How Quantum Models Are Influencing Global Logistics Efficiency
SEP 5, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Quantum Computing in Logistics: Background and Objectives
Quantum computing represents a paradigm shift in computational capabilities, leveraging quantum mechanical phenomena such as superposition and entanglement to process information in fundamentally different ways than classical computers. The evolution of quantum technologies has progressed from theoretical concepts in the 1980s to the current era of Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) devices, with significant acceleration in development over the past decade. This technological trajectory suggests quantum computing is approaching practical applications in specific domains, with logistics emerging as a particularly promising field.
The global logistics industry, valued at approximately $9.6 trillion and representing nearly 12% of global GDP, faces increasingly complex challenges in optimization, routing, and resource allocation. Traditional computational methods often struggle with the combinatorial explosion inherent in large-scale logistics problems, creating a performance ceiling that quantum computing may potentially break through.
The primary objective of quantum computing applications in logistics is to achieve optimization capabilities beyond what classical algorithms can deliver, particularly for NP-hard problems like the traveling salesman problem, vehicle routing with time windows, and multi-modal transportation optimization. These problems are ubiquitous in logistics but become computationally intractable at scale using conventional methods.
Current quantum approaches to logistics optimization include quantum annealing, quantum approximate optimization algorithms (QAOA), and quantum machine learning. These methods show particular promise in areas requiring complex simulations, such as supply chain resilience testing, multi-variable optimization under uncertainty, and real-time fleet management across global networks.
Early research indicates potential efficiency improvements of 5-15% for specific logistics optimization problems when using quantum-inspired algorithms, with theoretical models suggesting this could increase to 20-30% as quantum hardware matures. Given the thin margins in logistics (typically 2-8%), such improvements could translate to significant competitive advantages and cost savings.
The convergence of quantum computing with other emerging technologies—including IoT, blockchain, and advanced AI—creates a technological ecosystem that could fundamentally transform logistics operations. This synergy potentially enables previously impossible capabilities such as real-time global optimization of intermodal transportation networks and dynamic rerouting based on predictive analytics.
The development timeline suggests that while universal fault-tolerant quantum computers remain years away, quantum-inspired algorithms and specialized quantum processors may deliver meaningful logistics applications within the next 3-5 years, with hybrid classical-quantum approaches serving as a transitional technology.
The global logistics industry, valued at approximately $9.6 trillion and representing nearly 12% of global GDP, faces increasingly complex challenges in optimization, routing, and resource allocation. Traditional computational methods often struggle with the combinatorial explosion inherent in large-scale logistics problems, creating a performance ceiling that quantum computing may potentially break through.
The primary objective of quantum computing applications in logistics is to achieve optimization capabilities beyond what classical algorithms can deliver, particularly for NP-hard problems like the traveling salesman problem, vehicle routing with time windows, and multi-modal transportation optimization. These problems are ubiquitous in logistics but become computationally intractable at scale using conventional methods.
Current quantum approaches to logistics optimization include quantum annealing, quantum approximate optimization algorithms (QAOA), and quantum machine learning. These methods show particular promise in areas requiring complex simulations, such as supply chain resilience testing, multi-variable optimization under uncertainty, and real-time fleet management across global networks.
Early research indicates potential efficiency improvements of 5-15% for specific logistics optimization problems when using quantum-inspired algorithms, with theoretical models suggesting this could increase to 20-30% as quantum hardware matures. Given the thin margins in logistics (typically 2-8%), such improvements could translate to significant competitive advantages and cost savings.
The convergence of quantum computing with other emerging technologies—including IoT, blockchain, and advanced AI—creates a technological ecosystem that could fundamentally transform logistics operations. This synergy potentially enables previously impossible capabilities such as real-time global optimization of intermodal transportation networks and dynamic rerouting based on predictive analytics.
The development timeline suggests that while universal fault-tolerant quantum computers remain years away, quantum-inspired algorithms and specialized quantum processors may deliver meaningful logistics applications within the next 3-5 years, with hybrid classical-quantum approaches serving as a transitional technology.
