Examining Patented Technologies in HDR10 vs Dolby Vision
OCT 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HDR Technology Evolution and Objectives
High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology represents a significant advancement in visual display capabilities, evolving from the limitations of Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) to deliver enhanced contrast, brightness, and color accuracy. The journey began in the early 2000s with research into expanded luminance ranges, but commercial implementation only gained momentum around 2014-2015 when display hardware capabilities caught up with theoretical concepts.
The evolution of HDR technology has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, basic HDR formats emerged with limited metadata and standardization. This was followed by the development of HDR10, which introduced static metadata and wider color gamut capabilities based on the Rec.2020 color space. The subsequent introduction of Dolby Vision represented a significant leap forward with dynamic metadata that could adjust brightness and color settings on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis.
The primary objective of HDR technology development has been to create more immersive and realistic viewing experiences by more closely replicating the human visual system's capabilities. The human eye can perceive approximately 14 stops of dynamic range simultaneously, while traditional SDR displays could only reproduce about 6-8 stops. HDR technologies aim to bridge this gap, allowing content to be displayed with greater fidelity to the creator's intent.
In the competitive landscape between HDR10 and Dolby Vision, several technical objectives have driven development. These include increasing peak brightness capabilities (from around 1,000 nits in early HDR10 to 10,000 nits in advanced Dolby Vision specifications), expanding color volume, improving tone mapping algorithms, and enhancing metadata handling for more precise image reproduction across different display capabilities.
Another critical objective has been backward compatibility with existing infrastructure and content, allowing for gradual adoption without rendering previous investments obsolete. This has influenced the development of technologies like HDR10+ which aimed to add dynamic metadata capabilities to the open HDR10 standard without requiring the licensing structure of Dolby Vision.
The patent landscape surrounding these technologies reveals distinct approaches to achieving similar visual outcomes. Dolby's extensive patent portfolio for Vision technology focuses heavily on dynamic metadata processing, efficient encoding methods, and display-specific optimization. Meanwhile, HDR10's development has been guided more by industry consortium efforts, with patents distributed across multiple stakeholders focusing on standardization and interoperability.
Looking forward, the technical objectives in HDR development are increasingly centered on computational efficiency, reduced bandwidth requirements, and adaptation to emerging display technologies like microLED and advanced OLED variants, while maintaining the core goal of delivering more lifelike visual experiences.
The evolution of HDR technology has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, basic HDR formats emerged with limited metadata and standardization. This was followed by the development of HDR10, which introduced static metadata and wider color gamut capabilities based on the Rec.2020 color space. The subsequent introduction of Dolby Vision represented a significant leap forward with dynamic metadata that could adjust brightness and color settings on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis.
The primary objective of HDR technology development has been to create more immersive and realistic viewing experiences by more closely replicating the human visual system's capabilities. The human eye can perceive approximately 14 stops of dynamic range simultaneously, while traditional SDR displays could only reproduce about 6-8 stops. HDR technologies aim to bridge this gap, allowing content to be displayed with greater fidelity to the creator's intent.
In the competitive landscape between HDR10 and Dolby Vision, several technical objectives have driven development. These include increasing peak brightness capabilities (from around 1,000 nits in early HDR10 to 10,000 nits in advanced Dolby Vision specifications), expanding color volume, improving tone mapping algorithms, and enhancing metadata handling for more precise image reproduction across different display capabilities.
Another critical objective has been backward compatibility with existing infrastructure and content, allowing for gradual adoption without rendering previous investments obsolete. This has influenced the development of technologies like HDR10+ which aimed to add dynamic metadata capabilities to the open HDR10 standard without requiring the licensing structure of Dolby Vision.
The patent landscape surrounding these technologies reveals distinct approaches to achieving similar visual outcomes. Dolby's extensive patent portfolio for Vision technology focuses heavily on dynamic metadata processing, efficient encoding methods, and display-specific optimization. Meanwhile, HDR10's development has been guided more by industry consortium efforts, with patents distributed across multiple stakeholders focusing on standardization and interoperability.
Looking forward, the technical objectives in HDR development are increasingly centered on computational efficiency, reduced bandwidth requirements, and adaptation to emerging display technologies like microLED and advanced OLED variants, while maintaining the core goal of delivering more lifelike visual experiences.
Market Demand Analysis for Premium HDR Formats
The global market for premium HDR (High Dynamic Range) formats has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for superior visual experiences across various entertainment platforms. As content creators and distributors strive to deliver more immersive and lifelike viewing experiences, HDR technologies—particularly HDR10 and Dolby Vision—have emerged as leading solutions in the premium display market.
