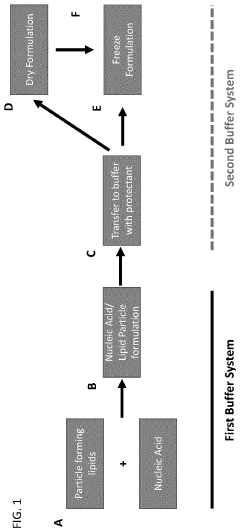
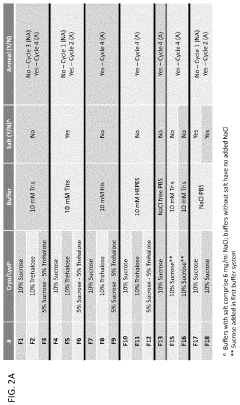
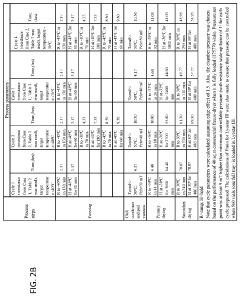
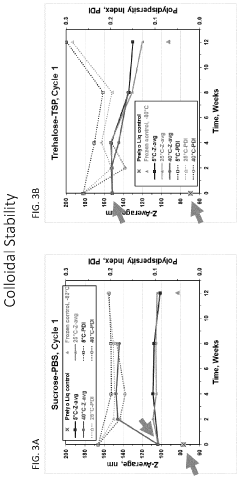
Analyzing Lipid Nanoparticle Stability in Variable Environments
OCT 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LNP Technology Background and Objectives
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have emerged as revolutionary delivery systems for nucleic acid therapeutics, most notably demonstrated by their crucial role in mRNA COVID-19 vaccines. The development of LNPs represents the culmination of decades of research in liposomal technology, beginning in the 1960s with the discovery of liposomes and evolving through various generations of lipid-based delivery systems. The technological evolution has been marked by significant improvements in stability, targeting efficiency, and controlled release capabilities.
The current LNP technology combines ionizable lipids, helper phospholipids, cholesterol, and PEGylated lipids to form complex structures capable of protecting sensitive cargo while facilitating cellular uptake. This sophisticated architecture has overcome many historical limitations of nucleic acid delivery, including susceptibility to enzymatic degradation and poor cellular penetration. However, stability across variable environmental conditions remains a critical challenge that limits broader application.
Environmental factors including temperature fluctuations, pH variations, ionic strength changes, and exposure to biological fluids significantly impact LNP integrity and functional performance. The technological goal of this research is to comprehensively characterize LNP stability determinants across diverse environmental conditions and develop predictive models that can inform formulation optimization. This addresses a fundamental gap in current knowledge that hampers the expansion of LNP applications beyond vaccines to therapeutics requiring different administration routes or storage conditions.
Recent technological trends indicate growing interest in rational design approaches that leverage computational modeling and high-throughput screening to develop environment-specific LNP formulations. The field is moving beyond empirical development toward mechanistic understanding of structure-function relationships that govern stability. This shift represents a critical inflection point in LNP technology evolution, potentially enabling precise engineering of nanoparticles with predetermined stability profiles.
The specific objectives of this technical investigation include: mapping stability profiles of various LNP compositions across temperature ranges (-80°C to 40°C), pH conditions (4.0-8.0), and biological media; identifying critical physicochemical parameters that predict stability; developing analytical methods for rapid stability assessment; and establishing design principles for environment-resistant LNP formulations. These objectives align with the broader industry goal of expanding LNP applications beyond vaccines to diverse therapeutic modalities including gene editing, protein replacement, and targeted cancer therapies.
Achieving these technological objectives would significantly advance the field by enabling the development of LNP formulations with tailored stability characteristics, ultimately expanding the therapeutic potential of nucleic acid medicines and addressing unmet medical needs across multiple disease categories.
The current LNP technology combines ionizable lipids, helper phospholipids, cholesterol, and PEGylated lipids to form complex structures capable of protecting sensitive cargo while facilitating cellular uptake. This sophisticated architecture has overcome many historical limitations of nucleic acid delivery, including susceptibility to enzymatic degradation and poor cellular penetration. However, stability across variable environmental conditions remains a critical challenge that limits broader application.
