Sodium silicate applications in the food packaging industry
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Silicate in Food Packaging: Background and Objectives
Sodium silicate, also known as water glass or liquid glass, has a long history of industrial applications dating back to the 19th century. In recent years, its potential in the food packaging industry has gained significant attention due to its unique properties and environmental benefits. The evolution of sodium silicate in this sector reflects the growing demand for sustainable and effective packaging solutions.
The primary objective of exploring sodium silicate applications in food packaging is to develop innovative, eco-friendly alternatives to traditional packaging materials. This aligns with the global trend towards reducing plastic waste and improving recyclability. Sodium silicate offers promising characteristics such as biodegradability, non-toxicity, and excellent barrier properties against moisture and gases, making it an attractive option for food preservation.
The technological trajectory of sodium silicate in food packaging has seen steady progress over the past decade. Initial applications focused on its use as a coating material for paper and cardboard packaging, enhancing their moisture resistance and structural integrity. As research advanced, more sophisticated applications emerged, including the development of edible films and coatings derived from sodium silicate.
Current technological goals in this field include optimizing the formulation of sodium silicate-based packaging materials to enhance their mechanical properties, improve their compatibility with various food products, and extend shelf life. Researchers are also exploring ways to incorporate active compounds into sodium silicate matrices, creating intelligent packaging systems capable of monitoring food quality and freshness.
Another critical objective is to scale up production processes for sodium silicate-based packaging materials, making them economically viable for widespread commercial adoption. This involves addressing challenges related to manufacturing efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and consistency in product quality.
The food packaging industry's interest in sodium silicate is driven by several factors, including stringent regulations on plastic use, consumer demand for sustainable products, and the need for advanced preservation techniques. As such, the technology aims to provide solutions that not only meet regulatory requirements but also satisfy consumer preferences for environmentally friendly packaging.
Looking ahead, the future of sodium silicate in food packaging is likely to involve interdisciplinary collaborations, combining materials science, food technology, and environmental studies. The goal is to create next-generation packaging solutions that offer superior performance while minimizing environmental impact. This may include the development of multi-functional packaging materials that incorporate sodium silicate with other sustainable components, further expanding its applications and benefits in the food industry.
The primary objective of exploring sodium silicate applications in food packaging is to develop innovative, eco-friendly alternatives to traditional packaging materials. This aligns with the global trend towards reducing plastic waste and improving recyclability. Sodium silicate offers promising characteristics such as biodegradability, non-toxicity, and excellent barrier properties against moisture and gases, making it an attractive option for food preservation.
The technological trajectory of sodium silicate in food packaging has seen steady progress over the past decade. Initial applications focused on its use as a coating material for paper and cardboard packaging, enhancing their moisture resistance and structural integrity. As research advanced, more sophisticated applications emerged, including the development of edible films and coatings derived from sodium silicate.
Current technological goals in this field include optimizing the formulation of sodium silicate-based packaging materials to enhance their mechanical properties, improve their compatibility with various food products, and extend shelf life. Researchers are also exploring ways to incorporate active compounds into sodium silicate matrices, creating intelligent packaging systems capable of monitoring food quality and freshness.
Another critical objective is to scale up production processes for sodium silicate-based packaging materials, making them economically viable for widespread commercial adoption. This involves addressing challenges related to manufacturing efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and consistency in product quality.
The food packaging industry's interest in sodium silicate is driven by several factors, including stringent regulations on plastic use, consumer demand for sustainable products, and the need for advanced preservation techniques. As such, the technology aims to provide solutions that not only meet regulatory requirements but also satisfy consumer preferences for environmentally friendly packaging.
Looking ahead, the future of sodium silicate in food packaging is likely to involve interdisciplinary collaborations, combining materials science, food technology, and environmental studies. The goal is to create next-generation packaging solutions that offer superior performance while minimizing environmental impact. This may include the development of multi-functional packaging materials that incorporate sodium silicate with other sustainable components, further expanding its applications and benefits in the food industry.
Market Analysis for Sodium Silicate-Based Food Packaging
The global food packaging industry has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for convenient, safe, and sustainable packaging solutions. Within this context, sodium silicate-based food packaging has emerged as a promising segment, offering unique properties that align with market trends and consumer preferences.
