Alkyl Functional Groups: Optimization in Synthesis Pathways
JUL 15, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Alkyl Group Optimization Background and Objectives
The optimization of alkyl functional groups in synthesis pathways has emerged as a critical area of research in organic chemistry and materials science. This field has evolved significantly over the past few decades, driven by the increasing demand for more efficient and sustainable chemical processes. The journey began with simple alkylation reactions and has progressed to sophisticated methodologies that allow for precise control over the structure and properties of target molecules.
The primary objective of alkyl group optimization is to enhance the efficiency, selectivity, and sustainability of synthetic processes. This involves developing new strategies for introducing, modifying, and removing alkyl groups in complex molecular structures. Researchers aim to achieve these goals while minimizing energy consumption, reducing waste generation, and improving overall atom economy.
One of the key trends in this field is the development of catalytic systems that enable more selective alkylation reactions. These catalysts, ranging from transition metal complexes to organocatalysts, have revolutionized the way chemists approach alkyl group manipulation. They offer the potential for milder reaction conditions, higher yields, and improved stereoselectivity, addressing many of the limitations associated with traditional alkylation methods.
Another significant trend is the integration of computational tools and machine learning algorithms in the design and optimization of alkylation reactions. These advanced techniques allow researchers to predict reaction outcomes, optimize reaction conditions, and even discover novel synthetic pathways. The synergy between experimental and computational approaches has accelerated progress in this field, leading to more rational and efficient strategies for alkyl group optimization.
Environmental considerations have also become increasingly important in the development of alkylation methodologies. There is a growing focus on green chemistry principles, with efforts directed towards developing solvent-free reactions, utilizing renewable feedstocks, and designing processes with improved atom economy. These environmentally friendly approaches not only reduce the ecological footprint of chemical synthesis but also often lead to more cost-effective and scalable processes.
The optimization of alkyl functional groups plays a crucial role in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science. In drug discovery, for example, the ability to fine-tune the alkyl substituents of lead compounds can dramatically affect their pharmacokinetic properties and biological activity. Similarly, in polymer science, precise control over alkyl group composition and distribution can lead to materials with tailored physical and chemical properties.
As we look to the future, the field of alkyl group optimization is poised for further advancements. Emerging technologies such as flow chemistry and photocatalysis offer new avenues for exploring and optimizing alkylation reactions. Additionally, the growing interest in sustainable chemistry is likely to drive innovation in bio-based alkylation strategies and the development of more efficient recycling methods for alkyl-containing compounds.
The primary objective of alkyl group optimization is to enhance the efficiency, selectivity, and sustainability of synthetic processes. This involves developing new strategies for introducing, modifying, and removing alkyl groups in complex molecular structures. Researchers aim to achieve these goals while minimizing energy consumption, reducing waste generation, and improving overall atom economy.
One of the key trends in this field is the development of catalytic systems that enable more selective alkylation reactions. These catalysts, ranging from transition metal complexes to organocatalysts, have revolutionized the way chemists approach alkyl group manipulation. They offer the potential for milder reaction conditions, higher yields, and improved stereoselectivity, addressing many of the limitations associated with traditional alkylation methods.
Another significant trend is the integration of computational tools and machine learning algorithms in the design and optimization of alkylation reactions. These advanced techniques allow researchers to predict reaction outcomes, optimize reaction conditions, and even discover novel synthetic pathways. The synergy between experimental and computational approaches has accelerated progress in this field, leading to more rational and efficient strategies for alkyl group optimization.
Environmental considerations have also become increasingly important in the development of alkylation methodologies. There is a growing focus on green chemistry principles, with efforts directed towards developing solvent-free reactions, utilizing renewable feedstocks, and designing processes with improved atom economy. These environmentally friendly approaches not only reduce the ecological footprint of chemical synthesis but also often lead to more cost-effective and scalable processes.
