Crystal UHD vs QLED: Understanding Key Differences
JUN 20, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Display Tech Evolution
The evolution of display technology has been a remarkable journey, marked by significant advancements in image quality, energy efficiency, and overall viewing experience. From the early days of cathode ray tubes (CRTs) to the current era of high-definition flat panel displays, the industry has witnessed a continuous push towards better picture quality and more immersive visual experiences.
In the 1990s and early 2000s, LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) technology began to dominate the market, offering thinner and more energy-efficient alternatives to CRTs. This period saw rapid improvements in LCD technology, including better color reproduction, wider viewing angles, and increased refresh rates. The introduction of LED backlighting further enhanced LCD performance, leading to brighter displays with improved contrast ratios.
The mid-2000s saw the emergence of plasma display technology, which offered superior black levels and contrast ratios compared to early LCDs. However, plasma displays were eventually phased out due to their higher power consumption and susceptibility to image retention.
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology entered the consumer market in the early 2010s, revolutionizing display quality with its ability to produce perfect blacks and infinite contrast ratios. OLED displays quickly became the gold standard for high-end televisions and smartphones, offering unparalleled picture quality and color accuracy.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards enhancing LCD technology to compete with OLED. This effort has led to the development of quantum dot technology, which forms the basis of QLED (Quantum-dot Light-Emitting Diode) displays. QLED technology uses a layer of quantum dots to improve color accuracy and brightness in LCD panels, narrowing the gap with OLED in terms of picture quality.
The latest development in this evolutionary path is the introduction of Crystal UHD technology by Samsung. Crystal UHD represents a further refinement of LCD technology, offering improved color volume and contrast through advanced image processing and panel design. While not as advanced as QLED in terms of color reproduction, Crystal UHD provides a significant upgrade over standard LED-LCD displays, offering consumers a high-quality viewing experience at a more accessible price point.
As display technology continues to evolve, we are seeing a convergence of different technologies and approaches. Manufacturers are exploring ways to combine the strengths of various display technologies, such as mini-LED backlighting for LCD panels, which promises OLED-like contrast levels with the brightness and longevity of LCD. The ongoing research into micro-LED technology also holds promise for future displays, potentially offering the best of both OLED and LCD technologies without their respective drawbacks.
In the 1990s and early 2000s, LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) technology began to dominate the market, offering thinner and more energy-efficient alternatives to CRTs. This period saw rapid improvements in LCD technology, including better color reproduction, wider viewing angles, and increased refresh rates. The introduction of LED backlighting further enhanced LCD performance, leading to brighter displays with improved contrast ratios.
The mid-2000s saw the emergence of plasma display technology, which offered superior black levels and contrast ratios compared to early LCDs. However, plasma displays were eventually phased out due to their higher power consumption and susceptibility to image retention.
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology entered the consumer market in the early 2010s, revolutionizing display quality with its ability to produce perfect blacks and infinite contrast ratios. OLED displays quickly became the gold standard for high-end televisions and smartphones, offering unparalleled picture quality and color accuracy.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards enhancing LCD technology to compete with OLED. This effort has led to the development of quantum dot technology, which forms the basis of QLED (Quantum-dot Light-Emitting Diode) displays. QLED technology uses a layer of quantum dots to improve color accuracy and brightness in LCD panels, narrowing the gap with OLED in terms of picture quality.
The latest development in this evolutionary path is the introduction of Crystal UHD technology by Samsung. Crystal UHD represents a further refinement of LCD technology, offering improved color volume and contrast through advanced image processing and panel design. While not as advanced as QLED in terms of color reproduction, Crystal UHD provides a significant upgrade over standard LED-LCD displays, offering consumers a high-quality viewing experience at a more accessible price point.
As display technology continues to evolve, we are seeing a convergence of different technologies and approaches. Manufacturers are exploring ways to combine the strengths of various display technologies, such as mini-LED backlighting for LCD panels, which promises OLED-like contrast levels with the brightness and longevity of LCD. The ongoing research into micro-LED technology also holds promise for future displays, potentially offering the best of both OLED and LCD technologies without their respective drawbacks.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for advanced display technologies continues to grow as consumers seek superior visual experiences in their homes and personal devices. Both Crystal UHD and QLED technologies have emerged as popular choices in the premium TV segment, catering to different consumer preferences and price points.
Crystal UHD, Samsung's branding for their high-end LED-LCD TVs, has gained traction in the mid-range market. These displays offer improved color accuracy and brightness compared to standard LED TVs, making them attractive to consumers looking for an upgrade without the higher costs associated with QLED or OLED technologies. The demand for Crystal UHD TVs has been steadily increasing, particularly in emerging markets where price sensitivity is a significant factor.
QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) technology, on the other hand, has positioned itself as a premium alternative to OLED displays. QLED TVs offer enhanced brightness, wider color gamut, and better energy efficiency compared to traditional LED-LCD TVs. The market for QLED displays has shown robust growth, especially in developed markets where consumers are willing to invest in cutting-edge technology for superior picture quality.
The global TV market has seen a shift towards larger screen sizes, with both Crystal UHD and QLED technologies benefiting from this trend. Consumers are increasingly opting for 55-inch and larger displays, driving demand for these advanced technologies that can deliver high-quality images on larger screens without compromising on clarity or color accuracy.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also influenced market demand, with increased time spent at home leading to higher investments in home entertainment systems. This has boosted sales of both Crystal UHD and QLED TVs, as consumers seek to enhance their viewing experiences for streaming content, gaming, and home cinema setups.
In terms of market segmentation, Crystal UHD has found a strong foothold in the upper mid-range segment, appealing to consumers who want improved picture quality without the premium price tag of QLED or OLED. QLED, meanwhile, has carved out a niche in the high-end market, competing directly with OLED technology and attracting consumers who prioritize brightness and color volume.
The gaming market has also become a significant driver for both technologies. With the rise of next-generation gaming consoles and PC gaming, there is an increasing demand for displays that can handle high refresh rates and low input lag. Both Crystal UHD and QLED TVs have been marketed towards gamers, with features such as variable refresh rate (VRR) and auto low latency mode (ALLM) becoming key selling points.
Crystal UHD, Samsung's branding for their high-end LED-LCD TVs, has gained traction in the mid-range market. These displays offer improved color accuracy and brightness compared to standard LED TVs, making them attractive to consumers looking for an upgrade without the higher costs associated with QLED or OLED technologies. The demand for Crystal UHD TVs has been steadily increasing, particularly in emerging markets where price sensitivity is a significant factor.
QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) technology, on the other hand, has positioned itself as a premium alternative to OLED displays. QLED TVs offer enhanced brightness, wider color gamut, and better energy efficiency compared to traditional LED-LCD TVs. The market for QLED displays has shown robust growth, especially in developed markets where consumers are willing to invest in cutting-edge technology for superior picture quality.
The global TV market has seen a shift towards larger screen sizes, with both Crystal UHD and QLED technologies benefiting from this trend. Consumers are increasingly opting for 55-inch and larger displays, driving demand for these advanced technologies that can deliver high-quality images on larger screens without compromising on clarity or color accuracy.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also influenced market demand, with increased time spent at home leading to higher investments in home entertainment systems. This has boosted sales of both Crystal UHD and QLED TVs, as consumers seek to enhance their viewing experiences for streaming content, gaming, and home cinema setups.
In terms of market segmentation, Crystal UHD has found a strong foothold in the upper mid-range segment, appealing to consumers who want improved picture quality without the premium price tag of QLED or OLED. QLED, meanwhile, has carved out a niche in the high-end market, competing directly with OLED technology and attracting consumers who prioritize brightness and color volume.
The gaming market has also become a significant driver for both technologies. With the rise of next-generation gaming consoles and PC gaming, there is an increasing demand for displays that can handle high refresh rates and low input lag. Both Crystal UHD and QLED TVs have been marketed towards gamers, with features such as variable refresh rate (VRR) and auto low latency mode (ALLM) becoming key selling points.
Crystal UHD vs QLED
Crystal UHD and QLED are two prominent display technologies in the modern television market, each offering unique features and benefits to consumers. Crystal UHD, developed by Samsung, is an enhanced version of traditional LED-LCD technology, utilizing a crystal layer to improve color accuracy and brightness. QLED, also pioneered by Samsung, stands for Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode and represents a more advanced display technology.
The key difference between Crystal UHD and QLED lies in their underlying technologies. Crystal UHD uses a crystal layer to refine the light produced by LED backlights, resulting in improved color reproduction and overall picture quality. QLED, on the other hand, employs quantum dots - tiny semiconductor particles that emit light when excited by electricity. These quantum dots are capable of producing more vibrant and accurate colors across a wider color gamut.
In terms of picture quality, QLED generally outperforms Crystal UHD. QLED displays can achieve higher peak brightness levels, making them better suited for HDR content and viewing in brightly lit environments. They also offer superior color volume, meaning they can maintain color accuracy even at high brightness levels. Crystal UHD, while still providing excellent picture quality, may not match the color intensity and brightness of QLED panels.
Contrast is another area where these technologies differ. QLED typically offers better contrast ratios due to its ability to produce deeper blacks and brighter whites. Crystal UHD, while capable of good contrast, may not achieve the same level of depth in dark scenes or brilliance in bright areas. However, both technologies have made significant strides in local dimming capabilities, which help improve contrast by selectively dimming or brightening different areas of the screen.
