How V8 Engines Revolutionized the Automotive Industry?
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
V8 Engine Evolution and Objectives
The V8 engine, a marvel of automotive engineering, has played a pivotal role in shaping the automotive industry since its inception in the early 20th century. This powerful and efficient engine configuration has undergone significant evolution, continuously adapting to meet changing market demands and technological advancements.
The development of the V8 engine can be traced back to 1902 when Léon Levavasseur patented the first V8 engine design. However, it wasn't until 1914 that Cadillac introduced the first mass-produced V8 engine, marking the beginning of a new era in automotive propulsion. The primary objective of early V8 engines was to provide increased power output while maintaining a compact design, allowing for improved vehicle performance without sacrificing space efficiency.
Throughout the 20th century, V8 engines continued to evolve, with manufacturers focusing on enhancing power, efficiency, and reliability. The 1950s and 1960s saw a surge in V8 popularity, particularly in the United States, where these engines became synonymous with muscle cars and high-performance vehicles. During this period, the objectives shifted towards maximizing horsepower and torque, often at the expense of fuel efficiency.
The oil crisis of the 1970s prompted a significant shift in V8 engine development. Manufacturers were forced to prioritize fuel efficiency and emissions reduction while maintaining performance. This led to the introduction of technologies such as electronic fuel injection, variable valve timing, and cylinder deactivation. These advancements aimed to strike a balance between power and efficiency, allowing V8 engines to remain relevant in an increasingly environmentally conscious market.
In recent decades, the evolution of V8 engines has been driven by the need to meet stringent emissions regulations and improve fuel economy. Modern V8 engines incorporate advanced technologies such as direct fuel injection, turbocharging, and lightweight materials to achieve these goals. The objective has shifted towards creating high-performance engines that can deliver impressive power output while minimizing environmental impact.
Looking towards the future, V8 engine development continues to focus on sustainability and efficiency. Manufacturers are exploring hybrid and electric assist technologies to complement V8 engines, further reducing emissions and fuel consumption. Additionally, research into alternative fuels and advanced combustion techniques aims to extend the lifespan of V8 engines in an increasingly electrified automotive landscape.
Throughout its history, the V8 engine has consistently adapted to meet changing market demands and regulatory requirements. From its origins as a powerful yet compact solution to its current role as a high-performance, technologically advanced powerplant, the V8 engine has remained a symbol of automotive innovation and engineering excellence. As the industry moves towards electrification, the future of V8 engines lies in their ability to evolve and integrate with new technologies, ensuring their continued relevance in the automotive world.
The development of the V8 engine can be traced back to 1902 when Léon Levavasseur patented the first V8 engine design. However, it wasn't until 1914 that Cadillac introduced the first mass-produced V8 engine, marking the beginning of a new era in automotive propulsion. The primary objective of early V8 engines was to provide increased power output while maintaining a compact design, allowing for improved vehicle performance without sacrificing space efficiency.
Throughout the 20th century, V8 engines continued to evolve, with manufacturers focusing on enhancing power, efficiency, and reliability. The 1950s and 1960s saw a surge in V8 popularity, particularly in the United States, where these engines became synonymous with muscle cars and high-performance vehicles. During this period, the objectives shifted towards maximizing horsepower and torque, often at the expense of fuel efficiency.
The oil crisis of the 1970s prompted a significant shift in V8 engine development. Manufacturers were forced to prioritize fuel efficiency and emissions reduction while maintaining performance. This led to the introduction of technologies such as electronic fuel injection, variable valve timing, and cylinder deactivation. These advancements aimed to strike a balance between power and efficiency, allowing V8 engines to remain relevant in an increasingly environmentally conscious market.
In recent decades, the evolution of V8 engines has been driven by the need to meet stringent emissions regulations and improve fuel economy. Modern V8 engines incorporate advanced technologies such as direct fuel injection, turbocharging, and lightweight materials to achieve these goals. The objective has shifted towards creating high-performance engines that can deliver impressive power output while minimizing environmental impact.