The optimization of alkyl functional groups plays a crucial role in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science. In drug discovery, for example, the ability to fine-tune the alkyl substituents of lead compounds can dramatically affect their pharmacokinetic properties and biological activity. Similarly, in polymer science, precise control over alkyl group composition and distribution can lead to materials with tailored physical and chemical properties.
As we look to the future, the field of alkyl group optimization is poised for further advancements. Emerging technologies such as flow chemistry and photocatalysis offer new avenues for exploring and optimizing alkylation reactions. Additionally, the growing interest in sustainable chemistry is likely to drive innovation in bio-based alkylation strategies and the development of more efficient recycling methods for alkyl-containing compounds.
Industrial Demand for Efficient Alkyl Group Synthesis
The demand for efficient alkyl group synthesis in industrial applications has been steadily increasing due to the widespread use of alkyl-containing compounds in various sectors. Pharmaceutical companies require optimized synthesis pathways for drug development, as many active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) contain alkyl functional groups. The fine chemicals industry relies heavily on alkyl group synthesis for producing fragrances, flavors, and specialty chemicals. Additionally, the polymer and materials science sectors utilize alkyl-functionalized monomers and additives to enhance product properties.
In the agrochemical industry, efficient alkyl group synthesis is crucial for developing effective pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers. The demand for environmentally friendly and sustainable agricultural products has driven research into more efficient and selective alkylation processes. The petrochemical industry also benefits from optimized alkyl group synthesis, particularly in the production of lubricants, fuel additives, and surfactants.
The electronics industry has seen a growing need for alkyl-functionalized materials in the development of organic semiconductors, photoresists, and other advanced materials for electronic devices. As the Internet of Things (IoT) and wearable technologies continue to expand, the demand for specialized alkyl-containing compounds in sensor technologies and flexible electronics is expected to rise.
Emerging applications in nanotechnology and advanced materials have further increased the industrial demand for efficient alkyl group synthesis. Researchers are exploring the use of alkyl-functionalized nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes for various applications, including drug delivery systems, energy storage devices, and advanced coatings.
The cosmetics and personal care industry has also contributed to the growing demand for optimized alkyl synthesis pathways. Alkyl-containing ingredients are essential in formulating stable and effective skincare products, hair care solutions, and cosmetic formulations. As consumers become more conscious of product ingredients, there is a push for more sustainable and bio-based alkyl sources, driving innovation in synthesis methods.
In the energy sector, the development of biofuels and renewable energy technologies has created new opportunities for alkyl group synthesis. Biodiesel production, for instance, relies on the transesterification of triglycerides with short-chain alcohols, highlighting the importance of efficient alkylation processes in this field.
As industries continue to prioritize sustainability and green chemistry principles, there is a growing emphasis on developing more environmentally friendly alkyl synthesis methods. This includes exploring bio-based feedstocks, catalytic processes with improved atom economy, and solvent-free reaction conditions. The industrial demand for efficient alkyl group synthesis is expected to drive further research and innovation in this field, leading to more sustainable and economically viable production methods across various sectors.
In the agrochemical industry, efficient alkyl group synthesis is crucial for developing effective pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers. The demand for environmentally friendly and sustainable agricultural products has driven research into more efficient and selective alkylation processes. The petrochemical industry also benefits from optimized alkyl group synthesis, particularly in the production of lubricants, fuel additives, and surfactants.
The electronics industry has seen a growing need for alkyl-functionalized materials in the development of organic semiconductors, photoresists, and other advanced materials for electronic devices. As the Internet of Things (IoT) and wearable technologies continue to expand, the demand for specialized alkyl-containing compounds in sensor technologies and flexible electronics is expected to rise.
Emerging applications in nanotechnology and advanced materials have further increased the industrial demand for efficient alkyl group synthesis. Researchers are exploring the use of alkyl-functionalized nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes for various applications, including drug delivery systems, energy storage devices, and advanced coatings.
The cosmetics and personal care industry has also contributed to the growing demand for optimized alkyl synthesis pathways. Alkyl-containing ingredients are essential in formulating stable and effective skincare products, hair care solutions, and cosmetic formulations. As consumers become more conscious of product ingredients, there is a push for more sustainable and bio-based alkyl sources, driving innovation in synthesis methods.