When it comes to viewing angles, both Crystal UHD and QLED face similar challenges inherent to LCD-based technologies. Off-angle viewing can result in some color shift and reduced contrast. However, recent advancements in panel design and optical films have helped mitigate these issues to some extent in both technologies.
Energy efficiency is an important consideration for consumers. Generally, Crystal UHD displays tend to be more energy-efficient than their QLED counterparts. This is primarily due to the simpler backlighting system used in Crystal UHD TVs. QLED displays, with their quantum dot layer and typically higher brightness capabilities, may consume more power, especially when displaying HDR content or operating at peak brightness levels.
In terms of lifespan and durability, both technologies are considered reliable and long-lasting. However, QLED may have a slight edge in terms of resistance to image retention or burn-in, which can be a concern with some display technologies over extended periods of use.
The key difference between Crystal UHD and QLED lies in their underlying technologies. Crystal UHD uses a crystal layer to refine the light produced by LED backlights, resulting in improved color reproduction and overall picture quality. QLED, on the other hand, employs quantum dots - tiny semiconductor particles that emit light when excited by electricity. These quantum dots are capable of producing more vibrant and accurate colors across a wider color gamut.
In terms of picture quality, QLED generally outperforms Crystal UHD. QLED displays can achieve higher peak brightness levels, making them better suited for HDR content and viewing in brightly lit environments. They also offer superior color volume, meaning they can maintain color accuracy even at high brightness levels. Crystal UHD, while still providing excellent picture quality, may not match the color intensity and brightness of QLED panels.
Contrast is another area where these technologies differ. QLED typically offers better contrast ratios due to its ability to produce deeper blacks and brighter whites. Crystal UHD, while capable of good contrast, may not achieve the same level of depth in dark scenes or brilliance in bright areas. However, both technologies have made significant strides in local dimming capabilities, which help improve contrast by selectively dimming or brightening different areas of the screen.
When it comes to viewing angles, both Crystal UHD and QLED face similar challenges inherent to LCD-based technologies. Off-angle viewing can result in some color shift and reduced contrast. However, recent advancements in panel design and optical films have helped mitigate these issues to some extent in both technologies.
Energy efficiency is an important consideration for consumers. Generally, Crystal UHD displays tend to be more energy-efficient than their QLED counterparts. This is primarily due to the simpler backlighting system used in Crystal UHD TVs. QLED displays, with their quantum dot layer and typically higher brightness capabilities, may consume more power, especially when displaying HDR content or operating at peak brightness levels.
In terms of lifespan and durability, both technologies are considered reliable and long-lasting. However, QLED may have a slight edge in terms of resistance to image retention or burn-in, which can be a concern with some display technologies over extended periods of use.
Current Display Solutions
01 QLED display technology
QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) displays use quantum dots to enhance color and brightness. This technology offers improved color accuracy, wider color gamut, and higher peak brightness compared to traditional LED displays. QLED displays can achieve better contrast ratios and more vibrant colors, resulting in a superior viewing experience.- Quantum dot technology in QLED displays: QLED displays utilize quantum dot technology to enhance color reproduction and brightness. Quantum dots are semiconductor nanocrystals that emit light of specific wavelengths when excited, resulting in more vibrant and accurate colors compared to traditional LED displays. This technology allows for a wider color gamut and improved overall picture quality.
- Crystal UHD display enhancements: Crystal UHD displays incorporate advanced technologies to improve image quality. These may include enhanced backlighting systems, improved color processing algorithms, and optimized panel designs. The result is a display with higher contrast ratios, better color accuracy, and improved overall picture clarity compared to standard UHD displays.
- Display panel structure and materials: Both Crystal UHD and QLED displays utilize advanced panel structures and materials to enhance display quality. This may include the use of specialized films, optical layers, and pixel arrangements to improve light transmission, reduce reflections, and enhance viewing angles. The choice of materials and panel design significantly impacts the overall display performance.
- Color processing and enhancement techniques: Advanced color processing algorithms and enhancement techniques are employed in both Crystal UHD and QLED displays to improve color accuracy and vibrancy. These may include dynamic color mapping, local dimming, and HDR processing. Such techniques help to optimize the display output based on the content being shown and the ambient lighting conditions.
- Display driver and control systems: Sophisticated display driver and control systems are crucial for maximizing the performance of Crystal UHD and QLED displays. These systems manage various aspects of display operation, including refresh rates, power consumption, and image processing. Advanced driver technologies can help reduce motion blur, improve response times, and enhance overall picture quality.
