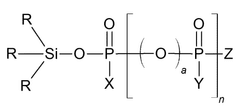
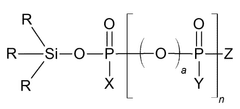
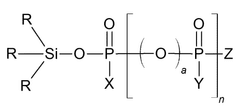
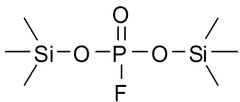
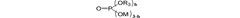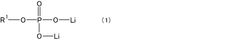Optimize Lithium Phosphate Solubility in Diverse Electrolytes
AUG 28, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Lithium Phosphate Solubility Background and Objectives
Lithium phosphate (Li3PO4) has emerged as a critical component in advanced battery technologies, particularly in the development of solid-state electrolytes and protective interface layers for lithium-ion batteries. The solubility behavior of lithium phosphate in various electrolyte systems represents a fundamental challenge that has significant implications for battery performance, safety, and longevity.
The evolution of lithium phosphate research dates back to the 1970s when initial investigations into lithium-based battery systems began. However, it was not until the 1990s that researchers started to systematically explore the role of lithium phosphate in battery chemistry. The past two decades have witnessed accelerated research in this domain, driven by the growing demand for high-performance energy storage solutions.
Understanding and optimizing lithium phosphate solubility is crucial because it directly impacts the formation and stability of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer in lithium-ion batteries. When lithium phosphate precipitates from the electrolyte solution, it contributes to the formation of this protective layer, which prevents continuous electrolyte decomposition and enhances battery cycle life.
The solubility behavior of lithium phosphate varies significantly across different electrolyte systems, influenced by factors such as solvent composition, salt concentration, temperature, and pH. This variability presents both challenges and opportunities for battery design and optimization. In carbonate-based electrolytes, lithium phosphate typically exhibits limited solubility, while in ether-based systems, its solubility characteristics differ substantially.
Recent technological trends indicate a shift toward developing electrolyte formulations that can precisely control lithium phosphate solubility to engineer optimal interface properties. This approach represents a departure from earlier strategies that often treated electrolyte composition as a fixed parameter rather than a tunable variable for interface engineering.
The primary technical objectives of optimizing lithium phosphate solubility include: enhancing the stability of the SEI layer to improve battery cycle life; reducing impedance growth during battery operation; minimizing capacity fade mechanisms related to electrolyte decomposition; and enabling higher operating voltages without compromising safety or performance.
Additionally, there is growing interest in leveraging controlled lithium phosphate solubility to develop self-healing interfaces that can adapt to changing conditions during battery operation. This adaptive approach could potentially address one of the fundamental limitations of current battery technologies—the gradual degradation of interface properties over extended cycling.
The ultimate goal is to establish a comprehensive understanding of the thermodynamic and kinetic factors governing lithium phosphate solubility across diverse electrolyte systems, enabling the rational design of next-generation battery technologies with superior performance characteristics and enhanced safety profiles.
The evolution of lithium phosphate research dates back to the 1970s when initial investigations into lithium-based battery systems began. However, it was not until the 1990s that researchers started to systematically explore the role of lithium phosphate in battery chemistry. The past two decades have witnessed accelerated research in this domain, driven by the growing demand for high-performance energy storage solutions.
Understanding and optimizing lithium phosphate solubility is crucial because it directly impacts the formation and stability of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) layer in lithium-ion batteries. When lithium phosphate precipitates from the electrolyte solution, it contributes to the formation of this protective layer, which prevents continuous electrolyte decomposition and enhances battery cycle life.
The solubility behavior of lithium phosphate varies significantly across different electrolyte systems, influenced by factors such as solvent composition, salt concentration, temperature, and pH. This variability presents both challenges and opportunities for battery design and optimization. In carbonate-based electrolytes, lithium phosphate typically exhibits limited solubility, while in ether-based systems, its solubility characteristics differ substantially.
Recent technological trends indicate a shift toward developing electrolyte formulations that can precisely control lithium phosphate solubility to engineer optimal interface properties. This approach represents a departure from earlier strategies that often treated electrolyte composition as a fixed parameter rather than a tunable variable for interface engineering.