Environmental factors including temperature fluctuations, pH variations, ionic strength changes, and exposure to biological fluids significantly impact LNP integrity and functional performance. The technological goal of this research is to comprehensively characterize LNP stability determinants across diverse environmental conditions and develop predictive models that can inform formulation optimization. This addresses a fundamental gap in current knowledge that hampers the expansion of LNP applications beyond vaccines to therapeutics requiring different administration routes or storage conditions.
Recent technological trends indicate growing interest in rational design approaches that leverage computational modeling and high-throughput screening to develop environment-specific LNP formulations. The field is moving beyond empirical development toward mechanistic understanding of structure-function relationships that govern stability. This shift represents a critical inflection point in LNP technology evolution, potentially enabling precise engineering of nanoparticles with predetermined stability profiles.
The specific objectives of this technical investigation include: mapping stability profiles of various LNP compositions across temperature ranges (-80°C to 40°C), pH conditions (4.0-8.0), and biological media; identifying critical physicochemical parameters that predict stability; developing analytical methods for rapid stability assessment; and establishing design principles for environment-resistant LNP formulations. These objectives align with the broader industry goal of expanding LNP applications beyond vaccines to diverse therapeutic modalities including gene editing, protein replacement, and targeted cancer therapies.
Achieving these technological objectives would significantly advance the field by enabling the development of LNP formulations with tailored stability characteristics, ultimately expanding the therapeutic potential of nucleic acid medicines and addressing unmet medical needs across multiple disease categories.
Market Applications and Demand Analysis
The lipid nanoparticle (LNP) market has experienced unprecedented growth following the successful deployment of mRNA vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic. This breakthrough application has significantly elevated market awareness and demand for LNP technology across multiple sectors. The global LNP market, valued at approximately $5.1 billion in 2022, is projected to reach $15.6 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.2% during this forecast period.
Pharmaceutical applications currently dominate the LNP market landscape, accounting for over 70% of total market share. Within this segment, vaccine development represents the largest application area, followed by gene therapy and targeted drug delivery systems. The success of mRNA-LNP vaccines has created a ripple effect, stimulating investment in LNP technology for treating various diseases including cancer, genetic disorders, and infectious diseases beyond COVID-19.
The diagnostic sector presents another significant growth opportunity for LNP technology. Advanced imaging applications utilizing LNPs as contrast agents are gaining traction in medical diagnostics, particularly for conditions requiring high-resolution visualization. This segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 18.7% through 2030, outpacing the overall market growth rate.
Geographically, North America leads the global LNP market with approximately 45% market share, followed by Europe (30%) and Asia-Pacific (20%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the fastest growth due to increasing healthcare expenditure, expanding biotechnology sectors in China and India, and growing awareness of personalized medicine approaches.
A critical market driver for LNP stability research stems from the stringent cold-chain requirements of current LNP formulations. The pharmaceutical industry faces significant challenges with the ultra-cold storage requirements (-70°C) for some LNP-based products, which limits accessibility in regions with underdeveloped infrastructure. Industry analysis indicates that developing temperature-stable LNP formulations could potentially expand the addressable market by 35-40%, particularly in emerging economies.
Consumer demand for personalized medicine and targeted therapies is further propelling research into LNP stability across variable environments. Market surveys indicate that 78% of healthcare providers consider storage and handling requirements as major factors influencing their adoption decisions for new therapeutic technologies. Consequently, pharmaceutical companies are increasingly prioritizing stability enhancement in their LNP development programs, with approximately 65% of ongoing LNP research projects including stability optimization as a primary objective.
Pharmaceutical applications currently dominate the LNP market landscape, accounting for over 70% of total market share. Within this segment, vaccine development represents the largest application area, followed by gene therapy and targeted drug delivery systems. The success of mRNA-LNP vaccines has created a ripple effect, stimulating investment in LNP technology for treating various diseases including cancer, genetic disorders, and infectious diseases beyond COVID-19.
The diagnostic sector presents another significant growth opportunity for LNP technology. Advanced imaging applications utilizing LNPs as contrast agents are gaining traction in medical diagnostics, particularly for conditions requiring high-resolution visualization. This segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 18.7% through 2030, outpacing the overall market growth rate.
Geographically, North America leads the global LNP market with approximately 45% market share, followed by Europe (30%) and Asia-Pacific (20%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to witness the fastest growth due to increasing healthcare expenditure, expanding biotechnology sectors in China and India, and growing awareness of personalized medicine approaches.