The market for sodium silicate-based food packaging is experiencing steady growth, primarily due to its versatility and eco-friendly characteristics. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, there is a growing demand for packaging materials that are recyclable, biodegradable, and have a lower carbon footprint. Sodium silicate-based packaging addresses these concerns, positioning itself as a sustainable alternative to traditional plastic packaging.
In terms of market size, the sodium silicate-based food packaging segment is expected to expand significantly over the next five years. This growth is attributed to several factors, including the increasing adoption of sustainable packaging solutions by food manufacturers, stringent regulations on plastic usage, and rising consumer awareness about environmental issues.
The food and beverage industry represents the largest end-user segment for sodium silicate-based packaging. Within this sector, there is particularly strong demand from the dairy, bakery, and ready-to-eat meal segments. These industries require packaging solutions that offer excellent barrier properties against moisture and oxygen, which sodium silicate-based materials can provide effectively.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market for sodium silicate-based food packaging. This growth is driven by rapid urbanization, changing lifestyles, and increasing disposable incomes in countries like China and India. North America and Europe also represent significant markets, with a strong focus on sustainable packaging solutions driving adoption.
One of the key market trends is the development of advanced sodium silicate-based coatings for food packaging. These coatings enhance the barrier properties of packaging materials, extending the shelf life of food products and reducing food waste. This trend aligns with the global focus on sustainability and food security, further driving market growth.
However, the market also faces certain challenges. The relatively higher cost of sodium silicate-based packaging compared to conventional plastic packaging remains a barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in price-sensitive markets. Additionally, there is a need for further research and development to improve the performance and cost-effectiveness of these materials.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for sodium silicate-based food packaging remains positive. The increasing focus on circular economy principles and the growing consumer preference for sustainable products are expected to drive continued innovation and market expansion in this sector.
The market for sodium silicate-based food packaging is experiencing steady growth, primarily due to its versatility and eco-friendly characteristics. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, there is a growing demand for packaging materials that are recyclable, biodegradable, and have a lower carbon footprint. Sodium silicate-based packaging addresses these concerns, positioning itself as a sustainable alternative to traditional plastic packaging.
In terms of market size, the sodium silicate-based food packaging segment is expected to expand significantly over the next five years. This growth is attributed to several factors, including the increasing adoption of sustainable packaging solutions by food manufacturers, stringent regulations on plastic usage, and rising consumer awareness about environmental issues.
The food and beverage industry represents the largest end-user segment for sodium silicate-based packaging. Within this sector, there is particularly strong demand from the dairy, bakery, and ready-to-eat meal segments. These industries require packaging solutions that offer excellent barrier properties against moisture and oxygen, which sodium silicate-based materials can provide effectively.
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market for sodium silicate-based food packaging. This growth is driven by rapid urbanization, changing lifestyles, and increasing disposable incomes in countries like China and India. North America and Europe also represent significant markets, with a strong focus on sustainable packaging solutions driving adoption.
One of the key market trends is the development of advanced sodium silicate-based coatings for food packaging. These coatings enhance the barrier properties of packaging materials, extending the shelf life of food products and reducing food waste. This trend aligns with the global focus on sustainability and food security, further driving market growth.
However, the market also faces certain challenges. The relatively higher cost of sodium silicate-based packaging compared to conventional plastic packaging remains a barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in price-sensitive markets. Additionally, there is a need for further research and development to improve the performance and cost-effectiveness of these materials.
Despite these challenges, the overall market outlook for sodium silicate-based food packaging remains positive. The increasing focus on circular economy principles and the growing consumer preference for sustainable products are expected to drive continued innovation and market expansion in this sector.
Current Applications and Challenges in Food Packaging
Sodium silicate, also known as water glass, has gained significant traction in the food packaging industry due to its versatile properties. Currently, it finds applications in various forms of food packaging, primarily as a coating agent and adhesive. As a coating, sodium silicate creates a thin, transparent layer on paper and cardboard packaging, enhancing their moisture resistance and barrier properties. This application is particularly valuable for packaging dry foods, where moisture protection is crucial for maintaining product quality and extending shelf life.