Looking towards the future, V8 engine development continues to focus on sustainability and efficiency. Manufacturers are exploring hybrid and electric assist technologies to complement V8 engines, further reducing emissions and fuel consumption. Additionally, research into alternative fuels and advanced combustion techniques aims to extend the lifespan of V8 engines in an increasingly electrified automotive landscape.
Throughout its history, the V8 engine has consistently adapted to meet changing market demands and regulatory requirements. From its origins as a powerful yet compact solution to its current role as a high-performance, technologically advanced powerplant, the V8 engine has remained a symbol of automotive innovation and engineering excellence. As the industry moves towards electrification, the future of V8 engines lies in their ability to evolve and integrate with new technologies, ensuring their continued relevance in the automotive world.
Market Demand Analysis for V8 Engines
The market demand for V8 engines has undergone significant shifts over the past decades, reflecting changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and regulatory pressures. Initially, V8 engines were synonymous with power, performance, and luxury in the automotive industry. Their popularity soared in the mid-20th century, particularly in North America, where large, powerful vehicles dominated the market.
During the 1960s and 1970s, the muscle car era saw a surge in demand for V8-powered vehicles. Consumers sought high-performance cars for both street use and drag racing, driving sales of V8-equipped models from manufacturers like Ford, Chevrolet, and Dodge. This period marked the peak of V8 engine popularity in the mass market.
However, the oil crises of the 1970s led to a shift in consumer preferences towards more fuel-efficient vehicles. This trend, coupled with increasingly stringent emissions regulations, began to challenge the dominance of V8 engines. Automakers responded by developing more efficient V8 designs and introducing smaller displacement options.
In the luxury and high-performance segments, V8 engines maintained their appeal. Premium brands like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Jaguar continued to offer V8 options in their flagship models, catering to customers who prioritized power and prestige. The sports car market also sustained demand for V8 engines, with iconic models from manufacturers like Ferrari and Chevrolet's Corvette.
The SUV boom of the 1990s and early 2000s provided a new market for V8 engines. Large SUVs and pickup trucks, particularly in North America, often featured V8 powerplants to deliver the towing capacity and performance desired by consumers. This trend helped sustain V8 production volumes despite declining use in passenger cars.
In recent years, market demand for V8 engines has faced increasing pressure from environmental concerns and tightening fuel economy standards. Many automakers have turned to turbocharged smaller-displacement engines or hybrid powertrains to meet these challenges. However, a niche market for V8 engines persists in high-performance vehicles, luxury cars, and certain truck applications.
Looking forward, the market for V8 engines is likely to continue evolving. While overall demand may decrease due to electrification and downsizing trends, there remains a dedicated consumer base that values the unique characteristics of V8 engines. Manufacturers are exploring ways to make V8 engines more efficient and environmentally friendly, potentially extending their market viability in specific segments.
During the 1960s and 1970s, the muscle car era saw a surge in demand for V8-powered vehicles. Consumers sought high-performance cars for both street use and drag racing, driving sales of V8-equipped models from manufacturers like Ford, Chevrolet, and Dodge. This period marked the peak of V8 engine popularity in the mass market.
However, the oil crises of the 1970s led to a shift in consumer preferences towards more fuel-efficient vehicles. This trend, coupled with increasingly stringent emissions regulations, began to challenge the dominance of V8 engines. Automakers responded by developing more efficient V8 designs and introducing smaller displacement options.
In the luxury and high-performance segments, V8 engines maintained their appeal. Premium brands like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Jaguar continued to offer V8 options in their flagship models, catering to customers who prioritized power and prestige. The sports car market also sustained demand for V8 engines, with iconic models from manufacturers like Ferrari and Chevrolet's Corvette.
The SUV boom of the 1990s and early 2000s provided a new market for V8 engines. Large SUVs and pickup trucks, particularly in North America, often featured V8 powerplants to deliver the towing capacity and performance desired by consumers. This trend helped sustain V8 production volumes despite declining use in passenger cars.
In recent years, market demand for V8 engines has faced increasing pressure from environmental concerns and tightening fuel economy standards. Many automakers have turned to turbocharged smaller-displacement engines or hybrid powertrains to meet these challenges. However, a niche market for V8 engines persists in high-performance vehicles, luxury cars, and certain truck applications.