A critical market driver for LNP stability research stems from the stringent cold-chain requirements of current LNP formulations. The pharmaceutical industry faces significant challenges with the ultra-cold storage requirements (-70°C) for some LNP-based products, which limits accessibility in regions with underdeveloped infrastructure. Industry analysis indicates that developing temperature-stable LNP formulations could potentially expand the addressable market by 35-40%, particularly in emerging economies.
Consumer demand for personalized medicine and targeted therapies is further propelling research into LNP stability across variable environments. Market surveys indicate that 78% of healthcare providers consider storage and handling requirements as major factors influencing their adoption decisions for new therapeutic technologies. Consequently, pharmaceutical companies are increasingly prioritizing stability enhancement in their LNP development programs, with approximately 65% of ongoing LNP research projects including stability optimization as a primary objective.
Current Stability Challenges and Limitations
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) face significant stability challenges that limit their widespread application despite their promising potential in drug delivery systems. One of the primary concerns is their physical instability during storage, where LNPs tend to aggregate or fuse over time, leading to increased particle size and polydispersity. This phenomenon is particularly problematic for pharmaceutical applications where precise dosing and consistent pharmacokinetic profiles are essential.
Temperature fluctuations represent another critical challenge for LNP stability. Exposure to temperatures outside the optimal range can trigger phase transitions within the lipid bilayers, causing structural reorganization and potential payload leakage. Most LNP formulations require cold chain storage (2-8°C), with some mRNA-LNP vaccines demanding ultra-cold conditions (-70°C), creating significant logistical hurdles for global distribution, especially in resource-limited settings.
The interaction between LNPs and biological fluids presents additional stability concerns. Upon administration, LNPs encounter various proteins and enzymes that can adsorb onto their surface, forming a protein corona that alters their physicochemical properties and biological identity. This protein adsorption may trigger premature release of encapsulated cargo, reduce cellular uptake efficiency, or activate immune responses, ultimately compromising therapeutic efficacy.
pH sensitivity further complicates LNP stability profiles. While pH-responsive behavior is advantageous for endosomal escape mechanisms, it also renders LNPs vulnerable to environmental pH fluctuations during manufacturing, storage, and administration. Deviations from optimal pH conditions can disrupt the electrostatic interactions maintaining LNP structural integrity, potentially leading to premature cargo release or particle disassembly.
Oxidative stress represents another significant limitation for LNP stability. Unsaturated lipids commonly used in LNP formulations are susceptible to peroxidation, which can compromise membrane integrity and accelerate degradation. This oxidative vulnerability necessitates the inclusion of antioxidants or specialized packaging solutions, adding complexity to formulation development and manufacturing processes.
Manufacturing consistency poses additional challenges for LNP stability. Minor variations in production parameters can significantly impact critical quality attributes such as particle size, lamellarity, and encapsulation efficiency. The complex interplay between formulation components during nanoprecipitation or microfluidic mixing processes makes reproducible manufacturing particularly challenging, often resulting in batch-to-batch variability that affects stability profiles.
Regulatory hurdles further complicate LNP development, as comprehensive stability data across various environmental conditions is required for approval. The lack of standardized analytical methods for characterizing LNP stability creates additional barriers, as different techniques may yield conflicting results, making comparative assessments difficult and regulatory submissions more challenging.
Temperature fluctuations represent another critical challenge for LNP stability. Exposure to temperatures outside the optimal range can trigger phase transitions within the lipid bilayers, causing structural reorganization and potential payload leakage. Most LNP formulations require cold chain storage (2-8°C), with some mRNA-LNP vaccines demanding ultra-cold conditions (-70°C), creating significant logistical hurdles for global distribution, especially in resource-limited settings.
The interaction between LNPs and biological fluids presents additional stability concerns. Upon administration, LNPs encounter various proteins and enzymes that can adsorb onto their surface, forming a protein corona that alters their physicochemical properties and biological identity. This protein adsorption may trigger premature release of encapsulated cargo, reduce cellular uptake efficiency, or activate immune responses, ultimately compromising therapeutic efficacy.
pH sensitivity further complicates LNP stability profiles. While pH-responsive behavior is advantageous for endosomal escape mechanisms, it also renders LNPs vulnerable to environmental pH fluctuations during manufacturing, storage, and administration. Deviations from optimal pH conditions can disrupt the electrostatic interactions maintaining LNP structural integrity, potentially leading to premature cargo release or particle disassembly.
