Quantum Computing in Streamlining Global Commerce Operations
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Quantum Computing in Commerce: Background and Objectives
Quantum computing represents a revolutionary paradigm in information processing, leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics to perform complex calculations at unprecedented speeds. In the context of global commerce operations, this emerging technology holds immense potential to streamline and optimize various aspects of international trade, supply chain management, and financial transactions.
The evolution of quantum computing can be traced back to the early 1980s when physicist Richard Feynman proposed the idea of using quantum systems to simulate quantum phenomena. Since then, the field has progressed rapidly, with significant milestones achieved in the development of quantum hardware, algorithms, and applications. The current state of quantum computing is characterized by the transition from theoretical concepts to practical implementations, with several tech giants and startups actively pursuing quantum supremacy.
In the realm of global commerce, the objectives of quantum computing research are multifaceted. Primarily, it aims to address the computational limitations faced by classical systems in handling the complexity and scale of international trade operations. This includes optimizing logistics networks, enhancing cryptographic security for financial transactions, and improving predictive analytics for market trends and consumer behavior.
One of the key goals is to develop quantum algorithms capable of solving optimization problems that are currently intractable for classical computers. These algorithms could revolutionize supply chain management by efficiently calculating optimal routes, inventory levels, and resource allocation across global networks. Additionally, quantum computing seeks to enhance the speed and security of cross-border financial transactions, potentially transforming the landscape of international payments and settlements.
Another critical objective is to harness quantum computing's potential in data analysis and machine learning. By processing vast amounts of market data at unprecedented speeds, quantum systems could provide more accurate and timely insights into global economic trends, enabling businesses to make better-informed decisions and adapt swiftly to market changes.
The integration of quantum computing into commerce operations also aims to address the growing concerns of cybersecurity in international trade. Quantum-resistant cryptography and secure communication protocols are being developed to safeguard sensitive commercial data against the threat of future quantum attacks.
As research in this field progresses, the ultimate goal is to create a quantum-enhanced global commerce ecosystem that is more efficient, secure, and responsive to the complexities of international trade. This involves not only technological advancements but also the development of new standards, regulations, and collaborative frameworks to ensure the responsible and equitable implementation of quantum technologies in the global marketplace.
The evolution of quantum computing can be traced back to the early 1980s when physicist Richard Feynman proposed the idea of using quantum systems to simulate quantum phenomena. Since then, the field has progressed rapidly, with significant milestones achieved in the development of quantum hardware, algorithms, and applications. The current state of quantum computing is characterized by the transition from theoretical concepts to practical implementations, with several tech giants and startups actively pursuing quantum supremacy.
In the realm of global commerce, the objectives of quantum computing research are multifaceted. Primarily, it aims to address the computational limitations faced by classical systems in handling the complexity and scale of international trade operations. This includes optimizing logistics networks, enhancing cryptographic security for financial transactions, and improving predictive analytics for market trends and consumer behavior.
One of the key goals is to develop quantum algorithms capable of solving optimization problems that are currently intractable for classical computers. These algorithms could revolutionize supply chain management by efficiently calculating optimal routes, inventory levels, and resource allocation across global networks. Additionally, quantum computing seeks to enhance the speed and security of cross-border financial transactions, potentially transforming the landscape of international payments and settlements.
Another critical objective is to harness quantum computing's potential in data analysis and machine learning. By processing vast amounts of market data at unprecedented speeds, quantum systems could provide more accurate and timely insights into global economic trends, enabling businesses to make better-informed decisions and adapt swiftly to market changes.
The integration of quantum computing into commerce operations also aims to address the growing concerns of cybersecurity in international trade. Quantum-resistant cryptography and secure communication protocols are being developed to safeguard sensitive commercial data against the threat of future quantum attacks.
As research in this field progresses, the ultimate goal is to create a quantum-enhanced global commerce ecosystem that is more efficient, secure, and responsive to the complexities of international trade. This involves not only technological advancements but also the development of new standards, regulations, and collaborative frameworks to ensure the responsible and equitable implementation of quantum technologies in the global marketplace.
