Structural Analysis of Phenolphthalein in Varying Solvents
Phenolphthalein Structure and Analysis Objectives
Phenolphthalein, a triarylmethane dye, has been a subject of extensive research due to its unique structural properties and versatile applications. The compound's ability to change color in response to pH variations has made it a valuable indicator in analytical chemistry and beyond. The structural analysis of phenolphthalein in varying solvents aims to elucidate the molecular behavior and conformational changes that occur under different environmental conditions.
The primary objective of this analysis is to gain a comprehensive understanding of phenolphthalein's structural dynamics in diverse solvent systems. By examining the molecule's behavior across a range of polarities and pH levels, researchers seek to uncover the fundamental mechanisms underlying its color-changing properties. This knowledge is crucial for optimizing its performance in existing applications and potentially discovering new uses in fields such as sensor technology and materials science.
One key aspect of the structural analysis involves investigating the intramolecular and intermolecular interactions that govern phenolphthalein's behavior in solution. These interactions play a pivotal role in determining the compound's solubility, stability, and spectroscopic properties. By systematically studying these factors, researchers aim to develop predictive models that can accurately describe phenolphthalein's behavior in complex solvent environments.
Another important objective is to explore the influence of solvent polarity on phenolphthalein's molecular conformation. The compound's structure can exist in different forms, including a colorless lactone and a colored quinoid, depending on the surrounding medium. Understanding how various solvents affect this equilibrium is essential for fine-tuning the indicator's sensitivity and response range in analytical applications.
The structural analysis also seeks to investigate the potential for developing novel phenolphthalein derivatives with enhanced properties. By identifying the key structural features responsible for its unique behavior, researchers can design modified versions of the molecule with improved stability, sensitivity, or specificity for particular applications. This could lead to the development of more robust pH indicators or advanced molecular switches for use in nanotechnology and smart materials.
Furthermore, the study aims to elucidate the kinetics of phenolphthalein's structural transitions in different solvents. This includes examining the rate of color change, the reversibility of the process, and any intermediate states that may form during the transition. Such information is crucial for applications requiring rapid and precise pH measurements or for developing systems with controlled release mechanisms based on environmental triggers.
In conclusion, the structural analysis of phenolphthalein in varying solvents represents a multifaceted research endeavor with far-reaching implications. By combining advanced spectroscopic techniques, computational modeling, and experimental approaches, this study aims to provide a comprehensive framework for understanding and manipulating the behavior of this important compound across diverse chemical environments.
Market Applications of Phenolphthalein
Phenolphthalein, a widely recognized pH indicator, has found extensive applications across various market sectors due to its unique color-changing properties. In the analytical chemistry field, phenolphthalein serves as a crucial tool for acid-base titrations, enabling precise endpoint detection in laboratories and industrial settings. Its ability to transition from colorless to pink in alkaline solutions makes it invaluable for quality control processes in manufacturing industries.
The medical and pharmaceutical sectors heavily rely on phenolphthalein for diagnostic purposes. It is commonly used in laxative formulations, although its use has been restricted in some countries due to potential health concerns. Nevertheless, phenolphthalein remains an essential component in certain medical tests, such as those for detecting occult blood in stool samples.
In the environmental monitoring industry, phenolphthalein plays a vital role in water quality assessment. It helps determine the alkalinity of water sources, which is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and ensuring the safety of drinking water supplies. This application extends to wastewater treatment facilities, where phenolphthalein aids in monitoring and adjusting pH levels during the purification process.
The forensic science field utilizes phenolphthalein in presumptive tests for blood detection. The Kastle-Meyer test, which employs phenolphthalein as a key reagent, allows investigators to quickly identify potential blood stains at crime scenes, providing valuable leads in criminal investigations.
In the education sector, phenolphthalein serves as an excellent teaching tool for demonstrating acid-base reactions and pH concepts. Its dramatic color change captivates students and helps reinforce fundamental chemistry principles in laboratory experiments.