In the energy sector, the development of biofuels and renewable energy technologies has created new opportunities for alkyl group synthesis. Biodiesel production, for instance, relies on the transesterification of triglycerides with short-chain alcohols, highlighting the importance of efficient alkylation processes in this field.
As industries continue to prioritize sustainability and green chemistry principles, there is a growing emphasis on developing more environmentally friendly alkyl synthesis methods. This includes exploring bio-based feedstocks, catalytic processes with improved atom economy, and solvent-free reaction conditions. The industrial demand for efficient alkyl group synthesis is expected to drive further research and innovation in this field, leading to more sustainable and economically viable production methods across various sectors.
Current Challenges in Alkyl Functionalization
The optimization of alkyl functional groups in synthesis pathways faces several significant challenges that hinder progress in this critical area of organic chemistry. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of selectivity in alkylation reactions. Traditional methods often result in a mixture of products, including over-alkylated compounds, which necessitates complex purification processes and reduces overall yield.
Another major challenge is the limited scope of substrates that can be effectively alkylated using current methodologies. Many existing protocols are substrate-specific, limiting their broad applicability across diverse chemical structures. This constraint hampers the development of universal alkylation strategies that could streamline synthetic processes across various industries.
The use of harsh reaction conditions in many alkylation procedures presents additional difficulties. High temperatures, strong bases, or reactive alkylating agents can lead to unwanted side reactions, degradation of sensitive functional groups, and poor atom economy. These factors not only reduce the efficiency of the synthesis but also raise environmental concerns due to the generation of hazardous waste.
Regioselectivity remains a persistent issue in alkyl functionalization, particularly for complex molecules with multiple potential reaction sites. Controlling the position of alkylation often requires elaborate protecting group strategies or the use of directing groups, which add steps and complexity to synthetic routes.
The challenge of stereoselectivity in alkylation reactions is equally significant. Achieving high levels of enantio- or diastereoselectivity is crucial for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other fine chemicals. However, many current methods struggle to provide the desired stereochemical control without the use of chiral catalysts or auxiliaries, which can be expensive and difficult to remove.
Scalability is another critical concern in the optimization of alkyl functional groups. Many laboratory-scale alkylation methods fail to translate effectively to industrial-scale processes due to issues with heat transfer, mixing, or the handling of reactive intermediates. This gap between academic research and industrial application slows the adoption of new alkylation technologies in large-scale manufacturing.
Lastly, the development of sustainable and green alkylation methods remains a significant challenge. Traditional alkylating agents are often toxic, and the processes generate substantial amounts of waste. There is a pressing need for environmentally benign alkylation strategies that utilize renewable resources, operate under mild conditions, and minimize the production of byproducts.
Another major challenge is the limited scope of substrates that can be effectively alkylated using current methodologies. Many existing protocols are substrate-specific, limiting their broad applicability across diverse chemical structures. This constraint hampers the development of universal alkylation strategies that could streamline synthetic processes across various industries.
The use of harsh reaction conditions in many alkylation procedures presents additional difficulties. High temperatures, strong bases, or reactive alkylating agents can lead to unwanted side reactions, degradation of sensitive functional groups, and poor atom economy. These factors not only reduce the efficiency of the synthesis but also raise environmental concerns due to the generation of hazardous waste.
Regioselectivity remains a persistent issue in alkyl functionalization, particularly for complex molecules with multiple potential reaction sites. Controlling the position of alkylation often requires elaborate protecting group strategies or the use of directing groups, which add steps and complexity to synthetic routes.
The challenge of stereoselectivity in alkylation reactions is equally significant. Achieving high levels of enantio- or diastereoselectivity is crucial for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other fine chemicals. However, many current methods struggle to provide the desired stereochemical control without the use of chiral catalysts or auxiliaries, which can be expensive and difficult to remove.