Market Demand Analysis for Quantum-Enhanced Commerce
The global market for quantum-enhanced commerce solutions is experiencing rapid growth, driven by the increasing complexity of international trade operations and the need for more efficient supply chain management. As businesses seek to streamline their global commerce operations, quantum computing offers unprecedented capabilities in optimization, data analysis, and secure transactions.
The demand for quantum-enhanced commerce solutions is particularly strong in sectors such as logistics, finance, and e-commerce. These industries face challenges in managing vast amounts of data, optimizing complex supply chains, and ensuring secure transactions across borders. Quantum computing's ability to process massive datasets and solve complex optimization problems in real-time makes it an attractive solution for addressing these challenges.
In the logistics sector, there is a growing need for quantum-enhanced route optimization and inventory management systems. Companies are looking to reduce transportation costs, minimize delivery times, and improve overall supply chain efficiency. Quantum algorithms have shown promise in solving complex routing problems exponentially faster than classical computers, potentially revolutionizing logistics operations.
The financial industry is another key driver of market demand for quantum-enhanced commerce solutions. Banks and financial institutions are exploring quantum computing applications for risk assessment, fraud detection, and high-frequency trading. The ability of quantum computers to analyze vast amounts of financial data and perform complex simulations in real-time could lead to more accurate risk models and faster trading decisions.
E-commerce platforms are also showing interest in quantum-enhanced solutions to improve personalized recommendations, optimize pricing strategies, and enhance cybersecurity. As online transactions continue to grow globally, the need for secure and efficient e-commerce operations becomes increasingly critical.
The market for quantum-enhanced commerce solutions is expected to expand significantly in the coming years. While exact market size predictions vary due to the nascent nature of quantum technologies, industry analysts project substantial growth. Factors contributing to this growth include increasing investments in quantum research and development, advancements in quantum hardware, and the growing awareness of quantum computing's potential among businesses.
However, the adoption of quantum-enhanced commerce solutions faces challenges such as the high cost of quantum hardware, the need for specialized skills, and the current limitations of quantum technologies. Despite these obstacles, the potential benefits of quantum computing in streamlining global commerce operations continue to drive market demand and investment in this field.
The demand for quantum-enhanced commerce solutions is particularly strong in sectors such as logistics, finance, and e-commerce. These industries face challenges in managing vast amounts of data, optimizing complex supply chains, and ensuring secure transactions across borders. Quantum computing's ability to process massive datasets and solve complex optimization problems in real-time makes it an attractive solution for addressing these challenges.
In the logistics sector, there is a growing need for quantum-enhanced route optimization and inventory management systems. Companies are looking to reduce transportation costs, minimize delivery times, and improve overall supply chain efficiency. Quantum algorithms have shown promise in solving complex routing problems exponentially faster than classical computers, potentially revolutionizing logistics operations.
The financial industry is another key driver of market demand for quantum-enhanced commerce solutions. Banks and financial institutions are exploring quantum computing applications for risk assessment, fraud detection, and high-frequency trading. The ability of quantum computers to analyze vast amounts of financial data and perform complex simulations in real-time could lead to more accurate risk models and faster trading decisions.
E-commerce platforms are also showing interest in quantum-enhanced solutions to improve personalized recommendations, optimize pricing strategies, and enhance cybersecurity. As online transactions continue to grow globally, the need for secure and efficient e-commerce operations becomes increasingly critical.
The market for quantum-enhanced commerce solutions is expected to expand significantly in the coming years. While exact market size predictions vary due to the nascent nature of quantum technologies, industry analysts project substantial growth. Factors contributing to this growth include increasing investments in quantum research and development, advancements in quantum hardware, and the growing awareness of quantum computing's potential among businesses.
However, the adoption of quantum-enhanced commerce solutions faces challenges such as the high cost of quantum hardware, the need for specialized skills, and the current limitations of quantum technologies. Despite these obstacles, the potential benefits of quantum computing in streamlining global commerce operations continue to drive market demand and investment in this field.
Current Quantum Computing Challenges in Global Trade
Quantum computing presents significant challenges when applied to global trade operations. One of the primary obstacles is the current limitation in qubit coherence time. While quantum computers have shown promise in solving complex optimization problems, the instability of qubits due to environmental interference restricts the duration and complexity of calculations that can be performed. This limitation hinders the ability to process large-scale global trade data effectively.
