Quantum Computing and its Influence on Virtual Reality Development
JUL 17, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Quantum VR Synergy
The convergence of quantum computing and virtual reality represents a groundbreaking synergy that has the potential to revolutionize both fields. Quantum computing's immense processing power and unique capabilities in handling complex calculations can significantly enhance various aspects of virtual reality development and user experience.
One of the most promising areas of quantum-VR synergy lies in the realm of real-time rendering and physics simulations. Quantum algorithms can potentially process vast amounts of data required for photorealistic graphics and complex physical interactions within virtual environments at unprecedented speeds. This could lead to virtual worlds with unparalleled visual fidelity and more accurate, lifelike behavior of objects and characters.
Quantum computing's ability to efficiently solve optimization problems could greatly benefit VR hardware design. For instance, quantum algorithms could optimize the layout of pixels in VR displays, leading to higher resolution and reduced screen-door effect. Similarly, they could enhance the design of VR optics, resulting in wider fields of view and reduced distortion.
In the domain of AI and machine learning, quantum computing could enable more sophisticated and responsive virtual entities. Quantum machine learning algorithms could process and adapt to user behavior in real-time, creating more intelligent and interactive virtual environments. This could lead to more engaging and personalized VR experiences, with virtual characters exhibiting more human-like intelligence and adaptability.
Quantum encryption techniques could also play a crucial role in securing VR experiences, especially in multi-user environments. Quantum key distribution could provide unhackable communication channels for VR users, ensuring privacy and data security in virtual spaces used for sensitive applications like remote collaboration or telemedicine.
Furthermore, quantum sensing technologies could revolutionize motion tracking and haptic feedback in VR systems. Quantum sensors could offer unprecedented accuracy in detecting user movements and environmental factors, leading to more immersive and responsive VR experiences. This could significantly reduce motion sickness and enhance the overall sense of presence in virtual environments.
The synergy between quantum computing and VR also opens up new possibilities for scientific visualization and simulation. Complex quantum systems could be visualized and manipulated in virtual environments, providing researchers with intuitive ways to explore and understand quantum phenomena. This could accelerate discoveries in fields like materials science, drug discovery, and fundamental physics.
One of the most promising areas of quantum-VR synergy lies in the realm of real-time rendering and physics simulations. Quantum algorithms can potentially process vast amounts of data required for photorealistic graphics and complex physical interactions within virtual environments at unprecedented speeds. This could lead to virtual worlds with unparalleled visual fidelity and more accurate, lifelike behavior of objects and characters.
Quantum computing's ability to efficiently solve optimization problems could greatly benefit VR hardware design. For instance, quantum algorithms could optimize the layout of pixels in VR displays, leading to higher resolution and reduced screen-door effect. Similarly, they could enhance the design of VR optics, resulting in wider fields of view and reduced distortion.
In the domain of AI and machine learning, quantum computing could enable more sophisticated and responsive virtual entities. Quantum machine learning algorithms could process and adapt to user behavior in real-time, creating more intelligent and interactive virtual environments. This could lead to more engaging and personalized VR experiences, with virtual characters exhibiting more human-like intelligence and adaptability.
Quantum encryption techniques could also play a crucial role in securing VR experiences, especially in multi-user environments. Quantum key distribution could provide unhackable communication channels for VR users, ensuring privacy and data security in virtual spaces used for sensitive applications like remote collaboration or telemedicine.
Furthermore, quantum sensing technologies could revolutionize motion tracking and haptic feedback in VR systems. Quantum sensors could offer unprecedented accuracy in detecting user movements and environmental factors, leading to more immersive and responsive VR experiences. This could significantly reduce motion sickness and enhance the overall sense of presence in virtual environments.
The synergy between quantum computing and VR also opens up new possibilities for scientific visualization and simulation. Complex quantum systems could be visualized and manipulated in virtual environments, providing researchers with intuitive ways to explore and understand quantum phenomena. This could accelerate discoveries in fields like materials science, drug discovery, and fundamental physics.
VR Market Quantum Shift
The virtual reality (VR) market is poised for a significant transformation, driven by the potential integration of quantum computing technologies. This quantum shift is expected to revolutionize the VR landscape, offering unprecedented capabilities and experiences to users while reshaping industry dynamics.