Looking forward, the market for V8 engines is likely to continue evolving. While overall demand may decrease due to electrification and downsizing trends, there remains a dedicated consumer base that values the unique characteristics of V8 engines. Manufacturers are exploring ways to make V8 engines more efficient and environmentally friendly, potentially extending their market viability in specific segments.
V8 Engine Technology Status and Challenges
V8 engines have played a pivotal role in shaping the automotive industry, with their current status and challenges reflecting both their enduring appeal and the need for adaptation in a changing landscape. These powerful engines continue to be widely used in high-performance vehicles, luxury cars, and trucks, valued for their smooth power delivery and impressive torque output.
One of the primary challenges facing V8 engines is the increasing pressure to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Stricter environmental regulations worldwide have forced manufacturers to innovate and develop more efficient V8 designs. This has led to the implementation of technologies such as cylinder deactivation, direct fuel injection, and variable valve timing, which help optimize fuel consumption without sacrificing performance.
Another significant challenge is the rise of alternative powertrains, particularly electric and hybrid vehicles. As the automotive industry shifts towards electrification, the long-term viability of V8 engines is being questioned. Manufacturers are exploring ways to integrate hybrid technology with V8 engines to create high-performance vehicles that meet emissions standards while still delivering the characteristic V8 experience.
The weight and size of V8 engines present additional challenges in modern vehicle design. As automakers strive for improved aerodynamics and weight reduction to enhance overall efficiency, the substantial mass of V8 engines can be a limiting factor. This has led to the development of more compact and lightweight V8 designs, often utilizing materials such as aluminum and magnesium alloys.
Despite these challenges, V8 engines continue to evolve. Advanced manufacturing techniques and materials science have enabled the creation of more durable and efficient V8 engines. Turbocharging and supercharging technologies are being increasingly employed to extract more power from smaller displacement V8s, addressing both performance and efficiency concerns.
The current technological landscape also sees V8 engines benefiting from sophisticated engine management systems and electronic controls. These advancements allow for precise tuning of engine parameters, optimizing performance across a wide range of operating conditions and further improving efficiency.
In the realm of motorsports, V8 engines remain a dominant force, particularly in disciplines such as NASCAR and V8 Supercars. This continued presence in high-profile racing series helps maintain the V8's iconic status and drives ongoing development that often trickles down to production vehicles.
Looking ahead, the future of V8 engines will likely involve a delicate balance between preserving their performance heritage and adapting to a more environmentally conscious automotive landscape. Innovations in fuel technology, such as synthetic fuels and hydrogen combustion, may offer new avenues for V8 engines to remain relevant in an increasingly electrified world.
One of the primary challenges facing V8 engines is the increasing pressure to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Stricter environmental regulations worldwide have forced manufacturers to innovate and develop more efficient V8 designs. This has led to the implementation of technologies such as cylinder deactivation, direct fuel injection, and variable valve timing, which help optimize fuel consumption without sacrificing performance.
Another significant challenge is the rise of alternative powertrains, particularly electric and hybrid vehicles. As the automotive industry shifts towards electrification, the long-term viability of V8 engines is being questioned. Manufacturers are exploring ways to integrate hybrid technology with V8 engines to create high-performance vehicles that meet emissions standards while still delivering the characteristic V8 experience.
The weight and size of V8 engines present additional challenges in modern vehicle design. As automakers strive for improved aerodynamics and weight reduction to enhance overall efficiency, the substantial mass of V8 engines can be a limiting factor. This has led to the development of more compact and lightweight V8 designs, often utilizing materials such as aluminum and magnesium alloys.
Despite these challenges, V8 engines continue to evolve. Advanced manufacturing techniques and materials science have enabled the creation of more durable and efficient V8 engines. Turbocharging and supercharging technologies are being increasingly employed to extract more power from smaller displacement V8s, addressing both performance and efficiency concerns.
The current technological landscape also sees V8 engines benefiting from sophisticated engine management systems and electronic controls. These advancements allow for precise tuning of engine parameters, optimizing performance across a wide range of operating conditions and further improving efficiency.
