K24 Engine: Unveiling Top Strategies for Improved Efficiency
JUL 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
K24 Engine Background
The K24 engine, developed by Honda Motor Company, represents a significant milestone in automotive engineering. First introduced in the late 1990s, this inline-four cylinder engine was designed to deliver a balance of performance, efficiency, and reliability. The K24 engine has been a staple in Honda's lineup, powering various models across the Honda and Acura brands.
Initially conceived as an evolution of Honda's F-series engines, the K24 was engineered to meet the growing demands for increased power output and improved fuel economy. Its design incorporated several advanced features, including a die-cast aluminum block, forged steel connecting rods, and a high-flow exhaust system. These elements contributed to the engine's robust performance and durability, making it a popular choice for both everyday drivers and automotive enthusiasts.
Over the years, the K24 engine has undergone several iterations and improvements. Early versions displaced 2.4 liters and produced around 160 horsepower, while later variants saw power outputs exceeding 200 horsepower. The engine's versatility allowed it to be used in a wide range of vehicles, from compact sedans to SUVs, demonstrating its adaptability to different automotive applications.
One of the key technological advancements in the K24 engine was the implementation of Honda's i-VTEC (intelligent Variable Valve Timing and Lift Electronic Control) system. This innovation allowed for optimized valve timing and lift across different engine speeds, resulting in improved power delivery and fuel efficiency. The i-VTEC system became a hallmark of Honda's engine technology, setting new standards in the industry for variable valve timing mechanisms.
As environmental concerns and fuel efficiency standards became more stringent, Honda continued to refine the K24 engine. Later versions incorporated direct fuel injection, reduced friction components, and advanced engine management systems. These enhancements were aimed at improving thermal efficiency, reducing emissions, and further optimizing fuel consumption without compromising performance.
The K24 engine's legacy extends beyond its factory applications. Its robust design and tuning potential have made it a favorite among aftermarket enthusiasts and racing teams. The engine's ability to withstand high levels of modification while maintaining reliability has contributed to its enduring popularity in the performance community.
As the automotive industry shifts towards electrification and alternative powertrains, the focus on improving internal combustion engines like the K24 remains relevant. Strategies for enhancing efficiency, reducing emissions, and maximizing power output continue to evolve, with lessons learned from the K24's development informing future engine designs and hybrid powertrains.
Initially conceived as an evolution of Honda's F-series engines, the K24 was engineered to meet the growing demands for increased power output and improved fuel economy. Its design incorporated several advanced features, including a die-cast aluminum block, forged steel connecting rods, and a high-flow exhaust system. These elements contributed to the engine's robust performance and durability, making it a popular choice for both everyday drivers and automotive enthusiasts.
Over the years, the K24 engine has undergone several iterations and improvements. Early versions displaced 2.4 liters and produced around 160 horsepower, while later variants saw power outputs exceeding 200 horsepower. The engine's versatility allowed it to be used in a wide range of vehicles, from compact sedans to SUVs, demonstrating its adaptability to different automotive applications.
One of the key technological advancements in the K24 engine was the implementation of Honda's i-VTEC (intelligent Variable Valve Timing and Lift Electronic Control) system. This innovation allowed for optimized valve timing and lift across different engine speeds, resulting in improved power delivery and fuel efficiency. The i-VTEC system became a hallmark of Honda's engine technology, setting new standards in the industry for variable valve timing mechanisms.
As environmental concerns and fuel efficiency standards became more stringent, Honda continued to refine the K24 engine. Later versions incorporated direct fuel injection, reduced friction components, and advanced engine management systems. These enhancements were aimed at improving thermal efficiency, reducing emissions, and further optimizing fuel consumption without compromising performance.
The K24 engine's legacy extends beyond its factory applications. Its robust design and tuning potential have made it a favorite among aftermarket enthusiasts and racing teams. The engine's ability to withstand high levels of modification while maintaining reliability has contributed to its enduring popularity in the performance community.