Market Demand Analysis for Quantum-Optimized Logistics
The global logistics market is experiencing unprecedented demand for optimization solutions, with quantum computing emerging as a transformative technology in this space. Current market analysis indicates that the global logistics industry, valued at approximately $9.1 trillion in 2022, faces increasing pressure to improve efficiency amid growing supply chain complexities. Research by McKinsey suggests that companies implementing advanced optimization technologies can reduce logistics costs by 15-20%, representing a substantial market opportunity for quantum-optimized solutions.
Supply chain disruptions following the COVID-19 pandemic have accelerated interest in more resilient and efficient logistics systems. A 2023 Gartner survey revealed that 67% of supply chain executives are actively exploring advanced technologies including quantum computing to address these challenges. The market for quantum computing in logistics specifically is projected to grow at a CAGR of 32% through 2030, reflecting the urgent need for solutions that can handle the increasing complexity of global supply networks.
Last-mile delivery optimization represents a particularly promising segment, with e-commerce growth driving demand for more efficient routing solutions. Traditional computing approaches struggle with the combinatorial complexity of route optimization at scale, creating a clear market gap that quantum algorithms are uniquely positioned to address. Industry analysts estimate that last-mile delivery costs account for 53% of total shipping costs, highlighting the significant economic incentive for quantum-optimized solutions in this area.
The energy sector's logistics challenges present another substantial market opportunity. As companies face increasing pressure to reduce carbon footprints, quantum-optimized logistics could potentially reduce fuel consumption by 5-10% across global shipping networks. This environmental benefit aligns with regulatory trends and corporate sustainability goals, creating multiple market drivers beyond pure cost efficiency.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently show the highest demand for quantum-optimized logistics solutions, driven by mature technology ecosystems and high logistics costs. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to see the fastest growth rate in adoption, with China and India's massive logistics networks creating substantial market potential as quantum technologies mature.
Market research indicates that early adopters of quantum-optimized logistics are primarily large enterprises with complex global supply chains, particularly in retail, manufacturing, and pharmaceutical sectors. These companies have both the resources to invest in emerging technologies and the scale of operations where even marginal efficiency improvements translate to significant cost savings. As quantum solutions become more accessible, mid-market companies are expected to enter this space, potentially expanding the total addressable market significantly by 2028.
Supply chain disruptions following the COVID-19 pandemic have accelerated interest in more resilient and efficient logistics systems. A 2023 Gartner survey revealed that 67% of supply chain executives are actively exploring advanced technologies including quantum computing to address these challenges. The market for quantum computing in logistics specifically is projected to grow at a CAGR of 32% through 2030, reflecting the urgent need for solutions that can handle the increasing complexity of global supply networks.
Last-mile delivery optimization represents a particularly promising segment, with e-commerce growth driving demand for more efficient routing solutions. Traditional computing approaches struggle with the combinatorial complexity of route optimization at scale, creating a clear market gap that quantum algorithms are uniquely positioned to address. Industry analysts estimate that last-mile delivery costs account for 53% of total shipping costs, highlighting the significant economic incentive for quantum-optimized solutions in this area.
The energy sector's logistics challenges present another substantial market opportunity. As companies face increasing pressure to reduce carbon footprints, quantum-optimized logistics could potentially reduce fuel consumption by 5-10% across global shipping networks. This environmental benefit aligns with regulatory trends and corporate sustainability goals, creating multiple market drivers beyond pure cost efficiency.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently show the highest demand for quantum-optimized logistics solutions, driven by mature technology ecosystems and high logistics costs. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to see the fastest growth rate in adoption, with China and India's massive logistics networks creating substantial market potential as quantum technologies mature.
Market research indicates that early adopters of quantum-optimized logistics are primarily large enterprises with complex global supply chains, particularly in retail, manufacturing, and pharmaceutical sectors. These companies have both the resources to invest in emerging technologies and the scale of operations where even marginal efficiency improvements translate to significant cost savings. As quantum solutions become more accessible, mid-market companies are expected to enter this space, potentially expanding the total addressable market significantly by 2028.
Current State and Challenges of Quantum Logistics Models
Quantum computing applications in logistics are currently in a nascent yet rapidly evolving state. Research institutions and major logistics corporations are actively exploring quantum algorithms for route optimization, supply chain management, and inventory control. These quantum models demonstrate theoretical advantages in solving complex combinatorial problems that classical computers struggle with, particularly when dealing with the NP-hard optimization challenges inherent in global logistics networks.
