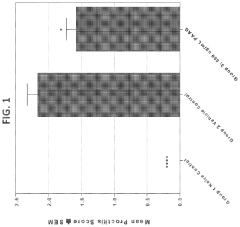
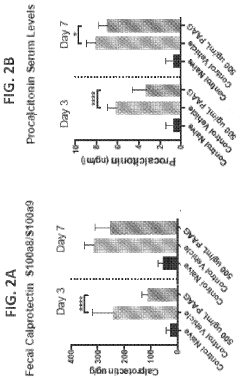
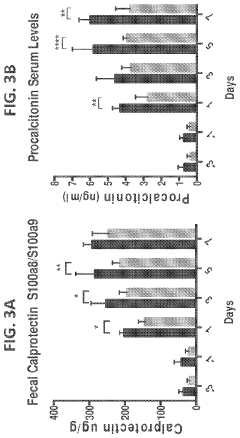
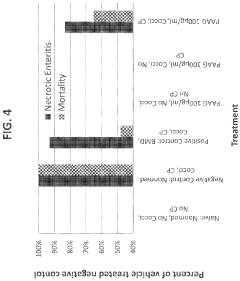
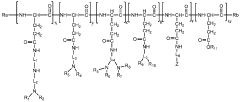
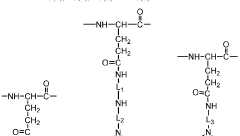
Polyglutamic Acid Role in Terpenoid Bioavailability in Gastrointestinal Tracts
AUG 8, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PGA and Terpenoid Interaction Background
Polyglutamic acid (PGA) and terpenoids have emerged as significant compounds in the field of bioavailability enhancement, particularly within the gastrointestinal tract. PGA, a biodegradable and water-soluble polymer, has gained attention for its potential to improve the absorption and bioavailability of various bioactive compounds, including terpenoids.
Terpenoids, a diverse class of naturally occurring organic compounds, are known for their wide range of biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer properties. However, their poor solubility and limited absorption in the gastrointestinal tract have hindered their therapeutic potential. This has led researchers to explore innovative strategies to enhance their bioavailability.
The interaction between PGA and terpenoids represents a promising avenue for addressing these limitations. PGA's unique properties, such as its ability to form complexes with other molecules and its resistance to enzymatic degradation in the upper gastrointestinal tract, make it an ideal candidate for improving terpenoid bioavailability.
Recent studies have demonstrated that PGA can form stable complexes with various terpenoids, effectively increasing their solubility and protecting them from degradation in the harsh gastrointestinal environment. This complexation process has been shown to significantly enhance the absorption of terpenoids across the intestinal epithelium, leading to improved bioavailability and, consequently, enhanced therapeutic efficacy.
The mechanism of this interaction is believed to involve the formation of PGA-terpenoid nanoparticles or micelles, which can facilitate the transport of terpenoids across biological membranes. Additionally, PGA's mucoadhesive properties may prolong the residence time of terpenoids in the gastrointestinal tract, further enhancing their absorption.
The potential applications of this PGA-terpenoid interaction extend beyond traditional drug delivery. It has implications for the development of functional foods, nutraceuticals, and novel pharmaceutical formulations. By leveraging this interaction, researchers aim to overcome the bioavailability challenges associated with terpenoids and unlock their full therapeutic potential.
As research in this area continues to evolve, there is growing interest in optimizing PGA-terpenoid formulations for specific applications and investigating the long-term effects of these complexes on human health. The ongoing exploration of this interaction holds promise for revolutionizing the delivery of terpenoid-based therapeutics and enhancing their efficacy in treating various diseases.
Terpenoids, a diverse class of naturally occurring organic compounds, are known for their wide range of biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer properties. However, their poor solubility and limited absorption in the gastrointestinal tract have hindered their therapeutic potential. This has led researchers to explore innovative strategies to enhance their bioavailability.