As the automotive industry shifts towards electrification and alternative powertrains, the focus on improving internal combustion engines like the K24 remains relevant. Strategies for enhancing efficiency, reducing emissions, and maximizing power output continue to evolve, with lessons learned from the K24's development informing future engine designs and hybrid powertrains.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for improved efficiency in K24 engines has been steadily growing, driven by several key factors in the automotive industry. As environmental regulations become increasingly stringent, automakers are under pressure to develop more fuel-efficient vehicles. This has led to a surge in demand for engines that can deliver better performance while consuming less fuel.
The K24 engine, known for its reliability and versatility, has been a popular choice among manufacturers. However, there is a growing need for enhanced versions that can meet the evolving requirements of modern vehicles. This demand is not limited to passenger cars but extends to light commercial vehicles and even some performance applications.
Consumer preferences have also shifted towards vehicles that offer a balance between power and efficiency. This trend has created a significant market opportunity for improved K24 engines that can deliver increased horsepower and torque without compromising fuel economy. The aftermarket sector has shown particular interest in performance upgrades for K24 engines, indicating a robust demand from enthusiasts and tuners.
In the context of electric vehicle adoption, there is still a substantial market for efficient internal combustion engines. Many regions lack the infrastructure for widespread EV adoption, and consumers in these areas continue to seek advanced gasoline engines. This creates a sustained demand for improved K24 engines in markets where electrification is progressing more slowly.
The commercial vehicle sector presents another avenue for growth. Fleet operators are increasingly focused on reducing operating costs, with fuel efficiency being a primary concern. Enhanced K24 engines that offer better fuel economy and lower emissions are highly sought after in this segment, as they can significantly impact the total cost of ownership for fleet vehicles.
Emerging markets represent a substantial growth opportunity for improved K24 engines. As these economies develop and vehicle ownership increases, there is a rising demand for reliable, efficient engines that can withstand diverse operating conditions. The K24's reputation for durability makes it an attractive option in these markets, provided it can meet evolving efficiency standards.
The potential market size for improved K24 engines is considerable. While specific figures vary depending on the source and market segment, industry analysts project continued growth in the global automotive engine market. The demand for more efficient four-cylinder engines, like the K24, is expected to remain strong in the coming years, driven by the factors mentioned above and the ongoing need for cost-effective, reliable powertrains in a wide range of vehicles.
The K24 engine, known for its reliability and versatility, has been a popular choice among manufacturers. However, there is a growing need for enhanced versions that can meet the evolving requirements of modern vehicles. This demand is not limited to passenger cars but extends to light commercial vehicles and even some performance applications.
Consumer preferences have also shifted towards vehicles that offer a balance between power and efficiency. This trend has created a significant market opportunity for improved K24 engines that can deliver increased horsepower and torque without compromising fuel economy. The aftermarket sector has shown particular interest in performance upgrades for K24 engines, indicating a robust demand from enthusiasts and tuners.
In the context of electric vehicle adoption, there is still a substantial market for efficient internal combustion engines. Many regions lack the infrastructure for widespread EV adoption, and consumers in these areas continue to seek advanced gasoline engines. This creates a sustained demand for improved K24 engines in markets where electrification is progressing more slowly.
The commercial vehicle sector presents another avenue for growth. Fleet operators are increasingly focused on reducing operating costs, with fuel efficiency being a primary concern. Enhanced K24 engines that offer better fuel economy and lower emissions are highly sought after in this segment, as they can significantly impact the total cost of ownership for fleet vehicles.
Emerging markets represent a substantial growth opportunity for improved K24 engines. As these economies develop and vehicle ownership increases, there is a rising demand for reliable, efficient engines that can withstand diverse operating conditions. The K24's reputation for durability makes it an attractive option in these markets, provided it can meet evolving efficiency standards.
The potential market size for improved K24 engines is considerable. While specific figures vary depending on the source and market segment, industry analysts project continued growth in the global automotive engine market. The demand for more efficient four-cylinder engines, like the K24, is expected to remain strong in the coming years, driven by the factors mentioned above and the ongoing need for cost-effective, reliable powertrains in a wide range of vehicles.
Technical Challenges
The K24 engine, while renowned for its performance, faces several technical challenges in achieving improved efficiency. One of the primary obstacles is the engine's high fuel consumption, particularly at higher RPMs. This issue stems from the engine's design, which prioritizes power output over fuel economy, leading to increased emissions and reduced overall efficiency.