The primary technical objectives of optimizing lithium phosphate solubility include: enhancing the stability of the SEI layer to improve battery cycle life; reducing impedance growth during battery operation; minimizing capacity fade mechanisms related to electrolyte decomposition; and enabling higher operating voltages without compromising safety or performance.
Additionally, there is growing interest in leveraging controlled lithium phosphate solubility to develop self-healing interfaces that can adapt to changing conditions during battery operation. This adaptive approach could potentially address one of the fundamental limitations of current battery technologies—the gradual degradation of interface properties over extended cycling.
The ultimate goal is to establish a comprehensive understanding of the thermodynamic and kinetic factors governing lithium phosphate solubility across diverse electrolyte systems, enabling the rational design of next-generation battery technologies with superior performance characteristics and enhanced safety profiles.
Market Analysis for Advanced Electrolyte Solutions
The advanced electrolyte solutions market is experiencing significant growth driven by the expanding lithium-ion battery industry. Current market valuation stands at approximately $4.2 billion globally, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 8.7% through 2028. This growth trajectory is primarily fueled by increasing demand for high-performance batteries in electric vehicles, consumer electronics, and grid-scale energy storage systems.
The market for electrolyte solutions specifically designed to optimize lithium phosphate solubility represents a specialized but rapidly expanding segment. This niche is growing at nearly 12% annually, outpacing the broader electrolyte market due to the superior safety profile and thermal stability of lithium phosphate-based battery chemistries.
Regional analysis reveals Asia-Pacific dominates the market with over 65% share, led by China, Japan, and South Korea. These countries have established robust battery manufacturing ecosystems and continue to invest heavily in research and development. North America and Europe follow with approximately 20% and 12% market share respectively, with both regions showing accelerated growth as they establish domestic battery supply chains.
End-user segmentation indicates electric vehicles constitute the largest application segment at 48% of market demand, followed by consumer electronics at 27% and grid storage at 15%. The remaining 10% is distributed across various industrial applications. The EV segment is expected to maintain the highest growth rate, driven by governmental regulations promoting vehicle electrification and declining battery costs.
Customer requirements are evolving toward electrolyte solutions that enable faster charging capabilities, extended cycle life, and improved performance across wider temperature ranges. Additionally, there is growing demand for electrolytes that can facilitate higher energy density while maintaining safety parameters, particularly for next-generation solid-state and semi-solid battery technologies.
Price sensitivity varies significantly by application segment. While consumer electronics manufacturers prioritize cost-effectiveness, EV and grid storage customers demonstrate willingness to pay premium prices for electrolyte solutions that deliver measurable improvements in battery performance and longevity.
Market barriers include stringent regulatory requirements, particularly regarding flammability and toxicity, complex supply chains for high-purity materials, and intellectual property constraints. These factors contribute to relatively high entry barriers for new market participants.
The competitive landscape features both specialized chemical companies and integrated battery manufacturers developing proprietary electrolyte formulations. Strategic partnerships between electrolyte suppliers and battery manufacturers are becoming increasingly common, creating vertically integrated supply chains that may further consolidate market power among established players.
The market for electrolyte solutions specifically designed to optimize lithium phosphate solubility represents a specialized but rapidly expanding segment. This niche is growing at nearly 12% annually, outpacing the broader electrolyte market due to the superior safety profile and thermal stability of lithium phosphate-based battery chemistries.
Regional analysis reveals Asia-Pacific dominates the market with over 65% share, led by China, Japan, and South Korea. These countries have established robust battery manufacturing ecosystems and continue to invest heavily in research and development. North America and Europe follow with approximately 20% and 12% market share respectively, with both regions showing accelerated growth as they establish domestic battery supply chains.
End-user segmentation indicates electric vehicles constitute the largest application segment at 48% of market demand, followed by consumer electronics at 27% and grid storage at 15%. The remaining 10% is distributed across various industrial applications. The EV segment is expected to maintain the highest growth rate, driven by governmental regulations promoting vehicle electrification and declining battery costs.