02 Crystal UHD display technology
Crystal UHD (Ultra High Definition) displays utilize advanced LCD technology with enhanced backlighting and color processing. These displays offer improved picture quality, higher resolution, and better color reproduction compared to standard UHD displays. Crystal UHD technology focuses on delivering clearer and more detailed images with enhanced contrast and brightness.Expand Specific Solutions03 Color enhancement and processing
Both Crystal UHD and QLED displays employ advanced color enhancement and processing techniques to improve image quality. These technologies may include local dimming, HDR (High Dynamic Range) support, and AI-powered upscaling to enhance color accuracy, contrast, and overall picture quality. The goal is to provide more lifelike and immersive viewing experiences.Expand Specific Solutions04 Display panel structure and materials
The display quality of Crystal UHD and QLED displays is influenced by their panel structure and materials used. This includes the arrangement of pixels, subpixel layout, and the use of specialized materials like quantum dots or advanced LCD crystals. These factors contribute to improved color reproduction, viewing angles, and overall display performance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Image processing and enhancement algorithms
Both display technologies utilize sophisticated image processing and enhancement algorithms to optimize picture quality. These algorithms may include noise reduction, motion smoothing, and dynamic contrast adjustment. Advanced processors in these displays analyze and adjust the image in real-time to deliver improved clarity, sharpness, and overall visual quality.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Display Manufacturers
The competition landscape for Crystal UHD vs QLED technology is characterized by a mature market with significant growth potential. The display industry is in a phase of rapid innovation, with major players like Samsung Display, LG Display, and BOE Technology Group leading the charge. The market size for advanced display technologies is expanding, driven by increasing demand for high-quality visual experiences. Technologically, both Crystal UHD and QLED are well-established, with companies like TCL China Star Optoelectronics and Sharp Corp. continuously refining their offerings. The competition is fierce, with each company striving to differentiate through enhanced color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency. As the technology matures, we're seeing a convergence in performance, making brand reputation and cost-effectiveness key differentiators in this highly competitive market.
TCL China Star Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: TCL CSOT has developed its own versions of Crystal UHD-like and QLED technologies. Their Crystal UHD equivalent uses advanced LCD panels with improved color filters and backlighting systems to enhance color accuracy and contrast. For QLED, TCL CSOT has invested in quantum dot technology, creating panels with a quantum dot film layer to produce more vibrant colors and higher brightness. Both technologies incorporate TCL's AiPQ Engine Gen 2, which uses machine-learning algorithms to optimize picture quality, color, contrast, and clarity in real-time.
TCL CSOT's Crystal UHD-like technology offers good picture quality at competitive prices, making it suitable for mid-range displays. Their QLED technology provides excellent color performance and brightness, rivaling other major brands. However, TCL's brand recognition in some markets may not be as strong as more established competitors in the high-end display segment.
Samsung Display Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung Display, as a subsidiary of Samsung Electronics, focuses on developing and manufacturing display panels for various technologies, including Crystal UHD and QLED. For Crystal UHD, they produce high-quality LCD panels with advanced color filters and improved light transmission. Their QLED panels feature a quantum dot layer integrated directly into the panel structure, allowing for enhanced color volume and brightness. Samsung Display also develops complementary technologies such as ultra-thin bezels and curved displays to enhance the overall viewing experience for both Crystal UHD and QLED TVs.
Samsung Display's panels offer excellent color accuracy and brightness for both Crystal UHD and QLED technologies. Their QLED panels provide superior color volume and HDR performance. However, the cost of QLED panel production is higher, which can impact the final product price.
