Quantum Computing and Bioinformatics: New Horizons in Research
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Quantum Bio Landscape
The convergence of quantum computing and bioinformatics represents a transformative frontier in scientific research, promising unprecedented advancements in our understanding of complex biological systems. This emerging field, often referred to as quantum bioinformatics, leverages the unique capabilities of quantum systems to address computational challenges that have long hindered progress in life sciences.
At the core of this landscape is the potential for quantum computers to revolutionize genomic analysis, protein folding simulations, and drug discovery processes. Quantum algorithms, such as quantum annealing and quantum approximate optimization, offer novel approaches to tackle the combinatorial complexity inherent in many bioinformatics problems. These methods could dramatically accelerate the processing of vast genomic datasets, enabling more comprehensive analyses of genetic variations and their implications for human health.
The quantum bio landscape is characterized by a symbiotic relationship between quantum physics and molecular biology. Quantum effects, once thought to be irrelevant at the macroscopic scale of biological systems, are now recognized as potentially crucial in phenomena such as photosynthesis and enzyme catalysis. This realization has sparked interest in quantum biology, a field that explores how quantum mechanical effects might influence biological processes at the molecular level.
In the realm of structural biology, quantum computing holds promise for unraveling the mysteries of protein folding. Classical computational methods often struggle with the astronomical number of possible conformations a protein can adopt. Quantum algorithms, however, could potentially explore this vast configurational space more efficiently, leading to breakthroughs in predicting protein structures and understanding their functions.
Drug discovery is another area poised for transformation by quantum bioinformatics. Quantum simulations could enable more accurate modeling of molecular interactions, potentially revolutionizing the design of new pharmaceuticals. This could lead to more targeted and effective therapies, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional drug development pipelines.
The quantum bio landscape also encompasses the development of quantum sensors for biological applications. These ultra-sensitive devices could enable the detection of minute changes in biological systems, opening new avenues for early disease diagnosis and personalized medicine. Quantum-enhanced imaging techniques, such as those based on nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond, promise to push the boundaries of biological imaging resolution.
As this field evolves, it faces significant challenges, including the need for error-corrected quantum computers and the development of quantum algorithms tailored to biological problems. However, the potential rewards are immense, offering the prospect of a new era in life sciences research and biotechnology innovation.
At the core of this landscape is the potential for quantum computers to revolutionize genomic analysis, protein folding simulations, and drug discovery processes. Quantum algorithms, such as quantum annealing and quantum approximate optimization, offer novel approaches to tackle the combinatorial complexity inherent in many bioinformatics problems. These methods could dramatically accelerate the processing of vast genomic datasets, enabling more comprehensive analyses of genetic variations and their implications for human health.
The quantum bio landscape is characterized by a symbiotic relationship between quantum physics and molecular biology. Quantum effects, once thought to be irrelevant at the macroscopic scale of biological systems, are now recognized as potentially crucial in phenomena such as photosynthesis and enzyme catalysis. This realization has sparked interest in quantum biology, a field that explores how quantum mechanical effects might influence biological processes at the molecular level.
In the realm of structural biology, quantum computing holds promise for unraveling the mysteries of protein folding. Classical computational methods often struggle with the astronomical number of possible conformations a protein can adopt. Quantum algorithms, however, could potentially explore this vast configurational space more efficiently, leading to breakthroughs in predicting protein structures and understanding their functions.
Drug discovery is another area poised for transformation by quantum bioinformatics. Quantum simulations could enable more accurate modeling of molecular interactions, potentially revolutionizing the design of new pharmaceuticals. This could lead to more targeted and effective therapies, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional drug development pipelines.
The quantum bio landscape also encompasses the development of quantum sensors for biological applications. These ultra-sensitive devices could enable the detection of minute changes in biological systems, opening new avenues for early disease diagnosis and personalized medicine. Quantum-enhanced imaging techniques, such as those based on nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond, promise to push the boundaries of biological imaging resolution.
As this field evolves, it faces significant challenges, including the need for error-corrected quantum computers and the development of quantum algorithms tailored to biological problems. However, the potential rewards are immense, offering the prospect of a new era in life sciences research and biotechnology innovation.
Bioinformatics Demand
The demand for bioinformatics solutions has been rapidly growing in recent years, driven by the exponential increase in biological data and the need for sophisticated computational tools to analyze and interpret this data. The integration of quantum computing with bioinformatics presents a promising frontier that could revolutionize the field and address many of its current challenges.
In the pharmaceutical industry, there is a pressing need for more efficient drug discovery processes. Traditional methods are time-consuming and costly, often taking over a decade and billions of dollars to bring a new drug to market. Quantum computing-enhanced bioinformatics could significantly accelerate this process by enabling faster and more accurate molecular simulations, protein folding predictions, and drug-target interactions analysis.