Consumer electronics retailers report that HDR-capable televisions now represent over 80% of premium TV sales, with a growing percentage of consumers specifically seeking advanced formats like Dolby Vision when making purchasing decisions. This trend is particularly pronounced in North America, Western Europe, and developed Asian markets where consumers demonstrate willingness to pay premium prices for enhanced visual experiences.
The streaming service sector has become a significant driver of HDR adoption, with major platforms including Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, and Apple TV+ all expanding their HDR content libraries. Industry analysis indicates that HDR content consumption has grown at approximately 40% annually since 2019, outpacing standard content growth rates by a considerable margin.
Content creators, including major film studios and television production companies, are increasingly shooting and mastering content in HDR formats to future-proof their assets and meet distribution requirements across multiple platforms. This upstream adoption has created a positive feedback loop, further accelerating consumer demand for compatible display technologies.
The gaming industry represents another substantial growth vector for premium HDR formats. Next-generation gaming consoles and high-end PC graphics cards now universally support HDR rendering, with game developers leveraging these capabilities to enhance visual fidelity and competitive differentiation. Gaming-focused displays with HDR certification have seen sales growth exceeding the broader monitor market by significant margins.
Regional analysis reveals varying adoption rates, with North America leading in HDR-capable device penetration, followed by Western Europe and East Asia. Emerging markets show accelerating growth from a smaller base, suggesting substantial future expansion potential as device costs decrease and content availability increases.
Forecast models predict continued strong growth for premium HDR formats through 2028, with particular acceleration in mobile device implementation as smartphone manufacturers increasingly adopt HDR-capable displays in mid-range and premium devices. The automotive display market also shows promising adoption trends as vehicle manufacturers integrate advanced display technologies into infotainment and passenger entertainment systems.
Consumer electronics retailers report that HDR-capable televisions now represent over 80% of premium TV sales, with a growing percentage of consumers specifically seeking advanced formats like Dolby Vision when making purchasing decisions. This trend is particularly pronounced in North America, Western Europe, and developed Asian markets where consumers demonstrate willingness to pay premium prices for enhanced visual experiences.
The streaming service sector has become a significant driver of HDR adoption, with major platforms including Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, and Apple TV+ all expanding their HDR content libraries. Industry analysis indicates that HDR content consumption has grown at approximately 40% annually since 2019, outpacing standard content growth rates by a considerable margin.
Content creators, including major film studios and television production companies, are increasingly shooting and mastering content in HDR formats to future-proof their assets and meet distribution requirements across multiple platforms. This upstream adoption has created a positive feedback loop, further accelerating consumer demand for compatible display technologies.
The gaming industry represents another substantial growth vector for premium HDR formats. Next-generation gaming consoles and high-end PC graphics cards now universally support HDR rendering, with game developers leveraging these capabilities to enhance visual fidelity and competitive differentiation. Gaming-focused displays with HDR certification have seen sales growth exceeding the broader monitor market by significant margins.
Regional analysis reveals varying adoption rates, with North America leading in HDR-capable device penetration, followed by Western Europe and East Asia. Emerging markets show accelerating growth from a smaller base, suggesting substantial future expansion potential as device costs decrease and content availability increases.
Forecast models predict continued strong growth for premium HDR formats through 2028, with particular acceleration in mobile device implementation as smartphone manufacturers increasingly adopt HDR-capable displays in mid-range and premium devices. The automotive display market also shows promising adoption trends as vehicle manufacturers integrate advanced display technologies into infotainment and passenger entertainment systems.
Current HDR Standards Landscape and Technical Barriers
The current HDR (High Dynamic Range) landscape is characterized by several competing standards, with HDR10 and Dolby Vision emerging as the two dominant technologies. HDR10, as an open standard, has gained widespread adoption across the industry due to its royalty-free nature and relatively straightforward implementation requirements. It utilizes static metadata that remains constant throughout content playback, providing a single set of instructions for display optimization.
In contrast, Dolby Vision represents a proprietary standard developed by Dolby Laboratories, implementing dynamic metadata that can adjust brightness, contrast, and color settings on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis. This technical approach allows for potentially superior image quality but requires more sophisticated processing capabilities and licensing agreements.
A significant technical barrier in the HDR ecosystem is the fragmentation of standards, creating implementation challenges for content creators and device manufacturers. Content must often be mastered multiple times to accommodate different HDR formats, increasing production costs and complexity. This fragmentation extends to consumer devices, where varying levels of HDR support create inconsistent viewing experiences across different platforms.
Hardware limitations present another substantial barrier, particularly for budget and mid-range displays that may lack the necessary brightness capabilities (measured in nits) to fully realize HDR content as intended. While premium displays can reach 1,000-2,000 nits or higher, many consumer-grade screens struggle to exceed 500-600 nits, compromising the HDR experience.