Core Display Innovations
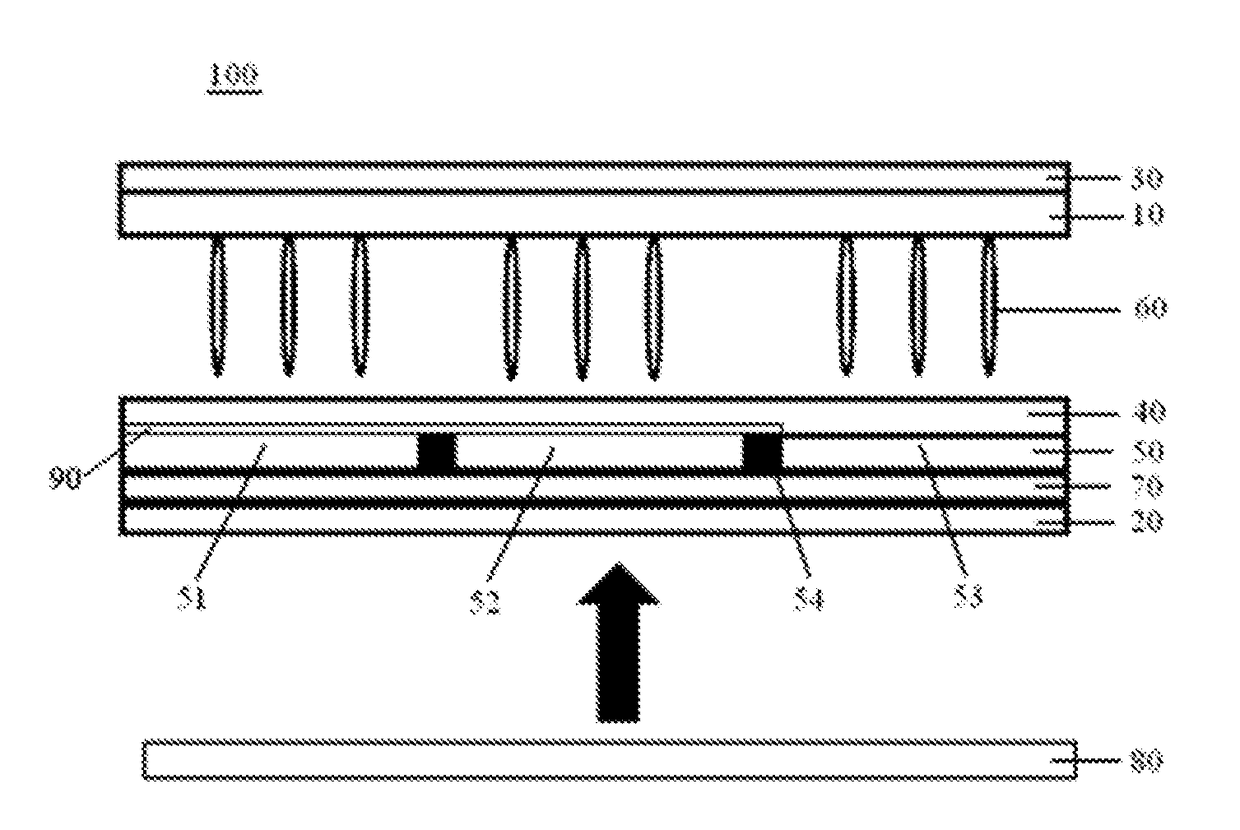
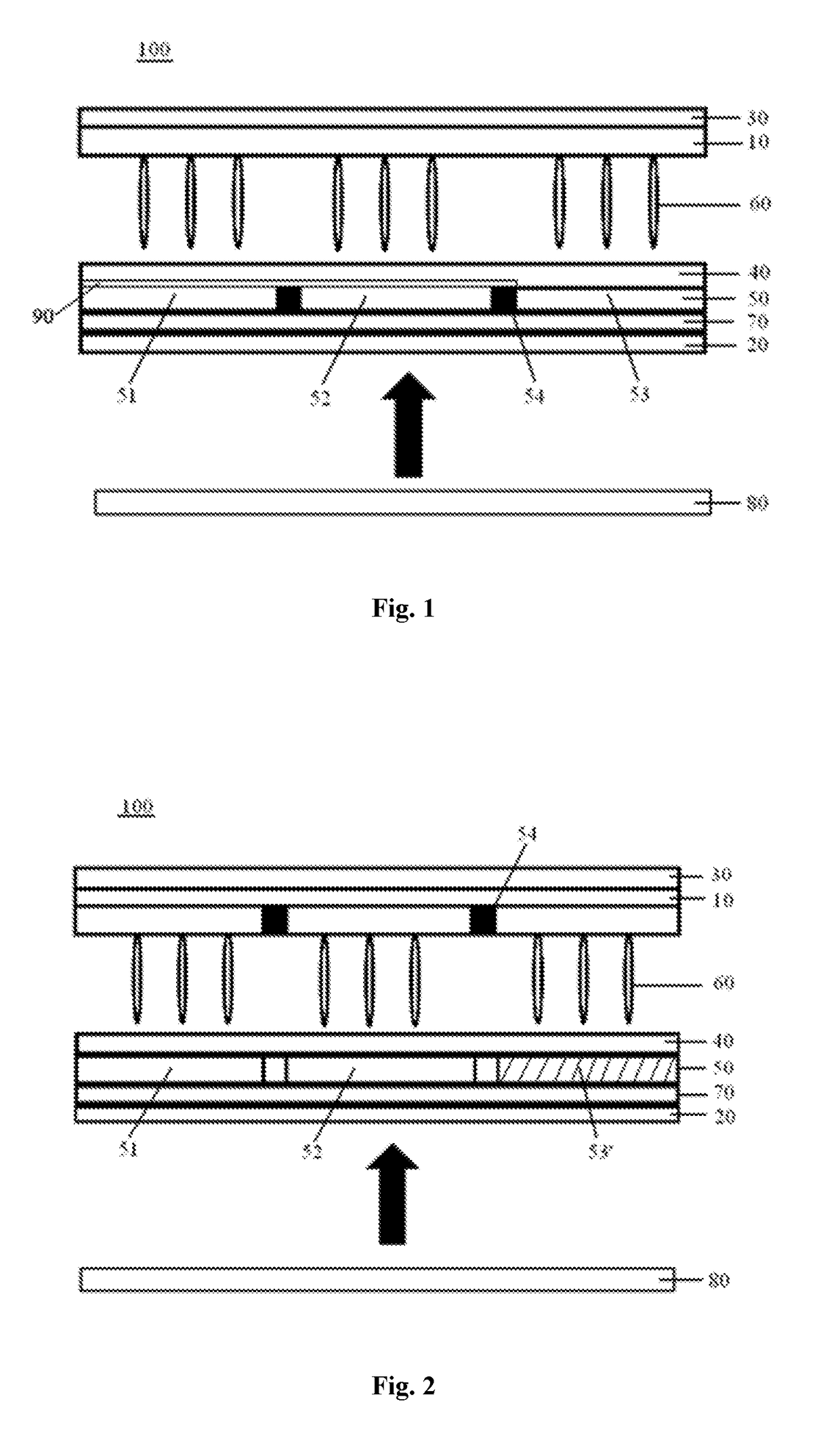
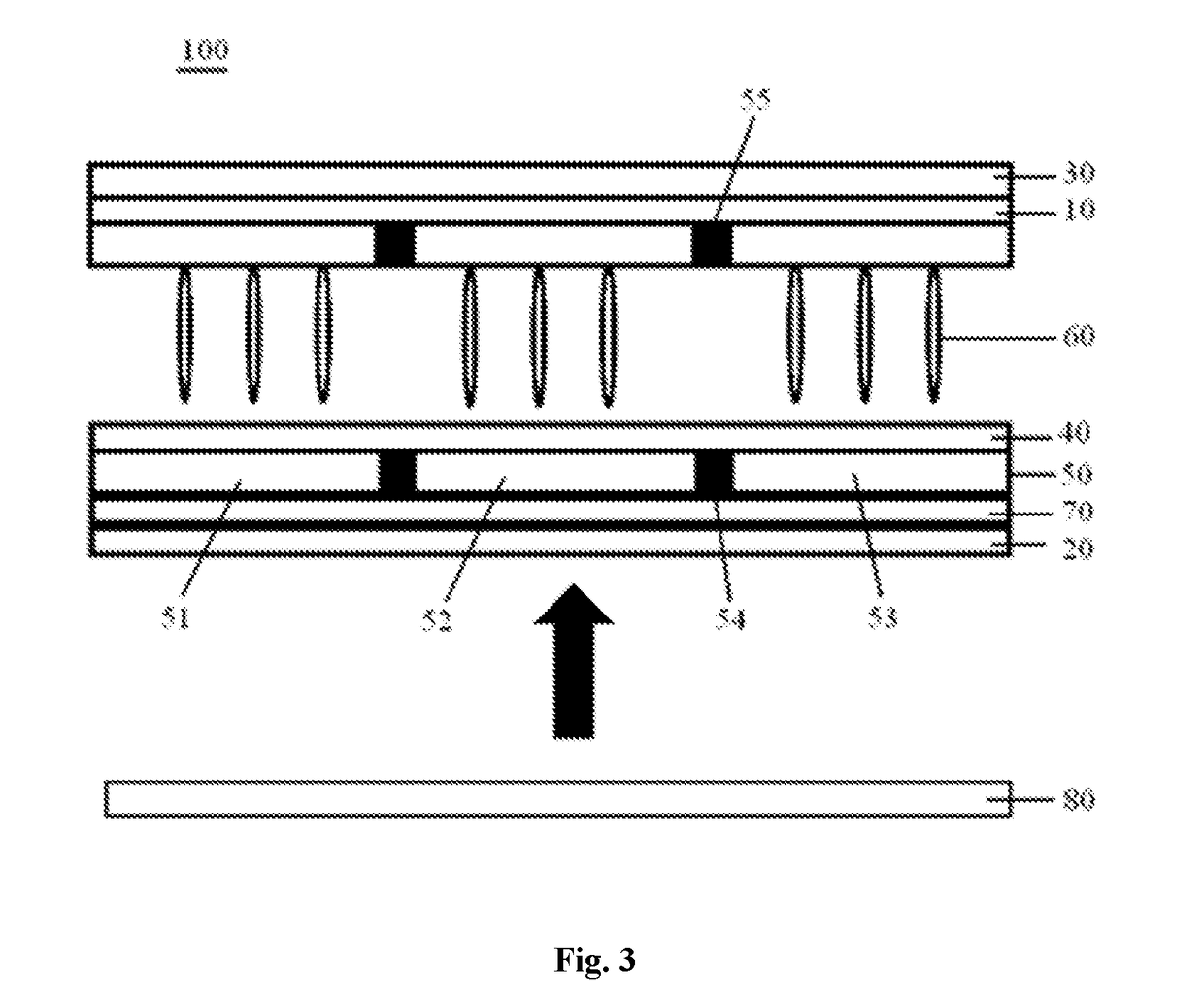
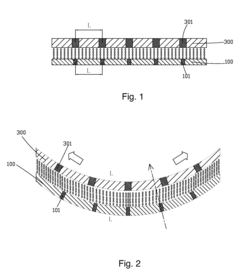
Liquid crystal display device
PatentInactiveUS20180157123A1
Innovation
- A liquid crystal display device design that includes a quantum-dot color film layer between the lower polarizing layer and the lower substrate, allowing incident light to first excite the quantum dots and form polarized light, enhancing color gamut and contrast, and using a second black matrix to resist external light disturbances.