Personalized medicine is another area where the demand for advanced bioinformatics tools is surging. Healthcare providers and researchers require powerful computational methods to analyze individual genetic profiles and predict disease risks or treatment responses. Quantum algorithms could potentially process vast amounts of genomic data more efficiently, leading to more precise and tailored medical interventions.
The field of genomics and proteomics is generating massive datasets that current computational methods struggle to handle effectively. There is a growing demand for tools that can process and analyze these large-scale datasets in reasonable timeframes. Quantum computing offers the potential to dramatically speed up sequence alignment, variant calling, and other computationally intensive tasks in genomic analysis.
Environmental and agricultural sectors are also increasingly relying on bioinformatics for tasks such as climate change impact assessment on ecosystems and crop improvement. The complexity of these biological systems requires advanced modeling and simulation capabilities that could benefit from quantum-enhanced algorithms.
In academic and research institutions, there is a constant demand for more powerful computational resources to tackle complex biological problems. Quantum computing could enable researchers to explore previously intractable questions in areas such as evolutionary biology, systems biology, and structural biology.
The cybersecurity sector is showing interest in quantum-resistant encryption methods for protecting sensitive genetic and health data. As quantum computers threaten to break current encryption standards, there is a growing need for quantum-safe bioinformatics data storage and transmission solutions.
Overall, the bioinformatics market is expected to continue its rapid growth, with some projections suggesting a compound annual growth rate of over 13% in the coming years. The integration of quantum computing into this field is likely to further accelerate this growth by opening up new possibilities and addressing long-standing computational bottlenecks in biological research and applications.
In the pharmaceutical industry, there is a pressing need for more efficient drug discovery processes. Traditional methods are time-consuming and costly, often taking over a decade and billions of dollars to bring a new drug to market. Quantum computing-enhanced bioinformatics could significantly accelerate this process by enabling faster and more accurate molecular simulations, protein folding predictions, and drug-target interactions analysis.
Personalized medicine is another area where the demand for advanced bioinformatics tools is surging. Healthcare providers and researchers require powerful computational methods to analyze individual genetic profiles and predict disease risks or treatment responses. Quantum algorithms could potentially process vast amounts of genomic data more efficiently, leading to more precise and tailored medical interventions.
The field of genomics and proteomics is generating massive datasets that current computational methods struggle to handle effectively. There is a growing demand for tools that can process and analyze these large-scale datasets in reasonable timeframes. Quantum computing offers the potential to dramatically speed up sequence alignment, variant calling, and other computationally intensive tasks in genomic analysis.
Environmental and agricultural sectors are also increasingly relying on bioinformatics for tasks such as climate change impact assessment on ecosystems and crop improvement. The complexity of these biological systems requires advanced modeling and simulation capabilities that could benefit from quantum-enhanced algorithms.
In academic and research institutions, there is a constant demand for more powerful computational resources to tackle complex biological problems. Quantum computing could enable researchers to explore previously intractable questions in areas such as evolutionary biology, systems biology, and structural biology.
The cybersecurity sector is showing interest in quantum-resistant encryption methods for protecting sensitive genetic and health data. As quantum computers threaten to break current encryption standards, there is a growing need for quantum-safe bioinformatics data storage and transmission solutions.
Overall, the bioinformatics market is expected to continue its rapid growth, with some projections suggesting a compound annual growth rate of over 13% in the coming years. The integration of quantum computing into this field is likely to further accelerate this growth by opening up new possibilities and addressing long-standing computational bottlenecks in biological research and applications.
Quantum Tech Challenges
Quantum computing presents significant challenges in its application to bioinformatics, despite its potential to revolutionize the field. One of the primary obstacles is the current limitation in qubit coherence time and fidelity. Quantum systems are highly sensitive to environmental disturbances, leading to decoherence and errors in computations. This sensitivity poses a substantial hurdle in maintaining quantum states long enough to perform complex bioinformatics calculations, which often require extensive computational time.
Another major challenge lies in the development of quantum algorithms specifically tailored for bioinformatics problems. While quantum algorithms like Shor's and Grover's have shown promise in certain areas, translating traditional bioinformatics algorithms into their quantum counterparts is not straightforward. The unique nature of quantum computation requires a fundamental rethinking of algorithmic approaches, which is both time-consuming and intellectually demanding.
The scalability of quantum systems also presents a significant hurdle. Current quantum computers have a limited number of qubits, restricting their ability to handle the large datasets typical in bioinformatics. Scaling up quantum systems while maintaining coherence and reducing error rates is a complex engineering challenge that requires substantial advancements in quantum hardware design and error correction techniques.