The technical complexity of HDR implementation also creates barriers for smaller manufacturers. Dolby Vision, with its sophisticated dynamic metadata approach, requires specialized hardware and software integration, along with licensing fees that may be prohibitive for some market segments. This has led to uneven adoption across the industry, with premium brands embracing comprehensive HDR support while budget options often limit implementation to basic HDR10.
Content delivery infrastructure presents additional challenges, as bandwidth limitations can constrain the delivery of high-bitrate HDR content, particularly in regions with less developed broadband infrastructure. The increased data requirements for HDR content delivery must be balanced against practical bandwidth constraints, often resulting in compression compromises that can diminish the intended visual experience.
Standardization efforts continue to evolve, with HDR10+ emerging as an attempt to bridge the gap between HDR10's accessibility and Dolby Vision's performance capabilities. However, the patent landscape surrounding these technologies creates complex licensing considerations that influence adoption decisions throughout the industry.
In contrast, Dolby Vision represents a proprietary standard developed by Dolby Laboratories, implementing dynamic metadata that can adjust brightness, contrast, and color settings on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis. This technical approach allows for potentially superior image quality but requires more sophisticated processing capabilities and licensing agreements.
A significant technical barrier in the HDR ecosystem is the fragmentation of standards, creating implementation challenges for content creators and device manufacturers. Content must often be mastered multiple times to accommodate different HDR formats, increasing production costs and complexity. This fragmentation extends to consumer devices, where varying levels of HDR support create inconsistent viewing experiences across different platforms.
Hardware limitations present another substantial barrier, particularly for budget and mid-range displays that may lack the necessary brightness capabilities (measured in nits) to fully realize HDR content as intended. While premium displays can reach 1,000-2,000 nits or higher, many consumer-grade screens struggle to exceed 500-600 nits, compromising the HDR experience.
The technical complexity of HDR implementation also creates barriers for smaller manufacturers. Dolby Vision, with its sophisticated dynamic metadata approach, requires specialized hardware and software integration, along with licensing fees that may be prohibitive for some market segments. This has led to uneven adoption across the industry, with premium brands embracing comprehensive HDR support while budget options often limit implementation to basic HDR10.
Content delivery infrastructure presents additional challenges, as bandwidth limitations can constrain the delivery of high-bitrate HDR content, particularly in regions with less developed broadband infrastructure. The increased data requirements for HDR content delivery must be balanced against practical bandwidth constraints, often resulting in compression compromises that can diminish the intended visual experience.
Standardization efforts continue to evolve, with HDR10+ emerging as an attempt to bridge the gap between HDR10's accessibility and Dolby Vision's performance capabilities. However, the patent landscape surrounding these technologies creates complex licensing considerations that influence adoption decisions throughout the industry.
Technical Implementation Approaches of HDR10 and Dolby Vision
01 HDR10 and Dolby Vision display technologies
High Dynamic Range (HDR10) and Dolby Vision are advanced display technologies that enhance visual content by providing greater brightness, contrast, and color accuracy. These technologies allow for more realistic and immersive viewing experiences by expanding the range of colors and luminance levels that can be displayed. Devices supporting these standards can process and display content with higher bit depth and wider color gamut than traditional displays.- HDR10 and Dolby Vision display technologies: High Dynamic Range (HDR10) and Dolby Vision are advanced display technologies that enhance video content by providing greater brightness, contrast, and color accuracy. These technologies allow for more realistic and immersive viewing experiences by supporting a wider range of colors and luminance levels than standard dynamic range displays. The implementation of these technologies in displays requires specific hardware and software configurations to properly render the enhanced content.
- Content encoding and processing for HDR formats: The encoding and processing of content for HDR10 and Dolby Vision formats involves specialized algorithms and methods to capture, convert, and optimize high dynamic range data. This includes techniques for tone mapping, color grading, and metadata handling that ensure the content maintains its visual quality across different display capabilities. These processes are essential for creating compatible content that can take full advantage of the enhanced capabilities offered by HDR display technologies.
- HDR signal transmission and compatibility: The transmission of HDR signals, including both HDR10 and Dolby Vision formats, requires specific protocols and standards to ensure compatibility across different devices and platforms. This includes methods for embedding metadata within the video signal, handling bandwidth constraints, and ensuring backward compatibility with standard dynamic range displays. These transmission technologies enable the seamless delivery of high-quality HDR content to end users.