Scalability is another critical concern in the optimization of alkyl functional groups. Many laboratory-scale alkylation methods fail to translate effectively to industrial-scale processes due to issues with heat transfer, mixing, or the handling of reactive intermediates. This gap between academic research and industrial application slows the adoption of new alkylation technologies in large-scale manufacturing.
Lastly, the development of sustainable and green alkylation methods remains a significant challenge. Traditional alkylating agents are often toxic, and the processes generate substantial amounts of waste. There is a pressing need for environmentally benign alkylation strategies that utilize renewable resources, operate under mild conditions, and minimize the production of byproducts.
Existing Alkyl Optimization Strategies
01 Optimization of alkyl chain length
The length of alkyl chains in functional groups can be optimized to enhance various properties of materials. This includes improving solubility, reactivity, and physical characteristics. Adjusting the chain length can affect the overall performance of the compound in different applications.- Optimization of alkyl chain length: The length of alkyl chains in functional groups can be optimized to enhance various properties of materials. This optimization can affect characteristics such as solubility, reactivity, and physical properties of the resulting compounds. Adjusting the alkyl chain length allows for fine-tuning of molecular interactions and performance in different applications.
- Branching in alkyl functional groups: Introducing branching in alkyl functional groups can significantly alter the properties of molecules. Branched alkyl groups can improve thermal stability, reduce melting points, and enhance solubility in certain solvents. The degree and position of branching can be optimized to achieve desired characteristics in various chemical and material applications.
- Alkyl functional group positioning: The position of alkyl functional groups on a molecule can greatly influence its properties and reactivity. Optimizing the placement of these groups can affect electronic distribution, steric hindrance, and overall molecular geometry. Strategic positioning of alkyl groups can be used to enhance specific chemical or physical properties in target compounds.
- Alkyl group substitution patterns: The pattern of alkyl group substitutions on a molecular framework can be optimized to achieve desired properties. This includes considerations of symmetry, distribution, and combinations of different alkyl groups. Tailoring substitution patterns can lead to improvements in areas such as polymer properties, drug efficacy, or material performance.
- Alkyl functional group interactions: Optimizing the interactions between alkyl functional groups and other molecular components is crucial for many applications. This includes considering factors such as hydrogen bonding, van der Waals forces, and steric effects. Proper optimization of these interactions can lead to enhanced material properties, improved catalytic activity, or better drug-target binding in pharmaceutical applications.
02 Branching and substitution patterns
Modifying the branching and substitution patterns of alkyl functional groups can significantly impact the properties of molecules. This optimization can lead to improved thermal stability, altered reactivity, and enhanced performance in specific applications such as polymers or catalysts.Expand Specific Solutions03 Alkyl group positioning
The position of alkyl functional groups on a molecule can be optimized to achieve desired properties. This includes considerations for steric effects, electronic properties, and overall molecular geometry. Proper positioning can enhance reactivity, selectivity, and functionality in various chemical processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Alkyl group interactions
Optimizing the interactions between multiple alkyl functional groups within a molecule or between different molecules can lead to improved material properties. This includes considerations for intermolecular forces, packing arrangements, and overall structural stability in applications such as crystal engineering or drug design.Expand Specific Solutions05 Alkyl functionalization for specific applications
Tailoring alkyl functional groups for specific applications involves optimizing their properties to meet particular requirements. This can include modifying alkyl groups for enhanced performance in areas such as lubricants, surfactants, or electronic materials. The optimization process considers factors like polarity, reactivity, and compatibility with other components.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Organic Synthesis Industry
The optimization of alkyl functional groups in synthesis pathways is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies, chemical manufacturers, and research institutions. Key players like Fresenius Kabi, Chugai Pharmaceutical, BASF, and Evonik are driving innovation in this field. The technology is maturing rapidly, with companies like Agilent Technologies and Micron Technology contributing to analytical and computational aspects. Academic institutions such as East China Normal University and the University of Basel are also playing crucial roles in advancing the fundamental understanding of alkyl group optimization, fostering collaborations between industry and academia.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a novel approach for optimizing alkyl functional groups in synthesis pathways, focusing on sustainable and efficient processes. Their method involves using computational chemistry and machine learning algorithms to predict optimal alkyl chain lengths and branching patterns for desired product properties[1]. This is combined with high-throughput experimentation to rapidly screen and validate potential candidates[3]. BASF's approach also incorporates green chemistry principles, utilizing bio-based feedstocks and catalytic processes to minimize waste and energy consumption[5]. The company has successfully applied this methodology to improve the performance of surfactants, polymers, and specialty chemicals, achieving enhanced product functionality and reduced environmental impact[2][4].