Another challenge lies in the error rates of quantum gates. Despite advancements in quantum error correction techniques, the high error rates in quantum operations still pose a significant barrier to achieving reliable results for intricate global trade algorithms. This issue becomes particularly pronounced when dealing with the vast and diverse datasets typical in international commerce.
The scalability of quantum systems also remains a critical challenge. Current quantum computers have a limited number of qubits, which constrains their ability to handle the multifaceted nature of global trade operations. Scaling up quantum systems while maintaining coherence and reducing error rates is a complex engineering feat that researchers are still grappling with.
Furthermore, the integration of quantum computing with classical systems presents a substantial hurdle. Global trade relies heavily on existing classical infrastructure, and creating seamless interfaces between quantum and classical systems is crucial for practical implementation. This integration challenge extends to developing hybrid algorithms that can leverage the strengths of both quantum and classical computing paradigms.
The lack of standardization in quantum hardware and software architectures also impedes progress in applying quantum computing to global trade. Different quantum computing approaches, such as superconducting qubits, trapped ions, and topological qubits, each have their own strengths and limitations. This diversity complicates the development of universal quantum software solutions for global trade applications.
Additionally, the shortage of quantum computing expertise in the global trade sector poses a significant challenge. The field requires a unique blend of skills in quantum physics, computer science, and domain-specific knowledge of international commerce. Bridging this skills gap is essential for effectively leveraging quantum computing in streamlining global trade operations.
Lastly, the high costs associated with quantum computing research and development present a barrier to widespread adoption in the global trade sector. The expensive infrastructure required for quantum systems, coupled with the uncertain timeline for achieving practical quantum advantage, makes it challenging for many organizations to justify significant investments in this technology for trade applications.
Another challenge lies in the error rates of quantum gates. Despite advancements in quantum error correction techniques, the high error rates in quantum operations still pose a significant barrier to achieving reliable results for intricate global trade algorithms. This issue becomes particularly pronounced when dealing with the vast and diverse datasets typical in international commerce.
The scalability of quantum systems also remains a critical challenge. Current quantum computers have a limited number of qubits, which constrains their ability to handle the multifaceted nature of global trade operations. Scaling up quantum systems while maintaining coherence and reducing error rates is a complex engineering feat that researchers are still grappling with.
Furthermore, the integration of quantum computing with classical systems presents a substantial hurdle. Global trade relies heavily on existing classical infrastructure, and creating seamless interfaces between quantum and classical systems is crucial for practical implementation. This integration challenge extends to developing hybrid algorithms that can leverage the strengths of both quantum and classical computing paradigms.
The lack of standardization in quantum hardware and software architectures also impedes progress in applying quantum computing to global trade. Different quantum computing approaches, such as superconducting qubits, trapped ions, and topological qubits, each have their own strengths and limitations. This diversity complicates the development of universal quantum software solutions for global trade applications.
Additionally, the shortage of quantum computing expertise in the global trade sector poses a significant challenge. The field requires a unique blend of skills in quantum physics, computer science, and domain-specific knowledge of international commerce. Bridging this skills gap is essential for effectively leveraging quantum computing in streamlining global trade operations.
Lastly, the high costs associated with quantum computing research and development present a barrier to widespread adoption in the global trade sector. The expensive infrastructure required for quantum systems, coupled with the uncertain timeline for achieving practical quantum advantage, makes it challenging for many organizations to justify significant investments in this technology for trade applications.
Existing Quantum Solutions for Commerce Streamlining
01 Quantum Circuit Design and Optimization
This area focuses on developing and optimizing quantum circuits for various applications. It involves creating efficient quantum gate sequences, reducing circuit depth, and improving qubit utilization. Techniques may include circuit compression, gate decomposition, and topology-aware mapping to enhance the performance of quantum algorithms on real quantum hardware.- Quantum Computing Architectures: This category focuses on the design and implementation of quantum computing systems. It includes innovations in qubit arrangements, circuit layouts, and overall system architectures to improve quantum computation efficiency and scalability.