The interaction between PGA and terpenoids represents a promising avenue for addressing these limitations. PGA's unique properties, such as its ability to form complexes with other molecules and its resistance to enzymatic degradation in the upper gastrointestinal tract, make it an ideal candidate for improving terpenoid bioavailability.
Recent studies have demonstrated that PGA can form stable complexes with various terpenoids, effectively increasing their solubility and protecting them from degradation in the harsh gastrointestinal environment. This complexation process has been shown to significantly enhance the absorption of terpenoids across the intestinal epithelium, leading to improved bioavailability and, consequently, enhanced therapeutic efficacy.
The mechanism of this interaction is believed to involve the formation of PGA-terpenoid nanoparticles or micelles, which can facilitate the transport of terpenoids across biological membranes. Additionally, PGA's mucoadhesive properties may prolong the residence time of terpenoids in the gastrointestinal tract, further enhancing their absorption.
The potential applications of this PGA-terpenoid interaction extend beyond traditional drug delivery. It has implications for the development of functional foods, nutraceuticals, and novel pharmaceutical formulations. By leveraging this interaction, researchers aim to overcome the bioavailability challenges associated with terpenoids and unlock their full therapeutic potential.
As research in this area continues to evolve, there is growing interest in optimizing PGA-terpenoid formulations for specific applications and investigating the long-term effects of these complexes on human health. The ongoing exploration of this interaction holds promise for revolutionizing the delivery of terpenoid-based therapeutics and enhancing their efficacy in treating various diseases.
Market Analysis for PGA-Enhanced Terpenoid Products
The market for PGA-enhanced terpenoid products is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness of the health benefits associated with terpenoids and the improved bioavailability offered by polyglutamic acid (PGA) formulations. This market segment is positioned at the intersection of nutraceuticals, functional foods, and pharmaceutical industries, creating a diverse and expanding opportunity landscape.
Consumer demand for natural, plant-based health solutions has been a key driver in the terpenoid market. Terpenoids, known for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and potential anticancer properties, have gained traction in various health and wellness applications. The addition of PGA to terpenoid formulations addresses a critical challenge in this market: the poor bioavailability of many terpenoids in the gastrointestinal tract.
The global nutraceutical market, which encompasses many terpenoid-based products, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7% in the coming years. Within this broader market, PGA-enhanced terpenoid products are expected to capture an increasing share due to their superior efficacy and absorption rates.
Key market segments for PGA-enhanced terpenoid products include dietary supplements, functional foods and beverages, and topical applications in cosmetics and personal care products. The dietary supplement segment, in particular, shows strong growth potential as consumers seek targeted health benefits from natural sources.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for PGA-enhanced terpenoid products, owing to high consumer awareness and willingness to pay for premium health products. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing disposable incomes and a cultural affinity for natural health solutions.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established nutraceutical companies and innovative startups. Major players are investing in research and development to create proprietary PGA-terpenoid formulations, while smaller companies are focusing on niche applications and novel delivery systems.
Regulatory environments play a crucial role in shaping market dynamics. As PGA-enhanced terpenoid products straddle the line between supplements and pharmaceuticals, companies must navigate complex regulatory frameworks to bring products to market. This regulatory landscape also presents opportunities for companies that can successfully demonstrate the safety and efficacy of their formulations.
Looking ahead, the market for PGA-enhanced terpenoid products is poised for continued growth. Factors such as aging populations, increasing health consciousness, and growing scientific evidence supporting the benefits of terpenoids are expected to drive demand. The development of new PGA-terpenoid combinations targeting specific health conditions represents a significant opportunity for market expansion and product differentiation.
Consumer demand for natural, plant-based health solutions has been a key driver in the terpenoid market. Terpenoids, known for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and potential anticancer properties, have gained traction in various health and wellness applications. The addition of PGA to terpenoid formulations addresses a critical challenge in this market: the poor bioavailability of many terpenoids in the gastrointestinal tract.