Strengths: Comprehensive approach combining computational methods and experimental validation; focus on sustainability and efficiency. Weaknesses: May require significant computational resources and specialized expertise.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has developed a proprietary platform for optimizing alkyl functional groups in various synthesis pathways. Their approach utilizes advanced catalytic systems and process intensification techniques to achieve precise control over alkyl chain length and branching[1]. The company employs a modular reactor design that allows for rapid screening of reaction conditions and catalyst formulations[3]. Evonik's technology also incorporates in-line analytics and artificial intelligence to optimize reaction parameters in real-time, resulting in improved yield and selectivity[2]. The platform has been successfully applied to the production of specialty chemicals, personal care ingredients, and pharmaceutical intermediates, demonstrating versatility across multiple industries[4][5].
Strengths: Modular and flexible approach; real-time optimization capabilities. Weaknesses: May require significant capital investment for implementation.
Innovative Approaches in Alkyl Group Synthesis
Method for alkylating acidic functional group
PatentPendingUS20240132431A1
Innovation
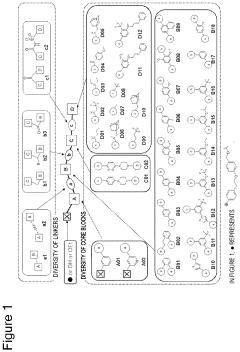
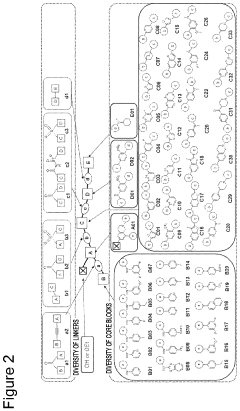
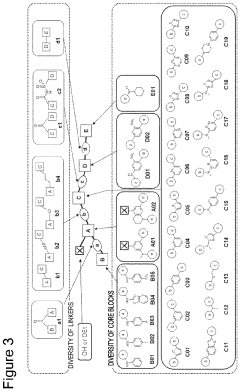
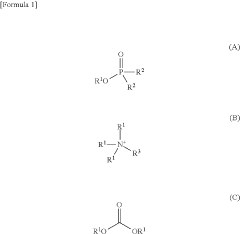
- A method involving the use of specific alkylating agents represented by formulas A, B, or C, in the presence of bases like phosphazenes, which enhance reactivity and selectivity, allowing for the alkylation of acidic functional groups in mixtures with high yield and regioselectivity, and include steps for removing impurities.
Process for obtaining alkylene glycols
PatentWO1997033850A1
Innovation
- The method involves using catalytic systems based on ion-exchange polymers with quaternary benzylmethylammonium groups in a bicarbonate form, operated at elevated temperatures and pressures, to enhance specific productivity and selectivity, and utilize anionites with specific functional groups to achieve high yields of alkylene glycols.
Green Chemistry Considerations
Green chemistry considerations play a crucial role in the optimization of alkyl functional groups in synthesis pathways. The principles of green chemistry emphasize the need for sustainable and environmentally friendly processes, which directly impact the selection and modification of alkyl groups in organic synthesis.
One of the primary considerations is the use of renewable feedstocks for alkyl group sources. Traditional petrochemical-based alkyl groups are being increasingly replaced by bio-based alternatives derived from plant oils, waste biomass, or other renewable resources. This shift not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also contributes to a more circular economy.