Quantum computing's impact on VR is multifaceted, with the potential to address current limitations and unlock new possibilities. One of the most significant areas of influence is in rendering and graphics processing. Quantum algorithms could dramatically enhance the computational power available for generating complex, realistic virtual environments in real-time. This advancement would lead to more immersive and visually stunning VR experiences, bridging the gap between virtual and physical realities.
Another crucial aspect of the VR market quantum shift lies in the realm of data processing and AI integration. Quantum computing's ability to handle vast amounts of data and perform complex calculations at speeds unattainable by classical computers could revolutionize AI-driven interactions within VR environments. This could lead to more intelligent and responsive virtual worlds, with NPCs (non-player characters) exhibiting more human-like behaviors and decision-making processes.
The quantum shift is also expected to impact VR hardware development. Quantum sensors could potentially enhance motion tracking and spatial awareness in VR systems, leading to more precise and responsive user interactions. Additionally, quantum-inspired optimization algorithms could contribute to the design of more efficient and powerful VR devices, potentially reducing size and weight while increasing performance.
In terms of market dynamics, the integration of quantum computing in VR is likely to create new opportunities and challenges for existing players and newcomers alike. Companies that successfully leverage quantum technologies in their VR offerings may gain significant competitive advantages. This could lead to a reshuffling of market leaders and the emergence of new dominant players in the VR industry.
The quantum shift in VR is also expected to expand the technology's applications beyond gaming and entertainment. Fields such as healthcare, education, and industrial design could see transformative changes as quantum-enhanced VR enables more sophisticated simulations and training environments. This expansion of use cases could significantly increase the overall market size and attract investment from diverse sectors.
However, it's important to note that the full realization of this quantum shift in the VR market is contingent on overcoming several technical challenges. These include the development of practical, scalable quantum computers and the creation of quantum algorithms specifically tailored for VR applications. As these hurdles are addressed, the VR market is likely to experience a gradual but profound transformation, ushering in a new era of immersive digital experiences.
Quantum computing's impact on VR is multifaceted, with the potential to address current limitations and unlock new possibilities. One of the most significant areas of influence is in rendering and graphics processing. Quantum algorithms could dramatically enhance the computational power available for generating complex, realistic virtual environments in real-time. This advancement would lead to more immersive and visually stunning VR experiences, bridging the gap between virtual and physical realities.
Another crucial aspect of the VR market quantum shift lies in the realm of data processing and AI integration. Quantum computing's ability to handle vast amounts of data and perform complex calculations at speeds unattainable by classical computers could revolutionize AI-driven interactions within VR environments. This could lead to more intelligent and responsive virtual worlds, with NPCs (non-player characters) exhibiting more human-like behaviors and decision-making processes.
The quantum shift is also expected to impact VR hardware development. Quantum sensors could potentially enhance motion tracking and spatial awareness in VR systems, leading to more precise and responsive user interactions. Additionally, quantum-inspired optimization algorithms could contribute to the design of more efficient and powerful VR devices, potentially reducing size and weight while increasing performance.
In terms of market dynamics, the integration of quantum computing in VR is likely to create new opportunities and challenges for existing players and newcomers alike. Companies that successfully leverage quantum technologies in their VR offerings may gain significant competitive advantages. This could lead to a reshuffling of market leaders and the emergence of new dominant players in the VR industry.
The quantum shift in VR is also expected to expand the technology's applications beyond gaming and entertainment. Fields such as healthcare, education, and industrial design could see transformative changes as quantum-enhanced VR enables more sophisticated simulations and training environments. This expansion of use cases could significantly increase the overall market size and attract investment from diverse sectors.
However, it's important to note that the full realization of this quantum shift in the VR market is contingent on overcoming several technical challenges. These include the development of practical, scalable quantum computers and the creation of quantum algorithms specifically tailored for VR applications. As these hurdles are addressed, the VR market is likely to experience a gradual but profound transformation, ushering in a new era of immersive digital experiences.