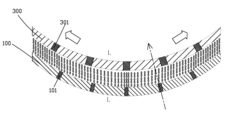
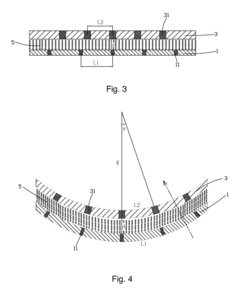
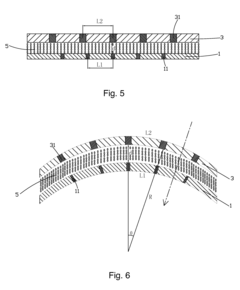
Curved liquid crystal panel
PatentInactiveUS20160041443A1
Innovation
- The gaps between data lines and the black matrix are set to have a proportional relation in flat state, ensuring radial coincidence in the curved state, maintaining pixel area matching between the TFT and CF substrates, with specific bending radius conditions for internal and external bending types.
Energy Efficiency Impact
When comparing Crystal UHD and QLED displays, energy efficiency is a crucial factor to consider, as it impacts both environmental sustainability and consumer costs. Crystal UHD technology, being a more traditional LED-LCD display, generally consumes less power compared to QLED displays. This is primarily due to the simpler backlighting system employed in Crystal UHD TVs.
QLED displays, on the other hand, utilize quantum dot technology to enhance color and brightness. While this results in superior picture quality, it often comes at the cost of increased power consumption. The quantum dots require additional energy to excite and emit light, leading to higher overall energy usage.
However, it's important to note that recent advancements in QLED technology have led to significant improvements in energy efficiency. Manufacturers have been focusing on developing more power-efficient quantum dot films and optimizing backlight control systems. These efforts have narrowed the gap in energy consumption between Crystal UHD and QLED displays.
The energy efficiency of both technologies can vary depending on the specific model and size of the display. Larger screens typically consume more power, regardless of the technology used. Additionally, the brightness settings chosen by the user can significantly impact energy consumption. QLED displays often have higher peak brightness capabilities, which can lead to increased power usage if utilized frequently.
When considering long-term usage, the energy efficiency of these displays can have a noticeable impact on electricity bills. Crystal UHD TVs may offer lower operating costs over time due to their generally lower power consumption. However, this advantage may be offset by the superior picture quality and potential longevity of QLED displays.
It's worth noting that both Crystal UHD and QLED technologies have made strides in implementing energy-saving features. These include automatic brightness adjustment based on ambient light conditions and power-saving modes that reduce energy consumption during periods of inactivity. Such features help mitigate the overall energy impact of these displays in real-world usage scenarios.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, manufacturers are likely to place even greater emphasis on improving the energy efficiency of both Crystal UHD and QLED displays. Future iterations of these technologies may see further reductions in power consumption while maintaining or even enhancing picture quality, potentially narrowing the energy efficiency gap between the two.
QLED displays, on the other hand, utilize quantum dot technology to enhance color and brightness. While this results in superior picture quality, it often comes at the cost of increased power consumption. The quantum dots require additional energy to excite and emit light, leading to higher overall energy usage.
However, it's important to note that recent advancements in QLED technology have led to significant improvements in energy efficiency. Manufacturers have been focusing on developing more power-efficient quantum dot films and optimizing backlight control systems. These efforts have narrowed the gap in energy consumption between Crystal UHD and QLED displays.