- Error Correction and Fault Tolerance: This area addresses the challenges of maintaining quantum coherence and mitigating errors in quantum systems. It involves techniques for error detection, correction, and fault-tolerant quantum computation to enhance the reliability of quantum operations.
- Quantum Algorithms and Applications: This category covers the development of quantum algorithms for various computational problems and their practical applications. It includes innovations in quantum simulation, optimization, machine learning, and cryptography using quantum systems.
- Quantum-Classical Hybrid Systems: This area focuses on integrating quantum and classical computing technologies. It includes methods for interfacing quantum and classical systems, hybrid algorithms, and architectures that leverage the strengths of both paradigms for enhanced computational capabilities.
- Quantum Hardware and Control: This category encompasses innovations in quantum hardware components and control systems. It includes advancements in qubit technologies, quantum gates, readout mechanisms, and precise control techniques for manipulating quantum states and operations.
02 Error Correction and Fault Tolerance
Error correction and fault tolerance are crucial for building reliable quantum computers. This field involves developing techniques to detect and correct quantum errors, designing fault-tolerant quantum gates, and creating error-resistant quantum memory. Strategies may include surface codes, topological quantum computing, and magic state distillation to mitigate the effects of decoherence and noise in quantum systems.Expand Specific Solutions03 Quantum-Classical Hybrid Algorithms
Hybrid algorithms combine classical and quantum computing to leverage the strengths of both paradigms. This approach involves developing algorithms that use quantum processors for specific subroutines while relying on classical computers for other parts of the computation. Examples include variational quantum eigensolvers and quantum approximate optimization algorithms, which are particularly useful for near-term quantum devices with limited qubit counts and coherence times.Expand Specific Solutions04 Quantum Machine Learning
Quantum machine learning explores the intersection of quantum computing and machine learning. This field aims to develop quantum algorithms for tasks such as classification, clustering, and pattern recognition. It includes quantum neural networks, quantum support vector machines, and quantum principal component analysis. The goal is to achieve quantum speedups for certain machine learning tasks and to explore new learning paradigms enabled by quantum mechanics.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quantum Hardware Architectures
This area focuses on designing and implementing physical quantum computing systems. It involves research into various qubit technologies such as superconducting circuits, trapped ions, and topological qubits. Key aspects include improving qubit coherence times, developing scalable qubit coupling mechanisms, and creating integrated control and readout systems. The goal is to build larger and more reliable quantum processors capable of supporting complex quantum algorithms.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Quantum Computing for Global Trade
The quantum computing landscape in global commerce operations is rapidly evolving, with the industry currently in its early growth stage. The market size is expanding, driven by increasing investments and technological advancements. While still in its nascent phase, the technology's maturity is progressing, with key players like IBM, Google, and Microsoft leading research and development efforts. Companies such as D-Wave Systems and Zapata Computing are focusing on specialized quantum solutions for commerce applications. Origin Quantum and Huawei are emerging as significant players in the Asian market, while established tech giants like Intel and Amazon are also investing heavily in quantum technologies. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both pure-play quantum companies and traditional tech firms vying for market share in this transformative field.
D-Wave Systems, Inc.
Technical Solution: D-Wave specializes in quantum annealing technology, which is particularly suited for optimization problems in global commerce. Their latest Advantage™ system, with over 5000 qubits, is designed to solve complex supply chain, logistics, and financial modeling problems [7]. D-Wave's hybrid solver service combines quantum and classical resources to tackle larger-scale commercial problems. They have demonstrated applications in portfolio optimization, freight logistics, and manufacturing process optimization, directly applicable to streamlining global commerce operations [8].
Strengths: Large-scale quantum annealing systems, commercially available quantum cloud service, and focus on practical business applications. Weaknesses: Limited to specific types of optimization problems, not suitable for all quantum computing tasks.
International Business Machines Corp.
Technical Solution: IBM's quantum computing approach for streamlining global commerce operations focuses on developing high-qubit systems and quantum-classical hybrid algorithms. Their latest 433-qubit 'Osprey' processor [1] demonstrates significant progress in scaling quantum systems. IBM's Qiskit Runtime containerized quantum computing service allows for improved workload orchestration and reduced latency in quantum-classical communication [2]. They are also exploring quantum machine learning techniques for supply chain optimization and financial risk analysis, potentially revolutionizing global trade logistics and financial operations [3].
