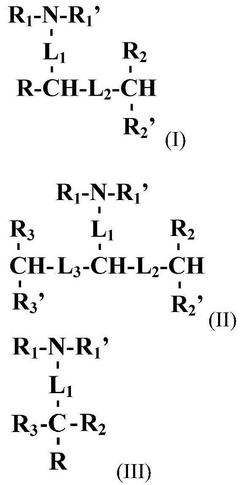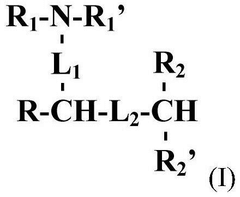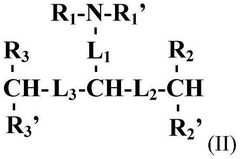Regulatory Impact on Lipid Nanoparticle Composition
OCT 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LNP Regulatory Evolution and Objectives
Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs) have emerged as a revolutionary delivery system for nucleic acid therapeutics, most notably showcased in mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines. The regulatory landscape governing LNP composition has evolved significantly over the past decade, reflecting growing understanding of their safety profiles, efficacy parameters, and manufacturing considerations.
Initially, regulatory frameworks for LNPs were largely adapted from existing guidelines for conventional drug delivery systems, failing to address the unique characteristics of these complex nanostructures. The period between 2010-2015 marked the beginning of specialized regulatory attention, with the FDA and EMA developing preliminary guidance documents that acknowledged the distinctive properties of nanomedicines, including LNPs.
A significant regulatory milestone occurred in 2018 when the FDA approved Patisiran (Onpattro), the first siRNA therapy utilizing LNP delivery. This approval established important precedents for safety assessment, characterization requirements, and manufacturing standards specific to LNP-based therapeutics. The regulatory focus during this period centered primarily on lipid excipient safety and consistent particle size distribution.
The COVID-19 pandemic catalyzed unprecedented regulatory adaptation, as emergency use authorizations for mRNA vaccines necessitated rapid yet rigorous evaluation of novel LNP formulations. This period saw regulatory bodies implementing accelerated review pathways while maintaining scientific rigor, resulting in refined guidelines for lipid component characterization, biodegradability assessments, and stability requirements.
Current regulatory objectives focus on establishing harmonized international standards for LNP composition, with particular emphasis on the ionizable lipids that significantly influence transfection efficiency and potential toxicity. Regulatory agencies now require comprehensive characterization of lipid purity profiles, degradation pathways, and potential metabolite toxicity.
Looking forward, regulatory evolution aims to address several critical objectives: developing standardized analytical methods for LNP characterization, establishing clearer guidelines for novel lipid component evaluation, creating streamlined pathways for LNP platform technologies, and implementing risk-based approaches that balance innovation with patient safety.
The regulatory landscape continues to evolve toward more predictive toxicology models specifically designed for LNP assessment, moving beyond traditional toxicology paradigms to account for the unique biodistribution and cellular interaction profiles of these delivery systems. This evolution reflects the growing recognition that LNP composition directly impacts safety, efficacy, and manufacturing consistency of advanced therapeutics.
Initially, regulatory frameworks for LNPs were largely adapted from existing guidelines for conventional drug delivery systems, failing to address the unique characteristics of these complex nanostructures. The period between 2010-2015 marked the beginning of specialized regulatory attention, with the FDA and EMA developing preliminary guidance documents that acknowledged the distinctive properties of nanomedicines, including LNPs.
A significant regulatory milestone occurred in 2018 when the FDA approved Patisiran (Onpattro), the first siRNA therapy utilizing LNP delivery. This approval established important precedents for safety assessment, characterization requirements, and manufacturing standards specific to LNP-based therapeutics. The regulatory focus during this period centered primarily on lipid excipient safety and consistent particle size distribution.
The COVID-19 pandemic catalyzed unprecedented regulatory adaptation, as emergency use authorizations for mRNA vaccines necessitated rapid yet rigorous evaluation of novel LNP formulations. This period saw regulatory bodies implementing accelerated review pathways while maintaining scientific rigor, resulting in refined guidelines for lipid component characterization, biodegradability assessments, and stability requirements.