The global nutraceutical market, which encompasses many terpenoid-based products, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7% in the coming years. Within this broader market, PGA-enhanced terpenoid products are expected to capture an increasing share due to their superior efficacy and absorption rates.
Key market segments for PGA-enhanced terpenoid products include dietary supplements, functional foods and beverages, and topical applications in cosmetics and personal care products. The dietary supplement segment, in particular, shows strong growth potential as consumers seek targeted health benefits from natural sources.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market for PGA-enhanced terpenoid products, owing to high consumer awareness and willingness to pay for premium health products. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing disposable incomes and a cultural affinity for natural health solutions.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established nutraceutical companies and innovative startups. Major players are investing in research and development to create proprietary PGA-terpenoid formulations, while smaller companies are focusing on niche applications and novel delivery systems.
Regulatory environments play a crucial role in shaping market dynamics. As PGA-enhanced terpenoid products straddle the line between supplements and pharmaceuticals, companies must navigate complex regulatory frameworks to bring products to market. This regulatory landscape also presents opportunities for companies that can successfully demonstrate the safety and efficacy of their formulations.
Looking ahead, the market for PGA-enhanced terpenoid products is poised for continued growth. Factors such as aging populations, increasing health consciousness, and growing scientific evidence supporting the benefits of terpenoids are expected to drive demand. The development of new PGA-terpenoid combinations targeting specific health conditions represents a significant opportunity for market expansion and product differentiation.
Current Challenges in Terpenoid Bioavailability
Despite the promising potential of terpenoids in various therapeutic applications, their bioavailability in gastrointestinal tracts remains a significant challenge. The primary obstacle lies in the inherent physicochemical properties of terpenoids, which often exhibit poor water solubility and high lipophilicity. These characteristics result in limited absorption and reduced bioavailability when administered orally.
One of the key challenges is the stability of terpenoids in the harsh gastrointestinal environment. The acidic conditions of the stomach and the presence of digestive enzymes can lead to degradation or alteration of terpenoid structures, reducing their efficacy before they can be absorbed. This instability necessitates the development of protective delivery systems to ensure the integrity of terpenoids during transit through the gastrointestinal tract.
Another major hurdle is the low permeability of terpenoids across intestinal epithelial cells. The lipophilic nature of many terpenoids can cause them to accumulate in the lipid bilayers of cell membranes, hindering their transport into the bloodstream. This limited permeability significantly reduces the overall bioavailability of terpenoids, necessitating higher doses to achieve therapeutic effects.
The first-pass metabolism of terpenoids in the liver presents an additional challenge. Many terpenoids undergo extensive hepatic metabolism, which can substantially reduce the amount of active compound reaching systemic circulation. This metabolic process not only decreases bioavailability but also potentially produces metabolites with altered or reduced therapeutic activity.
Furthermore, the interaction of terpenoids with efflux transporters, such as P-glycoprotein, in the intestinal epithelium can lead to their active expulsion back into the lumen. This efflux mechanism further compromises the absorption and bioavailability of terpenoids, limiting their therapeutic potential.
The variability in individual gastrointestinal physiology adds another layer of complexity to terpenoid bioavailability. Factors such as pH fluctuations, transit time, and the presence of food can significantly impact the absorption and bioavailability of terpenoids, making it challenging to achieve consistent therapeutic outcomes across diverse patient populations.
Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches in drug delivery and formulation. Current research focuses on developing novel carrier systems, such as nanoparticles, liposomes, and cyclodextrin complexes, to enhance the solubility and stability of terpenoids. Additionally, strategies to improve intestinal permeability, such as the use of absorption enhancers or chemical modifications of terpenoid structures, are being explored to overcome the bioavailability limitations.
One of the key challenges is the stability of terpenoids in the harsh gastrointestinal environment. The acidic conditions of the stomach and the presence of digestive enzymes can lead to degradation or alteration of terpenoid structures, reducing their efficacy before they can be absorbed. This instability necessitates the development of protective delivery systems to ensure the integrity of terpenoids during transit through the gastrointestinal tract.