Oxidative stress represents another significant limitation for LNP stability. Unsaturated lipids commonly used in LNP formulations are susceptible to peroxidation, which can compromise membrane integrity and accelerate degradation. This oxidative vulnerability necessitates the inclusion of antioxidants or specialized packaging solutions, adding complexity to formulation development and manufacturing processes.
Manufacturing consistency poses additional challenges for LNP stability. Minor variations in production parameters can significantly impact critical quality attributes such as particle size, lamellarity, and encapsulation efficiency. The complex interplay between formulation components during nanoprecipitation or microfluidic mixing processes makes reproducible manufacturing particularly challenging, often resulting in batch-to-batch variability that affects stability profiles.
Regulatory hurdles further complicate LNP development, as comprehensive stability data across various environmental conditions is required for approval. The lack of standardized analytical methods for characterizing LNP stability creates additional barriers, as different techniques may yield conflicting results, making comparative assessments difficult and regulatory submissions more challenging.
Existing Stability Enhancement Solutions
01 Lipid composition optimization for stability
The stability of lipid nanoparticles can be enhanced by optimizing the lipid composition. This includes selecting appropriate ratios of structural lipids, helper lipids, and cholesterol. The type and proportion of lipids significantly affect the physical stability, preventing aggregation and maintaining particle size distribution over time. Specific combinations of cationic, neutral, and PEGylated lipids can create more stable formulations with improved shelf-life.- Lipid composition optimization for stability: The stability of lipid nanoparticles can be significantly enhanced by optimizing the lipid composition. This includes selecting appropriate ratios of structural lipids, helper lipids, and cholesterol derivatives. The careful balance of saturated and unsaturated lipids contributes to membrane fluidity while maintaining structural integrity. Incorporating specific phospholipids and PEGylated lipids can create a protective shell that prevents aggregation and extends shelf-life of the nanoparticles.
- Surface modification techniques: Surface modification of lipid nanoparticles plays a crucial role in enhancing their stability. Techniques such as PEGylation, coating with hydrophilic polymers, or functionalization with specific ligands can prevent particle aggregation and opsonization. These modifications create steric hindrance and reduce surface energy, resulting in improved colloidal stability. Additionally, surface charge optimization through the incorporation of cationic or anionic lipids can prevent particle fusion and maintain size distribution during storage.
- Lyophilization and cryoprotection strategies: Freeze-drying (lyophilization) combined with appropriate cryoprotectants significantly improves the long-term stability of lipid nanoparticles. Cryoprotectants such as trehalose, sucrose, and mannitol prevent fusion and aggregation during the freezing process by replacing water molecules and maintaining the structural integrity of the lipid bilayers. The optimization of freezing rates, primary drying conditions, and secondary drying parameters is essential for preserving the physicochemical properties of the nanoparticles upon reconstitution.
- pH and buffer system optimization: The stability of lipid nanoparticles is highly dependent on the pH and buffer system used in the formulation. Maintaining optimal pH conditions prevents hydrolysis of lipid components and payload degradation. Buffer systems containing specific salts and chelating agents can minimize oxidation and hydrolysis reactions. The ionic strength of the medium affects the electrostatic interactions between particles, influencing their aggregation behavior. Careful selection of buffer components and pH adjusting agents is critical for maintaining the physical and chemical stability of lipid nanoparticles.
- Antioxidant incorporation and storage conditions: Lipid nanoparticles are susceptible to oxidative degradation, which can be mitigated by incorporating antioxidants such as alpha-tocopherol, butylated hydroxytoluene, or ascorbic acid derivatives. These compounds scavenge free radicals and prevent lipid peroxidation, thereby enhancing chemical stability. Additionally, optimizing storage conditions such as temperature, light exposure, and container materials significantly impacts long-term stability. Storage at refrigerated or frozen temperatures, protection from light, and use of inert gas overlays can minimize degradation reactions and extend the shelf-life of lipid nanoparticle formulations.