Quantum-VR Challenges
The integration of quantum computing and virtual reality presents significant challenges that require innovative solutions. One of the primary obstacles is the computational complexity inherent in rendering high-fidelity VR environments. Traditional computing systems struggle to process the vast amounts of data required for realistic, real-time simulations. Quantum computing's potential for parallel processing and complex calculations could address this issue, but bridging the gap between quantum algorithms and VR applications remains a formidable task.
Another challenge lies in the development of quantum-enhanced sensors for VR systems. While quantum sensors promise unprecedented accuracy and sensitivity, their integration into VR hardware poses technical difficulties. Issues such as maintaining quantum coherence in room-temperature environments and miniaturizing quantum components for wearable devices are yet to be fully resolved.
Data transmission and latency present additional hurdles. Quantum communication protocols could theoretically provide ultra-secure and high-bandwidth data transfer for VR applications. However, implementing these protocols in practical VR systems requires overcoming significant engineering challenges, including the development of reliable quantum repeaters and interfaces between quantum and classical networks.
The creation of quantum-inspired algorithms for VR content generation and interaction is another area of difficulty. While quantum algorithms show promise for tasks such as complex scene generation and physics simulations, translating these algorithms into forms compatible with current VR development frameworks is a complex undertaking. This requires not only technical expertise in both quantum computing and VR but also a reimagining of traditional VR development paradigms.
Lastly, the challenge of quantum error correction looms large. VR applications demand high precision and reliability, which current quantum systems struggle to provide consistently. Developing robust error correction methods that can maintain the integrity of quantum computations while meeting the real-time demands of VR experiences is a critical area of research.
These challenges collectively represent a frontier in technological development, where the potential synergies between quantum computing and virtual reality are as promising as they are daunting. Overcoming these obstacles will require interdisciplinary collaboration, significant research investment, and innovative approaches to both hardware and software design.
Another challenge lies in the development of quantum-enhanced sensors for VR systems. While quantum sensors promise unprecedented accuracy and sensitivity, their integration into VR hardware poses technical difficulties. Issues such as maintaining quantum coherence in room-temperature environments and miniaturizing quantum components for wearable devices are yet to be fully resolved.
Data transmission and latency present additional hurdles. Quantum communication protocols could theoretically provide ultra-secure and high-bandwidth data transfer for VR applications. However, implementing these protocols in practical VR systems requires overcoming significant engineering challenges, including the development of reliable quantum repeaters and interfaces between quantum and classical networks.
The creation of quantum-inspired algorithms for VR content generation and interaction is another area of difficulty. While quantum algorithms show promise for tasks such as complex scene generation and physics simulations, translating these algorithms into forms compatible with current VR development frameworks is a complex undertaking. This requires not only technical expertise in both quantum computing and VR but also a reimagining of traditional VR development paradigms.
Lastly, the challenge of quantum error correction looms large. VR applications demand high precision and reliability, which current quantum systems struggle to provide consistently. Developing robust error correction methods that can maintain the integrity of quantum computations while meeting the real-time demands of VR experiences is a critical area of research.
These challenges collectively represent a frontier in technological development, where the potential synergies between quantum computing and virtual reality are as promising as they are daunting. Overcoming these obstacles will require interdisciplinary collaboration, significant research investment, and innovative approaches to both hardware and software design.
Current Quantum-VR Tech
01 Quantum Circuit Design and Optimization
This area focuses on developing and optimizing quantum circuits for various applications. It involves creating efficient quantum gate sequences, reducing circuit depth, and improving overall performance of quantum algorithms. Techniques may include circuit compression, gate decomposition, and noise-aware circuit design to enhance the capabilities of quantum computers.- Quantum Computing Architectures: Various architectures for quantum computing systems are being developed, including superconducting circuits, trapped ions, and topological qubits. These architectures aim to improve qubit coherence, scalability, and error correction capabilities, enabling more powerful and reliable quantum computations.
- Quantum Error Correction and Fault Tolerance: Techniques for quantum error correction and fault-tolerant quantum computing are crucial for mitigating the effects of decoherence and errors in quantum systems. These methods involve encoding quantum information across multiple physical qubits and implementing error detection and correction protocols to maintain quantum coherence.