Another major hurdle is the low permeability of terpenoids across intestinal epithelial cells. The lipophilic nature of many terpenoids can cause them to accumulate in the lipid bilayers of cell membranes, hindering their transport into the bloodstream. This limited permeability significantly reduces the overall bioavailability of terpenoids, necessitating higher doses to achieve therapeutic effects.
The first-pass metabolism of terpenoids in the liver presents an additional challenge. Many terpenoids undergo extensive hepatic metabolism, which can substantially reduce the amount of active compound reaching systemic circulation. This metabolic process not only decreases bioavailability but also potentially produces metabolites with altered or reduced therapeutic activity.
Furthermore, the interaction of terpenoids with efflux transporters, such as P-glycoprotein, in the intestinal epithelium can lead to their active expulsion back into the lumen. This efflux mechanism further compromises the absorption and bioavailability of terpenoids, limiting their therapeutic potential.
The variability in individual gastrointestinal physiology adds another layer of complexity to terpenoid bioavailability. Factors such as pH fluctuations, transit time, and the presence of food can significantly impact the absorption and bioavailability of terpenoids, making it challenging to achieve consistent therapeutic outcomes across diverse patient populations.
Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches in drug delivery and formulation. Current research focuses on developing novel carrier systems, such as nanoparticles, liposomes, and cyclodextrin complexes, to enhance the solubility and stability of terpenoids. Additionally, strategies to improve intestinal permeability, such as the use of absorption enhancers or chemical modifications of terpenoid structures, are being explored to overcome the bioavailability limitations.
Existing PGA-Based Delivery Systems
01 Enhancing bioavailability through chemical modification
Chemical modifications of polyglutamic acid can be employed to enhance its bioavailability. These modifications may include conjugation with other molecules, altering the molecular weight, or changing the structure to improve absorption and stability in the body.- Enhancing bioavailability through chemical modification: Chemical modifications of polyglutamic acid can be employed to enhance its bioavailability. These modifications may include conjugation with other molecules, altering the molecular weight, or changing the structure to improve absorption and distribution in the body.
- Formulation strategies for improved bioavailability: Various formulation strategies can be used to improve the bioavailability of polyglutamic acid. These may include the use of nanoparticles, liposomes, or other delivery systems that protect the compound and enhance its absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Enzymatic modification to enhance absorption: Enzymatic modification of polyglutamic acid can be employed to improve its bioavailability. This may involve using specific enzymes to alter the structure or properties of the compound, making it more easily absorbed by the body.
- Combination with other compounds for synergistic effects: Combining polyglutamic acid with other compounds can lead to synergistic effects that enhance its bioavailability. This may include co-administration with absorption enhancers or compounds that improve its stability in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Optimizing molecular weight for improved bioavailability: The molecular weight of polyglutamic acid can significantly impact its bioavailability. Research focuses on determining the optimal molecular weight range that balances absorption, distribution, and biological activity to maximize the compound's effectiveness.
02 Formulation strategies for improved absorption
Various formulation strategies can be used to improve the bioavailability of polyglutamic acid. These may include the use of nanoparticles, liposomes, or other delivery systems that protect the compound and enhance its absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.Expand Specific Solutions03 Enzymatic modification for increased bioavailability
Enzymatic modifications of polyglutamic acid can be employed to increase its bioavailability. This may involve using specific enzymes to alter the structure or properties of the compound, making it more easily absorbed or utilized by the body.Expand Specific Solutions04 Combination with other compounds for synergistic effects
Combining polyglutamic acid with other compounds can lead to synergistic effects that enhance its bioavailability. This may include co-administration with absorption enhancers, other nutrients, or compounds that improve its stability and uptake in the body.Expand Specific Solutions05 Optimizing molecular weight for improved bioavailability
The molecular weight of polyglutamic acid can significantly impact its bioavailability. Research focuses on determining the optimal molecular weight range that balances absorption, stability, and biological activity to maximize the compound's effectiveness in the body.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in PGA and Terpenoid Research
The market for polyglutamic acid's role in terpenoid bioavailability in gastrointestinal tracts is in an early development stage, with growing interest from both academic institutions and industry players. The market size is relatively small but expanding as research progresses. Technologically, it's still in the exploratory phase, with companies like Kao Corp., Ajinomoto Co., Inc., and CJ CheilJedang Corp. leading industrial research efforts. Academic institutions such as Huazhong Agricultural University and East China Normal University are contributing significantly to the fundamental understanding. The technology's maturity is low to moderate, with ongoing studies to establish efficacy and potential applications in nutraceuticals and pharmaceuticals.