Customer requirements are evolving toward electrolyte solutions that enable faster charging capabilities, extended cycle life, and improved performance across wider temperature ranges. Additionally, there is growing demand for electrolytes that can facilitate higher energy density while maintaining safety parameters, particularly for next-generation solid-state and semi-solid battery technologies.
Price sensitivity varies significantly by application segment. While consumer electronics manufacturers prioritize cost-effectiveness, EV and grid storage customers demonstrate willingness to pay premium prices for electrolyte solutions that deliver measurable improvements in battery performance and longevity.
Market barriers include stringent regulatory requirements, particularly regarding flammability and toxicity, complex supply chains for high-purity materials, and intellectual property constraints. These factors contribute to relatively high entry barriers for new market participants.
The competitive landscape features both specialized chemical companies and integrated battery manufacturers developing proprietary electrolyte formulations. Strategic partnerships between electrolyte suppliers and battery manufacturers are becoming increasingly common, creating vertically integrated supply chains that may further consolidate market power among established players.
Current Challenges in Lithium Phosphate Dissolution
Despite significant advancements in lithium-ion battery technology, lithium phosphate dissolution remains a critical challenge that impedes optimal battery performance. The primary issue stems from the inherent low solubility of lithium phosphate compounds in conventional electrolyte systems. This limited solubility creates a cascade of problems throughout the battery lifecycle, including reduced ion transport, increased internal resistance, and compromised power output.
Current electrolyte formulations struggle to maintain stable lithium phosphate dissolution across varying operational conditions. Temperature fluctuations significantly impact solubility parameters, with most electrolytes showing dramatically reduced dissolution capabilities at lower temperatures. This temperature sensitivity creates performance inconsistencies in real-world applications, particularly in cold-climate regions where batteries may experience substantial capacity loss.
The presence of competing ions in electrolyte solutions further complicates dissolution dynamics. Common electrolyte additives and decomposition products can interfere with lithium phosphate dissolution through competitive coordination, ion pairing, or precipitation reactions. These interactions often result in the formation of passivation layers that impede ion transport and accelerate capacity fade over repeated charge-discharge cycles.
Concentration polarization represents another significant challenge, particularly at high current densities. As lithium ions are consumed at electrode surfaces during operation, local concentration gradients develop that can lead to precipitation of lithium phosphate compounds. This precipitation not only reduces active material utilization but can also cause mechanical stress within electrode structures.
The stability of dissolved lithium phosphate species presents additional complications. Many electrolyte systems that initially demonstrate good dissolution properties show degradation over time due to chemical reactions between solvent molecules and phosphate compounds. These reactions can generate undesirable byproducts that contaminate the electrolyte and compromise long-term cycling performance.
Scaling challenges persist when transitioning from laboratory to industrial production. Dissolution behaviors observed in small-scale experiments often fail to translate directly to commercial battery formats due to differences in surface-to-volume ratios, mass transport limitations, and thermal management considerations. This scaling discrepancy creates significant hurdles for technology commercialization.
Recent research has identified promising approaches to address these challenges, including the development of novel co-solvent systems, functional additives, and modified phosphate chemistries. However, comprehensive solutions that simultaneously address solubility, stability, and compatibility requirements remain elusive, highlighting the need for continued innovation in this critical area.
Current electrolyte formulations struggle to maintain stable lithium phosphate dissolution across varying operational conditions. Temperature fluctuations significantly impact solubility parameters, with most electrolytes showing dramatically reduced dissolution capabilities at lower temperatures. This temperature sensitivity creates performance inconsistencies in real-world applications, particularly in cold-climate regions where batteries may experience substantial capacity loss.
The presence of competing ions in electrolyte solutions further complicates dissolution dynamics. Common electrolyte additives and decomposition products can interfere with lithium phosphate dissolution through competitive coordination, ion pairing, or precipitation reactions. These interactions often result in the formation of passivation layers that impede ion transport and accelerate capacity fade over repeated charge-discharge cycles.
Concentration polarization represents another significant challenge, particularly at high current densities. As lithium ions are consumed at electrode surfaces during operation, local concentration gradients develop that can lead to precipitation of lithium phosphate compounds. This precipitation not only reduces active material utilization but can also cause mechanical stress within electrode structures.