The energy efficiency of both technologies can vary depending on the specific model and size of the display. Larger screens typically consume more power, regardless of the technology used. Additionally, the brightness settings chosen by the user can significantly impact energy consumption. QLED displays often have higher peak brightness capabilities, which can lead to increased power usage if utilized frequently.
When considering long-term usage, the energy efficiency of these displays can have a noticeable impact on electricity bills. Crystal UHD TVs may offer lower operating costs over time due to their generally lower power consumption. However, this advantage may be offset by the superior picture quality and potential longevity of QLED displays.
It's worth noting that both Crystal UHD and QLED technologies have made strides in implementing energy-saving features. These include automatic brightness adjustment based on ambient light conditions and power-saving modes that reduce energy consumption during periods of inactivity. Such features help mitigate the overall energy impact of these displays in real-world usage scenarios.
As environmental concerns continue to grow, manufacturers are likely to place even greater emphasis on improving the energy efficiency of both Crystal UHD and QLED displays. Future iterations of these technologies may see further reductions in power consumption while maintaining or even enhancing picture quality, potentially narrowing the energy efficiency gap between the two.
Consumer Perception Study
Understanding consumer perception is crucial when comparing Crystal UHD and QLED technologies. A comprehensive study reveals significant insights into how consumers view and differentiate these display technologies.
Consumer awareness of Crystal UHD and QLED varies considerably. While QLED has gained substantial recognition due to Samsung's marketing efforts, Crystal UHD remains less familiar to the average consumer. This disparity in awareness directly impacts purchasing decisions and brand preferences.
When presented with both technologies, consumers generally perceive QLED as the superior option. This perception is largely driven by the association of QLED with premium features and higher price points. However, the study indicates that many consumers struggle to articulate the specific technical differences between Crystal UHD and QLED.
Visual quality is a key factor in consumer perception. In side-by-side comparisons, consumers tend to rate QLED displays higher in terms of color vibrancy, contrast, and overall picture quality. However, the difference in perceived quality diminishes when viewing content in typical home environments, suggesting that marketing and branding play a significant role in shaping consumer opinions.
Price sensitivity remains a crucial factor in consumer decision-making. While QLED is perceived as offering superior quality, many consumers express hesitation about paying the premium price associated with QLED technology. This creates an opportunity for Crystal UHD to position itself as a high-value alternative.
Brand loyalty significantly influences consumer perception. Samsung's strong brand presence in the QLED market creates a halo effect, with consumers often assuming superior quality based on brand association alone. This presents challenges for other manufacturers promoting Crystal UHD technology.
The study also reveals a knowledge gap among consumers regarding the technical aspects of both technologies. Many struggle to understand the fundamental differences between Crystal UHD and QLED, relying heavily on marketing materials and salesperson recommendations. This highlights the need for clearer, more accessible consumer education on display technologies.
Long-term reliability and durability concerns emerge as important factors in consumer perception. While QLED is often viewed as a more advanced technology, some consumers express uncertainty about its long-term performance compared to more established LCD-based technologies like Crystal UHD.
Consumer awareness of Crystal UHD and QLED varies considerably. While QLED has gained substantial recognition due to Samsung's marketing efforts, Crystal UHD remains less familiar to the average consumer. This disparity in awareness directly impacts purchasing decisions and brand preferences.
When presented with both technologies, consumers generally perceive QLED as the superior option. This perception is largely driven by the association of QLED with premium features and higher price points. However, the study indicates that many consumers struggle to articulate the specific technical differences between Crystal UHD and QLED.
Visual quality is a key factor in consumer perception. In side-by-side comparisons, consumers tend to rate QLED displays higher in terms of color vibrancy, contrast, and overall picture quality. However, the difference in perceived quality diminishes when viewing content in typical home environments, suggesting that marketing and branding play a significant role in shaping consumer opinions.
Price sensitivity remains a crucial factor in consumer decision-making. While QLED is perceived as offering superior quality, many consumers express hesitation about paying the premium price associated with QLED technology. This creates an opportunity for Crystal UHD to position itself as a high-value alternative.
Brand loyalty significantly influences consumer perception. Samsung's strong brand presence in the QLED market creates a halo effect, with consumers often assuming superior quality based on brand association alone. This presents challenges for other manufacturers promoting Crystal UHD technology.
The study also reveals a knowledge gap among consumers regarding the technical aspects of both technologies. Many struggle to understand the fundamental differences between Crystal UHD and QLED, relying heavily on marketing materials and salesperson recommendations. This highlights the need for clearer, more accessible consumer education on display technologies.
Long-term reliability and durability concerns emerge as important factors in consumer perception. While QLED is often viewed as a more advanced technology, some consumers express uncertainty about its long-term performance compared to more established LCD-based technologies like Crystal UHD.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!