The food and beverage industry also benefits from phenolphthalein's properties. While not used directly in food products, it is employed in quality control processes to ensure proper pH levels in various food items and beverages. This application is particularly important in the dairy industry for monitoring milk freshness and in the production of fermented foods.
Textile and paper industries utilize phenolphthalein in specialized applications. It can be incorporated into certain fabrics or papers to create products that change color in response to pH variations, serving both functional and novelty purposes.
As research into the structural behavior of phenolphthalein in different solvents continues, new applications are likely to emerge. The potential for developing advanced sensor technologies based on phenolphthalein's unique properties could open up opportunities in fields such as smart packaging, wearable technology, and environmental monitoring devices.
Current Challenges in Phenolphthalein Solvent Analysis
The structural analysis of phenolphthalein in varying solvents presents several significant challenges that researchers and analysts must navigate. One of the primary difficulties lies in the complex molecular behavior of phenolphthalein when exposed to different solvent environments. The compound's structure can undergo substantial changes depending on the solvent's polarity, pH, and other physicochemical properties, making it challenging to obtain consistent and reproducible results across different experimental conditions.
Another major hurdle is the sensitivity of phenolphthalein to environmental factors such as light and temperature. These external influences can alter the compound's structural integrity and spectroscopic properties, potentially leading to misinterpretation of analytical data. Researchers must implement stringent control measures to mitigate these effects, which can be both time-consuming and resource-intensive.
The choice of analytical techniques also presents challenges. While spectroscopic methods like UV-Vis and fluorescence spectroscopy are commonly used, they may not provide sufficient structural information in all solvent systems. Advanced techniques such as NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography can offer more detailed structural insights but are often limited by solubility issues in certain solvents or the difficulty in obtaining suitable crystals for analysis.
Furthermore, the dynamic nature of phenolphthalein's structural changes in solution poses a significant challenge for real-time analysis. The rapid equilibrium between different structural forms of the molecule in various solvents makes it difficult to capture and characterize transient species or intermediate states, which are crucial for understanding the complete structural behavior of phenolphthalein.
The interpretation of analytical data is another area of concern. The complex interplay between phenolphthalein and different solvents can lead to spectral shifts, peak broadening, or the appearance of new signals that are not easily attributable to specific structural changes. This complexity requires sophisticated data analysis techniques and often necessitates the use of computational modeling to support experimental findings.
Lastly, the development of standardized protocols for phenolphthalein analysis across different solvent systems remains a challenge. The lack of universally accepted methodologies makes it difficult to compare results between different studies and laboratories, hindering the broader scientific community's ability to build upon existing knowledge and advance the field collectively.
Existing Analytical Methods for Phenolphthalein
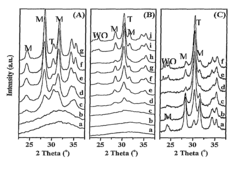
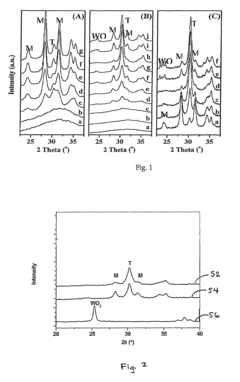
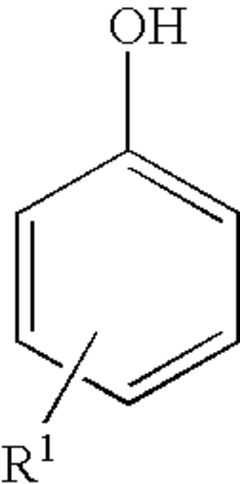
01 Basic structure of phenolphthalein
Phenolphthalein is a triphenylmethane compound consisting of two phenol groups attached to a phthalide group. Its structure is characterized by a central carbon atom bonded to two phenol rings and a lactone ring. This unique structure is responsible for its pH-sensitive color-changing properties, making it useful as an acid-base indicator.- Basic structure of phenolphthalein: Phenolphthalein is a triphenylmethane compound consisting of two phenol groups attached to a phthalide group. This structure is responsible for its pH-sensitive color-changing properties, making it useful as an acid-base indicator in various applications.