- HDR-compatible hardware implementations: Hardware implementations for supporting HDR10 and Dolby Vision include specialized components and architectures in displays, processors, and media players. These hardware solutions are designed to efficiently decode, process, and render HDR content with the appropriate brightness, contrast, and color accuracy. The hardware must be capable of interpreting the metadata associated with HDR content and adjusting display parameters accordingly to deliver the intended visual experience.
- Dynamic range optimization techniques: Dynamic range optimization techniques for HDR10 and Dolby Vision involve methods for analyzing and adjusting content to maximize visual quality across different viewing conditions and display capabilities. These techniques include adaptive tone mapping, local contrast enhancement, and brightness adjustment algorithms that can optimize the presentation of HDR content in real-time. Such optimizations ensure that viewers experience the best possible image quality regardless of their specific display technology or viewing environment.
02 Implementation of HDR content processing systems
Systems for processing HDR content involve specialized hardware and software components that can encode, decode, and display high dynamic range video signals. These systems include processors capable of handling the increased data requirements of HDR formats, color mapping algorithms, and tone mapping techniques to adapt content for different display capabilities. The processing systems ensure compatibility between various HDR standards and optimize content for specific viewing environments.Expand Specific Solutions03 HDR signal transmission and compatibility solutions
Transmission of HDR signals requires specialized protocols and interfaces to maintain the integrity of the enhanced visual data. These solutions address challenges in bandwidth management, signal compression, and ensuring backward compatibility with standard dynamic range (SDR) displays. Technologies include adaptive bit rate streaming for HDR content, metadata handling for dynamic range information, and conversion methods between different HDR formats to ensure content can be properly displayed across various devices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Enhanced color management for HDR displays
Color management systems for HDR displays involve sophisticated algorithms and hardware solutions that accurately reproduce the expanded color gamut and luminance range of HDR content. These systems include color space conversion, gamut mapping, and calibration techniques specific to HDR10 and Dolby Vision standards. Advanced color processing ensures that the wider color spectrum available in HDR content is faithfully represented on compatible displays, providing viewers with more vibrant and lifelike images.Expand Specific Solutions05 User interface and control systems for HDR content
User interface and control systems designed for HDR content provide viewers with tools to optimize their viewing experience. These systems include on-screen display menus with HDR-specific settings, automatic content detection and mode switching, and user preference profiles for different types of HDR content. Control systems may also include ambient light sensing to adjust HDR parameters based on viewing conditions, ensuring optimal image quality regardless of the environment.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in HDR Technology Ecosystem
The HDR10 vs Dolby Vision technology landscape is currently in a mature growth phase, with the global HDR market expected to reach $36.7 billion by 2027. Dolby Laboratories maintains dominant positioning in premium HDR with its proprietary Dolby Vision technology, while Samsung leads the open-standard HDR10+ development. The competitive field includes major technology players like Microsoft, Google, Apple, and Sony who have invested significantly in HDR patent portfolios. Chinese manufacturers including Huawei, OPPO, and Skyworth are rapidly expanding their HDR capabilities. The ecosystem shows technological maturity with established implementation across consumer electronics, though innovation continues in dynamic metadata processing, display calibration, and content creation workflows.
Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp.
Technical Solution: Dolby Vision represents Dolby's proprietary HDR technology that utilizes dynamic metadata to optimize picture quality on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis. The technology supports up to 12-bit color depth, allowing for over 68 billion colors, and can achieve peak brightness levels of up to 10,000 nits[1]. Dolby Vision's patented technology includes advanced color grading tools that enable content creators to preserve their creative intent across different display capabilities. The system employs a dual-layer approach where a base HDR10 layer is complemented by an enhancement layer containing dynamic metadata for Dolby Vision-enabled displays[2]. This metadata includes instructions for how each scene should be displayed regarding brightness, color, and contrast, ensuring optimal viewing experience across various hardware specifications.
Strengths: Superior image quality with dynamic metadata allowing scene-by-scene optimization; wider color gamut and higher brightness capabilities; better preservation of creative intent across different displays. Weaknesses: Requires licensing fees for manufacturers; more complex implementation; limited content availability compared to open standards; requires compatible hardware throughout the chain.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has developed HDR10+ as its answer to Dolby Vision, building upon the open HDR10 standard. HDR10+ incorporates dynamic metadata similar to Dolby Vision but maintains an open, royalty-free licensing model[3]. Samsung's patented technologies in this space include methods for tone mapping optimization that adjust brightness levels dynamically based on display capabilities and ambient lighting conditions. Their implementation includes scene-by-scene brightness adjustment algorithms that analyze content characteristics to determine optimal luminance levels[4]. Samsung has also developed specific color processing technologies that enhance the rendering of HDR content on their quantum dot displays, with patents covering the conversion between different color spaces while preserving the expanded color gamut of HDR content[5]. Their technology includes backward compatibility features that allow HDR10+ content to be displayed on standard HDR10 devices.