In the realm of adhesives, sodium silicate serves as a key component in the production of corrugated cardboard boxes, widely used for shipping and storing food products. Its strong bonding properties ensure the structural integrity of these boxes, even under challenging environmental conditions. Additionally, sodium silicate is utilized in the manufacturing of glass containers for food and beverages, where it acts as a binding agent and helps improve the durability of the glass.
Despite its widespread use, the application of sodium silicate in food packaging faces several challenges. One primary concern is the potential migration of silicate compounds into food products, especially in acidic or high-moisture environments. This necessitates careful consideration of the packaging design and thorough testing to ensure compliance with food safety regulations. Another challenge lies in the balance between barrier properties and recyclability. While sodium silicate coatings enhance protection, they can complicate the recycling process of paper-based packaging materials.
The food industry's increasing focus on sustainability presents both opportunities and challenges for sodium silicate applications. On one hand, its ability to improve the performance of paper-based packaging aligns with the trend towards more environmentally friendly packaging solutions. On the other hand, the industry is seeking alternatives that offer similar benefits with enhanced recyclability and biodegradability.
Technological advancements are addressing some of these challenges. Research is ongoing to develop modified sodium silicate formulations that provide improved barrier properties while minimizing migration risks. Additionally, efforts are being made to optimize coating processes to achieve better performance with thinner layers, potentially easing recycling concerns. The development of bio-based alternatives to traditional sodium silicate is also an area of active research, aiming to meet the growing demand for more sustainable packaging solutions in the food industry.
In the realm of adhesives, sodium silicate serves as a key component in the production of corrugated cardboard boxes, widely used for shipping and storing food products. Its strong bonding properties ensure the structural integrity of these boxes, even under challenging environmental conditions. Additionally, sodium silicate is utilized in the manufacturing of glass containers for food and beverages, where it acts as a binding agent and helps improve the durability of the glass.
Despite its widespread use, the application of sodium silicate in food packaging faces several challenges. One primary concern is the potential migration of silicate compounds into food products, especially in acidic or high-moisture environments. This necessitates careful consideration of the packaging design and thorough testing to ensure compliance with food safety regulations. Another challenge lies in the balance between barrier properties and recyclability. While sodium silicate coatings enhance protection, they can complicate the recycling process of paper-based packaging materials.
The food industry's increasing focus on sustainability presents both opportunities and challenges for sodium silicate applications. On one hand, its ability to improve the performance of paper-based packaging aligns with the trend towards more environmentally friendly packaging solutions. On the other hand, the industry is seeking alternatives that offer similar benefits with enhanced recyclability and biodegradability.
Technological advancements are addressing some of these challenges. Research is ongoing to develop modified sodium silicate formulations that provide improved barrier properties while minimizing migration risks. Additionally, efforts are being made to optimize coating processes to achieve better performance with thinner layers, potentially easing recycling concerns. The development of bio-based alternatives to traditional sodium silicate is also an area of active research, aiming to meet the growing demand for more sustainable packaging solutions in the food industry.
Existing Sodium Silicate-Based Packaging Solutions
01 Use in detergent compositions
Sodium silicate is commonly used in detergent compositions due to its alkaline properties and ability to act as a builder. It helps to soften water, remove dirt and stains, and protect washing machines from corrosion. The inclusion of sodium silicate in detergent formulations can enhance cleaning performance and provide additional benefits such as fabric care.- Use in detergent compositions: Sodium silicate is commonly used in detergent compositions as a builder and alkalinity source. It helps to soften water, remove dirt and stains, and protect washing machines from corrosion. The inclusion of sodium silicate in detergent formulations can improve cleaning performance and stability of the product.
- Application in cement and concrete: Sodium silicate is utilized in the production of cement and concrete materials. It acts as a binder, accelerator, and waterproofing agent. The addition of sodium silicate can enhance the strength, durability, and setting time of cement-based products, making it valuable in construction applications.
- Use in fire-resistant coatings: Sodium silicate is employed in the formulation of fire-resistant coatings and materials. When exposed to high temperatures, it forms a protective barrier that helps prevent the spread of fire. This property makes it useful in various applications, including building materials and industrial coatings.
- Application in water treatment: Sodium silicate is used in water treatment processes for various purposes. It can act as a coagulant aid, helping to remove suspended particles from water. Additionally, it can be used to control corrosion in water distribution systems and adjust pH levels in industrial water treatment applications.