- Derivatives and modifications of phenolphthalein: Various derivatives of phenolphthalein can be synthesized by modifying its basic structure. These modifications can alter its properties, such as solubility, color change range, or reactivity, allowing for tailored applications in different fields like analytical chemistry or pharmaceuticals.
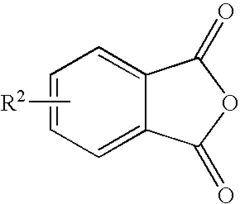
- Synthesis methods for phenolphthalein: Different methods for synthesizing phenolphthalein and its derivatives have been developed. These may involve condensation reactions between phthalic anhydride and phenol, or other approaches to form the triphenylmethane structure with specific functional groups.
- Applications of phenolphthalein in analytical chemistry: Phenolphthalein is widely used in analytical chemistry, particularly as a pH indicator in acid-base titrations. Its structure allows for a sharp color change from colorless to pink in basic solutions, making it valuable for precise endpoint determination in various analytical procedures.
- Phenolphthalein in polymer and material science: The unique structure of phenolphthalein allows for its incorporation into various polymers and materials. This can impart pH-sensitive properties or other functionalities to the resulting materials, opening up applications in areas such as smart materials, sensors, or controlled-release systems.
02 Derivatives and modifications of phenolphthalein
Various derivatives of phenolphthalein can be synthesized by modifying its basic structure. These modifications can include substitutions on the phenol rings, alterations to the lactone ring, or addition of functional groups. Such structural changes can affect the compound's properties, including its color transition range, solubility, and reactivity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Synthesis methods for phenolphthalein
Phenolphthalein can be synthesized through various methods, typically involving the condensation of phthalic anhydride with phenol in the presence of a catalyst. Different synthetic routes and reaction conditions can be employed to optimize yield and purity. Some methods focus on green chemistry approaches or the use of alternative catalysts to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions04 Structural analysis and characterization techniques
Various analytical techniques can be used to study and confirm the structure of phenolphthalein and its derivatives. These may include spectroscopic methods such as NMR, IR, and mass spectrometry, as well as X-ray crystallography for determining the precise three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in the molecule. Such analyses are crucial for verifying the structure and purity of synthesized compounds.Expand Specific Solutions05 Structure-property relationships
The structure of phenolphthalein directly influences its chemical and physical properties. Understanding these structure-property relationships is crucial for developing new applications or improving existing ones. For instance, the arrangement of hydroxyl groups affects its pH-sensitive color change, while modifications to the core structure can alter its solubility, stability, or reactivity in various environments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Research Institutions and Companies
The structural analysis of phenolphthalein in varying solvents represents a mature field within analytical chemistry, with established techniques and methodologies. The market for this research is relatively stable, primarily driven by academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies. Key players in this area include Sichuan University, Kyoto University, and The Scripps Research Institute, which contribute to fundamental research. Industrial applications are pursued by companies like Asahi Kasei Corp., Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd., and BioMarin Pharmaceutical, Inc., focusing on practical applications in areas such as pH indicators, drug development, and chemical synthesis. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of academic and industrial research, with ongoing efforts to refine analytical methods and explore new applications for phenolphthalein and related compounds.
Sichuan University
The Scripps Research Institute
Innovative Techniques in Structural Analysis
- The use of an ionic liquid catalyst composition, comprising a combination of an ionic liquid and a metal halide, facilitates the efficient separation and potential reuse of the catalyst, reducing waste and improving purity by reacting phenolic and phthalic anhydride compounds at controlled temperatures.
- A method using a heterogeneous catalyst comprising a calcination product of a heteropolyacid composition on a porous support, such as silicotungstic acid or tungstophosphoric acid, to facilitate the separation and regeneration of the catalyst, reducing waste and energy consumption while maintaining high purity of phenolphthalein production.