In the realm of motorsports, V8 engines remain a dominant force, particularly in disciplines such as NASCAR and V8 Supercars. This continued presence in high-profile racing series helps maintain the V8's iconic status and drives ongoing development that often trickles down to production vehicles.
Looking ahead, the future of V8 engines will likely involve a delicate balance between preserving their performance heritage and adapting to a more environmentally conscious automotive landscape. Innovations in fuel technology, such as synthetic fuels and hydrogen combustion, may offer new avenues for V8 engines to remain relevant in an increasingly electrified world.
Current V8 Engine Design Solutions
01 V8 Engine Design and Configuration
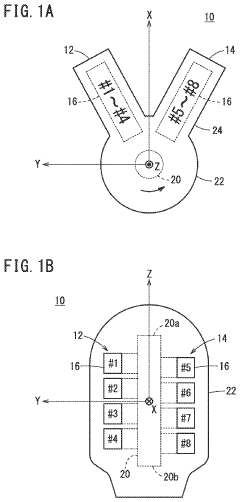
V8 engines are designed with eight cylinders arranged in two banks of four, forming a V-shape. This configuration allows for a compact design, improved balance, and higher power output. Various aspects of V8 engine design, including cylinder arrangement, crankshaft configuration, and valve train systems, are continuously improved to enhance performance and efficiency.- V8 Engine Design and Configuration: V8 engines are designed with eight cylinders arranged in two banks of four, forming a V-shape. This configuration allows for a compact design while providing high power output. The design often includes features for improved performance, fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions.
- Fuel Injection Systems for V8 Engines: Advanced fuel injection systems are developed for V8 engines to optimize fuel delivery and combustion. These systems may include direct injection, multi-port injection, or a combination of both, aimed at improving engine efficiency and power output while reducing fuel consumption.
- Valve Train and Camshaft Innovations: Innovations in valve train and camshaft designs for V8 engines focus on improving engine breathing and overall performance. This may include variable valve timing, lift systems, and advanced camshaft profiles to enhance power delivery across different engine speeds.
- Turbocharging and Supercharging V8 Engines: Forced induction systems, such as turbochargers and superchargers, are applied to V8 engines to significantly increase power output. These systems compress the intake air, allowing for more fuel to be burned and resulting in higher engine performance.
- Cooling and Lubrication Systems for V8 Engines: Specialized cooling and lubrication systems are developed for V8 engines to manage heat and reduce friction. These systems may include advanced oil pumps, cooling channels, and thermal management strategies to ensure optimal engine performance and longevity.
02 Fuel Injection and Combustion Systems
Advanced fuel injection and combustion systems are developed for V8 engines to optimize fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. These systems may include direct injection, variable valve timing, and advanced engine management systems to precisely control fuel delivery and combustion processes.Expand Specific Solutions03 Turbocharging and Supercharging
Forced induction systems, such as turbochargers and superchargers, are often employed in V8 engines to increase power output and improve efficiency. These systems compress the intake air, allowing more fuel to be burned and generating more power from the same engine displacement.Expand Specific Solutions04 Engine Block and Component Materials
Advancements in materials science have led to the development of lightweight and durable engine blocks and components for V8 engines. Materials such as aluminum alloys, high-strength steel, and composite materials are used to reduce weight while maintaining structural integrity and performance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Cooling and Lubrication Systems
Efficient cooling and lubrication systems are crucial for V8 engine performance and longevity. Innovations in these areas include advanced coolant formulations, improved oil circulation systems, and optimized heat management strategies to maintain optimal operating temperatures and reduce wear on engine components.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in V8 Engine Manufacturing
The V8 engine's impact on the automotive industry has been significant, with major players like BMW, Honda, Toyota, and GM leading the technological advancements. The market for V8 engines has matured, with a stable but potentially declining market size due to increasing focus on fuel efficiency and environmental regulations. However, the technology remains relevant in high-performance and luxury segments. Companies like Ford, Nissan, and Hyundai continue to innovate, improving power output and efficiency. The technology's maturity is evident in its widespread adoption, but ongoing research by manufacturers and institutions like Zhejiang University suggests potential for further optimization and evolution in response to changing market demands and regulatory pressures.