Error correction in quantum systems is another critical challenge. Unlike classical computers, quantum computers are inherently prone to errors due to quantum decoherence and gate imperfections. Developing robust quantum error correction codes that can effectively mitigate these errors without significantly increasing the number of physical qubits required is an ongoing area of research.
The integration of quantum and classical systems poses another challenge. Many bioinformatics applications will likely require hybrid quantum-classical approaches, necessitating the development of efficient interfaces between quantum and classical components. This integration is crucial for leveraging the strengths of both paradigms and overcoming the limitations of current quantum systems.
Lastly, there is a significant knowledge gap in the bioinformatics community regarding quantum computing principles and applications. Bridging this gap requires interdisciplinary collaboration and education, which takes time and resources to develop. The lack of quantum computing expertise among bioinformatics researchers hinders the rapid development and adoption of quantum techniques in the field.
Another major challenge lies in the development of quantum algorithms specifically tailored for bioinformatics problems. While quantum algorithms like Shor's and Grover's have shown promise in certain areas, translating traditional bioinformatics algorithms into their quantum counterparts is not straightforward. The unique nature of quantum computation requires a fundamental rethinking of algorithmic approaches, which is both time-consuming and intellectually demanding.
The scalability of quantum systems also presents a significant hurdle. Current quantum computers have a limited number of qubits, restricting their ability to handle the large datasets typical in bioinformatics. Scaling up quantum systems while maintaining coherence and reducing error rates is a complex engineering challenge that requires substantial advancements in quantum hardware design and error correction techniques.
Error correction in quantum systems is another critical challenge. Unlike classical computers, quantum computers are inherently prone to errors due to quantum decoherence and gate imperfections. Developing robust quantum error correction codes that can effectively mitigate these errors without significantly increasing the number of physical qubits required is an ongoing area of research.
The integration of quantum and classical systems poses another challenge. Many bioinformatics applications will likely require hybrid quantum-classical approaches, necessitating the development of efficient interfaces between quantum and classical components. This integration is crucial for leveraging the strengths of both paradigms and overcoming the limitations of current quantum systems.
Lastly, there is a significant knowledge gap in the bioinformatics community regarding quantum computing principles and applications. Bridging this gap requires interdisciplinary collaboration and education, which takes time and resources to develop. The lack of quantum computing expertise among bioinformatics researchers hinders the rapid development and adoption of quantum techniques in the field.
Current Quantum-Bio
01 Quantum algorithms for genomic data analysis
Quantum computing techniques are applied to analyze large-scale genomic data, offering potential improvements in speed and accuracy for tasks such as sequence alignment, variant calling, and phylogenetic tree construction. These quantum algorithms leverage the principles of superposition and entanglement to process complex biological datasets more efficiently than classical methods.- Quantum algorithms for genomic data analysis: Quantum computing techniques are applied to analyze large-scale genomic data, offering potential improvements in speed and accuracy compared to classical methods. These algorithms can be used for tasks such as sequence alignment, variant calling, and phylogenetic tree construction, potentially revolutionizing bioinformatics workflows.
- Quantum-inspired machine learning for biological data: Quantum-inspired machine learning algorithms are developed to process and interpret complex biological datasets. These approaches leverage quantum principles to enhance pattern recognition, feature extraction, and predictive modeling in bioinformatics applications, potentially leading to new insights in areas such as protein folding and drug discovery.
- Quantum simulation of biological systems: Quantum computers are used to simulate complex biological systems and processes at the molecular level. This approach enables more accurate modeling of protein-protein interactions, enzyme catalysis, and other biochemical phenomena, potentially accelerating drug development and enhancing our understanding of cellular mechanisms.
- Quantum-enhanced optimization for bioinformatics problems: Quantum optimization techniques are applied to solve computationally intensive bioinformatics problems. These methods can potentially improve the efficiency of tasks such as protein structure prediction, metabolic network analysis, and genome assembly, leading to faster and more accurate results in biological research.
- Quantum-secure bioinformatics data management: Quantum-resistant cryptographic methods are developed to protect sensitive bioinformatics data from potential threats posed by future quantum computers. These techniques ensure the long-term security and privacy of genomic and health-related information in the post-quantum era, addressing concerns in data storage, transmission, and analysis.