Current regulatory objectives focus on establishing harmonized international standards for LNP composition, with particular emphasis on the ionizable lipids that significantly influence transfection efficiency and potential toxicity. Regulatory agencies now require comprehensive characterization of lipid purity profiles, degradation pathways, and potential metabolite toxicity.
Looking forward, regulatory evolution aims to address several critical objectives: developing standardized analytical methods for LNP characterization, establishing clearer guidelines for novel lipid component evaluation, creating streamlined pathways for LNP platform technologies, and implementing risk-based approaches that balance innovation with patient safety.
The regulatory landscape continues to evolve toward more predictive toxicology models specifically designed for LNP assessment, moving beyond traditional toxicology paradigms to account for the unique biodistribution and cellular interaction profiles of these delivery systems. This evolution reflects the growing recognition that LNP composition directly impacts safety, efficacy, and manufacturing consistency of advanced therapeutics.
Market Analysis of LNP-based Therapeutics
The global market for Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP) based therapeutics has experienced unprecedented growth following the successful deployment of mRNA vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic. As of 2023, the LNP drug delivery market is valued at approximately $5.6 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 13.8% through 2030, reaching an estimated $15.1 billion.
The success of Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna mRNA vaccines has significantly accelerated investment in this sector, with venture capital funding for LNP-related startups increasing by 215% between 2019 and 2022. This surge in funding reflects growing confidence in LNP technology as a versatile delivery platform beyond vaccines.
Market segmentation reveals that oncology applications currently dominate the LNP therapeutics landscape, accounting for 38% of development programs. Rare genetic disorders follow at 27%, while infectious diseases represent 22% of the market. Emerging applications in immunology and cardiovascular medicine collectively constitute the remaining 13%, indicating diversification of therapeutic targets.
Geographically, North America leads the market with 52% share, followed by Europe at 31% and Asia-Pacific at 14%. The remaining 3% is distributed across other regions. This distribution correlates strongly with regulatory environments that have established clear pathways for LNP-based product approval.
Key market drivers include the demonstrated efficacy of LNP delivery systems, expanding applications beyond mRNA delivery to include small molecules and gene editing components, and significant improvements in manufacturing scalability. The latter has reduced production costs by approximately 40% since 2020, enhancing commercial viability.
Market restraints primarily stem from regulatory uncertainties regarding lipid composition requirements. Companies report that regulatory reviews focusing on novel lipid components add an average of 7-9 months to development timelines. Additionally, patent landscapes around key LNP formulations have created market entry barriers, with licensing costs representing 15-20% of development budgets for new entrants.
Consumer acceptance presents another challenge, with surveys indicating that 22% of healthcare providers and 35% of patients express concerns about the long-term safety profiles of LNP-delivered therapeutics. This perception gap represents a significant market education opportunity.
The competitive landscape features pharmaceutical giants like Pfizer, Moderna, and AstraZeneca alongside specialized LNP technology companies such as Acuitas Therapeutics, Precision NanoSystems, and Genevant Sciences. Recent strategic acquisitions, including Sanofi's $3.2 billion purchase of Translate Bio, highlight the increasing value placed on proprietary LNP delivery platforms.
The success of Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna mRNA vaccines has significantly accelerated investment in this sector, with venture capital funding for LNP-related startups increasing by 215% between 2019 and 2022. This surge in funding reflects growing confidence in LNP technology as a versatile delivery platform beyond vaccines.
Market segmentation reveals that oncology applications currently dominate the LNP therapeutics landscape, accounting for 38% of development programs. Rare genetic disorders follow at 27%, while infectious diseases represent 22% of the market. Emerging applications in immunology and cardiovascular medicine collectively constitute the remaining 13%, indicating diversification of therapeutic targets.
Geographically, North America leads the market with 52% share, followed by Europe at 31% and Asia-Pacific at 14%. The remaining 3% is distributed across other regions. This distribution correlates strongly with regulatory environments that have established clear pathways for LNP-based product approval.
Key market drivers include the demonstrated efficacy of LNP delivery systems, expanding applications beyond mRNA delivery to include small molecules and gene editing components, and significant improvements in manufacturing scalability. The latter has reduced production costs by approximately 40% since 2020, enhancing commercial viability.
Market restraints primarily stem from regulatory uncertainties regarding lipid composition requirements. Companies report that regulatory reviews focusing on novel lipid components add an average of 7-9 months to development timelines. Additionally, patent landscapes around key LNP formulations have created market entry barriers, with licensing costs representing 15-20% of development budgets for new entrants.