Strengths: Industry-leading qubit count, robust quantum software ecosystem, and strong partnerships with global enterprises. Weaknesses: Quantum systems still require extreme cooling, limiting widespread deployment in diverse commerce environments.
Core Quantum Innovations for Trade Optimization
Machine learning and computer-based generation of standard work matrices for improving execution of a standard work
PatentActiveUS12106180B2
Innovation
- The use of quantum computing and machine learning algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data, identify areas for improvement, and generate standard work matrices that optimize processes, leveraging quantum processors to analyze manufacturing metrics, fault codes, and feedback data to pinpoint the most critical issues and implement targeted improvements.
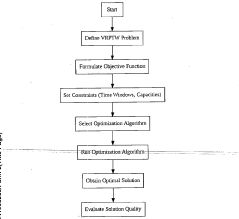
Quantum parallelism for real-time route optimization in supply chains
PatentPendingIN202441008263A
Innovation
- A quantum computing algorithm utilizing superposition, quantum gates like the Grover diffusion operator and Hadamard gate, and a quantum oracle to encode VRPTW, enabling simultaneous exploration of multiple solutions and amplifying viable routes, thereby overcoming scalability problems and improving computational efficiency.
Quantum Computing Security Implications for Trade
The integration of quantum computing into global commerce operations brings significant security implications that must be carefully considered. As quantum computers become more powerful, they pose a potential threat to current cryptographic systems that secure international trade transactions. The ability of quantum computers to solve complex mathematical problems exponentially faster than classical computers could render many existing encryption methods obsolete, potentially compromising sensitive trade data and financial information.
One of the primary concerns is the vulnerability of widely-used public-key cryptography systems, such as RSA and ECC, to quantum attacks. These systems form the backbone of secure communications and digital signatures in global trade. Quantum computers, leveraging algorithms like Shor's algorithm, could theoretically break these cryptographic systems, exposing confidential trade agreements, intellectual property, and financial transactions to unauthorized access.
To address these security challenges, the development and implementation of quantum-resistant cryptography is crucial. Post-quantum cryptography (PQC) algorithms are being researched and standardized to ensure the continued security of global trade in the quantum era. These new cryptographic methods aim to resist attacks from both classical and quantum computers, providing a long-term solution for securing trade operations.
Furthermore, quantum key distribution (QKD) offers a promising approach to secure communication in international trade. QKD leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to create and distribute encryption keys that are theoretically impossible to intercept without detection. This technology could provide an additional layer of security for sensitive trade communications, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of cross-border transactions.
However, the transition to quantum-safe security measures in global commerce presents significant logistical and technical challenges. Upgrading existing infrastructure, protocols, and systems across multiple countries and organizations requires substantial coordination and investment. Additionally, the interoperability of quantum-safe solutions with legacy systems must be carefully managed to ensure seamless trade operations during the transition period.
As quantum computing advances, regulatory bodies and international trade organizations must also adapt their policies and standards to address the new security landscape. This includes developing new certification processes for quantum-safe technologies and establishing guidelines for their implementation in global trade systems. Collaborative efforts between governments, industry leaders, and academic institutions are essential to create a robust and standardized approach to quantum security in international commerce.
One of the primary concerns is the vulnerability of widely-used public-key cryptography systems, such as RSA and ECC, to quantum attacks. These systems form the backbone of secure communications and digital signatures in global trade. Quantum computers, leveraging algorithms like Shor's algorithm, could theoretically break these cryptographic systems, exposing confidential trade agreements, intellectual property, and financial transactions to unauthorized access.
To address these security challenges, the development and implementation of quantum-resistant cryptography is crucial. Post-quantum cryptography (PQC) algorithms are being researched and standardized to ensure the continued security of global trade in the quantum era. These new cryptographic methods aim to resist attacks from both classical and quantum computers, providing a long-term solution for securing trade operations.