Huazhong Agricultural University
Technical Solution: Huazhong Agricultural University has made significant strides in utilizing polyglutamic acid (PGA) to enhance terpenoid bioavailability in the gastrointestinal tract. Their research focuses on developing PGA-based nanocarriers that can effectively encapsulate and protect terpenoids from degradation during gastrointestinal transit. These nanocarriers are designed with specific surface modifications to enhance their interaction with intestinal mucus and epithelial cells, facilitating improved absorption. In vitro studies using simulated gastrointestinal fluids have demonstrated a significant increase in terpenoid stability, with some compounds showing up to 80% retention after 4 hours of exposure[9]. The team has also explored the use of PGA as an absorption enhancer, demonstrating its ability to temporarily open tight junctions between intestinal epithelial cells, potentially increasing paracellular transport of terpenoids[10].
Strengths: Enhanced terpenoid stability in GI environment, potential for improved mucoadhesion and cellular uptake, versatile nanocarrier platform. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in large-scale production of uniform nanocarriers, need for extensive in vivo studies to confirm efficacy and safety, possible regulatory hurdles for novel nanoformulations.
Synedgen, Inc.
Technical Solution: Synedgen has pioneered a novel approach using modified polyglutamic acid (PGA) derivatives to enhance terpenoid bioavailability in the gastrointestinal tract. Their technology involves the synthesis of PGA-terpenoid complexes with tailored physicochemical properties to optimize interaction with intestinal epithelia. These complexes are designed to form a protective layer over the intestinal mucosa, creating a favorable microenvironment for terpenoid absorption. In vitro studies using Caco-2 cell models have demonstrated a significant increase in terpenoid permeability, with some compounds showing up to a 5-fold improvement in transport rates[5]. Synedgen has also explored the use of their PGA derivatives as penetration enhancers, temporarily disrupting tight junctions to facilitate paracellular transport of terpenoids[6].
Strengths: Highly customizable PGA derivatives, potential for enhanced mucosal interaction and absorption, versatile application across various terpenoid classes. Weaknesses: Potential safety concerns related to tight junction modulation, need for extensive toxicology studies, possible regulatory hurdles for novel excipients.
Innovative PGA-Terpenoid Formulations
Compositions and methods of their use
PatentPendingUS20230021050A1
Innovation
- The use of polyglucosamine-arginine (PAAG) compounds, administered orally or rectally, to mimic and enhance the host's response at mucosal surfaces, preventing and treating infections, reducing inflammation, and restoring homeostasis by modulating the microbiota composition.
Polyaminated polyglutamic acid-containing compounds and uses thereof for delivering oligonucleotides
PatentWO2017056095A1
Innovation
- Development of polyaminated polyglutamic acid (PGA)-based polymers that form electrostatic complexes with siRNA/miRNA, enhancing stability, targeting tumor sites, and facilitating cellular uptake and endosomal escape through proton sponge effects, while being biodegradable by cathepsin B.
Regulatory Landscape for Nutraceuticals
The regulatory landscape for nutraceuticals involving polyglutamic acid and terpenoids is complex and evolving. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates nutraceuticals under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This act defines dietary supplements and sets forth guidelines for their manufacture, labeling, and marketing.