02 Quantum-inspired classical algorithms for bioinformatics
Researchers are developing classical algorithms inspired by quantum computing concepts to address bioinformatics challenges. These algorithms aim to bridge the gap between current classical computing capabilities and future quantum systems, providing improved performance for tasks such as protein folding prediction and drug discovery without requiring quantum hardware.Expand Specific Solutions03 Quantum machine learning for biological data
Quantum machine learning techniques are being explored to enhance the analysis and interpretation of biological data. These methods combine quantum computing principles with machine learning algorithms to improve pattern recognition, feature extraction, and predictive modeling in areas such as gene expression analysis and protein structure prediction.Expand Specific Solutions04 Quantum-enhanced simulation of biological systems
Quantum computing is being utilized to simulate complex biological systems and molecular interactions with higher accuracy and efficiency. This approach enables researchers to model and study intricate biological processes, such as enzyme catalysis and protein-ligand interactions, potentially accelerating drug discovery and understanding of cellular mechanisms.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quantum error correction for bioinformatics applications
Researchers are developing quantum error correction techniques specifically tailored for bioinformatics applications. These methods aim to mitigate the effects of noise and decoherence in quantum systems, ensuring the reliability and accuracy of quantum computations when processing sensitive biological data and performing complex bioinformatics tasks.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The quantum computing and bioinformatics landscape is rapidly evolving, with the field currently in its early growth stage. The market size is expanding, driven by increasing investments and potential applications in drug discovery, genomics, and personalized medicine. While the technology is still maturing, several key players are making significant strides. Companies like IBM, D-Wave Systems, and Origin Quantum are at the forefront of quantum hardware development, while others like Zapata Computing and QC Ware focus on quantum software solutions. Established bioinformatics firms such as Illumina and Affymetrix are also exploring quantum applications. The convergence of these technologies promises to revolutionize research capabilities, though widespread commercial adoption remains a future prospect.
Zapata Computing, Inc.
Technical Solution: Zapata Computing specializes in quantum software and algorithms, with a focus on near-term quantum applications in various fields, including bioinformatics. Their Orquestra platform integrates classical and quantum computing resources, allowing researchers to develop and deploy quantum-classical hybrid solutions for bioinformatics challenges[7]. Zapata has developed quantum machine learning algorithms for genomic data analysis, showing potential improvements in classification and clustering of genetic sequences. Their work on variational quantum algorithms has applications in protein structure prediction and drug-target interaction prediction[8]. Zapata's approach emphasizes quantum-ready algorithms that can run on both classical computers and quantum hardware as it becomes available, ensuring scalability and future-proofing of bioinformatics solutions[9].
Strengths: Strong focus on near-term quantum applications, versatile software platform, and expertise in quantum-classical hybrid algorithms. Weaknesses: Reliance on third-party quantum hardware, which may limit control over full-stack optimization.
International Business Machines Corp.
Technical Solution: IBM has been at the forefront of quantum computing and bioinformatics integration. Their quantum-classical approach combines quantum algorithms with classical computing for genomic analysis. IBM's quantum systems, such as IBM Q System One, provide up to 127 qubits for complex bioinformatics tasks[1]. They've developed quantum algorithms for protein folding prediction and drug discovery, potentially revolutionizing personalized medicine. IBM's Qiskit Runtime allows researchers to execute quantum circuits for genomic data analysis up to 120 times faster than previous methods[2]. Their quantum-enhanced machine learning models have shown promise in identifying genetic markers for diseases with higher accuracy than classical methods[3].
Strengths: Industry-leading quantum hardware, extensive software ecosystem (Qiskit), and strong research partnerships. Weaknesses: Quantum systems still require extreme cooling, limiting widespread adoption, and quantum error correction remains a challenge.
Quantum-Bio Innovations
Quantum bio-computing
PatentPendingIN202411020299A
Innovation
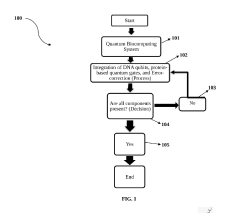
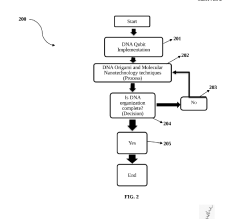
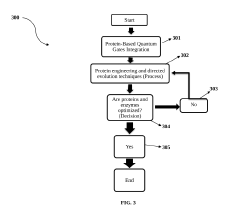
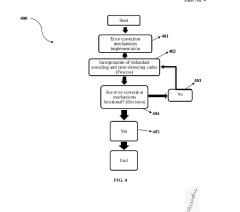
- Integration of DNA molecules as qubits and proteins/enzymes as quantum gates within a quantum bio-computing framework, leveraging biological molecules' intrinsic quantum characteristics for enhanced computational capabilities and error correction mechanisms.