Consumer acceptance presents another challenge, with surveys indicating that 22% of healthcare providers and 35% of patients express concerns about the long-term safety profiles of LNP-delivered therapeutics. This perception gap represents a significant market education opportunity.
The competitive landscape features pharmaceutical giants like Pfizer, Moderna, and AstraZeneca alongside specialized LNP technology companies such as Acuitas Therapeutics, Precision NanoSystems, and Genevant Sciences. Recent strategic acquisitions, including Sanofi's $3.2 billion purchase of Translate Bio, highlight the increasing value placed on proprietary LNP delivery platforms.
Global Regulatory Landscape and Technical Barriers
The regulatory landscape for lipid nanoparticle (LNP) composition varies significantly across different regions, creating a complex environment for pharmaceutical companies and researchers. In the United States, the FDA has established specific guidelines for LNP-based drug products through its Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) and Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER). These guidelines focus on characterization requirements, stability testing, and manufacturing consistency, with particular emphasis on lipid impurity profiles and their potential impact on safety.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has developed a somewhat different approach, implementing the Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMP) framework that includes specific provisions for nanomedicine products. European regulations tend to place greater emphasis on environmental risk assessments and long-term safety monitoring compared to their US counterparts, creating additional hurdles for LNP formulation approval.
In Asia, regulatory frameworks show considerable variation. Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has established nanomedicine-specific guidelines that include detailed requirements for LNP characterization. China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has recently strengthened its regulatory oversight of nanomedicines, though specific guidance on LNP composition remains less developed than in Western markets.
A significant technical barrier across all jurisdictions is the lack of standardized analytical methods for LNP characterization. This creates challenges in demonstrating batch-to-batch consistency and meeting varying regulatory expectations. The absence of internationally harmonized reference standards for lipid components further complicates regulatory compliance across multiple markets.
Manufacturing scale-up presents another critical challenge, as regulatory bodies increasingly require demonstration that the physicochemical properties of LNPs remain consistent between clinical trial and commercial production scales. Changes in lipid composition ratios, even minor ones, may trigger requirements for additional clinical studies, substantially increasing development costs and timelines.
Stability testing requirements vary significantly between jurisdictions, with some requiring extensive real-time stability data while others accept accelerated testing protocols. This inconsistency creates difficulties in global development programs and may necessitate region-specific formulation adjustments.
Emerging regulations concerning novel excipients present a particular challenge for innovative LNP compositions. Both FDA and EMA have established specialized pathways for novel excipient evaluation, but these often require substantial additional toxicology studies and safety data, creating significant barriers to the introduction of new lipid components that might enhance delivery efficiency or reduce toxicity.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has developed a somewhat different approach, implementing the Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMP) framework that includes specific provisions for nanomedicine products. European regulations tend to place greater emphasis on environmental risk assessments and long-term safety monitoring compared to their US counterparts, creating additional hurdles for LNP formulation approval.
In Asia, regulatory frameworks show considerable variation. Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has established nanomedicine-specific guidelines that include detailed requirements for LNP characterization. China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has recently strengthened its regulatory oversight of nanomedicines, though specific guidance on LNP composition remains less developed than in Western markets.
A significant technical barrier across all jurisdictions is the lack of standardized analytical methods for LNP characterization. This creates challenges in demonstrating batch-to-batch consistency and meeting varying regulatory expectations. The absence of internationally harmonized reference standards for lipid components further complicates regulatory compliance across multiple markets.
Manufacturing scale-up presents another critical challenge, as regulatory bodies increasingly require demonstration that the physicochemical properties of LNPs remain consistent between clinical trial and commercial production scales. Changes in lipid composition ratios, even minor ones, may trigger requirements for additional clinical studies, substantially increasing development costs and timelines.
Stability testing requirements vary significantly between jurisdictions, with some requiring extensive real-time stability data while others accept accelerated testing protocols. This inconsistency creates difficulties in global development programs and may necessitate region-specific formulation adjustments.
Emerging regulations concerning novel excipients present a particular challenge for innovative LNP compositions. Both FDA and EMA have established specialized pathways for novel excipient evaluation, but these often require substantial additional toxicology studies and safety data, creating significant barriers to the introduction of new lipid components that might enhance delivery efficiency or reduce toxicity.