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG
Technical Solution: BMW has been at the forefront of V8 engine innovation, particularly with their TwinPower Turbo V8 engines. These engines utilize advanced technologies such as High Precision Injection, VALVETRONIC variable valve timing, and Double-VANOS variable camshaft control[1]. BMW's V8 engines have evolved to incorporate twin-scroll turbochargers, which significantly improve power delivery and efficiency. The company has also implemented a cross-bank exhaust manifold design, enhancing exhaust gas flow and turbocharger response[2]. BMW's latest V8 engines feature a hot-V configuration, placing the turbochargers within the V of the engine, reducing lag and improving thermal efficiency[3].
Strengths: High power output, improved fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions. Weaknesses: Complexity leading to potentially higher maintenance costs and the challenge of meeting increasingly stringent emissions regulations.
Toyota Motor Corp.
Technical Solution: Toyota's approach to V8 engine development has focused on balancing power with reliability and efficiency. Their UR series V8 engines, particularly the 1UR-FE, incorporate dual overhead camshafts, four valves per cylinder, and Toyota's Dual VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing with intelligence) system[4]. Toyota has also developed direct injection V8 engines, such as the 2UR-GSE used in Lexus performance vehicles, which combines port and direct injection for improved power and efficiency[5]. In recent years, Toyota has explored hybrid V8 technologies, as seen in the Lexus LS 500h, which pairs a V6 engine with electric motors to achieve V8-like performance with improved fuel economy[6].
Strengths: Renowned reliability, smooth power delivery, and integration with hybrid systems. Weaknesses: Relatively conservative approach to high-performance applications compared to some competitors.
Core V8 Engine Innovations
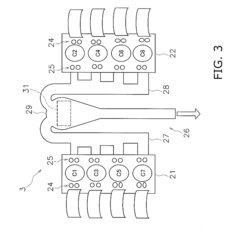
V8 engine
PatentActiveUS11821359B2
Innovation
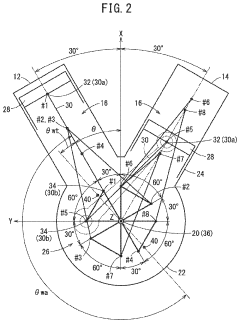
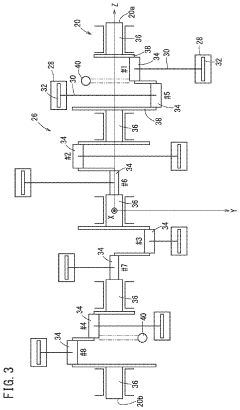
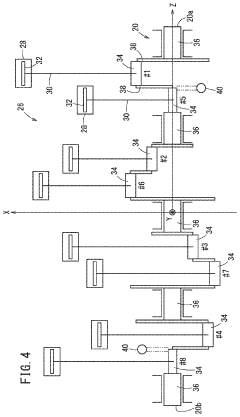
- The V8 engine configuration features crank pins arranged at 90° intervals on one bank and offset by 60° on the other bank, allowing for cancellation of primary inertia couples without additional specialized parts by optimizing the arrangement of crank pins and connecting rods.
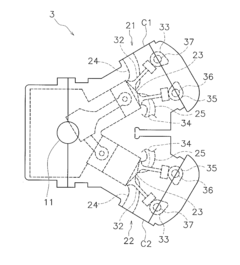
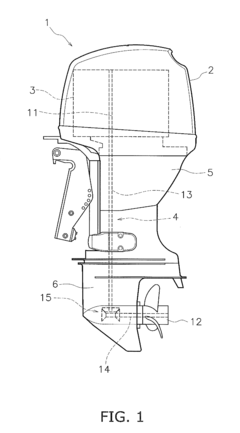
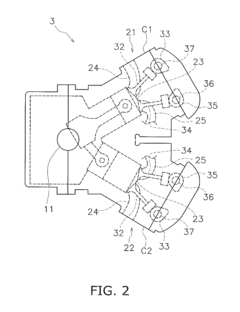
V8 engine and outboard motor
PatentActiveUS20160341097A1
Innovation
- A V8 engine design with a simple construction featuring aggregated exhaust pathways and adjustable exhaust cams, where the central angle of exhaust cams for each cylinder is optimized to minimize valve overlap and reduce exhaust interference, allowing for even firing intervals and improved exhaust gas management.