Another significant challenge lies in the engine's thermal management. The K24's high-performance nature results in substantial heat generation, especially during prolonged operation or under heavy loads. Efficient heat dissipation is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing premature wear of engine components. Current cooling systems struggle to manage this heat effectively, potentially leading to reduced engine longevity and performance degradation over time.
The engine's variable valve timing (VVT) system, while innovative, presents its own set of challenges. The complexity of the VVT mechanism can lead to reliability issues and increased maintenance requirements. Optimizing the VVT system for both performance and efficiency across a wide range of operating conditions remains a significant technical hurdle.
Weight reduction is another area of concern for the K24 engine. As automotive manufacturers strive for improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions, the relatively heavy construction of the K24 becomes a limiting factor. Balancing the need for durability and performance with weight reduction goals poses a substantial engineering challenge.
The integration of modern emissions control technologies with the K24 engine's architecture presents additional complications. Stricter environmental regulations require advanced catalytic converters and exhaust gas recirculation systems, which can potentially impact engine performance and efficiency if not carefully designed and implemented.
Lastly, the K24 engine faces challenges in adapting to emerging automotive technologies. As the industry moves towards electrification and hybrid powertrains, integrating the K24 into these new systems while maintaining its performance characteristics and improving efficiency becomes increasingly complex. This adaptation requires significant re-engineering and may necessitate fundamental changes to the engine's design and operation principles.
Addressing these technical challenges is crucial for improving the K24 engine's efficiency and ensuring its relevance in an evolving automotive landscape. Innovative solutions in materials science, thermal management, combustion optimization, and electronic control systems will be key to overcoming these obstacles and enhancing the engine's overall performance and efficiency.
Another significant challenge lies in the engine's thermal management. The K24's high-performance nature results in substantial heat generation, especially during prolonged operation or under heavy loads. Efficient heat dissipation is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing premature wear of engine components. Current cooling systems struggle to manage this heat effectively, potentially leading to reduced engine longevity and performance degradation over time.
The engine's variable valve timing (VVT) system, while innovative, presents its own set of challenges. The complexity of the VVT mechanism can lead to reliability issues and increased maintenance requirements. Optimizing the VVT system for both performance and efficiency across a wide range of operating conditions remains a significant technical hurdle.
Weight reduction is another area of concern for the K24 engine. As automotive manufacturers strive for improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions, the relatively heavy construction of the K24 becomes a limiting factor. Balancing the need for durability and performance with weight reduction goals poses a substantial engineering challenge.
The integration of modern emissions control technologies with the K24 engine's architecture presents additional complications. Stricter environmental regulations require advanced catalytic converters and exhaust gas recirculation systems, which can potentially impact engine performance and efficiency if not carefully designed and implemented.
Lastly, the K24 engine faces challenges in adapting to emerging automotive technologies. As the industry moves towards electrification and hybrid powertrains, integrating the K24 into these new systems while maintaining its performance characteristics and improving efficiency becomes increasingly complex. This adaptation requires significant re-engineering and may necessitate fundamental changes to the engine's design and operation principles.
Addressing these technical challenges is crucial for improving the K24 engine's efficiency and ensuring its relevance in an evolving automotive landscape. Innovative solutions in materials science, thermal management, combustion optimization, and electronic control systems will be key to overcoming these obstacles and enhancing the engine's overall performance and efficiency.
Current Efficiency Solutions
01 Improved combustion efficiency
Enhancements to the K24 engine's combustion process, including optimized fuel injection systems, advanced ignition timing, and improved air-fuel mixture control, contribute to increased engine efficiency. These modifications result in more complete fuel burning and reduced energy waste.- Improved combustion efficiency: Various techniques are employed to enhance the combustion efficiency of K24 engines. These include optimizing fuel injection systems, improving air intake designs, and implementing advanced ignition timing control. Such improvements lead to better fuel economy and increased power output.
- Advanced engine management systems: K24 engines utilize sophisticated engine management systems to optimize performance and efficiency. These systems incorporate sensors and control units that continuously monitor and adjust engine parameters such as fuel mixture, ignition timing, and valve timing to ensure optimal operation under various conditions.