02 Stabilization through surface modification
Surface modification techniques can significantly improve lipid nanoparticle stability. The addition of PEGylated lipids creates a hydrophilic shield that prevents particle aggregation and opsonization. Other surface modifications include the incorporation of charged molecules to enhance electrostatic repulsion between particles, or specific ligands that not only improve stability but can also enhance targeting capabilities. These modifications help maintain colloidal stability in biological environments.Expand Specific Solutions03 Freeze-drying and lyophilization techniques
Freeze-drying and lyophilization are critical processes for enhancing the long-term stability of lipid nanoparticles. These techniques remove water content while preserving the structural integrity of the nanoparticles. The addition of cryoprotectants such as trehalose, sucrose, or mannitol during the process prevents fusion and aggregation of particles during freezing and subsequent storage. Optimized freeze-drying cycles with controlled freezing rates and primary/secondary drying parameters are essential for maintaining particle size distribution and encapsulation efficiency after reconstitution.Expand Specific Solutions04 pH and buffer system optimization
The stability of lipid nanoparticles is highly dependent on the pH and buffer system used in the formulation. Maintaining optimal pH prevents hydrolysis of lipid components and degradation of encapsulated cargo. Buffer systems containing specific salts and stabilizing agents can enhance electrostatic interactions and prevent particle aggregation. The choice of buffer components also affects zeta potential, which is crucial for colloidal stability. Careful selection of buffer capacity and ionic strength can significantly extend shelf-life and improve stability under various storage conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Antioxidants and preservatives for chemical stability
Incorporating antioxidants and preservatives into lipid nanoparticle formulations prevents oxidative degradation and microbial contamination. Lipid components are susceptible to oxidation, which can compromise particle integrity and lead to instability. Antioxidants such as alpha-tocopherol, butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), and ascorbic acid derivatives can scavenge free radicals and prevent lipid peroxidation. Preservatives protect against microbial growth during storage. The combination of these additives with proper storage conditions (temperature, light protection) significantly enhances both chemical and physical stability of lipid nanoparticles over extended periods.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitive Landscape
The lipid nanoparticle (LNP) stability market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by mRNA therapeutics and vaccine applications. The global market size is estimated to exceed $2 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of approximately 15%. Technologically, the field shows moderate maturity with established players like Moderna and Translate Bio leading commercial applications, while companies such as ETHRIS, SiSaf, and Arcturus Therapeutics are advancing novel stabilization technologies. Academic institutions including University of Copenhagen and Case Western Reserve University contribute fundamental research, while pharmaceutical giants like Eli Lilly and Kyowa Kirin are strategically entering the space through partnerships. The competitive landscape features specialized biotech firms developing proprietary LNP formulations alongside established pharmaceutical companies integrating LNP technology into their delivery platforms.
ModernaTX, Inc.
Technical Solution: Moderna has developed a proprietary lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery system that enhances mRNA stability across variable environments. Their technology employs ionizable lipids with pKa values optimized for endosomal escape (pKa ~6.2-6.5), allowing for neutral charge in circulation and positive charge in acidic endosomes. Moderna's LNPs incorporate specialized PEGylated lipids (typically 1.5-3 mol%) that create a hydration layer, preventing aggregation and extending circulation time. Their formulation includes precise ratios of helper phospholipids (DSPC) and cholesterol that maintain membrane fluidity across temperature ranges (4-40°C) and protect against enzymatic degradation. Moderna has implemented a microfluidic mixing platform that produces LNPs with consistent size distribution (80-100nm diameter) and high encapsulation efficiency (>90%), critical for maintaining stability during storage and administration.
Strengths: Industry-leading encapsulation efficiency and extended shelf-life stability (up to 6 months at -20°C, 30 days at 2-8°C). Robust manufacturing process with high batch-to-batch consistency. Weaknesses: Limited stability at room temperature, requiring cold chain logistics. Higher production costs compared to conventional delivery systems.
Translate Bio, Inc.
Technical Solution: Translate Bio has developed the MRT platform (Messenger RNA Therapeutics) utilizing advanced LNP technology optimized for stability across variable physiological environments. Their proprietary ionizable lipid structures feature branched alkyl chains that create flexible lipid bilayers, maintaining structural integrity across temperature fluctuations (4-40°C). The company employs a proprietary microfluidic rapid mixing process that produces LNPs with tight size distribution (70-90nm) and high encapsulation efficiency (>85%). Their formulations incorporate specialized helper lipids with optimized transition temperatures that maintain membrane fluidity across physiological conditions while preventing premature cargo release. Translate Bio's LNPs feature a proprietary PEG-lipid component with optimized molecular weight (2-5 kDa) and lipid anchor length that creates an effective steric barrier against aggregation and protein adsorption in biological fluids. The company has developed specialized buffer systems containing antioxidants and stabilizing agents that protect LNPs against oxidative degradation and hydrolysis during storage and administration.