- Use in catalysts and adsorbents: Sodium silicate serves as a precursor in the synthesis of catalysts and adsorbents. It can be used to produce zeolites, silica gels, and other porous materials with high surface areas. These materials find applications in various industries, including petrochemicals, environmental remediation, and gas separation.
02 Application in cement and concrete
Sodium silicate is utilized in the production of cement and concrete materials. It can act as a binder, accelerator, or sealant in various cement-based applications. The addition of sodium silicate can improve the strength, durability, and water resistance of concrete structures. It is also used in the manufacture of refractory cements and as a component in fireproofing materials.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in water treatment
Sodium silicate finds applications in water treatment processes. It can be used as a coagulant aid in water purification, helping to remove suspended particles and impurities. Additionally, sodium silicate can be employed to control corrosion in water distribution systems and industrial cooling systems by forming protective silicate films on metal surfaces.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application in paper and pulp industry
Sodium silicate is used in the paper and pulp industry for various purposes. It can serve as a sizing agent, improving the paper's resistance to liquid penetration. Sodium silicate is also employed in de-inking processes during paper recycling and as a retention aid in papermaking. Its use can enhance paper quality and production efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Use in catalysis and zeolite synthesis
Sodium silicate plays a role in catalysis and the synthesis of zeolites. It serves as a precursor for the production of various silica-based materials, including catalysts and molecular sieves. In zeolite synthesis, sodium silicate acts as a silicon source and helps control the pH of the reaction mixture. These applications are important in industries such as petrochemicals and fine chemicals manufacturing.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sodium Silicate Food Packaging Industry
The applications of sodium silicate in the food packaging industry are in a growth phase, with increasing market size driven by demand for sustainable and functional packaging solutions. The technology is relatively mature, with established players like J. M. Huber Corp., Evonik Operations GmbH, and AGC, Inc. leading innovation. These companies are leveraging their expertise in specialty chemicals and materials science to develop advanced sodium silicate-based solutions for food packaging. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of large multinational corporations and specialized chemical companies, with ongoing research and development efforts focused on enhancing performance properties and expanding applications in active and intelligent packaging systems.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has developed advanced sodium silicate formulations for food packaging applications, focusing on creating high-performance barrier coatings. Their technology involves modifying sodium silicate structures to enhance their barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and grease. Evonik's approach includes the development of nano-structured sodium silicate coatings that can be applied in ultra-thin layers, providing excellent barrier properties without significantly increasing packaging weight or thickness[10]. The company has also worked on incorporating their sodium silicate technology into biodegradable packaging materials, addressing both performance and sustainability concerns. Evonik reports that their sodium silicate coatings can reduce oxygen transmission rates by up to 90% compared to uncoated substrates[11]. Furthermore, they have developed water-based sodium silicate formulations that are easy to apply and compatible with existing coating equipment in the packaging industry[12].
Strengths: High-performance barrier properties, compatibility with biodegradable materials, and ease of application. Weaknesses: Potential higher costs associated with nano-structured formulations, may require specialized handling in some cases.
AGC, Inc. (Japan)
Technical Solution: AGC has developed innovative sodium silicate-based coatings for food packaging applications, leveraging their expertise in glass and chemical technologies. Their approach focuses on creating transparent, thin-film coatings that provide excellent barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and UV light. AGC's sodium silicate coatings are designed to be applied to various substrates, including plastics and paper-based materials, enhancing their protective qualities without compromising transparency or flexibility[13]. The company has reported achieving oxygen transmission rates below 1 cc/m²/day with their sodium silicate coatings, making them suitable for sensitive food products[14]. AGC has also worked on improving the durability and scratch resistance of their coatings, ensuring that the barrier properties are maintained throughout the packaging lifecycle. Additionally, they have developed eco-friendly formulations that align with increasing sustainability demands in the food packaging industry[15].
Strengths: Excellent barrier properties, versatility in application to different substrates, and improved durability. Weaknesses: May require specialized application processes, potential limitations in extreme temperature conditions.
Innovative Sodium Silicate Applications in Food Packaging
Process for the preparation of sodium silicate from Kimberlite tailing
PatentInactiveUS20070104634A1
Innovation
- A process involving the treatment of Kimberlite tailings with hydrochloric acid to enrich silica content, followed by digestion with sodium hydroxide at moderate temperatures and atmospheric pressure to produce sodium silicate, maximizing silica recovery and reducing waste generation.