- Thermal management and heat recovery: Efficient thermal management systems are implemented in K24 engines to reduce heat losses and improve overall efficiency. This includes advanced cooling systems, exhaust heat recovery mechanisms, and thermal insulation techniques to maintain optimal operating temperatures and convert waste heat into useful energy.
- Friction reduction and lubrication improvements: K24 engine efficiency is enhanced through various friction reduction techniques and improved lubrication systems. This includes the use of low-friction coatings, optimized piston and ring designs, and advanced lubricants to minimize energy losses due to friction between moving parts.
- Variable valve timing and lift systems: K24 engines incorporate advanced variable valve timing and lift systems to optimize engine breathing and combustion efficiency across different operating conditions. These systems allow for precise control of valve events, improving power output, fuel economy, and emissions performance.
02 Advanced thermal management
Implementation of sophisticated thermal management systems in the K24 engine helps maintain optimal operating temperatures, reducing friction and improving overall efficiency. This includes enhanced cooling systems, heat recovery mechanisms, and temperature-responsive components.Expand Specific Solutions03 Friction reduction technologies
Incorporation of low-friction materials, surface treatments, and advanced lubricants in the K24 engine design reduces internal friction, leading to improved mechanical efficiency and reduced energy losses. This includes optimized piston ring designs and bearing surfaces.Expand Specific Solutions04 Variable valve timing and lift
Implementation of advanced variable valve timing and lift systems in the K24 engine allows for optimized air intake and exhaust flow across different operating conditions. This results in improved volumetric efficiency, power output, and fuel economy.Expand Specific Solutions05 Engine control unit optimization
Sophisticated engine control unit (ECU) programming and calibration for the K24 engine enable real-time adjustments to various engine parameters. This includes adaptive learning algorithms, precise fuel mapping, and integration with other vehicle systems to maximize overall efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The K24 Engine efficiency improvement landscape is characterized by intense competition in a mature automotive industry. The market for engine optimization technologies is substantial, driven by global demand for fuel-efficient vehicles and stringent emissions regulations. Major players like GM, Toyota, Hyundai, and Bosch are investing heavily in research and development to enhance engine performance. Emerging companies such as Tula Technology are introducing innovative software solutions, while established manufacturers like Caterpillar and Cummins focus on heavy-duty applications. The technology is relatively mature, with ongoing incremental advancements rather than disruptive breakthroughs. Collaboration between automakers, suppliers, and research institutions is common, as evidenced by partnerships involving companies like Intel and universities such as Tsinghua.
GM Global Technology Operations LLC
Technical Solution: GM's approach to improving K24 engine efficiency focuses on advanced combustion technologies and electrification. They have developed a Dynamic Fuel Management system that can deactivate cylinders in 17 different patterns, optimizing fuel efficiency based on driving conditions[1]. GM has also integrated start-stop technology and implemented a new generation of Active Fuel Management, which can shut down half of the engine's cylinders during light load conditions[2]. Additionally, GM is exploring hybrid powertrains that combine the K24 engine with electric motors to further enhance fuel economy and reduce emissions[3].
Strengths: Versatile cylinder deactivation, proven fuel management systems, and hybrid integration capabilities. Weaknesses: Complexity of systems may increase maintenance costs, and full electrification trends could eventually overshadow these improvements.
Toyota Motor Corp.
Technical Solution: Toyota's strategy for K24 engine efficiency improvements revolves around their D-4S (Direct injection 4-stroke gasoline engine Superior version) technology. This system combines direct and port fuel injection, allowing for precise fuel delivery and improved combustion efficiency[4]. Toyota has also implemented Variable Valve Timing with intelligence (VVT-i) on both intake and exhaust camshafts, optimizing valve timing across the entire rpm range[5]. Furthermore, Toyota has developed a high compression ratio of 13:1 for some K24 variants, utilizing advanced piston designs and cooling systems to prevent knock and improve thermal efficiency[6].
Strengths: High compression ratios, dual injection system for improved fuel atomization, and advanced valve timing control. Weaknesses: Higher production costs due to complex technologies, and potential reliability concerns with high-pressure direct injection systems.