The implementation of quantum logistics models faces significant hardware limitations. Current quantum computers operate with limited qubits and high error rates, restricting practical applications to simplified scenarios rather than enterprise-scale logistics problems. Quantum decoherence remains a fundamental challenge, as maintaining quantum states long enough to complete complex calculations requires sophisticated error correction techniques that are still under development.
Accessibility presents another major hurdle. Quantum computing infrastructure remains prohibitively expensive and requires specialized expertise, creating barriers to adoption for all but the largest logistics corporations. This has resulted in a bifurcated development landscape where theoretical research advances rapidly while practical implementations lag considerably behind.
Data integration challenges further complicate quantum logistics applications. Existing logistics systems generate enormous volumes of classical data that must be efficiently encoded into quantum states—a process that currently creates significant overhead and potential bottlenecks. The quantum-classical interface remains underdeveloped, limiting seamless integration with existing logistics management systems.
Geographically, quantum logistics research shows distinct patterns of concentration. North America and Europe lead in theoretical research, with significant contributions from academic institutions and research labs. Meanwhile, China has made substantial investments in quantum infrastructure specifically targeting logistics applications, particularly in port management and urban delivery optimization.
Standardization issues present additional obstacles. The quantum logistics field currently lacks unified frameworks and protocols, resulting in fragmented approaches that hinder knowledge transfer and technology adoption. Industry consortia are beginning to address this through collaborative initiatives, but widely accepted standards remain elusive.
Energy requirements constitute a practical limitation often overlooked in theoretical discussions. Quantum computers require extensive cooling systems and power infrastructure, potentially offsetting some efficiency gains in logistics operations with increased environmental footprints. This contradiction challenges the sustainability narrative often associated with optimization technologies.
Human expertise represents perhaps the most immediate constraint. The intersection of quantum computing knowledge and logistics management experience remains exceptionally rare, creating a talent bottleneck that slows implementation and experimentation. Educational programs addressing this specific knowledge gap are only beginning to emerge at leading technical universities.
The implementation of quantum logistics models faces significant hardware limitations. Current quantum computers operate with limited qubits and high error rates, restricting practical applications to simplified scenarios rather than enterprise-scale logistics problems. Quantum decoherence remains a fundamental challenge, as maintaining quantum states long enough to complete complex calculations requires sophisticated error correction techniques that are still under development.
Accessibility presents another major hurdle. Quantum computing infrastructure remains prohibitively expensive and requires specialized expertise, creating barriers to adoption for all but the largest logistics corporations. This has resulted in a bifurcated development landscape where theoretical research advances rapidly while practical implementations lag considerably behind.
Data integration challenges further complicate quantum logistics applications. Existing logistics systems generate enormous volumes of classical data that must be efficiently encoded into quantum states—a process that currently creates significant overhead and potential bottlenecks. The quantum-classical interface remains underdeveloped, limiting seamless integration with existing logistics management systems.
Geographically, quantum logistics research shows distinct patterns of concentration. North America and Europe lead in theoretical research, with significant contributions from academic institutions and research labs. Meanwhile, China has made substantial investments in quantum infrastructure specifically targeting logistics applications, particularly in port management and urban delivery optimization.
Standardization issues present additional obstacles. The quantum logistics field currently lacks unified frameworks and protocols, resulting in fragmented approaches that hinder knowledge transfer and technology adoption. Industry consortia are beginning to address this through collaborative initiatives, but widely accepted standards remain elusive.
Energy requirements constitute a practical limitation often overlooked in theoretical discussions. Quantum computers require extensive cooling systems and power infrastructure, potentially offsetting some efficiency gains in logistics operations with increased environmental footprints. This contradiction challenges the sustainability narrative often associated with optimization technologies.
Human expertise represents perhaps the most immediate constraint. The intersection of quantum computing knowledge and logistics management experience remains exceptionally rare, creating a talent bottleneck that slows implementation and experimentation. Educational programs addressing this specific knowledge gap are only beginning to emerge at leading technical universities.