- Quantum Algorithms and Applications: Development of quantum algorithms for various applications, including optimization, machine learning, cryptography, and simulation of quantum systems. These algorithms leverage quantum superposition and entanglement to potentially outperform classical algorithms for specific problems.
- Quantum-Classical Hybrid Systems: Integration of quantum and classical computing systems to create hybrid architectures that leverage the strengths of both paradigms. These systems aim to optimize resource allocation, improve overall performance, and enable practical applications of quantum computing in the near term.
- Quantum Communication and Networking: Development of quantum communication protocols and networks for secure information transfer and distributed quantum computing. This includes quantum key distribution, quantum repeaters, and quantum internet technologies to enable long-distance quantum information processing and secure communication.
02 Error Correction and Fault Tolerance
Error correction and fault tolerance are crucial for building reliable quantum computers. This field involves developing techniques to detect and correct quantum errors, implementing fault-tolerant quantum gates, and designing quantum error correction codes. These methods aim to mitigate the effects of decoherence and improve the stability of quantum systems.Expand Specific Solutions03 Quantum-Classical Hybrid Algorithms
Hybrid algorithms combine classical and quantum computing techniques to solve complex problems. This approach leverages the strengths of both classical and quantum systems, allowing for more efficient problem-solving in areas such as optimization, machine learning, and chemistry simulations. Hybrid algorithms can help bridge the gap between current quantum hardware limitations and practical applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Quantum Hardware Architecture
This area focuses on the physical implementation of quantum computers, including the design of qubits, quantum processors, and supporting infrastructure. It involves developing new qubit technologies, improving coherence times, and scaling up quantum systems. Research in this field aims to create more stable and scalable quantum hardware platforms for practical quantum computing.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quantum Software and Programming Tools
Quantum software and programming tools are essential for developing and running quantum algorithms. This field includes creating quantum programming languages, compilers, and development environments tailored for quantum computers. It also involves designing software frameworks that can interface between classical systems and quantum hardware, making quantum computing more accessible to researchers and developers.Expand Specific Solutions
Quantum-VR Pioneers
The quantum computing and virtual reality development landscape is in an early growth stage, with significant potential for market expansion. The technology is still evolving, with varying levels of maturity across different applications. Key players like Google, IBM, and Intel are investing heavily in quantum research, while companies such as Rigetti Computing and Zapata Computing are focusing on specialized quantum solutions. The market is characterized by a mix of established tech giants and innovative startups, each contributing to advancements in quantum hardware, software, and applications. As the technology progresses, we can expect increased integration between quantum computing and virtual reality, potentially revolutionizing fields such as simulation, modeling, and data visualization.
Intel Corp.
Technical Solution: Intel is advancing quantum computing for VR applications through its neuromorphic computing research. Their Loihi neuromorphic chip, inspired by the human brain's neural structure, is being explored for quantum-like parallel processing in VR environments[5]. Intel's approach combines quantum principles with neuromorphic architecture to enhance VR rendering and physics simulations. They are developing quantum-inspired algorithms for more efficient graphics processing and real-time environmental interactions in VR. Intel's research also focuses on reducing the power consumption of VR systems through quantum-inspired optimizations, potentially enabling longer and more immersive VR experiences. Additionally, they are exploring the integration of their quantum efforts with their existing high-performance computing solutions to create hybrid systems capable of supporting advanced VR applications[6].
Strengths: Strong hardware expertise, established presence in computing industry, and innovative approach combining quantum and neuromorphic technologies. Weaknesses: Relatively new to quantum computing compared to some competitors, may face challenges in fully integrating quantum technologies with existing VR hardware.
Google LLC
Technical Solution: Google is at the forefront of quantum computing research and its application to virtual reality. Their Sycamore quantum processor has demonstrated quantum supremacy[1], processing tasks in minutes that would take classical supercomputers thousands of years. In the context of VR, Google is exploring quantum algorithms for improved graphics rendering and physics simulations. They are developing quantum machine learning techniques to enhance AI-driven VR experiences, potentially revolutionizing user interactions and environment generation in virtual worlds[2]. Google's quantum-assisted VR aims to create more realistic and responsive virtual environments, with real-time quantum calculations powering complex simulations that were previously computationally infeasible.
