster prediction. Many organizations involved in disaster management and forecasting may lack the resources or expertise to implement and maintain quantum-based solutions, limiting the practical application of this technology in real-world scenarios.
Another major challenge lies in the development of quantum algorithms specifically tailored for natural disaster prediction. Traditional forecasting models rely heavily on classical computing methods, and translating these into quantum-compatible algorithms is a complex task. Researchers are grappling with the need to reformulate existing prediction models to harness the unique properties of quantum systems, such as superposition and entanglement, effectively.
Data integration and management pose additional hurdles in quantum-based disaster prediction. The sheer volume and variety of data sources involved in forecasting natural disasters, including satellite imagery, weather station readings, and historical climate data, require sophisticated quantum data handling techniques that are still in early stages of development. Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of quantum computations when dealing with such diverse and extensive datasets remains a significant challenge.
The issue of error correction in quantum systems is particularly critical for disaster prediction applications. Quantum bits (qubits) are highly sensitive to environmental disturbances, leading to decoherence and errors in computations. Developing robust error correction methods is essential to ensure the reliability of quantum-based predictions, especially given the high stakes involved in natural disaster forecasting.
Furthermore, the interdisciplinary nature of quantum-based disaster prediction demands collaboration between quantum physicists, climate scientists, and disaster management experts. Bridging the knowledge gap between these fields and fostering effective communication and cooperation is a ongoing challenge that impacts the progress of quantum applications in this domain.
Lastly, the high cost and technical complexity of quantum computing systems present barriers to widespread adoption in disaster prediction. Many organizations involved in disaster management and forecasting may lack the resources or expertise to implement and maintain quantum-based solutions, limiting the practical application of this technology in real-world scenarios.
Existing Quantum Solutions for Natural Disaster Prediction
01 Quantum-enhanced forecasting algorithms
Quantum computing techniques are applied to enhance forecasting algorithms, potentially improving accuracy in various fields such as finance, weather prediction, and market trends. These algorithms leverage quantum superposition and entanglement to process complex data sets more efficiently than classical methods, potentially leading to more accurate and timely predictions.- Quantum-enhanced forecasting algorithms: Quantum computing techniques are applied to enhance forecasting algorithms, potentially improving accuracy in various fields such as finance, weather prediction, and market trends. These algorithms leverage quantum superposition and entanglement to process complex data sets more efficiently than classical methods.
- Hybrid quantum-classical systems for prediction: Combining quantum and classical computing approaches creates hybrid systems that can optimize forecasting accuracy. These systems utilize the strengths of both quantum and classical architectures to handle different aspects of the prediction process, potentially leading to more robust and accurate forecasts.
- Quantum machine learning for improved forecasting: Quantum machine learning algorithms are developed to enhance forecasting accuracy. These algorithms can process high-dimensional data more efficiently, potentially uncovering patterns and relationships that classical machine learning methods might miss, leading to more accurate predictions in complex systems.
- Error correction and noise mitigation in quantum forecasting: Techniques for error correction and noise mitigation in quantum systems are crucial for improving the accuracy of quantum-based forecasting. These methods aim to reduce the impact of quantum decoherence and other sources of error, thereby enhancing the reliability and precision of quantum forecasting algorithms.
- Quantum-inspired classical algorithms for forecasting: Classical algorithms inspired by quantum computing principles are developed to improve forecasting accuracy. These algorithms mimic certain aspects of quantum computation on classical hardware, potentially offering some of the benefits of quantum approaches without requiring actual quantum hardware.
02 Hybrid quantum-classical systems for forecasting
Combining quantum and classical computing resources creates hybrid systems that can optimize forecasting accuracy. These systems utilize quantum processors for specific computationally intensive tasks while leveraging classical infrastructure for data preparation and result interpretation, potentially offering a balance between quantum advantages and practical implementation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Quantum machine learning for predictive analytics
Quantum machine learning algorithms are developed to enhance predictive analytics capabilities. These approaches use quantum circuits to process and analyze large datasets, potentially uncovering patterns and correlations that classical machine learning might miss, thereby improving the accuracy of forecasts and predictions across various domains.Expand Specific Solutions04 Error mitigation in quantum forecasting
Techniques are developed to mitigate errors in quantum forecasting systems, addressing challenges such as decoherence and gate errors. These methods aim to improve the reliability and accuracy of quantum-based predictions by reducing noise and enhancing the stability of quantum computations used in forecasting models.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quantum-inspired classical algorithms for forecasting
Classical algorithms inspired by quantum computing principles are developed to enhance forecasting accuracy. These algorithms simulate certain aspects of quantum behavior on classical hardware, potentially offering improved performance over traditional forecasting methods without requiring actual quantum hardware, making them more accessible for immediate implementation.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Quantum Computing and Disaster Forecasting
The quantum computing landscape for forecasting natural disasters is in its early stages, with significant potential for growth. The market size is expanding as governments and organizations recognize the need for more accurate predictions. Technologically, it's still evolving, with companies like Google, Intel, and Amazon leading research efforts. Origin Quantum and Equal1 Labs are developing specialized quantum hardware, while established players like IBM and Microsoft are integrating quantum algorithms into their existing forecasting models. Universities such as Zhejiang University and the University of Chicago are contributing fundamental research. The field is characterized by a mix of tech giants, startups, and academic institutions collaborating to overcome technical challenges and realize practical applications.