Environmental Impact of Phenolphthalein Use
The use of phenolphthalein in various applications has raised concerns about its potential environmental impact. As a widely used pH indicator and laxative, phenolphthalein can enter the environment through multiple pathways, including wastewater discharge from laboratories and pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities, as well as human excretion.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with phenolphthalein is its persistence in aquatic ecosystems. Studies have shown that phenolphthalein can remain stable in water for extended periods, potentially affecting aquatic organisms and disrupting ecosystem balance. The compound's ability to change color based on pH levels may interfere with natural signaling processes in aquatic environments, potentially impacting the behavior and reproduction of various species.
Soil contamination is another area of concern. Phenolphthalein can adsorb to soil particles, leading to potential accumulation in terrestrial ecosystems. This accumulation may affect soil microorganisms and plant growth, although more research is needed to fully understand the long-term consequences of phenolphthalein exposure in soil environments.
The biodegradation of phenolphthalein in the environment is a complex process influenced by various factors, including temperature, pH, and the presence of specific microorganisms. While some studies have demonstrated the potential for microbial degradation of phenolphthalein, the rate and efficiency of this process can vary significantly depending on environmental conditions.
Bioaccumulation of phenolphthalein in the food chain is another potential environmental risk. Although limited data is available on this aspect, there is concern that the compound could accumulate in aquatic organisms and potentially transfer to higher trophic levels, including humans through the consumption of contaminated fish or shellfish.
The environmental fate of phenolphthalein metabolites and breakdown products is an area requiring further investigation. These compounds may have different environmental behaviors and toxicological profiles compared to the parent compound, potentially introducing additional ecological risks.
Efforts to mitigate the environmental impact of phenolphthalein use include improved wastewater treatment technologies, stricter regulations on industrial discharges, and the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives for pH indication and laxative applications. Additionally, ongoing research aims to better understand the ecological effects of phenolphthalein and develop strategies for its safe use and disposal.
Regulatory Framework for Chemical Analysis
The regulatory framework for chemical analysis plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, quality, and reliability of analytical procedures and results. In the context of structural analysis of phenolphthalein in varying solvents, several regulatory bodies and guidelines are relevant.
The International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) provides guidelines that are widely adopted in the pharmaceutical industry. Specifically, ICH Q2(R1) on Validation of Analytical Procedures offers guidance on the characteristics to be considered during the validation of analytical procedures, including specificity, linearity, range, accuracy, and precision.
The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Pharmacopoeia (EP) are influential compendia that set standards for chemical analysis in pharmaceutical applications. These pharmacopoeias provide detailed monographs and general chapters on analytical methods, including those relevant to structural analysis of compounds like phenolphthalein.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of analytical methods used in drug development and quality control. The FDA's Guidance for Industry on Analytical Procedures and Methods Validation for Drugs and Biologics provides recommendations on method development, validation, and transfer of analytical procedures.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also plays a role in regulating chemical analysis, particularly when it comes to environmental monitoring and assessment. EPA Method 8000D, for instance, provides guidance on determinative chromatographic separations, which may be applicable to the analysis of phenolphthalein in various matrices.
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) standards, such as ISO/IEC 17025:2017, provide general requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories. This standard is crucial for ensuring the reliability and consistency of analytical results across different laboratories.
For research involving phenolphthalein, adherence to Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) regulations is essential, especially if the results are intended to support regulatory submissions. GLP ensures the quality and integrity of non-clinical laboratory studies and data.
Researchers must also consider specific regulations related to the use and handling of solvents. Many countries have implemented the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), which provides a standardized approach to communicating chemical hazards.
In conclusion, the regulatory framework for chemical analysis of phenolphthalein in varying solvents encompasses a wide range of guidelines, standards, and regulations. Compliance with these frameworks ensures the validity, reproducibility, and safety of analytical procedures, ultimately contributing to the reliability of structural analysis results.