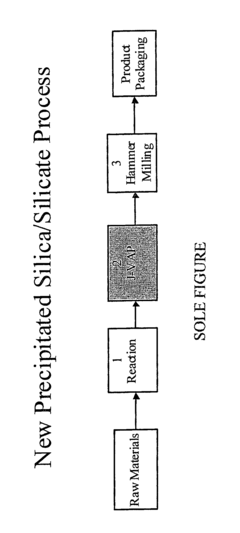
Method for making precipitated silica or silicate compositions and products thereof
PatentInactiveUS7125432B2
Innovation
- A method involving direct dewatering and milling of precipitated silica and silicate materials using a hydraulic chamber press and vacuum dewatering, eliminating the need for conventional drying processes like spray or flash drying, which allows for the production of silica and silicate particles with a narrow particle size distribution and high transmittance, suitable for clear dental formulations.
Environmental Impact of Sodium Silicate in Packaging
The use of sodium silicate in food packaging has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. As a widely used material in the industry, its environmental impact spans the entire lifecycle of packaging products, from production to disposal.
During the manufacturing process of sodium silicate-based packaging, energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions are notable concerns. The production of sodium silicate involves high-temperature processes, which contribute to carbon dioxide emissions. However, compared to some alternative packaging materials, the energy requirements for sodium silicate production are relatively moderate.
In terms of resource utilization, sodium silicate offers some advantages. It is derived from abundant natural materials, primarily sand and soda ash, which are generally considered sustainable resources. This reduces the strain on more limited raw materials used in other packaging solutions. Additionally, the long shelf life and durability of sodium silicate-based packaging can lead to reduced material waste over time.
Water consumption and potential water pollution are important factors to consider. The production of sodium silicate requires substantial amounts of water, and improper handling of waste products can lead to alkaline runoff. However, modern manufacturing processes have significantly improved water recycling and waste management, mitigating these risks.
One of the most positive environmental aspects of sodium silicate in packaging is its recyclability. Many sodium silicate-based packaging materials can be easily recycled, contributing to a circular economy model. This recyclability helps reduce the overall environmental footprint of the packaging industry by decreasing the demand for virgin materials and lowering the volume of waste sent to landfills.
Biodegradability is another crucial environmental consideration. While sodium silicate itself is not biodegradable, its use in composite packaging materials can enhance the overall biodegradability of the final product. This is particularly relevant in the development of eco-friendly packaging solutions that aim to reduce long-term environmental impact.
The end-of-life phase of sodium silicate packaging also presents both challenges and opportunities. When disposed of in landfills, sodium silicate-based materials generally have a lower environmental impact compared to many plastics, as they do not release harmful chemicals or microplastics into the environment. However, the alkaline nature of sodium silicate can potentially affect soil pH levels if not properly managed.
In conclusion, while the use of sodium silicate in food packaging does have environmental impacts, particularly in terms of energy use and water consumption during production, its overall environmental profile is relatively favorable when compared to many alternative packaging materials. The recyclability, durability, and potential for enhancing biodegradability in composite materials make it a valuable component in the ongoing efforts to develop more sustainable packaging solutions for the food industry.
During the manufacturing process of sodium silicate-based packaging, energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions are notable concerns. The production of sodium silicate involves high-temperature processes, which contribute to carbon dioxide emissions. However, compared to some alternative packaging materials, the energy requirements for sodium silicate production are relatively moderate.
In terms of resource utilization, sodium silicate offers some advantages. It is derived from abundant natural materials, primarily sand and soda ash, which are generally considered sustainable resources. This reduces the strain on more limited raw materials used in other packaging solutions. Additionally, the long shelf life and durability of sodium silicate-based packaging can lead to reduced material waste over time.
Water consumption and potential water pollution are important factors to consider. The production of sodium silicate requires substantial amounts of water, and improper handling of waste products can lead to alkaline runoff. However, modern manufacturing processes have significantly improved water recycling and waste management, mitigating these risks.
One of the most positive environmental aspects of sodium silicate in packaging is its recyclability. Many sodium silicate-based packaging materials can be easily recycled, contributing to a circular economy model. This recyclability helps reduce the overall environmental footprint of the packaging industry by decreasing the demand for virgin materials and lowering the volume of waste sent to landfills.