Strengths: Enhanced stability in biological fluids with reduced protein corona formation. Efficient endosomal escape mechanisms leading to improved functional delivery. Weaknesses: Requires cold chain storage conditions for long-term stability. Manufacturing complexity requiring specialized equipment and expertise.
Critical Patents and Research on LNP Stability
Stable non-aggregating nucleic acid lipid particle formulations
PatentActiveUS20150165039A1
Innovation
- A pharmaceutical formulation comprising lipid nanoparticles in a non-ionic or de-ionized medium, with a pH below the pKa of the cationic lipid, substantially free of anions, and with specific particle size stability characteristics, inhibits aggregation and maintains stability during mechanical disturbances.
Compositions and methods for stabilization of lipid nanoparticle mRNA vaccines
PatentPendingUS20240041785A1
Innovation
- Development of LNP formulations comprising specific lipid components like ((4-hydroxybutyl)azanediyl)bis(hexane-6,1-diyl)bis(2-hexyldecanoate), 2-[(polyethylene glycol)-2000]-N,N-ditetradecylacetamide, distearoylphosphatidylcholine, and cholesterol, with sucrose or trehalose, and Tris buffer, enabling stability and handling at temperatures up to 25°C or room temperature, and allowing for dry or frozen formulations.
Regulatory Framework for LNP-based Products
The regulatory landscape for Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP) products presents a complex framework that varies significantly across global jurisdictions. In the United States, the FDA has established specific guidelines for LNP-based therapeutics, particularly following the emergency use authorization of mRNA vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic. These regulations emphasize stability testing across various environmental conditions as a critical component of product approval, requiring manufacturers to demonstrate consistent particle size distribution, encapsulation efficiency, and chemical integrity under different temperature, humidity, and storage conditions.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has developed parallel but distinct regulatory pathways for LNP products, implementing the Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMP) framework that includes additional requirements for environmental risk assessment. Japanese regulatory authorities, through the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA), have established an expedited review process for innovative LNP technologies while maintaining stringent stability requirements.
International harmonization efforts, primarily through the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), have produced guidelines specifically addressing nanomedicine stability testing. The ICH Q1A(R2) guideline on stability testing has been supplemented with considerations for nanomedicines, including LNPs, recommending stress testing under various environmental conditions to predict product shelf life and storage requirements.
Regulatory bodies increasingly require manufacturers to implement Quality by Design (QbD) principles in LNP development, necessitating thorough understanding of how environmental factors affect critical quality attributes. This approach demands robust analytical methods for characterizing LNP stability across the product lifecycle, from development through commercial distribution.
Recent regulatory trends indicate movement toward more standardized protocols for evaluating LNP stability in variable environments, with particular emphasis on freeze-thaw cycles, light exposure, and mechanical stress during transportation. The FDA's 2022 draft guidance specifically addresses the need for accelerated stability studies that simulate real-world distribution conditions for LNP products.
Compliance with these evolving regulations presents significant challenges for developers, particularly regarding the establishment of appropriate specifications for stability indicators and the validation of analytical methods across different environmental conditions. Regulatory agencies are increasingly requesting real-time stability data in addition to accelerated testing, creating longer development timelines but potentially more robust products.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has developed parallel but distinct regulatory pathways for LNP products, implementing the Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMP) framework that includes additional requirements for environmental risk assessment. Japanese regulatory authorities, through the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA), have established an expedited review process for innovative LNP technologies while maintaining stringent stability requirements.
International harmonization efforts, primarily through the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), have produced guidelines specifically addressing nanomedicine stability testing. The ICH Q1A(R2) guideline on stability testing has been supplemented with considerations for nanomedicines, including LNPs, recommending stress testing under various environmental conditions to predict product shelf life and storage requirements.
Regulatory bodies increasingly require manufacturers to implement Quality by Design (QbD) principles in LNP development, necessitating thorough understanding of how environmental factors affect critical quality attributes. This approach demands robust analytical methods for characterizing LNP stability across the product lifecycle, from development through commercial distribution.
Recent regulatory trends indicate movement toward more standardized protocols for evaluating LNP stability in variable environments, with particular emphasis on freeze-thaw cycles, light exposure, and mechanical stress during transportation. The FDA's 2022 draft guidance specifically addresses the need for accelerated stability studies that simulate real-world distribution conditions for LNP products.