Method and apparatus for quantum clustering
PatentActiveUS20040117403A1
Innovation
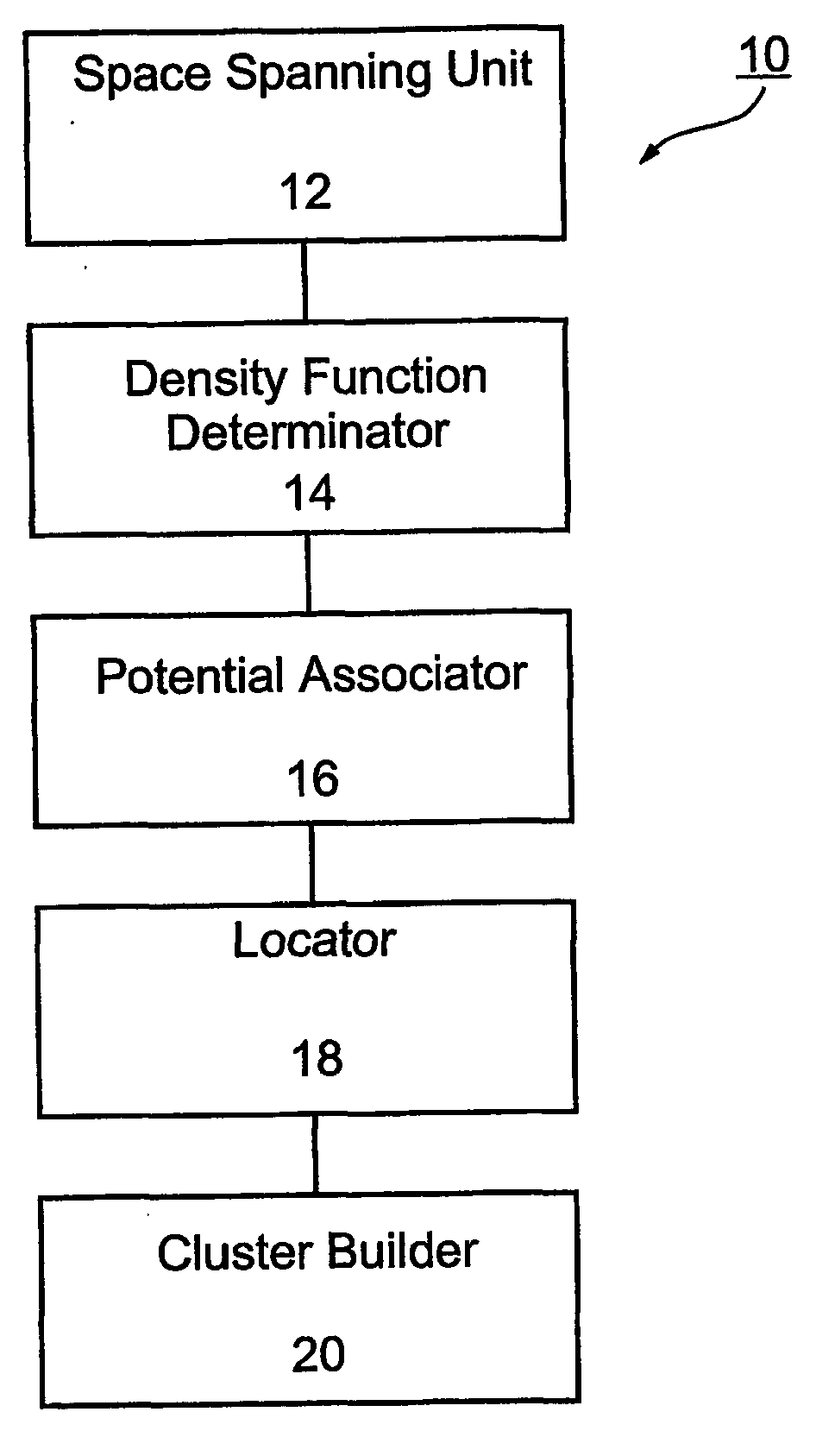
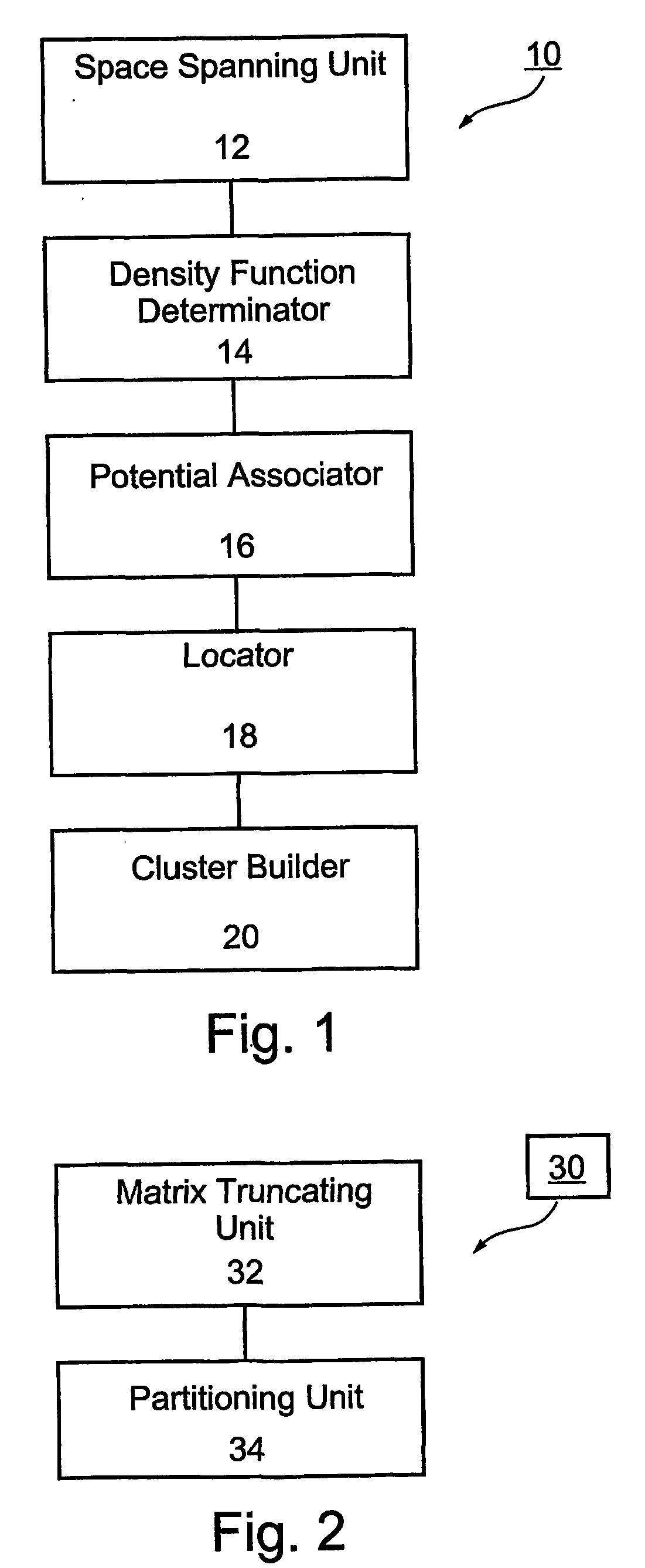
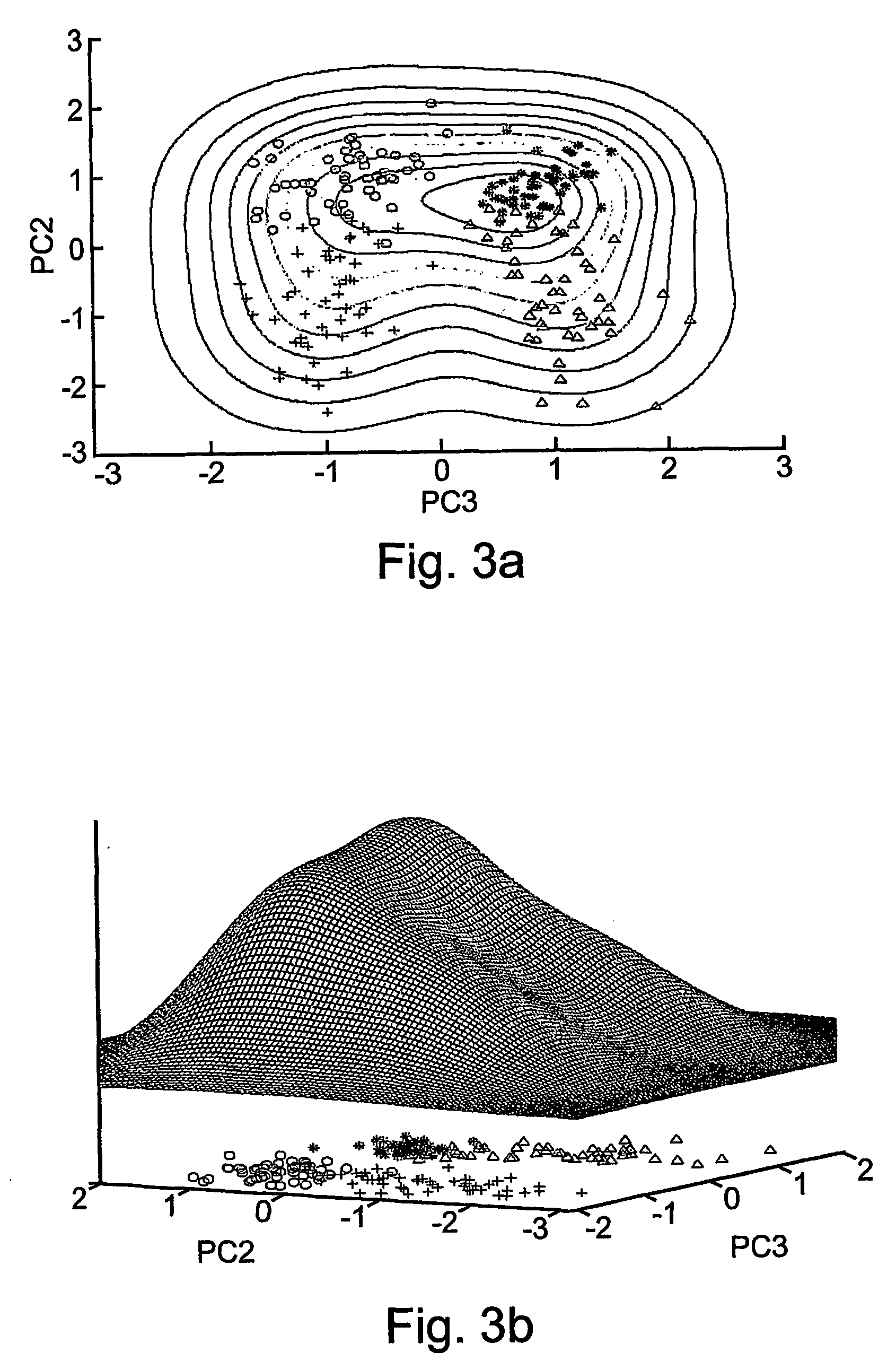
- A method and apparatus that span multidimensional data spaces, determine density functions, associate potentials, locate local minima, and attribute points to form clusters, using quantum mechanical techniques to reduce dimensionality and iteratively merge clusters, allowing for stable and reproducible clustering.
Quantum Ethics in Bio
The intersection of quantum computing and bioinformatics raises significant ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed. As these technologies advance, they have the potential to revolutionize our understanding of biological systems and enable unprecedented capabilities in genetic analysis and manipulation. However, this power comes with great responsibility.
One primary ethical concern is the potential misuse of quantum-enhanced bioinformatics for genetic discrimination or unauthorized genetic profiling. The ability to rapidly process and analyze vast amounts of genetic data could lead to privacy breaches on an unprecedented scale. Safeguards must be implemented to protect individuals' genetic information and prevent its exploitation for malicious purposes.