Solvent selection is another critical aspect of green chemistry in alkyl group optimization. Water-based systems or bio-derived solvents are preferred over conventional organic solvents, which often pose environmental and health risks. In cases where organic solvents are necessary, efforts are made to use less toxic and more easily recyclable options.
Catalysis plays a significant role in improving the efficiency and selectivity of alkyl group transformations. Green chemistry principles encourage the development of heterogeneous catalysts that can be easily recovered and reused, reducing waste and improving process economics. Additionally, biocatalysts and enzyme-mediated reactions are gaining traction for their high specificity and mild reaction conditions.
Energy efficiency is a key consideration in the optimization process. Researchers are exploring room-temperature reactions, microwave-assisted synthesis, and flow chemistry techniques to reduce energy consumption associated with heating and cooling cycles in traditional batch processes.
Atom economy and waste reduction are fundamental to green chemistry and directly impact alkyl group optimization. Synthetic routes are designed to maximize the incorporation of reactants into the final product, minimizing by-product formation. This approach not only improves yield but also reduces the environmental footprint of the process.
Safety considerations are paramount in green chemistry approaches. The optimization of alkyl functional groups often involves the use of less hazardous reagents and the development of inherently safer processes. This includes avoiding highly reactive or toxic alkylating agents and designing processes with reduced risk of runaway reactions or explosions.
Lifecycle analysis is increasingly being applied to alkyl group optimization strategies. This holistic approach considers the environmental impact of the entire process, from raw material extraction to product disposal. Such analyses help identify areas for improvement and guide the selection of truly sustainable synthetic pathways.
In conclusion, the integration of green chemistry principles in the optimization of alkyl functional groups is driving innovation towards more sustainable, efficient, and environmentally benign synthesis pathways. These considerations not only address environmental concerns but also often lead to improved process economics and product quality.
One of the primary considerations is the use of renewable feedstocks for alkyl group sources. Traditional petrochemical-based alkyl groups are being increasingly replaced by bio-based alternatives derived from plant oils, waste biomass, or other renewable resources. This shift not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also contributes to a more circular economy.
Solvent selection is another critical aspect of green chemistry in alkyl group optimization. Water-based systems or bio-derived solvents are preferred over conventional organic solvents, which often pose environmental and health risks. In cases where organic solvents are necessary, efforts are made to use less toxic and more easily recyclable options.
Catalysis plays a significant role in improving the efficiency and selectivity of alkyl group transformations. Green chemistry principles encourage the development of heterogeneous catalysts that can be easily recovered and reused, reducing waste and improving process economics. Additionally, biocatalysts and enzyme-mediated reactions are gaining traction for their high specificity and mild reaction conditions.
Energy efficiency is a key consideration in the optimization process. Researchers are exploring room-temperature reactions, microwave-assisted synthesis, and flow chemistry techniques to reduce energy consumption associated with heating and cooling cycles in traditional batch processes.
Atom economy and waste reduction are fundamental to green chemistry and directly impact alkyl group optimization. Synthetic routes are designed to maximize the incorporation of reactants into the final product, minimizing by-product formation. This approach not only improves yield but also reduces the environmental footprint of the process.
Safety considerations are paramount in green chemistry approaches. The optimization of alkyl functional groups often involves the use of less hazardous reagents and the development of inherently safer processes. This includes avoiding highly reactive or toxic alkylating agents and designing processes with reduced risk of runaway reactions or explosions.
Lifecycle analysis is increasingly being applied to alkyl group optimization strategies. This holistic approach considers the environmental impact of the entire process, from raw material extraction to product disposal. Such analyses help identify areas for improvement and guide the selection of truly sustainable synthetic pathways.
In conclusion, the integration of green chemistry principles in the optimization of alkyl functional groups is driving innovation towards more sustainable, efficient, and environmentally benign synthesis pathways. These considerations not only address environmental concerns but also often lead to improved process economics and product quality.