Environmental Impact of V8 Engines
The environmental impact of V8 engines has been a subject of significant concern and debate since their widespread adoption in the automotive industry. These powerful engines, known for their high performance and distinctive sound, have left a considerable ecological footprint over the decades.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with V8 engines is their high fuel consumption. Due to their larger displacement and increased number of cylinders, V8 engines typically consume more fuel than their smaller counterparts. This increased fuel consumption directly translates to higher carbon dioxide emissions, contributing to the greenhouse effect and global warming.
Emissions from V8 engines extend beyond carbon dioxide. These engines also produce higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, which are known to have detrimental effects on air quality and human health. In urban areas, where vehicle concentration is high, the cumulative impact of V8 emissions can significantly contribute to smog formation and respiratory issues.
The manufacturing process of V8 engines also carries environmental implications. The production of larger, more complex engines requires additional raw materials and energy, leading to increased resource consumption and industrial emissions. The heavier weight of V8 engines compared to smaller alternatives also necessitates the use of more robust vehicle components, further amplifying the environmental cost of production.
However, it's important to note that technological advancements have led to improvements in V8 engine efficiency over time. Modern V8 engines often incorporate features such as variable valve timing, direct fuel injection, and cylinder deactivation, which help to reduce fuel consumption and emissions when compared to their older counterparts.
The automotive industry has also responded to environmental concerns by developing hybrid and electric alternatives to traditional V8-powered vehicles. These eco-friendly options aim to provide similar performance characteristics while significantly reducing or eliminating tailpipe emissions.
Despite these advancements, the overall environmental impact of V8 engines remains a challenge. As global environmental regulations become increasingly stringent, manufacturers are under pressure to further improve the efficiency of V8 engines or phase them out in favor of more sustainable alternatives.
The future of V8 engines in the context of environmental sustainability is uncertain. While they continue to be popular in certain vehicle segments, particularly in high-performance and luxury markets, their long-term viability may depend on breakthrough technologies that can dramatically reduce their environmental footprint without compromising their characteristic power and appeal.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with V8 engines is their high fuel consumption. Due to their larger displacement and increased number of cylinders, V8 engines typically consume more fuel than their smaller counterparts. This increased fuel consumption directly translates to higher carbon dioxide emissions, contributing to the greenhouse effect and global warming.
Emissions from V8 engines extend beyond carbon dioxide. These engines also produce higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, which are known to have detrimental effects on air quality and human health. In urban areas, where vehicle concentration is high, the cumulative impact of V8 emissions can significantly contribute to smog formation and respiratory issues.
The manufacturing process of V8 engines also carries environmental implications. The production of larger, more complex engines requires additional raw materials and energy, leading to increased resource consumption and industrial emissions. The heavier weight of V8 engines compared to smaller alternatives also necessitates the use of more robust vehicle components, further amplifying the environmental cost of production.
However, it's important to note that technological advancements have led to improvements in V8 engine efficiency over time. Modern V8 engines often incorporate features such as variable valve timing, direct fuel injection, and cylinder deactivation, which help to reduce fuel consumption and emissions when compared to their older counterparts.
The automotive industry has also responded to environmental concerns by developing hybrid and electric alternatives to traditional V8-powered vehicles. These eco-friendly options aim to provide similar performance characteristics while significantly reducing or eliminating tailpipe emissions.
Despite these advancements, the overall environmental impact of V8 engines remains a challenge. As global environmental regulations become increasingly stringent, manufacturers are under pressure to further improve the efficiency of V8 engines or phase them out in favor of more sustainable alternatives.