Another critical issue is the potential for quantum computing to accelerate the development of biological weapons or other harmful agents. The enhanced computational power could be used to design and simulate new pathogens or toxins, posing significant risks to global security and public health. Strict regulations and oversight mechanisms must be established to prevent such misuse.
The use of quantum computing in genetic engineering and synthetic biology also raises ethical questions about the limits of human intervention in natural biological processes. As our ability to manipulate and design living organisms increases, we must carefully consider the long-term implications for biodiversity, ecosystem balance, and the very definition of life itself.
Furthermore, the potential for quantum-enhanced bioinformatics to exacerbate existing inequalities in healthcare and biotechnology access must be addressed. If these advanced technologies remain accessible only to wealthy nations or individuals, it could widen the global health divide and create new forms of technological colonialism.
Ethical frameworks must also be developed to guide decision-making in scenarios where quantum bioinformatics provides conflicting or ambiguous results. For instance, how should we handle situations where quantum-enhanced analysis suggests genetic interventions that conflict with established medical practices or cultural beliefs?
As we navigate these ethical challenges, it is crucial to foster interdisciplinary collaboration between quantum physicists, bioinformaticians, ethicists, policymakers, and sociologists. Only through such comprehensive dialogue can we develop robust ethical guidelines that balance scientific progress with societal well-being and individual rights.
One primary ethical concern is the potential misuse of quantum-enhanced bioinformatics for genetic discrimination or unauthorized genetic profiling. The ability to rapidly process and analyze vast amounts of genetic data could lead to privacy breaches on an unprecedented scale. Safeguards must be implemented to protect individuals' genetic information and prevent its exploitation for malicious purposes.
Another critical issue is the potential for quantum computing to accelerate the development of biological weapons or other harmful agents. The enhanced computational power could be used to design and simulate new pathogens or toxins, posing significant risks to global security and public health. Strict regulations and oversight mechanisms must be established to prevent such misuse.