Furthermore, quantum key distribution (QKD) offers a promising approach to secure communication in international trade. QKD leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to create and distribute encryption keys that are theoretically impossible to intercept without detection. This technology could provide an additional layer of security for sensitive trade communications, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of cross-border transactions.
However, the transition to quantum-safe security measures in global commerce presents significant logistical and technical challenges. Upgrading existing infrastructure, protocols, and systems across multiple countries and organizations requires substantial coordination and investment. Additionally, the interoperability of quantum-safe solutions with legacy systems must be carefully managed to ensure seamless trade operations during the transition period.
As quantum computing advances, regulatory bodies and international trade organizations must also adapt their policies and standards to address the new security landscape. This includes developing new certification processes for quantum-safe technologies and establishing guidelines for their implementation in global trade systems. Collaborative efforts between governments, industry leaders, and academic institutions are essential to create a robust and standardized approach to quantum security in international commerce.
Regulatory Framework for Quantum in Global Commerce
The regulatory framework for quantum computing in global commerce operations is a complex and evolving landscape. As quantum technologies advance and their potential applications in international trade become more apparent, governments and international bodies are grappling with the need to establish comprehensive guidelines and regulations.
Currently, there is no unified global regulatory framework specifically addressing quantum computing in commerce. However, several existing regulations and initiatives are being adapted or expanded to encompass quantum technologies. The European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) are examples of data protection laws that may need to be updated to address the unique challenges posed by quantum computing, particularly in areas such as data encryption and privacy.
International organizations like the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) are beginning to explore the implications of quantum technologies on global trade. The WTO's Information Technology Agreement (ITA) may need to be expanded to include quantum computing hardware and software, ensuring fair trade practices in this emerging sector.
In the United States, the National Quantum Initiative Act of 2018 has laid the groundwork for developing quantum technologies, including their applications in commerce. This legislation emphasizes the need for international cooperation in quantum research and development, which could influence future regulatory frameworks for global commerce operations.
The financial sector is particularly attentive to the potential impact of quantum computing on global commerce. The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and the Financial Stability Board (FSB) are actively studying the implications of quantum technologies on financial stability and cybersecurity. Their findings are likely to inform future regulations governing the use of quantum computing in cross-border financial transactions and risk management.
Standardization efforts are also underway to ensure interoperability and security in quantum-enabled commerce systems. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) are developing standards for quantum computing and quantum-safe cryptography, which will be crucial for establishing a coherent regulatory framework.
As quantum computing advances, concerns about its potential to break current encryption methods are driving the development of post-quantum cryptography standards. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the U.S. is leading efforts to standardize quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms, which will be essential for securing global commerce operations in the quantum era.
Currently, there is no unified global regulatory framework specifically addressing quantum computing in commerce. However, several existing regulations and initiatives are being adapted or expanded to encompass quantum technologies. The European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) are examples of data protection laws that may need to be updated to address the unique challenges posed by quantum computing, particularly in areas such as data encryption and privacy.
International organizations like the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) are beginning to explore the implications of quantum technologies on global trade. The WTO's Information Technology Agreement (ITA) may need to be expanded to include quantum computing hardware and software, ensuring fair trade practices in this emerging sector.
In the United States, the National Quantum Initiative Act of 2018 has laid the groundwork for developing quantum technologies, including their applications in commerce. This legislation emphasizes the need for international cooperation in quantum research and development, which could influence future regulatory frameworks for global commerce operations.
The financial sector is particularly attentive to the potential impact of quantum computing on global commerce. The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and the Financial Stability Board (FSB) are actively studying the implications of quantum technologies on financial stability and cybersecurity. Their findings are likely to inform future regulations governing the use of quantum computing in cross-border financial transactions and risk management.
Standardization efforts are also underway to ensure interoperability and security in quantum-enabled commerce systems. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) are developing standards for quantum computing and quantum-safe cryptography, which will be crucial for establishing a coherent regulatory framework.
As quantum computing advances, concerns about its potential to break current encryption methods are driving the development of post-quantum cryptography standards. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the U.S. is leading efforts to standardize quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms, which will be essential for securing global commerce operations in the quantum era.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!