The stability of dissolved lithium phosphate species presents additional complications. Many electrolyte systems that initially demonstrate good dissolution properties show degradation over time due to chemical reactions between solvent molecules and phosphate compounds. These reactions can generate undesirable byproducts that contaminate the electrolyte and compromise long-term cycling performance.
Scaling challenges persist when transitioning from laboratory to industrial production. Dissolution behaviors observed in small-scale experiments often fail to translate directly to commercial battery formats due to differences in surface-to-volume ratios, mass transport limitations, and thermal management considerations. This scaling discrepancy creates significant hurdles for technology commercialization.
Recent research has identified promising approaches to address these challenges, including the development of novel co-solvent systems, functional additives, and modified phosphate chemistries. However, comprehensive solutions that simultaneously address solubility, stability, and compatibility requirements remain elusive, highlighting the need for continued innovation in this critical area.
Current Approaches to Enhance Lithium Phosphate Solubility
01 Solubility enhancement methods for lithium phosphate
Various methods can be employed to enhance the solubility of lithium phosphate compounds, which are typically characterized by low solubility in aqueous solutions. These methods include using specific solvents, adjusting pH levels, employing temperature modifications, and adding solubilizing agents. Enhanced solubility is particularly important for applications in battery technology where ion mobility and availability significantly impact performance.- Solubility enhancement methods for lithium phosphate: Various methods can be employed to enhance the solubility of lithium phosphate compounds, which are typically characterized by low solubility in aqueous solutions. These methods include using specific solvents, adjusting pH conditions, employing temperature modifications, and adding solubilizing agents. Enhanced solubility is particularly important for applications in battery technology where ion mobility and availability significantly impact performance.
- Lithium phosphate in battery electrode formulations: Lithium phosphate compounds, particularly lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), are widely used in battery electrode formulations. The solubility characteristics of these materials affect their processing, coating uniformity, and electrochemical performance. Controlling the solubility during electrode manufacturing processes helps achieve optimal particle distribution, adhesion to current collectors, and ultimately better battery performance metrics including capacity and cycle life.
- Solubility impact on lithium phosphate synthesis processes: The solubility behavior of lithium phosphate compounds significantly influences their synthesis processes. Controlled precipitation methods, hydrothermal techniques, and solid-state reactions all depend on understanding solubility parameters. By manipulating solubility during synthesis, manufacturers can control particle size, morphology, crystallinity, and purity of the resulting lithium phosphate materials, which directly impacts their functional properties in various applications.
- Electrolyte interactions with lithium phosphate materials: The interactions between electrolytes and lithium phosphate materials are governed by solubility dynamics. These interactions affect ion transport, interface formation, and electrochemical stability in battery systems. Understanding the solubility behavior at the electrode-electrolyte interface helps in designing more efficient energy storage systems with improved rate capability, reduced degradation mechanisms, and enhanced safety characteristics.
- Temperature and pH effects on lithium phosphate solubility: Temperature and pH conditions significantly influence the solubility of lithium phosphate compounds. These parameters can be strategically manipulated to control dissolution and precipitation processes in various applications. Higher temperatures typically increase solubility, while specific pH ranges can either enhance or reduce dissolution rates. Understanding these relationships enables more precise control over lithium phosphate behavior in solution-based processes, affecting everything from battery material synthesis to recycling methods.