The use of quantum computing in genetic engineering and synthetic biology also raises ethical questions about the limits of human intervention in natural biological processes. As our ability to manipulate and design living organisms increases, we must carefully consider the long-term implications for biodiversity, ecosystem balance, and the very definition of life itself.
Furthermore, the potential for quantum-enhanced bioinformatics to exacerbate existing inequalities in healthcare and biotechnology access must be addressed. If these advanced technologies remain accessible only to wealthy nations or individuals, it could widen the global health divide and create new forms of technological colonialism.
Ethical frameworks must also be developed to guide decision-making in scenarios where quantum bioinformatics provides conflicting or ambiguous results. For instance, how should we handle situations where quantum-enhanced analysis suggests genetic interventions that conflict with established medical practices or cultural beliefs?
As we navigate these ethical challenges, it is crucial to foster interdisciplinary collaboration between quantum physicists, bioinformaticians, ethicists, policymakers, and sociologists. Only through such comprehensive dialogue can we develop robust ethical guidelines that balance scientific progress with societal well-being and individual rights.
Quantum-Bio Education
The integration of quantum computing and bioinformatics is revolutionizing the landscape of scientific research, necessitating a paradigm shift in educational approaches. Quantum-Bio Education emerges as a critical frontier, bridging the gap between these two rapidly evolving fields. This interdisciplinary domain requires a comprehensive educational framework that combines principles of quantum mechanics, computer science, and biological sciences.
At the core of Quantum-Bio Education lies the need to develop curricula that foster a deep understanding of quantum algorithms and their applications in biological data analysis. Students must be equipped with the skills to navigate complex quantum systems while simultaneously grasping the intricacies of genomic and proteomic data structures. This dual expertise is essential for leveraging quantum computing's potential in solving computationally intensive bioinformatics problems.
Educational institutions are increasingly recognizing the importance of incorporating quantum computing concepts into bioinformatics programs. This integration involves introducing quantum mechanics principles, quantum algorithms, and quantum information theory alongside traditional bioinformatics topics. Courses are being designed to cover quantum-enhanced machine learning techniques, quantum-inspired optimization algorithms, and quantum simulation methods applicable to molecular dynamics and drug discovery processes.
Hands-on experience with quantum computing platforms is becoming a crucial component of Quantum-Bio Education. Universities and research centers are establishing partnerships with quantum hardware providers to give students access to real quantum devices. This practical exposure allows learners to implement quantum algorithms for biological data processing, fostering a deeper understanding of the challenges and opportunities in this emerging field.
The development of specialized software tools and programming environments tailored for quantum bioinformatics is another key aspect of this educational paradigm. These tools aim to simplify the process of designing and executing quantum algorithms for biological applications, making the field more accessible to researchers from diverse backgrounds.
As the field advances, there is a growing need for interdisciplinary collaboration in curriculum development. Experts from quantum physics, computer science, and biology must work together to create comprehensive educational materials that address the unique challenges of quantum bioinformatics. This collaborative approach ensures that students receive a well-rounded education that prepares them for the complexities of real-world research and development in this cutting-edge domain.
At the core of Quantum-Bio Education lies the need to develop curricula that foster a deep understanding of quantum algorithms and their applications in biological data analysis. Students must be equipped with the skills to navigate complex quantum systems while simultaneously grasping the intricacies of genomic and proteomic data structures. This dual expertise is essential for leveraging quantum computing's potential in solving computationally intensive bioinformatics problems.
Educational institutions are increasingly recognizing the importance of incorporating quantum computing concepts into bioinformatics programs. This integration involves introducing quantum mechanics principles, quantum algorithms, and quantum information theory alongside traditional bioinformatics topics. Courses are being designed to cover quantum-enhanced machine learning techniques, quantum-inspired optimization algorithms, and quantum simulation methods applicable to molecular dynamics and drug discovery processes.
Hands-on experience with quantum computing platforms is becoming a crucial component of Quantum-Bio Education. Universities and research centers are establishing partnerships with quantum hardware providers to give students access to real quantum devices. This practical exposure allows learners to implement quantum algorithms for biological data processing, fostering a deeper understanding of the challenges and opportunities in this emerging field.
The development of specialized software tools and programming environments tailored for quantum bioinformatics is another key aspect of this educational paradigm. These tools aim to simplify the process of designing and executing quantum algorithms for biological applications, making the field more accessible to researchers from diverse backgrounds.
As the field advances, there is a growing need for interdisciplinary collaboration in curriculum development. Experts from quantum physics, computer science, and biology must work together to create comprehensive educational materials that address the unique challenges of quantum bioinformatics. This collaborative approach ensures that students receive a well-rounded education that prepares them for the complexities of real-world research and development in this cutting-edge domain.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!