Biodegradability is another crucial environmental consideration. While sodium silicate itself is not biodegradable, its use in composite packaging materials can enhance the overall biodegradability of the final product. This is particularly relevant in the development of eco-friendly packaging solutions that aim to reduce long-term environmental impact.
The end-of-life phase of sodium silicate packaging also presents both challenges and opportunities. When disposed of in landfills, sodium silicate-based materials generally have a lower environmental impact compared to many plastics, as they do not release harmful chemicals or microplastics into the environment. However, the alkaline nature of sodium silicate can potentially affect soil pH levels if not properly managed.
In conclusion, while the use of sodium silicate in food packaging does have environmental impacts, particularly in terms of energy use and water consumption during production, its overall environmental profile is relatively favorable when compared to many alternative packaging materials. The recyclability, durability, and potential for enhancing biodegradability in composite materials make it a valuable component in the ongoing efforts to develop more sustainable packaging solutions for the food industry.
Regulatory Framework for Food Contact Materials
The regulatory framework for food contact materials plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and compliance of sodium silicate applications in the food packaging industry. Various regulatory bodies worldwide have established guidelines and standards to govern the use of materials that come into direct or indirect contact with food products.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates food contact materials under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. The FDA maintains a list of substances that are Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for use in food packaging, which includes sodium silicate under certain conditions. Manufacturers must ensure that their use of sodium silicate in food packaging complies with FDA regulations and does not pose any health risks to consumers.
The European Union has implemented comprehensive legislation for food contact materials through Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004. This regulation sets out general principles of safety and inertness for all food contact materials. Additionally, the EU has specific measures for certain materials, such as plastics, which may incorporate sodium silicate. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with these regulations through appropriate documentation and testing.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare oversees the regulation of food contact materials. The Japanese Food Sanitation Law includes a positive list of substances approved for use in food packaging, which manufacturers must adhere to when incorporating sodium silicate into their products.
Many other countries have their own regulatory frameworks for food contact materials, often drawing inspiration from or harmonizing with international standards. These regulations typically require manufacturers to demonstrate that their packaging materials do not transfer harmful substances to food under normal conditions of use.
To ensure compliance with these diverse regulatory requirements, manufacturers using sodium silicate in food packaging must conduct thorough testing and maintain detailed documentation. This often includes migration studies to assess the potential transfer of substances from the packaging to food, as well as toxicological evaluations to demonstrate safety.
As regulations continue to evolve, manufacturers must stay informed about changes in regulatory requirements across different markets. This may involve ongoing testing, certification processes, and adjustments to formulations or manufacturing processes to maintain compliance and ensure the safety of food packaging materials containing sodium silicate.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates food contact materials under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. The FDA maintains a list of substances that are Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for use in food packaging, which includes sodium silicate under certain conditions. Manufacturers must ensure that their use of sodium silicate in food packaging complies with FDA regulations and does not pose any health risks to consumers.
The European Union has implemented comprehensive legislation for food contact materials through Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004. This regulation sets out general principles of safety and inertness for all food contact materials. Additionally, the EU has specific measures for certain materials, such as plastics, which may incorporate sodium silicate. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with these regulations through appropriate documentation and testing.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare oversees the regulation of food contact materials. The Japanese Food Sanitation Law includes a positive list of substances approved for use in food packaging, which manufacturers must adhere to when incorporating sodium silicate into their products.
Many other countries have their own regulatory frameworks for food contact materials, often drawing inspiration from or harmonizing with international standards. These regulations typically require manufacturers to demonstrate that their packaging materials do not transfer harmful substances to food under normal conditions of use.
To ensure compliance with these diverse regulatory requirements, manufacturers using sodium silicate in food packaging must conduct thorough testing and maintain detailed documentation. This often includes migration studies to assess the potential transfer of substances from the packaging to food, as well as toxicological evaluations to demonstrate safety.
As regulations continue to evolve, manufacturers must stay informed about changes in regulatory requirements across different markets. This may involve ongoing testing, certification processes, and adjustments to formulations or manufacturing processes to maintain compliance and ensure the safety of food packaging materials containing sodium silicate.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!