Compliance with these evolving regulations presents significant challenges for developers, particularly regarding the establishment of appropriate specifications for stability indicators and the validation of analytical methods across different environmental conditions. Regulatory agencies are increasingly requesting real-time stability data in addition to accelerated testing, creating longer development timelines but potentially more robust products.
Scale-up Manufacturing Considerations
The transition from laboratory-scale production to industrial manufacturing of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) presents significant challenges that must be addressed to maintain stability across variable environments. Scaling up LNP production requires careful consideration of manufacturing parameters that directly impact particle size distribution, encapsulation efficiency, and overall stability. Conventional methods such as microfluidic mixing, which work effectively at small scales, face limitations when production volumes increase by orders of magnitude.
Critical to successful scale-up is the implementation of continuous manufacturing processes that can maintain precise control over mixing conditions. Tangential flow filtration (TFF) and crossflow filtration systems have emerged as preferred methods for large-scale purification of LNPs, replacing laboratory-scale techniques like dialysis. These systems must be designed to minimize shear stress, which can disrupt lipid bilayers and compromise nanoparticle integrity during processing.
Temperature control represents another vital consideration in scaled manufacturing. Industrial-scale equipment must maintain narrow temperature ranges throughout production, as lipid phase transitions are highly temperature-dependent. Deviations as small as 2-3°C can significantly alter LNP formation kinetics and stability profiles. Implementation of sophisticated heat exchange systems with rapid response capabilities is essential for consistent batch-to-batch quality.
Raw material sourcing becomes increasingly critical at commercial scale. Variations in lipid purity between suppliers or batches can dramatically affect LNP stability characteristics. Establishing robust supplier qualification programs and implementing comprehensive analytical testing protocols for incoming materials are necessary quality assurance measures. Additionally, the economic considerations of sourcing pharmaceutical-grade lipids at scale must be factored into manufacturing strategies.
Equipment selection must prioritize materials that minimize potential interactions with LNP components. Stainless steel, certain medical-grade polymers, and specialized coatings have demonstrated compatibility with lipid formulations. However, the surface area-to-volume ratio changes significantly during scale-up, potentially altering adsorption dynamics and necessitating reformulation of stabilizer concentrations.
Regulatory considerations further complicate scale-up efforts. Process analytical technology (PAT) implementation enables real-time monitoring of critical quality attributes during manufacturing. This approach supports quality-by-design principles and facilitates regulatory compliance while providing opportunities to detect stability issues before they impact final product quality. Establishing in-process controls specifically targeting stability indicators is essential for robust commercial manufacturing.
Critical to successful scale-up is the implementation of continuous manufacturing processes that can maintain precise control over mixing conditions. Tangential flow filtration (TFF) and crossflow filtration systems have emerged as preferred methods for large-scale purification of LNPs, replacing laboratory-scale techniques like dialysis. These systems must be designed to minimize shear stress, which can disrupt lipid bilayers and compromise nanoparticle integrity during processing.
Temperature control represents another vital consideration in scaled manufacturing. Industrial-scale equipment must maintain narrow temperature ranges throughout production, as lipid phase transitions are highly temperature-dependent. Deviations as small as 2-3°C can significantly alter LNP formation kinetics and stability profiles. Implementation of sophisticated heat exchange systems with rapid response capabilities is essential for consistent batch-to-batch quality.
Raw material sourcing becomes increasingly critical at commercial scale. Variations in lipid purity between suppliers or batches can dramatically affect LNP stability characteristics. Establishing robust supplier qualification programs and implementing comprehensive analytical testing protocols for incoming materials are necessary quality assurance measures. Additionally, the economic considerations of sourcing pharmaceutical-grade lipids at scale must be factored into manufacturing strategies.
Equipment selection must prioritize materials that minimize potential interactions with LNP components. Stainless steel, certain medical-grade polymers, and specialized coatings have demonstrated compatibility with lipid formulations. However, the surface area-to-volume ratio changes significantly during scale-up, potentially altering adsorption dynamics and necessitating reformulation of stabilizer concentrations.
Regulatory considerations further complicate scale-up efforts. Process analytical technology (PAT) implementation enables real-time monitoring of critical quality attributes during manufacturing. This approach supports quality-by-design principles and facilitates regulatory compliance while providing opportunities to detect stability issues before they impact final product quality. Establishing in-process controls specifically targeting stability indicators is essential for robust commercial manufacturing.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!