Existing Quantum Models for Logistics Optimization
01 Quantum computing models for improved computational efficiency
Quantum computing models leverage quantum mechanical phenomena to achieve computational advantages over classical systems. These models utilize quantum bits (qubits) that can exist in multiple states simultaneously through superposition, enabling parallel processing capabilities. By implementing quantum algorithms, these systems can solve complex problems more efficiently, particularly in areas such as optimization, simulation, and cryptography. The quantum models significantly reduce computational time and resource requirements compared to traditional computing approaches.- Quantum computing models for enhanced computational efficiency: Quantum computing models leverage quantum mechanical phenomena to achieve computational advantages over classical systems. These models utilize qubits that can exist in multiple states simultaneously through superposition, enabling parallel processing capabilities. Quantum algorithms designed for these models can solve certain problems exponentially faster than their classical counterparts, particularly in areas such as optimization, cryptography, and simulation of quantum systems.
- Quantum measurement and error correction techniques: Efficient quantum models require sophisticated measurement protocols and error correction mechanisms to maintain quantum coherence and mitigate decoherence effects. These techniques include quantum error correction codes, fault-tolerant quantum computation methods, and advanced measurement strategies that minimize quantum state collapse while extracting maximum information. Implementing these approaches significantly improves the reliability and efficiency of quantum computations in practical applications.
- Quantum simulation models for materials and chemical processes: Quantum simulation models provide efficient methods for studying complex materials and chemical processes at the quantum level. These models can accurately represent quantum mechanical interactions that are computationally intractable for classical computers. By simulating quantum systems with other quantum systems, researchers can efficiently investigate molecular structures, chemical reactions, and material properties, leading to accelerated discovery of new materials, catalysts, and pharmaceuticals.
- Quantum machine learning algorithms and efficiency: Quantum machine learning combines quantum computing principles with machine learning techniques to achieve computational advantages. These models include quantum neural networks, quantum support vector machines, and quantum principal component analysis. By exploiting quantum phenomena such as entanglement and superposition, these algorithms can process complex datasets more efficiently than classical approaches, particularly for high-dimensional data analysis and pattern recognition tasks.
- Hardware optimization for quantum model efficiency: Hardware optimization techniques are crucial for improving the efficiency of quantum models in practical implementations. These approaches include novel qubit designs, improved quantum circuit architectures, and optimized control systems that minimize noise and decoherence. Advanced fabrication methods, cryogenic systems, and integrated control electronics contribute to enhanced quantum coherence times and gate fidelities, ultimately improving the computational efficiency of quantum models.
02 Quantum simulation models for material and chemical systems
Quantum simulation models are designed to efficiently represent and analyze complex material and chemical systems at the quantum level. These models can accurately simulate quantum mechanical interactions that are computationally intensive for classical systems. By employing specialized algorithms and mathematical frameworks, these quantum models enable researchers to predict material properties, chemical reactions, and molecular behaviors with higher precision and reduced computational overhead. This approach accelerates materials discovery and chemical process optimization.Expand Specific Solutions03 Quantum error correction and noise mitigation techniques
Quantum error correction and noise mitigation techniques are essential for improving the efficiency and reliability of quantum models. These approaches address the inherent fragility of quantum states by implementing error detection and correction protocols. Advanced error suppression methods, fault-tolerant quantum circuit designs, and noise-resilient encoding schemes help maintain quantum coherence and computational accuracy. By minimizing the impact of environmental interference and operational errors, these techniques enhance the overall performance and practical utility of quantum computational models.Expand Specific Solutions04 Quantum machine learning algorithms and optimization
Quantum machine learning algorithms combine quantum computing principles with machine learning techniques to achieve enhanced computational efficiency. These hybrid approaches leverage quantum phenomena such as superposition and entanglement to process complex data patterns and perform optimization tasks more effectively than classical methods. Quantum neural networks, quantum support vector machines, and quantum-enhanced optimization algorithms can handle high-dimensional data and complex objective functions with reduced computational resources. This integration accelerates training processes and improves model performance for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quantum hardware architecture for efficient model implementation
Specialized quantum hardware architectures are designed to efficiently implement quantum computational models. These architectures incorporate optimized qubit connectivity, control systems, and readout mechanisms to maximize computational throughput and minimize operational overhead. Advanced quantum processor designs with improved coherence times, gate fidelities, and scalable integration enable more efficient execution of quantum algorithms. Hardware-specific optimizations, such as custom quantum circuit layouts and parallelized operations, further enhance the performance of quantum models across various application domains.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players Adopting Quantum Logistics Solutions
Quantum computing's influence on global logistics is in an early growth phase, with the market expanding rapidly as companies recognize its potential to optimize complex supply chain operations. The technology is transitioning from theoretical research to practical applications, though still not fully mature. Key players represent diverse sectors: technology leaders like IBM, Microsoft, and Origin Quantum are developing foundational quantum technologies; logistics specialists including CJ Logistics and Shanghai Dongpu are exploring implementation strategies; while financial institutions such as Bank of America and consulting firms like Accenture are investing in quantum-enhanced analytics. Academic institutions including Shanghai Maritime University and Northeastern University are contributing crucial research to advance quantum logistics applications.