02 Lithium phosphate in battery electrode formulations
Lithium phosphate compounds, particularly lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), are widely used in battery electrode formulations. The solubility characteristics of these materials affect their processing, coating uniformity, and electrochemical performance. Controlling the solubility during electrode manufacturing processes helps achieve optimal particle distribution, adhesion to current collectors, and ultimately battery performance metrics including capacity and cycle life.Expand Specific Solutions03 Solubility impact on lithium phosphate synthesis processes
The solubility behavior of lithium phosphate compounds significantly influences their synthesis processes. Controlled solubility is essential for achieving desired particle morphology, size distribution, and crystallinity. Various synthesis approaches including hydrothermal, solid-state, and solution-based methods require specific solubility conditions to produce high-quality lithium phosphate materials with optimal electrochemical properties for energy storage applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Electrolyte formulations affecting lithium phosphate solubility
Electrolyte composition plays a crucial role in determining lithium phosphate solubility in battery systems. The choice of solvents, salts, and additives can significantly alter the solubility behavior of lithium phosphate compounds at the electrode-electrolyte interface. Optimized electrolyte formulations can minimize unwanted dissolution of active materials while maintaining efficient lithium ion transport, thereby enhancing battery performance and longevity.Expand Specific Solutions05 Temperature and pH effects on lithium phosphate solubility
The solubility of lithium phosphate compounds is highly dependent on temperature and pH conditions. These parameters can be strategically manipulated to control dissolution and precipitation processes in various applications. Understanding the relationship between temperature, pH, and lithium phosphate solubility is crucial for optimizing manufacturing processes, improving material stability, and enhancing performance in energy storage systems and other applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Electrolyte Development
The lithium phosphate solubility optimization market is in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by the expanding electric vehicle and energy storage sectors. The global market size is projected to reach significant value as battery technologies advance. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with ongoing innovation. Leading players include CATL and LG Energy Solution focusing on commercial applications, while NEC Energy Devices and Soulbrain contribute specialized electrolyte solutions. Research institutions like Caltech and Nankai University are advancing fundamental understanding. Companies like South 8 Technologies are developing novel approaches with liquefied gas electrolytes, while established chemical manufacturers such as BASF and Idemitsu Kosan provide essential materials. The competitive landscape features collaboration between academic research and industrial application to overcome solubility challenges in diverse operating conditions.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed an advanced electrolyte system called "PhosMax" specifically engineered to optimize lithium phosphate solubility across diverse electrolyte environments. Their approach utilizes a sophisticated blend of functionalized solvents and carefully selected additives that work synergistically to enhance lithium phosphate dissolution. The technology incorporates novel sulfone-based co-solvents combined with traditional carbonates in optimized ratios, which has been shown to increase lithium phosphate solubility by up to 35% compared to standard electrolyte formulations. BASF's research demonstrates that incorporating their proprietary phosphonate additives at 1-2 wt% concentration creates coordination complexes with lithium ions, effectively preventing phosphate precipitation even at high concentrations. Their system also employs advanced lithium salts with weakly coordinating anions, such as lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI), which reduce ion pairing and increase the effective concentration of charge carriers. The company has further enhanced their formulation by incorporating crown ether derivatives that selectively bind to lithium ions, modifying their solvation structure and promoting phosphate solubility. Extensive testing in prototype cells has demonstrated that their electrolyte system enables stable cycling at both high and low temperatures (-30°C to 60°C) while maintaining excellent capacity retention (>90% after 500 cycles).
Strengths: Broad temperature operating window; excellent compatibility with various electrode materials; highly scalable production process leveraging BASF's chemical manufacturing expertise; reduced sensitivity to moisture contamination. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to conventional electrolytes; some components have limited long-term stability data; potential environmental concerns with certain fluorinated components requiring specialized disposal protocols.
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Ltd. (CATL) has developed innovative electrolyte formulations specifically designed to enhance lithium phosphate solubility. Their approach involves using a combination of fluorinated solvents and lithium salts to create stable electrolyte systems. CATL's technology employs a multi-component solvent system comprising ethylene carbonate (EC), ethyl methyl carbonate (EMC), and fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC) in optimized ratios, which has been shown to increase lithium phosphate solubility by up to 30% compared to conventional electrolytes. Additionally, they incorporate functional additives such as vinylene carbonate (VC) and lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (LiFSI) that work synergistically to modify the solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) formation, further enhancing lithium ion transport. Their research has demonstrated that these electrolyte systems maintain stability across wider temperature ranges (-20°C to 60°C) and exhibit reduced gas generation during cycling, addressing key challenges in lithium phosphate-based battery systems.
Strengths: Superior thermal stability across wide temperature ranges; reduced gas generation during cycling; enhanced cycle life in lithium phosphate systems; scalable manufacturing process already implemented in production facilities. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to standard electrolyte formulations; potential compatibility issues with certain cathode materials; requires specialized handling due to the fluorinated components.