Strengths: Cutting-edge quantum hardware, vast computational resources, and expertise in both quantum computing and VR. Weaknesses: Quantum technology is still in early stages, with challenges in scalability and error correction for practical VR applications.
Quantum-VR Breakthroughs
Interactive System and Method Providing Real-Time Virtual Reality Visualization of Simulation Data
PatentActiveUS20210327138A1
Innovation
- A system comprising a file import component, simulation model data component, data translator component, and visualization component that optimizes data structures and enables real-time computation and visualization of CAD and CAE models within a virtual reality environment, allowing users to query and interact with complex data in immersive VR experiences.
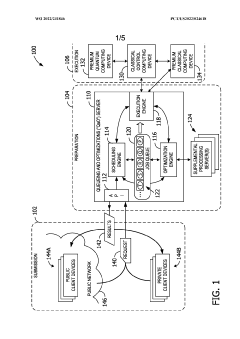
System and method of in-queue optimizations for quantum cloud computing
PatentWO2022231846A1
Innovation
- A quantum computing system with a queueing and optimizations (QaO) server that performs in-queue optimizations, including prediction models for execution times and machine calibration, to improve the quality of quantum circuit execution, reduce wait times, and balance performance characteristics, utilizing both intra-job and inter-job optimizations to enhance fidelity and throughput.
Quantum-VR Standards
The development of quantum computing and its integration with virtual reality (VR) technologies necessitates the establishment of robust standards to ensure interoperability, security, and optimal performance. Quantum-VR standards are crucial for creating a unified framework that allows seamless integration of quantum computing capabilities into VR systems and applications.
One key area of focus for Quantum-VR standards is the development of quantum-resistant cryptographic protocols. As quantum computers have the potential to break many current encryption methods, it is essential to establish new standards for secure communication and data protection within VR environments. These standards should address quantum key distribution, post-quantum cryptography, and quantum-safe authentication mechanisms.
Another critical aspect of Quantum-VR standards is the definition of quantum-enhanced rendering protocols. These standards should outline how quantum algorithms can be utilized to improve the rendering of complex 3D environments, physics simulations, and real-time interactions within VR systems. This includes standardizing the interface between quantum processors and traditional graphics processing units (GPUs) to optimize performance and reduce latency.
Quantum-VR standards must also address the integration of quantum sensors and quantum-enhanced input devices. This involves defining protocols for quantum-based motion tracking, haptic feedback, and other sensory inputs that can enhance the immersive experience in VR. Standardizing these interfaces will ensure compatibility across different hardware platforms and software applications.
Data representation and storage standards for quantum-enhanced VR systems are equally important. These standards should define how quantum states and quantum-processed data can be efficiently stored, transmitted, and manipulated within VR environments. This includes standardizing quantum data compression techniques and quantum-resistant data storage protocols.
Furthermore, Quantum-VR standards need to establish guidelines for quantum-enhanced AI and machine learning integration in VR applications. This involves defining standardized interfaces for quantum machine learning algorithms to interact with VR environments, enabling more sophisticated and responsive virtual worlds.
Lastly, Quantum-VR standards should address the ethical considerations and privacy concerns associated with the convergence of quantum computing and VR technologies. This includes establishing guidelines for quantum-enhanced user authentication, data privacy protection, and ethical use of quantum-powered simulations in VR environments.
One key area of focus for Quantum-VR standards is the development of quantum-resistant cryptographic protocols. As quantum computers have the potential to break many current encryption methods, it is essential to establish new standards for secure communication and data protection within VR environments. These standards should address quantum key distribution, post-quantum cryptography, and quantum-safe authentication mechanisms.
Another critical aspect of Quantum-VR standards is the definition of quantum-enhanced rendering protocols. These standards should outline how quantum algorithms can be utilized to improve the rendering of complex 3D environments, physics simulations, and real-time interactions within VR systems. This includes standardizing the interface between quantum processors and traditional graphics processing units (GPUs) to optimize performance and reduce latency.