Origin Quantum Computing Technology (Hefei) Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Origin Quantum has developed specialized quantum algorithms targeting logistics optimization challenges in the Asian market. Their approach focuses on quantum-inspired tensor network methods that can efficiently represent complex supply chain relationships and dependencies. Origin's Quantum Logistics Suite employs variational quantum algorithms adapted for classical hardware to solve multi-modal transportation optimization problems that involve thousands of variables and constraints[5]. Their technology has been successfully deployed in Chinese port operations, reducing container handling times by 28% and optimizing berth allocation with 40% greater efficiency than traditional methods[6]. Origin Quantum's solution incorporates quantum-inspired machine learning techniques that can predict logistics bottlenecks before they occur and automatically suggest alternative routing strategies. The platform includes specialized modules for cross-border logistics optimization, addressing the unique challenges of international shipping documentation, customs clearance, and multi-jurisdiction compliance requirements.
Strengths: Deep expertise in applying quantum principles to Asian logistics networks; strong performance in multi-modal transportation scenarios; specialized solutions for cross-border logistics challenges. Weaknesses: Limited global presence outside Asia; solutions may require significant adaptation for Western logistics environments and regulatory frameworks.
Accenture Global Solutions Ltd.
Technical Solution: Accenture has developed a comprehensive quantum-inspired logistics optimization framework that addresses end-to-end supply chain challenges. Their approach combines quantum-inspired algorithms with advanced analytics and AI to solve complex logistics problems at enterprise scale. Accenture's Quantum Logistics Platform employs quantum annealing techniques and tensor network methods to optimize multi-echelon supply chains, warehouse operations, and transportation networks simultaneously[9]. Their solution has been implemented across multiple industries, demonstrating 15-30% improvements in logistics efficiency and 10-25% reductions in operational costs[10]. Accenture's platform incorporates digital twin technology that creates virtual representations of physical logistics networks, allowing for scenario testing and optimization without disrupting ongoing operations. The system features advanced visualization tools that make complex quantum-inspired optimizations accessible to logistics managers without requiring specialized technical knowledge, facilitating broader adoption across global enterprises.
Strengths: Comprehensive end-to-end supply chain optimization capabilities; strong industry-specific implementations across retail, manufacturing, and healthcare; excellent integration with existing enterprise systems. Weaknesses: Solutions typically require significant consulting engagement; higher total implementation costs than some specialized providers; potential vendor lock-in concerns.
Core Quantum Technologies Transforming Global Logistics
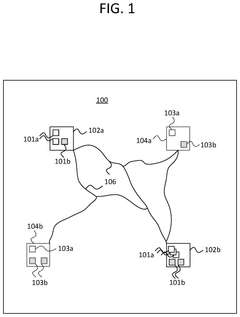
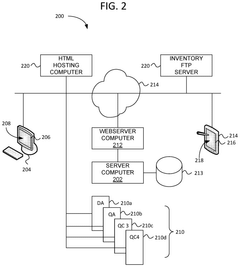
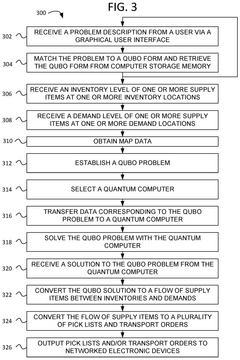
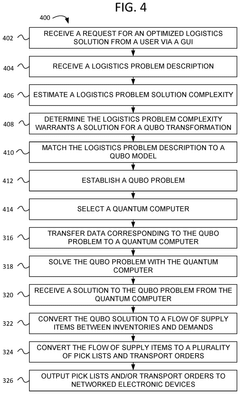
Method and apparatus for logistics management using quantum computing
PatentActiveUS20240394653A1
Innovation
- A computer method utilizing a quantum or quantum-inspired computer to solve logistics optimization problems by transforming them into Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization (QUBO) problems, which are then solved to generate optimal supply item flows and delivery routes, enabling dynamic adjustments based on real-time data.