Amazon Technologies, Inc.
Technical Solution: Amazon is leveraging its cloud infrastructure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), to develop quantum computing solutions for natural disaster forecasting. The company's Amazon Braket service provides a development environment for creating and testing quantum algorithms[4]. For disaster prediction, Amazon is focusing on hybrid quantum-classical approaches, where quantum computers handle specific complex calculations while classical systems manage data preprocessing and result interpretation. This hybrid model aims to improve the speed and accuracy of simulations for phenomena like extreme weather events and seismic activities[5]. Amazon is also investing in the development of error-corrected quantum systems, which could significantly enhance the reliability of long-term disaster predictions[6].
Strengths: Robust cloud infrastructure, extensive data centers, and expertise in large-scale data processing. Weaknesses: Relatively new entrant in quantum hardware development compared to some competitors.
Origin Quantum Computing Technology (Hefei) Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Origin Quantum, a leading Chinese quantum computing company, is developing superconducting quantum chips and full-stack quantum computing systems[10]. For natural disaster forecasting, the company is focusing on quantum algorithms that can efficiently process and analyze large-scale geospatial and meteorological data. Origin Quantum is collaborating with Chinese meteorological agencies to integrate quantum computing capabilities into existing weather forecasting models, potentially improving the accuracy of typhoon and flood predictions[11]. The company is also exploring the application of quantum machine learning techniques to identify subtle patterns in historical disaster data that might be missed by classical methods[12].
Strengths: Strong government support, close collaboration with Chinese research institutions. Weaknesses: Limited international partnerships, potential geopolitical challenges in global market access.
Core Quantum Algorithms for Improved Disaster Forecasting
Numerical weather forecasting method and device, storage medium, and electronic device
PatentWO2024088092A1
Innovation
- Using quantum computing methods, by constructing quantum circuits used to solve the weather evolution process, obtain the initial values of the variables to be forecast and run the quantum circuits to obtain predicted values, using the characteristics of quantum computing to accelerate calculations.
Natural disaster prediction and early warning systems
PatentPendingIN202311084560A
Innovation
- The integration of quantum sensors, Quantum Computing, Neuro-Inspired Computing, Biological Sensors, Smart Dust Sensors, and a Public Alert System using Augmented Reality, which collectively provide real-time data analysis and location-specific alerts, enhancing predictive analytics and enabling proactive disaster mitigation.
Environmental Impact of Quantum-Enhanced Disaster Forecasting
The environmental impact of quantum-enhanced disaster forecasting is multifaceted and potentially far-reaching. By leveraging the power of quantum computing, scientists and meteorologists can significantly improve the accuracy and timeliness of natural disaster predictions. This enhanced forecasting capability has profound implications for environmental management and disaster preparedness.
One of the primary environmental benefits of quantum-enhanced disaster forecasting is the potential reduction in the overall impact of natural disasters. With more precise predictions, authorities can implement targeted evacuation plans and preventive measures, minimizing the destruction of natural habitats and ecosystems. For instance, in the case of wildfires, early and accurate predictions can allow for more effective containment strategies, potentially saving vast areas of forest and wildlife.
Quantum computing's ability to process complex climate models at unprecedented speeds enables a more comprehensive understanding of long-term environmental trends. This improved modeling can lead to better-informed policies on climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies. By providing a clearer picture of future environmental scenarios, quantum-enhanced forecasting can guide sustainable development practices and resource management.
The increased accuracy in predicting extreme weather events can also contribute to more efficient resource allocation. For example, water management systems can be optimized based on precise rainfall predictions, reducing water waste and improving agricultural practices. This optimization extends to energy consumption as well, as power grids can be better prepared for sudden spikes or drops in demand due to extreme weather conditions.
Moreover, quantum-enhanced disaster forecasting can play a crucial role in preserving biodiversity. By providing advanced warning of events like hurricanes or tsunamis, conservation efforts can be mobilized to protect vulnerable species and habitats. This proactive approach to environmental protection could be instrumental in maintaining ecological balance in the face of increasing climate-related challenges.
The improved forecasting capabilities also have implications for urban planning and infrastructure development. Cities can be designed or retrofitted with a better understanding of future environmental risks, leading to more resilient and sustainable urban environments. This foresight can help in reducing the long-term environmental impact of human settlements, particularly in coastal areas or regions prone to natural disasters.
However, it is important to note that while quantum-enhanced disaster forecasting offers significant environmental benefits, it also raises questions about energy consumption. Quantum computers currently require substantial energy to operate and maintain, which could potentially offset some of the environmental gains. As the technology evolves, addressing this energy efficiency challenge will be crucial to maximizing the net positive environmental impact of quantum-enhanced forecasting systems.
One of the primary environmental benefits of quantum-enhanced disaster forecasting is the potential reduction in the overall impact of natural disasters. With more precise predictions, authorities can implement targeted evacuation plans and preventive measures, minimizing the destruction of natural habitats and ecosystems. For instance, in the case of wildfires, early and accurate predictions can allow for more effective containment strategies, potentially saving vast areas of forest and wildlife.