Current Compliance Strategies for LNP Formulations
01 Lipid nanoparticle composition for drug delivery
Lipid nanoparticles are designed with specific compositions to enhance drug delivery efficiency. These formulations typically include a combination of ionizable lipids, helper lipids, and stabilizing agents that work together to encapsulate therapeutic agents and facilitate their delivery to target tissues. The composition can be optimized to improve stability, cellular uptake, and release kinetics of the encapsulated drugs.- Lipid nanoparticle compositions for drug delivery: Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) can be formulated as effective delivery systems for various therapeutic agents, including small molecules, proteins, and nucleic acids. These formulations typically contain a combination of ionizable lipids, helper lipids, and stabilizing components that enhance drug encapsulation efficiency and improve targeted delivery to specific tissues. The composition can be optimized to control release kinetics and increase bioavailability of the encapsulated therapeutic agents.
- mRNA delivery systems using lipid nanoparticles: Specialized lipid nanoparticle compositions have been developed specifically for mRNA delivery applications, including vaccines and gene therapies. These formulations typically contain cationic or ionizable lipids that complex with negatively charged mRNA, along with helper lipids such as cholesterol and PEG-lipids that enhance stability and circulation time. The precise ratio of lipid components can be adjusted to optimize transfection efficiency while minimizing toxicity, enabling effective delivery of mRNA to target cells.
- Novel lipid components for enhanced nanoparticle performance: Innovative lipid components have been developed to improve the performance of lipid nanoparticles. These include novel ionizable lipids with optimized pKa values, biodegradable lipids that reduce toxicity concerns, and lipids with targeting moieties that enhance cell-specific delivery. The incorporation of these specialized lipids into nanoparticle formulations can significantly improve therapeutic efficacy, reduce side effects, and enable more precise control over drug release profiles.
- Manufacturing processes for lipid nanoparticles: Various manufacturing techniques have been developed for producing lipid nanoparticles with consistent size distribution, high encapsulation efficiency, and scalable production. These methods include microfluidic mixing, ethanol injection, thin-film hydration, and high-pressure homogenization. The choice of manufacturing process significantly impacts the physicochemical properties of the resulting nanoparticles, including size, polydispersity, zeta potential, and morphology, which in turn affect their biological performance and stability.
- Stabilization strategies for lipid nanoparticle formulations: Various approaches have been developed to enhance the stability of lipid nanoparticle formulations during storage and administration. These include the incorporation of antioxidants to prevent lipid oxidation, cryoprotectants for freeze-drying, pH buffers to maintain optimal conditions, and surface modifications to prevent aggregation. Additionally, lyophilization techniques and specialized packaging materials can be employed to extend shelf life and maintain the integrity of the nanoparticle structure and its encapsulated cargo under various environmental conditions.
02 mRNA delivery systems using lipid nanoparticles
Specialized lipid nanoparticle compositions are developed for the delivery of mRNA therapeutics. These formulations contain specific lipid components that protect the mRNA from degradation and facilitate its cellular uptake and expression. The composition typically includes cationic or ionizable lipids that complex with the negatively charged mRNA, along with helper lipids that enhance membrane fusion and intracellular release of the payload.Expand Specific Solutions03 Novel lipid components for enhanced nanoparticle performance
Innovative lipid components are being developed to improve the performance of lipid nanoparticles. These include novel ionizable lipids, PEGylated lipids, and structural lipids with unique properties that enhance stability, reduce toxicity, or improve targeting capabilities. The specific chemical structures of these lipids can be tailored to optimize the pharmacokinetic profile and therapeutic index of the nanoparticle formulations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Manufacturing processes for lipid nanoparticles
Various manufacturing processes are employed to produce lipid nanoparticles with controlled size, composition, and morphology. These include microfluidic mixing, ethanol injection, and high-pressure homogenization techniques. The manufacturing parameters significantly influence the physicochemical properties of the resulting nanoparticles, including their size distribution, encapsulation efficiency, and stability, which in turn affect their biological performance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Targeted lipid nanoparticle formulations
Lipid nanoparticles can be formulated with targeting moieties to enhance their specificity for certain tissues or cell types. These formulations incorporate ligands or antibodies on the nanoparticle surface that recognize specific receptors on target cells. Additionally, the lipid composition can be adjusted to respond to environmental triggers such as pH or enzymatic activity, allowing for site-specific release of therapeutic cargo.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Regulatory Bodies and Pharmaceutical Stakeholders
The regulatory landscape for Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP) composition is evolving rapidly as this technology reaches commercial maturity, particularly in the mRNA therapeutics space. The market is currently in a growth phase, with major players like ModernaTX, Pfizer/BioNTech, and Acuitas Therapeutics leading commercialization efforts following COVID-19 vaccine success. Pharmaceutical giants (AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly) are expanding their presence, while specialized companies (Genevant Sciences, Intellia Therapeutics, Beam Therapeutics) focus on advancing LNP technology for gene editing applications. Academic institutions (Monash University, Zhejiang University) continue contributing fundamental research. Regulatory frameworks are becoming more defined but remain challenging as authorities balance innovation with safety concerns, particularly regarding novel lipid components and their biodistribution profiles.