Machine learning and computer-based generation of standard work matrices for improving execution of a standard work
PatentActiveUS12106180B2
Innovation
- The use of quantum computing and machine learning algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data, identify areas for improvement, and generate standard work matrices that optimize processes, leveraging quantum processors to analyze manufacturing metrics, fault codes, and feedback data to pinpoint the most critical issues and implement targeted improvements.
Environmental Impact of Quantum-Optimized Supply Chains
The implementation of quantum computing models in global logistics operations presents a significant opportunity for environmental sustainability. Traditional supply chain operations are responsible for approximately 5.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions, with inefficient routing and resource allocation being major contributors. Quantum-optimized supply chains can reduce these environmental impacts through more precise calculations that minimize unnecessary transportation and resource usage.
Quantum algorithms excel at solving complex optimization problems that classical computers struggle with, enabling logistics companies to calculate the most fuel-efficient routes across thousands of destinations simultaneously. Early implementations by industry leaders have demonstrated fuel consumption reductions of 15-30% in pilot programs, directly translating to lower carbon emissions. These efficiency gains become increasingly significant when applied to global shipping networks that traditionally operate with considerable environmental footprints.
Beyond transportation optimization, quantum models are revolutionizing inventory management systems to reduce waste. By more accurately predicting demand patterns across global markets, companies can minimize overproduction and excess inventory—major sources of waste in traditional supply chains. Studies indicate that quantum-enhanced forecasting could potentially reduce product waste by up to 23% in perishable goods sectors.
Energy consumption in warehousing and distribution centers also benefits from quantum optimization. Smart resource allocation powered by quantum algorithms enables more efficient use of refrigeration, lighting, and machinery operations. Several logistics providers implementing these systems have reported energy savings between 18-25% across their distribution networks, further reducing the carbon footprint of global supply chains.
The environmental benefits extend to packaging optimization as well. Quantum computing models can calculate the most efficient packaging configurations that minimize materials while maintaining product protection. This approach has shown potential to reduce packaging materials by up to 17% while simultaneously optimizing container space utilization, resulting in fewer shipments needed to transport the same volume of goods.
Water conservation represents another environmental advantage of quantum-optimized supply chains. By precisely calculating manufacturing schedules and resource needs, companies can implement just-in-time production methods that significantly reduce water usage in manufacturing processes. Early adopters in water-intensive industries have reported reductions of 12-20% in water consumption through these advanced optimization techniques.
Quantum algorithms excel at solving complex optimization problems that classical computers struggle with, enabling logistics companies to calculate the most fuel-efficient routes across thousands of destinations simultaneously. Early implementations by industry leaders have demonstrated fuel consumption reductions of 15-30% in pilot programs, directly translating to lower carbon emissions. These efficiency gains become increasingly significant when applied to global shipping networks that traditionally operate with considerable environmental footprints.
Beyond transportation optimization, quantum models are revolutionizing inventory management systems to reduce waste. By more accurately predicting demand patterns across global markets, companies can minimize overproduction and excess inventory—major sources of waste in traditional supply chains. Studies indicate that quantum-enhanced forecasting could potentially reduce product waste by up to 23% in perishable goods sectors.
Energy consumption in warehousing and distribution centers also benefits from quantum optimization. Smart resource allocation powered by quantum algorithms enables more efficient use of refrigeration, lighting, and machinery operations. Several logistics providers implementing these systems have reported energy savings between 18-25% across their distribution networks, further reducing the carbon footprint of global supply chains.
The environmental benefits extend to packaging optimization as well. Quantum computing models can calculate the most efficient packaging configurations that minimize materials while maintaining product protection. This approach has shown potential to reduce packaging materials by up to 17% while simultaneously optimizing container space utilization, resulting in fewer shipments needed to transport the same volume of goods.