Quantum computing's ability to process complex climate models at unprecedented speeds enables a more comprehensive understanding of long-term environmental trends. This improved modeling can lead to better-informed policies on climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies. By providing a clearer picture of future environmental scenarios, quantum-enhanced forecasting can guide sustainable development practices and resource management.
The increased accuracy in predicting extreme weather events can also contribute to more efficient resource allocation. For example, water management systems can be optimized based on precise rainfall predictions, reducing water waste and improving agricultural practices. This optimization extends to energy consumption as well, as power grids can be better prepared for sudden spikes or drops in demand due to extreme weather conditions.
Moreover, quantum-enhanced disaster forecasting can play a crucial role in preserving biodiversity. By providing advanced warning of events like hurricanes or tsunamis, conservation efforts can be mobilized to protect vulnerable species and habitats. This proactive approach to environmental protection could be instrumental in maintaining ecological balance in the face of increasing climate-related challenges.
The improved forecasting capabilities also have implications for urban planning and infrastructure development. Cities can be designed or retrofitted with a better understanding of future environmental risks, leading to more resilient and sustainable urban environments. This foresight can help in reducing the long-term environmental impact of human settlements, particularly in coastal areas or regions prone to natural disasters.
However, it is important to note that while quantum-enhanced disaster forecasting offers significant environmental benefits, it also raises questions about energy consumption. Quantum computers currently require substantial energy to operate and maintain, which could potentially offset some of the environmental gains. As the technology evolves, addressing this energy efficiency challenge will be crucial to maximizing the net positive environmental impact of quantum-enhanced forecasting systems.
Ethical Implications of Quantum-Based Disaster Prediction
The integration of quantum computing into disaster prediction systems raises significant ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed. As these advanced forecasting capabilities become more precise and far-reaching, they have the potential to dramatically alter how societies prepare for and respond to natural disasters. One primary ethical concern is the equitable distribution of this technology's benefits. Developed nations with greater resources may gain earlier access to quantum-enhanced prediction systems, potentially exacerbating existing global inequalities in disaster preparedness and response.
Privacy and data security present another critical ethical challenge. Quantum-based disaster prediction may require the processing of vast amounts of personal and environmental data, raising questions about data ownership, consent, and the potential for misuse. Striking a balance between the public good of improved disaster forecasting and individual privacy rights will be crucial.
The increased accuracy of quantum-enhanced predictions could also lead to ethical dilemmas in decision-making processes. Policymakers and emergency responders may face difficult choices when acting on highly precise forecasts, particularly in scenarios where evacuation or resource allocation decisions could have significant economic or social impacts. The potential for false positives or negatives, even if reduced, still exists and could lead to issues of accountability and trust in the technology.
There are also concerns about the potential militarization of quantum-based disaster prediction technology. The strategic advantages offered by superior forecasting capabilities could be exploited for geopolitical gain, potentially destabilizing international relations or exacerbating conflicts over resources in disaster-prone regions.
Furthermore, the reliance on quantum-enhanced prediction systems may lead to a reduction in traditional disaster preparedness measures and local knowledge, potentially increasing vulnerability if these systems were to fail or be compromised. Maintaining a balance between technological advancement and preserving diverse approaches to disaster resilience is essential.
Lastly, the ethical implications extend to the realm of public communication and media responsibility. The dissemination of highly accurate disaster predictions could lead to panic or complacency, depending on how the information is presented and interpreted. Developing ethical guidelines for communicating quantum-based forecasts to the public will be crucial in ensuring responsible use of this powerful technology.
Privacy and data security present another critical ethical challenge. Quantum-based disaster prediction may require the processing of vast amounts of personal and environmental data, raising questions about data ownership, consent, and the potential for misuse. Striking a balance between the public good of improved disaster forecasting and individual privacy rights will be crucial.
The increased accuracy of quantum-enhanced predictions could also lead to ethical dilemmas in decision-making processes. Policymakers and emergency responders may face difficult choices when acting on highly precise forecasts, particularly in scenarios where evacuation or resource allocation decisions could have significant economic or social impacts. The potential for false positives or negatives, even if reduced, still exists and could lead to issues of accountability and trust in the technology.
There are also concerns about the potential militarization of quantum-based disaster prediction technology. The strategic advantages offered by superior forecasting capabilities could be exploited for geopolitical gain, potentially destabilizing international relations or exacerbating conflicts over resources in disaster-prone regions.
Furthermore, the reliance on quantum-enhanced prediction systems may lead to a reduction in traditional disaster preparedness measures and local knowledge, potentially increasing vulnerability if these systems were to fail or be compromised. Maintaining a balance between technological advancement and preserving diverse approaches to disaster resilience is essential.
Lastly, the ethical implications extend to the realm of public communication and media responsibility. The dissemination of highly accurate disaster predictions could lead to panic or complacency, depending on how the information is presented and interpreted. Developing ethical guidelines for communicating quantum-based forecasts to the public will be crucial in ensuring responsible use of this powerful technology.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!