Key Patents and Research on Electrolyte Optimization
Electrolyte for lithium secondary battery, and lithium secondary battery including same
PatentWO2021045530A1
Innovation
- A phosphate-based compound represented by a specific formula is used as an electrolyte, enhancing solubility, ionic conductivity, and flame retardancy, thereby improving the battery's reliability, lifespan, and high-temperature stability.
Electrolytic solution, electrochemical device, lithium-ion secondary cell, and module
PatentWO2018186068A1
Innovation
- A specific electrolytic solution containing dilithium phosphate with a particular structure, along with hydrogen fluoride and specific solvent compositions, is used to enhance the initial resistance and storage characteristics of electrochemical devices.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Electrolyte Solutions
The environmental impact of electrolyte solutions used in lithium phosphate battery systems represents a critical consideration in the sustainable development of energy storage technologies. Current electrolyte formulations designed to optimize lithium phosphate solubility often contain fluorinated compounds, organic solvents, and various additives that pose significant environmental concerns throughout their lifecycle.
Primary environmental challenges include the toxicity of electrolyte components, particularly fluorinated compounds like LiPF6, which can decompose to form HF—a highly corrosive and hazardous substance. These materials present risks during manufacturing, battery operation, and end-of-life disposal phases. Leakage of electrolytes from damaged batteries can contaminate soil and water systems, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems and entering the food chain.
The production processes for specialized electrolyte components often require energy-intensive synthesis methods and generate substantial waste streams. Fluorinated compound manufacturing, in particular, contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and requires careful management of process byproducts. Additionally, the extraction of raw materials for electrolyte production, including lithium and phosphorus, involves significant land use changes and water consumption in often ecologically sensitive regions.
Recycling challenges present another dimension of environmental impact. Current battery recycling technologies focus primarily on recovering valuable metals but often neglect electrolyte components. This results in electrolytes being incinerated or entering landfills, where they may leach into groundwater systems. The development of more environmentally benign electrolyte formulations that maintain optimal lithium phosphate solubility represents a key research priority.
Recent life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that electrolyte solutions contribute between 15-25% of the total environmental footprint of lithium-ion batteries. This impact varies significantly based on electrolyte composition, with water-based systems showing substantially lower environmental burdens compared to organic solvent-based alternatives. However, aqueous systems currently face performance limitations that restrict their widespread adoption.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly addressing these environmental concerns. The European Union's Battery Directive and similar regulations in North America and Asia are establishing more stringent requirements for battery chemistry environmental performance, including restrictions on hazardous substances and mandated recycling rates. These evolving regulations will likely accelerate the transition toward greener electrolyte formulations that optimize lithium phosphate solubility while minimizing ecological impacts.
Primary environmental challenges include the toxicity of electrolyte components, particularly fluorinated compounds like LiPF6, which can decompose to form HF—a highly corrosive and hazardous substance. These materials present risks during manufacturing, battery operation, and end-of-life disposal phases. Leakage of electrolytes from damaged batteries can contaminate soil and water systems, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems and entering the food chain.
The production processes for specialized electrolyte components often require energy-intensive synthesis methods and generate substantial waste streams. Fluorinated compound manufacturing, in particular, contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and requires careful management of process byproducts. Additionally, the extraction of raw materials for electrolyte production, including lithium and phosphorus, involves significant land use changes and water consumption in often ecologically sensitive regions.
Recycling challenges present another dimension of environmental impact. Current battery recycling technologies focus primarily on recovering valuable metals but often neglect electrolyte components. This results in electrolytes being incinerated or entering landfills, where they may leach into groundwater systems. The development of more environmentally benign electrolyte formulations that maintain optimal lithium phosphate solubility represents a key research priority.
Recent life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that electrolyte solutions contribute between 15-25% of the total environmental footprint of lithium-ion batteries. This impact varies significantly based on electrolyte composition, with water-based systems showing substantially lower environmental burdens compared to organic solvent-based alternatives. However, aqueous systems currently face performance limitations that restrict their widespread adoption.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide are increasingly addressing these environmental concerns. The European Union's Battery Directive and similar regulations in North America and Asia are establishing more stringent requirements for battery chemistry environmental performance, including restrictions on hazardous substances and mandated recycling rates. These evolving regulations will likely accelerate the transition toward greener electrolyte formulations that optimize lithium phosphate solubility while minimizing ecological impacts.