ModernaTX, Inc.
Technical Solution: Moderna has developed a proprietary lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery system optimized for mRNA therapeutics that addresses regulatory challenges through precise composition control. Their LNP technology incorporates ionizable lipids (SM-102) specifically designed to respond to pH changes, facilitating endosomal escape while maintaining biocompatibility. Moderna's regulatory strategy includes extensive characterization of lipid components and their metabolic pathways to satisfy FDA requirements. They've implemented quality control systems that monitor critical quality attributes of LNP composition with high precision, including lipid ratios, particle size distribution, and encapsulation efficiency. Their regulatory approach includes comprehensive toxicology studies addressing the unique safety profiles of novel lipid components, which has enabled successful regulatory approvals for their COVID-19 vaccine and other pipeline products[1][3].
Strengths: Proprietary ionizable lipid technology with established regulatory approval pathway; extensive manufacturing experience with consistent quality control systems. Weaknesses: Higher production costs associated with proprietary lipid components; potential challenges with intellectual property restrictions limiting formulation flexibility to address specific regulatory concerns.
Pfizer Inc.
Technical Solution: Pfizer has developed a comprehensive regulatory strategy for LNP-based therapeutics that addresses composition challenges through systematic risk assessment and mitigation. Their approach includes detailed characterization of critical quality attributes for each lipid component and their interactions within the final formulation. Pfizer's LNP technology, developed in partnership with BioNTech and using Acuitas' lipid components, incorporates ALC-0315 (ionizable lipid), ALC-0159 (PEGylated lipid), DSPC, and cholesterol in precisely controlled ratios. Their regulatory approach emphasizes manufacturing consistency through implementation of in-process controls and release specifications that ensure tight control of lipid composition variability. Pfizer has established analytical methods validated to regulatory standards for characterizing LNP composition, including HPLC, mass spectrometry, and dynamic light scattering techniques. Their successful navigation of emergency use authorization and subsequent full approval for the COVID-19 vaccine established important regulatory precedents for LNP-based therapeutics[4][6].
Strengths: Robust manufacturing infrastructure with demonstrated ability to scale production while maintaining regulatory compliance; extensive experience navigating global regulatory frameworks for novel delivery technologies. Weaknesses: Reliance on external technology for core LNP components may create dependencies in regulatory strategy; complex supply chain for specialized lipid components presents regulatory challenges for global distribution.
Critical Regulatory Guidelines Affecting LNP Design
Lipid compound and the composition thereof
PatentActiveAU2021245162A1
Innovation
- Development of novel ionizable lipid compounds with aliphatic chains formed by ester groups of glycerol and ether groups, combined with PEG lipid, structural lipid, and phospholipid to create lipid nanoparticles that facilitate efficient intracellular delivery and reduce toxicity.
Lipid compound and lipid nanoparticle composition
PatentWO2024199282A1
Innovation
- Develop lipid compounds combined with other lipid components to form lipid nanoparticles to deliver therapeutic agents such as locked nucleic acids (LNA), peptide nucleic acids (PNA), and nucleic acid mimetics such as morpholino cyclic oligonucleotides to improve their Delivery efficiency in vivo and in vitro.