The future of V8 engines in the context of environmental sustainability is uncertain. While they continue to be popular in certain vehicle segments, particularly in high-performance and luxury markets, their long-term viability may depend on breakthrough technologies that can dramatically reduce their environmental footprint without compromising their characteristic power and appeal.
V8 Engine Performance Metrics
V8 engines have long been synonymous with high performance in the automotive industry. To understand their impact, it's crucial to examine key performance metrics that set V8 engines apart from their counterparts. One of the most significant metrics is horsepower, where V8 engines typically excel. High-performance V8s can produce upwards of 700 horsepower, with some specialized racing engines exceeding 1000 horsepower. This raw power translates to exceptional acceleration and top speed capabilities.
Torque is another critical metric where V8 engines shine. The V8 configuration allows for substantial torque output, often peaking at lower RPMs compared to smaller engines. This characteristic provides robust low-end power, making V8-equipped vehicles particularly adept at towing and hauling heavy loads. Many V8 engines can generate over 500 lb-ft of torque, with some high-performance variants surpassing 700 lb-ft.
Efficiency, while historically not a strong suit for V8 engines, has seen significant improvements in recent years. Modern V8s employ technologies like direct injection, variable valve timing, and cylinder deactivation to enhance fuel economy. Some contemporary V8 engines can achieve fuel efficiency ratings comparable to smaller six-cylinder engines under certain driving conditions.
Durability and longevity are also noteworthy performance metrics for V8 engines. The inherent balance of the V8 configuration reduces vibration and stress on engine components, potentially leading to increased engine life. Many V8 engines are known to surpass 200,000 miles with proper maintenance, a testament to their robust design and construction.
Noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) characteristics are another area where V8 engines often excel. The V8's firing order and inherent balance contribute to a smooth power delivery and a distinctive, often desirable exhaust note. This aspect of performance, while less quantifiable, significantly impacts the driving experience and perceived quality of a vehicle.
Power-to-weight ratio is a crucial metric in assessing overall vehicle performance. V8 engines, despite their size, often contribute to favorable power-to-weight ratios in performance vehicles. This is achieved through the use of lightweight materials and compact designs, allowing for impressive acceleration and handling characteristics.
Lastly, the versatility of V8 engines across various applications is a testament to their performance capabilities. From high-performance sports cars to luxury sedans, and from heavy-duty trucks to racing vehicles, V8 engines have demonstrated their ability to meet diverse performance requirements across a wide spectrum of automotive applications.
Torque is another critical metric where V8 engines shine. The V8 configuration allows for substantial torque output, often peaking at lower RPMs compared to smaller engines. This characteristic provides robust low-end power, making V8-equipped vehicles particularly adept at towing and hauling heavy loads. Many V8 engines can generate over 500 lb-ft of torque, with some high-performance variants surpassing 700 lb-ft.
Efficiency, while historically not a strong suit for V8 engines, has seen significant improvements in recent years. Modern V8s employ technologies like direct injection, variable valve timing, and cylinder deactivation to enhance fuel economy. Some contemporary V8 engines can achieve fuel efficiency ratings comparable to smaller six-cylinder engines under certain driving conditions.
Durability and longevity are also noteworthy performance metrics for V8 engines. The inherent balance of the V8 configuration reduces vibration and stress on engine components, potentially leading to increased engine life. Many V8 engines are known to surpass 200,000 miles with proper maintenance, a testament to their robust design and construction.
Noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) characteristics are another area where V8 engines often excel. The V8's firing order and inherent balance contribute to a smooth power delivery and a distinctive, often desirable exhaust note. This aspect of performance, while less quantifiable, significantly impacts the driving experience and perceived quality of a vehicle.
Power-to-weight ratio is a crucial metric in assessing overall vehicle performance. V8 engines, despite their size, often contribute to favorable power-to-weight ratios in performance vehicles. This is achieved through the use of lightweight materials and compact designs, allowing for impressive acceleration and handling characteristics.
Lastly, the versatility of V8 engines across various applications is a testament to their performance capabilities. From high-performance sports cars to luxury sedans, and from heavy-duty trucks to racing vehicles, V8 engines have demonstrated their ability to meet diverse performance requirements across a wide spectrum of automotive applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!