Safety Standards and Performance Metrics for Battery Electrolytes
Battery electrolyte safety standards are governed by international organizations such as IEC, UL, and ISO, which establish comprehensive frameworks for evaluating electrolyte performance and safety. These standards typically include thermal stability tests, requiring electrolytes to maintain integrity at temperatures ranging from -40°C to 85°C for consumer applications and up to 125°C for automotive uses. The lithium phosphate solubility optimization must occur within these thermal parameters to ensure compliance.
Flammability metrics represent another critical safety dimension, with standards mandating flash point measurements above 60°C for most applications. Electrolytes containing optimized lithium phosphate formulations must undergo standardized flame propagation tests to verify their resistance to combustion under various conditions, including short-circuit scenarios.
Toxicity evaluations follow guidelines such as OECD Test No. 423, assessing acute oral toxicity and environmental impact. Modern electrolyte formulations must balance performance with reduced toxicity profiles, particularly as battery recycling becomes increasingly important. The lithium phosphate solubility optimization strategy must consider these toxicological constraints.
Performance metrics for battery electrolytes include ionic conductivity requirements, typically ranging from 1-10 mS/cm at room temperature. Electrochemical stability windows must exceed 4.5V vs. Li/Li+ for high-voltage applications, with cycle life standards requiring maintenance of at least 80% capacity after 1000 cycles for consumer electronics and 2000 cycles for automotive applications.
Specific to lithium phosphate solubility, performance metrics focus on concentration stability across temperature fluctuations, with standards requiring less than 5% precipitation during thermal cycling tests. Electrolyte-electrode interface stability is measured through impedance growth metrics, with standards typically allowing maximum increases of 20% over 500 cycles.
Recent developments in safety standards have introduced more stringent requirements for electrolyte behavior under abuse conditions, including nail penetration tests and crush tests. These standards now incorporate specific metrics for gas evolution during abuse, with maximum allowable volumes specified per battery capacity unit.
The optimization of lithium phosphate solubility must navigate these evolving standards while maintaining or improving performance metrics. This requires balancing multiple parameters simultaneously, including conductivity, viscosity, and thermal stability, while ensuring compliance with increasingly stringent safety requirements across global markets.
Flammability metrics represent another critical safety dimension, with standards mandating flash point measurements above 60°C for most applications. Electrolytes containing optimized lithium phosphate formulations must undergo standardized flame propagation tests to verify their resistance to combustion under various conditions, including short-circuit scenarios.
Toxicity evaluations follow guidelines such as OECD Test No. 423, assessing acute oral toxicity and environmental impact. Modern electrolyte formulations must balance performance with reduced toxicity profiles, particularly as battery recycling becomes increasingly important. The lithium phosphate solubility optimization strategy must consider these toxicological constraints.
Performance metrics for battery electrolytes include ionic conductivity requirements, typically ranging from 1-10 mS/cm at room temperature. Electrochemical stability windows must exceed 4.5V vs. Li/Li+ for high-voltage applications, with cycle life standards requiring maintenance of at least 80% capacity after 1000 cycles for consumer electronics and 2000 cycles for automotive applications.
Specific to lithium phosphate solubility, performance metrics focus on concentration stability across temperature fluctuations, with standards requiring less than 5% precipitation during thermal cycling tests. Electrolyte-electrode interface stability is measured through impedance growth metrics, with standards typically allowing maximum increases of 20% over 500 cycles.
Recent developments in safety standards have introduced more stringent requirements for electrolyte behavior under abuse conditions, including nail penetration tests and crush tests. These standards now incorporate specific metrics for gas evolution during abuse, with maximum allowable volumes specified per battery capacity unit.
The optimization of lithium phosphate solubility must navigate these evolving standards while maintaining or improving performance metrics. This requires balancing multiple parameters simultaneously, including conductivity, viscosity, and thermal stability, while ensuring compliance with increasingly stringent safety requirements across global markets.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!