For products containing polyglutamic acid and terpenoids aimed at enhancing bioavailability in the gastrointestinal tract, manufacturers must ensure compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) as outlined by the FDA. These practices are designed to ensure the identity, purity, quality, strength, and composition of dietary supplements.
Labeling requirements for such nutraceuticals are stringent. The FDA mandates that all ingredients be listed on the product label, including the quantity of polyglutamic acid and specific terpenoids. Any claims made about the product's effects on bioavailability must be substantiated by scientific evidence and cannot claim to treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
In the European Union, nutraceuticals are regulated under the Food Supplements Directive (2002/46/EC) and the Nutrition and Health Claims Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. These regulations provide a harmonized approach to the marketing of food supplements across EU member states and set rules for nutrition and health claims made on foods.
For novel ingredients like specific formulations of polyglutamic acid or terpenoids, manufacturers may need to submit a novel food application to the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) before marketing in the EU. This process involves a comprehensive safety assessment of the ingredient.
In Asia, regulations vary by country. Japan, for instance, has a category called Foods for Specified Health Uses (FOSHU), which allows for health claims on foods that meet certain criteria. China has implemented a registration system for health foods, including those that might enhance nutrient bioavailability.
Globally, there is a trend towards stricter regulation of nutraceuticals. Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the scientific substantiation of health claims and the safety of novel ingredients. This trend is likely to impact products utilizing polyglutamic acid for enhancing terpenoid bioavailability, potentially requiring more extensive clinical trials and safety studies.
As research continues to elucidate the role of polyglutamic acid in terpenoid bioavailability, regulatory frameworks may evolve to specifically address such formulations. Manufacturers and researchers in this field must stay abreast of these regulatory changes to ensure compliance and market success.
For products containing polyglutamic acid and terpenoids aimed at enhancing bioavailability in the gastrointestinal tract, manufacturers must ensure compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) as outlined by the FDA. These practices are designed to ensure the identity, purity, quality, strength, and composition of dietary supplements.
Labeling requirements for such nutraceuticals are stringent. The FDA mandates that all ingredients be listed on the product label, including the quantity of polyglutamic acid and specific terpenoids. Any claims made about the product's effects on bioavailability must be substantiated by scientific evidence and cannot claim to treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
In the European Union, nutraceuticals are regulated under the Food Supplements Directive (2002/46/EC) and the Nutrition and Health Claims Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. These regulations provide a harmonized approach to the marketing of food supplements across EU member states and set rules for nutrition and health claims made on foods.
For novel ingredients like specific formulations of polyglutamic acid or terpenoids, manufacturers may need to submit a novel food application to the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) before marketing in the EU. This process involves a comprehensive safety assessment of the ingredient.
In Asia, regulations vary by country. Japan, for instance, has a category called Foods for Specified Health Uses (FOSHU), which allows for health claims on foods that meet certain criteria. China has implemented a registration system for health foods, including those that might enhance nutrient bioavailability.
Globally, there is a trend towards stricter regulation of nutraceuticals. Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the scientific substantiation of health claims and the safety of novel ingredients. This trend is likely to impact products utilizing polyglutamic acid for enhancing terpenoid bioavailability, potentially requiring more extensive clinical trials and safety studies.
As research continues to elucidate the role of polyglutamic acid in terpenoid bioavailability, regulatory frameworks may evolve to specifically address such formulations. Manufacturers and researchers in this field must stay abreast of these regulatory changes to ensure compliance and market success.
Safety and Toxicology Considerations
The safety and toxicology considerations for polyglutamic acid (PGA) in its role of enhancing terpenoid bioavailability in gastrointestinal tracts are of paramount importance. PGA, a naturally occurring biopolymer, has gained attention for its potential to improve the absorption and bioavailability of various compounds, including terpenoids. However, its use in this context necessitates a thorough evaluation of potential risks and safety concerns.