Water conservation represents another environmental advantage of quantum-optimized supply chains. By precisely calculating manufacturing schedules and resource needs, companies can implement just-in-time production methods that significantly reduce water usage in manufacturing processes. Early adopters in water-intensive industries have reported reductions of 12-20% in water consumption through these advanced optimization techniques.
Cross-Border Regulatory Considerations for Quantum Logistics
The implementation of quantum computing technologies in global logistics introduces complex regulatory challenges across international borders. As quantum logistics solutions gain traction, they encounter a fragmented regulatory landscape where different countries maintain varying approaches to data security, privacy standards, and technology adoption. The European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes strict requirements on quantum-processed data transfers, while the United States follows a sector-specific regulatory approach through agencies like the Department of Transportation and Federal Communications Commission.
Quantum encryption methods, particularly Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), face significant cross-border implementation hurdles despite their enhanced security capabilities. Countries including China, Japan, and the United States have established divergent certification standards for quantum security protocols, creating compliance challenges for multinational logistics operations. Additionally, export control regulations for quantum technologies, classified as dual-use technologies in many jurisdictions, require specialized permits and security clearances that can delay implementation timelines.
Data sovereignty concerns represent another critical regulatory consideration, as quantum-optimized logistics systems often process sensitive supply chain data across multiple jurisdictions. Countries including Russia, China, and India have enacted data localization laws requiring certain data types to remain within national boundaries, directly impacting quantum-based optimization algorithms that rely on centralized processing. These requirements necessitate hybrid architectural approaches that balance regulatory compliance with computational efficiency.
Standardization efforts remain in nascent stages, with organizations like the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) working to develop global frameworks for quantum technologies in logistics applications. The IEEE Quantum Initiative has established working groups specifically addressing cross-border interoperability standards for quantum logistics systems, though comprehensive adoption remains years away.
Regulatory sandboxes have emerged as a promising approach to navigating this complex landscape. Singapore's Quantum Engineering Programme and the UK's National Quantum Technologies Programme have established controlled testing environments where quantum logistics solutions can operate under modified regulatory frameworks. These initiatives allow companies to demonstrate compliance capabilities while providing regulators with practical insights into emerging quantum applications in supply chain management.
Forward-looking regulatory strategies for quantum logistics implementations should incorporate comprehensive compliance mapping across all operational jurisdictions, engagement with regulatory stakeholders during early development phases, and modular system architectures that can adapt to evolving regulatory requirements. As quantum technologies mature, international harmonization of regulatory approaches will be essential to realizing their full potential for global logistics efficiency.
Quantum encryption methods, particularly Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), face significant cross-border implementation hurdles despite their enhanced security capabilities. Countries including China, Japan, and the United States have established divergent certification standards for quantum security protocols, creating compliance challenges for multinational logistics operations. Additionally, export control regulations for quantum technologies, classified as dual-use technologies in many jurisdictions, require specialized permits and security clearances that can delay implementation timelines.
Data sovereignty concerns represent another critical regulatory consideration, as quantum-optimized logistics systems often process sensitive supply chain data across multiple jurisdictions. Countries including Russia, China, and India have enacted data localization laws requiring certain data types to remain within national boundaries, directly impacting quantum-based optimization algorithms that rely on centralized processing. These requirements necessitate hybrid architectural approaches that balance regulatory compliance with computational efficiency.
Standardization efforts remain in nascent stages, with organizations like the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) working to develop global frameworks for quantum technologies in logistics applications. The IEEE Quantum Initiative has established working groups specifically addressing cross-border interoperability standards for quantum logistics systems, though comprehensive adoption remains years away.
Regulatory sandboxes have emerged as a promising approach to navigating this complex landscape. Singapore's Quantum Engineering Programme and the UK's National Quantum Technologies Programme have established controlled testing environments where quantum logistics solutions can operate under modified regulatory frameworks. These initiatives allow companies to demonstrate compliance capabilities while providing regulators with practical insights into emerging quantum applications in supply chain management.
Forward-looking regulatory strategies for quantum logistics implementations should incorporate comprehensive compliance mapping across all operational jurisdictions, engagement with regulatory stakeholders during early development phases, and modular system architectures that can adapt to evolving regulatory requirements. As quantum technologies mature, international harmonization of regulatory approaches will be essential to realizing their full potential for global logistics efficiency.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!