Core Innovations
Smart engine management and performance optimization system for peak vehicle efficiency
PatentPendingIN202311081489A
Innovation
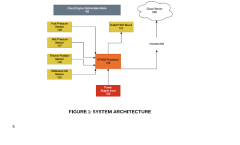
- A Smart Engine Management and Performance Optimization System that integrates sensors like Wideband O2, Fuel Pressure, and Throttle Position with an STM32 Processor for real-time data analysis and modification of critical engine parameters, coupled with cloud-based storage and remote access via a NuttyFi WiFi Board, enabling users to customize engine behavior through a mobile or web application.
Systems and methods for improving the efficiency of a vehicle
PatentInactiveEP2472230A2
Innovation
- A system and method that calculates an optimized vehicle route and operational profile based on GPS data and vehicle attributes, monitoring parameters like acceleration, speed, and gear selection to prompt operators for efficient driving practices or automatically adjust vehicle systems for better fuel efficiency.
Emissions Regulations
Emissions regulations play a crucial role in shaping the development and implementation of engine technologies, including the K24 engine. These regulations are designed to reduce harmful emissions and improve air quality, driving manufacturers to innovate and optimize their engine designs for better efficiency and cleaner operation.
In recent years, emissions standards have become increasingly stringent worldwide, with notable examples including the Euro 6 standards in Europe and the Tier 3 standards in the United States. These regulations set strict limits on various pollutants, such as carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PM). As a result, engine manufacturers must continuously adapt their designs to meet these evolving requirements.
For the K24 engine, compliance with emissions regulations has been a key factor in its development and ongoing improvements. The engine's design incorporates several features aimed at reducing emissions while maintaining performance. These include advanced fuel injection systems, variable valve timing, and improved combustion chamber designs. Additionally, the integration of exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems helps to lower NOx emissions by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber.
To further enhance emissions control, the K24 engine often employs catalytic converters and particulate filters in its exhaust system. These aftertreatment devices work to reduce harmful pollutants before they are released into the atmosphere. The catalytic converter converts toxic gases like CO and NOx into less harmful substances, while particulate filters capture and store soot particles from the exhaust.
As emissions regulations continue to evolve, manufacturers are exploring new technologies to ensure compliance while improving engine efficiency. For the K24 engine, this may include the adoption of more advanced materials, such as ceramic coatings, to reduce friction and improve thermal management. Additionally, the integration of hybrid technologies or mild hybridization could further reduce emissions by allowing for engine shut-off during idle periods and providing electric assist during acceleration.
Looking ahead, the push for even cleaner engines may lead to the development of new combustion strategies for the K24 engine. These could include low-temperature combustion techniques or the use of alternative fuels, such as hydrogen or synthetic fuels, to further reduce emissions while maintaining or improving engine performance.
In conclusion, emissions regulations serve as a driving force for innovation in engine design, including the K24 engine. As these standards become more stringent, manufacturers must continue to develop and implement new technologies to ensure compliance while striving for improved efficiency and performance.
In recent years, emissions standards have become increasingly stringent worldwide, with notable examples including the Euro 6 standards in Europe and the Tier 3 standards in the United States. These regulations set strict limits on various pollutants, such as carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PM). As a result, engine manufacturers must continuously adapt their designs to meet these evolving requirements.
For the K24 engine, compliance with emissions regulations has been a key factor in its development and ongoing improvements. The engine's design incorporates several features aimed at reducing emissions while maintaining performance. These include advanced fuel injection systems, variable valve timing, and improved combustion chamber designs. Additionally, the integration of exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems helps to lower NOx emissions by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber.
To further enhance emissions control, the K24 engine often employs catalytic converters and particulate filters in its exhaust system. These aftertreatment devices work to reduce harmful pollutants before they are released into the atmosphere. The catalytic converter converts toxic gases like CO and NOx into less harmful substances, while particulate filters capture and store soot particles from the exhaust.
As emissions regulations continue to evolve, manufacturers are exploring new technologies to ensure compliance while improving engine efficiency. For the K24 engine, this may include the adoption of more advanced materials, such as ceramic coatings, to reduce friction and improve thermal management. Additionally, the integration of hybrid technologies or mild hybridization could further reduce emissions by allowing for engine shut-off during idle periods and providing electric assist during acceleration.