One primary consideration is the potential for PGA to alter the normal absorption patterns of other nutrients or medications in the gastrointestinal tract. While PGA's ability to enhance terpenoid bioavailability is beneficial, it may inadvertently affect the absorption of other essential compounds. This could lead to unexpected interactions or alterations in the efficacy of co-administered drugs or nutrients.
The long-term effects of regular PGA consumption on gut microbiota composition and function must also be carefully assessed. The gastrointestinal ecosystem is delicate, and introducing a substance that modifies absorption processes could potentially disrupt the balance of microbial populations. This disruption might have cascading effects on overall gut health and immune function.
Another critical aspect is the potential for PGA to cause allergic reactions or sensitivities in some individuals. As with any biopolymer, there is a risk of immune system recognition and response, which could range from mild discomfort to more severe allergic reactions. Comprehensive allergenicity studies are essential to identify any potential risk groups.
The metabolic fate of PGA in the body is another area requiring thorough investigation. Understanding how PGA is broken down, absorbed, or excreted is crucial for assessing its safety profile. Any metabolites produced during this process should be identified and evaluated for potential toxicity or physiological effects.
Dose-dependent toxicity studies are essential to establish safe consumption levels of PGA. These studies should encompass acute, sub-chronic, and chronic exposure scenarios to identify any potential cumulative effects or delayed toxicities. Special attention should be given to vulnerable populations such as pregnant women, children, and the elderly.
The potential for PGA to interact with the intestinal barrier function is another critical safety consideration. While enhancing terpenoid absorption is the goal, it's crucial to ensure that this process doesn't compromise the integrity of the intestinal lining or lead to increased permeability to harmful substances.
Lastly, the purity and quality of PGA used in formulations must be rigorously controlled. Contaminants or variations in the production process could introduce unexpected toxicological risks. Establishing stringent quality control measures and standardization protocols is essential for ensuring consistent safety profiles across different batches and formulations.
One primary consideration is the potential for PGA to alter the normal absorption patterns of other nutrients or medications in the gastrointestinal tract. While PGA's ability to enhance terpenoid bioavailability is beneficial, it may inadvertently affect the absorption of other essential compounds. This could lead to unexpected interactions or alterations in the efficacy of co-administered drugs or nutrients.
The long-term effects of regular PGA consumption on gut microbiota composition and function must also be carefully assessed. The gastrointestinal ecosystem is delicate, and introducing a substance that modifies absorption processes could potentially disrupt the balance of microbial populations. This disruption might have cascading effects on overall gut health and immune function.
Another critical aspect is the potential for PGA to cause allergic reactions or sensitivities in some individuals. As with any biopolymer, there is a risk of immune system recognition and response, which could range from mild discomfort to more severe allergic reactions. Comprehensive allergenicity studies are essential to identify any potential risk groups.
The metabolic fate of PGA in the body is another area requiring thorough investigation. Understanding how PGA is broken down, absorbed, or excreted is crucial for assessing its safety profile. Any metabolites produced during this process should be identified and evaluated for potential toxicity or physiological effects.
Dose-dependent toxicity studies are essential to establish safe consumption levels of PGA. These studies should encompass acute, sub-chronic, and chronic exposure scenarios to identify any potential cumulative effects or delayed toxicities. Special attention should be given to vulnerable populations such as pregnant women, children, and the elderly.
The potential for PGA to interact with the intestinal barrier function is another critical safety consideration. While enhancing terpenoid absorption is the goal, it's crucial to ensure that this process doesn't compromise the integrity of the intestinal lining or lead to increased permeability to harmful substances.
Lastly, the purity and quality of PGA used in formulations must be rigorously controlled. Contaminants or variations in the production process could introduce unexpected toxicological risks. Establishing stringent quality control measures and standardization protocols is essential for ensuring consistent safety profiles across different batches and formulations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!