Safety and Toxicity Considerations in LNP Development
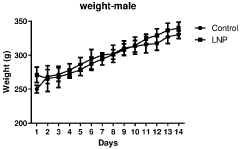
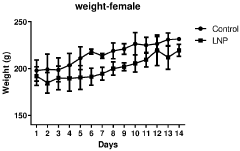
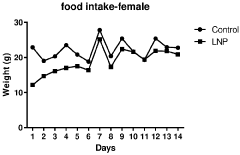
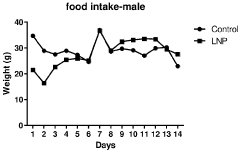
The safety and toxicity profile of Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs) represents a critical consideration in their development and regulatory approval process. As delivery systems for nucleic acid therapeutics, LNPs must demonstrate acceptable safety margins while maintaining therapeutic efficacy. Current regulatory frameworks require comprehensive toxicological assessments of individual lipid components and the complete LNP formulation.
Acute toxicity concerns with LNPs primarily involve inflammatory responses, which can manifest as cytokine release syndrome in severe cases. These reactions are often attributed to the cationic lipid components, which can interact with cell membranes and trigger immune activation. Regulatory bodies increasingly demand dose-escalation studies to establish safety thresholds and identify potential immunological triggers.
Chronic toxicity evaluations focus on biodistribution patterns and potential accumulation in tissues. Regulatory guidelines now emphasize the need for extended observation periods in preclinical models, particularly examining liver, spleen, and kidney tissues where LNPs tend to concentrate. The lipid composition directly influences these biodistribution profiles, with more hydrophobic formulations showing prolonged tissue retention that may raise regulatory concerns.
Genotoxicity and reproductive toxicity assessments have become mandatory components of the regulatory submission package for LNP-based therapeutics. Recent regulatory decisions indicate heightened scrutiny of novel lipid components without established safety records. Manufacturers must now provide extensive data demonstrating the absence of DNA damage potential and reproductive system effects, particularly for LNPs intended for repeated administration.
Excipient selection faces increasing regulatory oversight, with authorities requiring justification for each component in the LNP formulation. PEGylated lipids, while enhancing circulation time, have raised concerns regarding hypersensitivity reactions and anti-PEG antibody formation. Regulatory agencies now recommend alternative PEG densities or structures to mitigate these risks while maintaining functional benefits.
Impurity profiles and degradation products represent another critical regulatory focus area. Lipid oxidation products and manufacturing-related impurities must be characterized and controlled within strict limits. The stability of the lipid components under various storage conditions directly impacts the safety profile, with regulatory authorities requiring comprehensive stability data to support shelf-life claims.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate a move toward harmonized international standards for LNP safety assessment, though regional differences persist. The FDA and EMA have recently published guidance documents specifically addressing nanomedicine safety considerations, with particular emphasis on characterizing the relationship between lipid composition and toxicological outcomes.
Acute toxicity concerns with LNPs primarily involve inflammatory responses, which can manifest as cytokine release syndrome in severe cases. These reactions are often attributed to the cationic lipid components, which can interact with cell membranes and trigger immune activation. Regulatory bodies increasingly demand dose-escalation studies to establish safety thresholds and identify potential immunological triggers.
Chronic toxicity evaluations focus on biodistribution patterns and potential accumulation in tissues. Regulatory guidelines now emphasize the need for extended observation periods in preclinical models, particularly examining liver, spleen, and kidney tissues where LNPs tend to concentrate. The lipid composition directly influences these biodistribution profiles, with more hydrophobic formulations showing prolonged tissue retention that may raise regulatory concerns.
Genotoxicity and reproductive toxicity assessments have become mandatory components of the regulatory submission package for LNP-based therapeutics. Recent regulatory decisions indicate heightened scrutiny of novel lipid components without established safety records. Manufacturers must now provide extensive data demonstrating the absence of DNA damage potential and reproductive system effects, particularly for LNPs intended for repeated administration.
Excipient selection faces increasing regulatory oversight, with authorities requiring justification for each component in the LNP formulation. PEGylated lipids, while enhancing circulation time, have raised concerns regarding hypersensitivity reactions and anti-PEG antibody formation. Regulatory agencies now recommend alternative PEG densities or structures to mitigate these risks while maintaining functional benefits.