Quantum-VR standards must also address the integration of quantum sensors and quantum-enhanced input devices. This involves defining protocols for quantum-based motion tracking, haptic feedback, and other sensory inputs that can enhance the immersive experience in VR. Standardizing these interfaces will ensure compatibility across different hardware platforms and software applications.
Data representation and storage standards for quantum-enhanced VR systems are equally important. These standards should define how quantum states and quantum-processed data can be efficiently stored, transmitted, and manipulated within VR environments. This includes standardizing quantum data compression techniques and quantum-resistant data storage protocols.
Furthermore, Quantum-VR standards need to establish guidelines for quantum-enhanced AI and machine learning integration in VR applications. This involves defining standardized interfaces for quantum machine learning algorithms to interact with VR environments, enabling more sophisticated and responsive virtual worlds.
Lastly, Quantum-VR standards should address the ethical considerations and privacy concerns associated with the convergence of quantum computing and VR technologies. This includes establishing guidelines for quantum-enhanced user authentication, data privacy protection, and ethical use of quantum-powered simulations in VR environments.
Quantum-VR Ethics
The integration of quantum computing and virtual reality technologies raises significant ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed. As these fields converge, concerns about privacy, security, and the potential manipulation of human perception become increasingly prominent. Quantum computing's ability to process vast amounts of data at unprecedented speeds could enable the creation of hyper-realistic virtual environments that blur the line between reality and simulation. This raises questions about the psychological impact on users and the potential for addiction or detachment from the physical world.
Furthermore, the enhanced computational power of quantum systems may lead to more sophisticated data collection and analysis within virtual reality experiences. This could result in unprecedented levels of user profiling and behavioral prediction, potentially infringing on personal privacy and autonomy. The ethical implications of such capabilities extend to issues of consent, data ownership, and the responsible use of information gathered in virtual spaces.
Another critical ethical consideration is the potential for quantum-enhanced virtual reality to be used for manipulation or deception. Advanced simulations could be employed to create convincing false narratives or alter perceptions of real-world events, raising concerns about the spread of misinformation and the integrity of shared experiences. The development of quantum-VR technologies must therefore be accompanied by robust safeguards and ethical guidelines to prevent misuse and protect users' mental and emotional well-being.
The accessibility and equitable distribution of quantum-VR technologies also present ethical challenges. As these advanced systems become more prevalent, there is a risk of exacerbating existing digital divides and creating new forms of social inequality. Ensuring fair access to the benefits of quantum-enhanced virtual reality while mitigating potential harm to vulnerable populations should be a priority for developers and policymakers alike.
Moreover, the potential use of quantum-VR technologies in sensitive areas such as healthcare, education, and military applications necessitates careful consideration of ethical implications. The development of ethical frameworks and governance structures that can keep pace with rapid technological advancements is crucial to harness the positive potential of quantum-VR while minimizing risks and protecting individual rights.
Furthermore, the enhanced computational power of quantum systems may lead to more sophisticated data collection and analysis within virtual reality experiences. This could result in unprecedented levels of user profiling and behavioral prediction, potentially infringing on personal privacy and autonomy. The ethical implications of such capabilities extend to issues of consent, data ownership, and the responsible use of information gathered in virtual spaces.
Another critical ethical consideration is the potential for quantum-enhanced virtual reality to be used for manipulation or deception. Advanced simulations could be employed to create convincing false narratives or alter perceptions of real-world events, raising concerns about the spread of misinformation and the integrity of shared experiences. The development of quantum-VR technologies must therefore be accompanied by robust safeguards and ethical guidelines to prevent misuse and protect users' mental and emotional well-being.
The accessibility and equitable distribution of quantum-VR technologies also present ethical challenges. As these advanced systems become more prevalent, there is a risk of exacerbating existing digital divides and creating new forms of social inequality. Ensuring fair access to the benefits of quantum-enhanced virtual reality while mitigating potential harm to vulnerable populations should be a priority for developers and policymakers alike.
Moreover, the potential use of quantum-VR technologies in sensitive areas such as healthcare, education, and military applications necessitates careful consideration of ethical implications. The development of ethical frameworks and governance structures that can keep pace with rapid technological advancements is crucial to harness the positive potential of quantum-VR while minimizing risks and protecting individual rights.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!