Scalability and Process Engineering Aspects
The scalability and process engineering aspects of optimizing alkyl functional groups in synthesis pathways are crucial for industrial applications. As the complexity of target molecules increases, the need for efficient and scalable processes becomes paramount. One key consideration is the selection of appropriate reagents and catalysts that can be easily scaled up without compromising yield or selectivity. For instance, the use of organometallic reagents may be effective on a laboratory scale but can pose significant challenges in large-scale production due to their air and moisture sensitivity.
Process intensification techniques play a vital role in improving the scalability of alkyl group optimization. Continuous flow chemistry, for example, offers advantages such as improved heat and mass transfer, precise control over reaction parameters, and enhanced safety profiles. This approach can be particularly beneficial for reactions involving unstable intermediates or those requiring precise temperature control. Additionally, the use of microreactors can facilitate rapid optimization of reaction conditions and enable seamless scale-up from laboratory to production scale.
The development of robust and scalable purification methods is another critical aspect of process engineering in this context. Chromatographic techniques, while effective for small-scale purification, often become impractical at industrial scales due to high solvent consumption and limited throughput. Alternative approaches such as crystallization, distillation, or membrane-based separations may offer more scalable solutions, depending on the specific properties of the alkylated products.
Consideration of green chemistry principles is increasingly important in process engineering for alkyl group optimization. This includes the use of less hazardous solvents, atom-efficient reactions, and catalysts that can be easily recovered and recycled. For instance, the development of water-tolerant catalysts for alkylation reactions can significantly simplify process design and reduce environmental impact.
Process analytical technology (PAT) is becoming an integral part of scalable synthesis pathways. Real-time monitoring of reaction progress and product quality can enable adaptive process control, ensuring consistent product quality across different scales of production. This is particularly relevant for complex alkylation reactions where subtle changes in reaction conditions can significantly impact product distribution.
Lastly, the integration of computational tools in process engineering can greatly enhance the scalability of alkyl group optimization. Predictive models for reaction kinetics, thermodynamics, and mass transfer can guide process design and optimization, reducing the need for extensive experimental work. Machine learning algorithms can also be employed to identify optimal reaction conditions and predict scale-up challenges, further streamlining the development of industrial-scale processes for alkyl functional group optimization.
Process intensification techniques play a vital role in improving the scalability of alkyl group optimization. Continuous flow chemistry, for example, offers advantages such as improved heat and mass transfer, precise control over reaction parameters, and enhanced safety profiles. This approach can be particularly beneficial for reactions involving unstable intermediates or those requiring precise temperature control. Additionally, the use of microreactors can facilitate rapid optimization of reaction conditions and enable seamless scale-up from laboratory to production scale.
The development of robust and scalable purification methods is another critical aspect of process engineering in this context. Chromatographic techniques, while effective for small-scale purification, often become impractical at industrial scales due to high solvent consumption and limited throughput. Alternative approaches such as crystallization, distillation, or membrane-based separations may offer more scalable solutions, depending on the specific properties of the alkylated products.
Consideration of green chemistry principles is increasingly important in process engineering for alkyl group optimization. This includes the use of less hazardous solvents, atom-efficient reactions, and catalysts that can be easily recovered and recycled. For instance, the development of water-tolerant catalysts for alkylation reactions can significantly simplify process design and reduce environmental impact.
Process analytical technology (PAT) is becoming an integral part of scalable synthesis pathways. Real-time monitoring of reaction progress and product quality can enable adaptive process control, ensuring consistent product quality across different scales of production. This is particularly relevant for complex alkylation reactions where subtle changes in reaction conditions can significantly impact product distribution.
Lastly, the integration of computational tools in process engineering can greatly enhance the scalability of alkyl group optimization. Predictive models for reaction kinetics, thermodynamics, and mass transfer can guide process design and optimization, reducing the need for extensive experimental work. Machine learning algorithms can also be employed to identify optimal reaction conditions and predict scale-up challenges, further streamlining the development of industrial-scale processes for alkyl functional group optimization.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!