Looking ahead, the push for even cleaner engines may lead to the development of new combustion strategies for the K24 engine. These could include low-temperature combustion techniques or the use of alternative fuels, such as hydrogen or synthetic fuels, to further reduce emissions while maintaining or improving engine performance.
In conclusion, emissions regulations serve as a driving force for innovation in engine design, including the K24 engine. As these standards become more stringent, manufacturers must continue to develop and implement new technologies to ensure compliance while striving for improved efficiency and performance.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
The cost-benefit analysis of implementing strategies for improved efficiency in the K24 Engine reveals a complex interplay of financial investments and potential returns. Initial costs associated with research and development, retooling manufacturing processes, and updating existing systems can be substantial. However, these upfront expenditures must be weighed against the long-term benefits of enhanced engine performance and reduced operational costs.
One of the primary advantages of improving K24 Engine efficiency is the potential for significant fuel savings. By optimizing combustion processes and reducing energy losses, fuel consumption can be lowered, resulting in decreased operating expenses for end-users. This benefit extends beyond individual consumers to fleet operators and businesses reliant on transportation, where even marginal improvements in fuel efficiency can translate to substantial cost reductions over time.
Moreover, enhanced engine efficiency often correlates with improved durability and longevity. By reducing wear and tear on engine components through more efficient operation, maintenance intervals may be extended, and the overall lifespan of the engine increased. This can lead to reduced maintenance costs and fewer replacements, providing additional economic benefits to owners and operators.
From an environmental perspective, the improved efficiency of the K24 Engine can result in reduced emissions. While this benefit may not directly translate to monetary savings for individual users, it can lead to broader societal benefits and potential cost savings in terms of healthcare and environmental remediation. Additionally, as environmental regulations become more stringent, engines with superior efficiency may become more valuable in the marketplace, potentially commanding higher prices or market share.
The implementation of advanced materials and manufacturing techniques, while initially costly, can lead to economies of scale as production volumes increase. This can result in a gradual reduction in the cost of producing high-efficiency K24 Engines, improving the overall cost-benefit ratio over time. Furthermore, the development of innovative technologies for the K24 Engine may lead to valuable intellectual property, creating additional revenue streams through licensing or technology transfer.
It is important to note that the full realization of benefits from efficiency improvements may require a certain period to materialize. The payback period for investments in engine efficiency enhancements can vary depending on factors such as usage patterns, fuel prices, and the specific improvements implemented. However, given the long service life of many engines, even improvements with longer payback periods can ultimately prove economically advantageous.
One of the primary advantages of improving K24 Engine efficiency is the potential for significant fuel savings. By optimizing combustion processes and reducing energy losses, fuel consumption can be lowered, resulting in decreased operating expenses for end-users. This benefit extends beyond individual consumers to fleet operators and businesses reliant on transportation, where even marginal improvements in fuel efficiency can translate to substantial cost reductions over time.
Moreover, enhanced engine efficiency often correlates with improved durability and longevity. By reducing wear and tear on engine components through more efficient operation, maintenance intervals may be extended, and the overall lifespan of the engine increased. This can lead to reduced maintenance costs and fewer replacements, providing additional economic benefits to owners and operators.
From an environmental perspective, the improved efficiency of the K24 Engine can result in reduced emissions. While this benefit may not directly translate to monetary savings for individual users, it can lead to broader societal benefits and potential cost savings in terms of healthcare and environmental remediation. Additionally, as environmental regulations become more stringent, engines with superior efficiency may become more valuable in the marketplace, potentially commanding higher prices or market share.
The implementation of advanced materials and manufacturing techniques, while initially costly, can lead to economies of scale as production volumes increase. This can result in a gradual reduction in the cost of producing high-efficiency K24 Engines, improving the overall cost-benefit ratio over time. Furthermore, the development of innovative technologies for the K24 Engine may lead to valuable intellectual property, creating additional revenue streams through licensing or technology transfer.
It is important to note that the full realization of benefits from efficiency improvements may require a certain period to materialize. The payback period for investments in engine efficiency enhancements can vary depending on factors such as usage patterns, fuel prices, and the specific improvements implemented. However, given the long service life of many engines, even improvements with longer payback periods can ultimately prove economically advantageous.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!