Impurity profiles and degradation products represent another critical regulatory focus area. Lipid oxidation products and manufacturing-related impurities must be characterized and controlled within strict limits. The stability of the lipid components under various storage conditions directly impacts the safety profile, with regulatory authorities requiring comprehensive stability data to support shelf-life claims.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate a move toward harmonized international standards for LNP safety assessment, though regional differences persist. The FDA and EMA have recently published guidance documents specifically addressing nanomedicine safety considerations, with particular emphasis on characterizing the relationship between lipid composition and toxicological outcomes.
Cross-Border Harmonization of LNP Regulatory Frameworks
The global nature of pharmaceutical development and the increasing importance of lipid nanoparticle (LNP) technology in drug delivery systems necessitate a coordinated approach to regulatory frameworks across different jurisdictions. Currently, significant disparities exist in how regulatory bodies in various countries evaluate and approve LNP-based formulations, creating challenges for pharmaceutical companies operating in multiple markets.
The United States FDA, European Medicines Agency (EMA), and Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) have established distinct requirements for LNP composition assessment, with varying emphasis on lipid characterization, impurity profiles, and stability parameters. These differences often require manufacturers to conduct redundant studies and prepare multiple submission packages, increasing development costs and delaying patient access to innovative therapies.
Recent initiatives by the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) have begun addressing these inconsistencies. The proposed ICH Q3E guideline specifically targets extractables and leachables in drug products, with potential implications for LNP component analysis. Similarly, the ICH M13 guideline under development aims to harmonize bioequivalence standards, which could impact how LNP formulation changes are evaluated across borders.
Industry consortia, including the LNP Alliance and Global Lipid Nanoparticle Consortium (GLNC), are actively engaging with regulatory authorities to establish standardized analytical methods for LNP characterization. These efforts focus on creating universally accepted protocols for assessing critical quality attributes such as particle size distribution, encapsulation efficiency, and lipid degradation products.
Bilateral agreements between major regulatory agencies represent another promising avenue for harmonization. The FDA-EMA mutual recognition agreement for GMP inspections provides a template that could be expanded to include consensus on LNP composition requirements. Similarly, the PMDA's participation in the Global Coalition of Regulatory Science Research (GCRSR) offers opportunities for scientific collaboration on emerging technologies like LNPs.
Achieving meaningful cross-border harmonization will require addressing several key challenges, including reconciling different risk assessment philosophies, accommodating region-specific health concerns, and ensuring that harmonized standards remain flexible enough to incorporate rapidly evolving LNP technologies. A phased approach, beginning with alignment on fundamental analytical methods and gradually expanding to cover more complex aspects of LNP regulation, offers the most practical path forward.
The United States FDA, European Medicines Agency (EMA), and Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) have established distinct requirements for LNP composition assessment, with varying emphasis on lipid characterization, impurity profiles, and stability parameters. These differences often require manufacturers to conduct redundant studies and prepare multiple submission packages, increasing development costs and delaying patient access to innovative therapies.
Recent initiatives by the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) have begun addressing these inconsistencies. The proposed ICH Q3E guideline specifically targets extractables and leachables in drug products, with potential implications for LNP component analysis. Similarly, the ICH M13 guideline under development aims to harmonize bioequivalence standards, which could impact how LNP formulation changes are evaluated across borders.
Industry consortia, including the LNP Alliance and Global Lipid Nanoparticle Consortium (GLNC), are actively engaging with regulatory authorities to establish standardized analytical methods for LNP characterization. These efforts focus on creating universally accepted protocols for assessing critical quality attributes such as particle size distribution, encapsulation efficiency, and lipid degradation products.
Bilateral agreements between major regulatory agencies represent another promising avenue for harmonization. The FDA-EMA mutual recognition agreement for GMP inspections provides a template that could be expanded to include consensus on LNP composition requirements. Similarly, the PMDA's participation in the Global Coalition of Regulatory Science Research (GCRSR) offers opportunities for scientific collaboration on emerging technologies like LNPs.
Achieving meaningful cross-border harmonization will require addressing several key challenges, including reconciling different risk assessment philosophies, accommodating region-specific health concerns, and ensuring that harmonized standards remain flexible enough to incorporate rapidly evolving LNP technologies. A phased approach, beginning with alignment on fundamental analytical methods and gradually expanding to cover more complex aspects of LNP regulation, offers the most practical path forward.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!