Strengths: Royalty-free licensing model encouraging wider adoption; strong hardware integration with Samsung's display technologies; growing content partnerships with streaming services. Weaknesses: Less established than Dolby Vision in professional content creation workflows; potentially less consistent implementation across different manufacturers; slightly lower theoretical specifications than Dolby Vision.
Patent Analysis of Core HDR Technologies
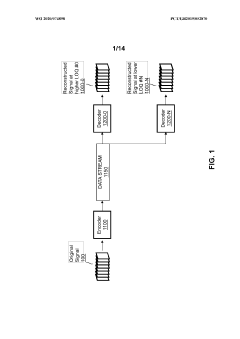
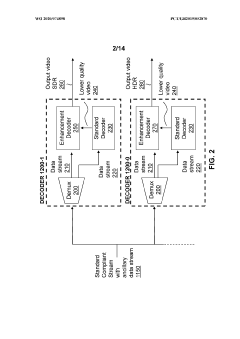
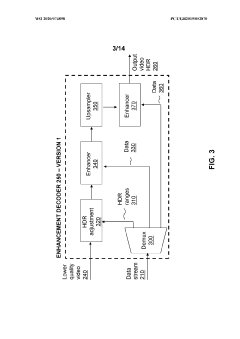
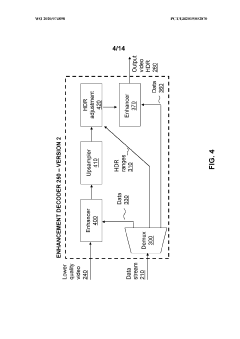
Enhancement decoder for video signals with multi-level enhancement and coding format adjustment
PatentWO2020074898A1
Innovation
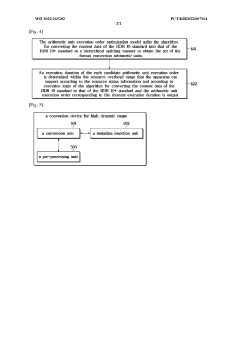
- A hierarchical coding scheme that allows for the encoding and decoding of HDR-type signals to be compatible with both HDR and SDR displays, using an enhancement decoder that includes an interface for receiving video streams, de-multiplexing enhancement data, and a coding format adjustment module to convert between different bit lengths and resolutions, ensuring backwards compatibility and flexibility in signal processing.
Conversion method and device for high dynamic range format
PatentWO2022265282A1
Innovation
- A conversion method and device that split the HDR10 to HDR10+ algorithm into hierarchical arithmetic units and determine an execution order to minimize processing duration, allowing for concurrent processing and reduced power consumption.
Content Creation Workflow Comparison
The content creation workflows for HDR10 and Dolby Vision represent significantly different approaches to high dynamic range video production, with distinct implications for creators, studios, and post-production facilities.
HDR10 employs a relatively straightforward workflow that utilizes static metadata throughout the entire content. Content creators establish key parameters such as maximum brightness, color primaries, and transfer characteristics once for the entire program. This approach offers simplicity and efficiency, particularly beneficial for productions with limited resources or tight deadlines. The mastering process typically involves color grading on HDR-capable monitors that support at least 1,000 nits of peak brightness, with the final output conforming to the HDR10 specification.
In contrast, Dolby Vision implements a more sophisticated dual-layer production pipeline. The workflow begins with creating a high-quality master that serves as the foundation for all deliverables. Unique to Dolby Vision is the dynamic metadata generation process, where scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame analysis occurs to optimize HDR presentation. This requires specialized tools like the Dolby Vision Content Mapping Unit (CMU) or software equivalents integrated into color grading systems.
Patent analysis reveals that Dolby holds significant intellectual property around dynamic metadata processing (US9685120B2, US9685139B2), which enables real-time content optimization based on display capabilities. HDR10, being an open standard, relies on fewer patented technologies, though Samsung and other manufacturers hold patents related to tone mapping implementations (US9961156B2).
The divergence in workflows creates notable production implications. Dolby Vision productions typically require 20-30% more time for post-production compared to HDR10-only workflows, primarily due to the additional metadata creation and quality control processes. However, this investment enables greater creative control and display-specific optimization.
For studios producing content for multiple distribution channels, the recommended approach has evolved toward a "single master" workflow. This involves creating a Dolby Vision master first, from which HDR10 versions can be automatically derived. This strategy, supported by patents like US10341632B2, allows content creators to maximize efficiency while maintaining quality across different HDR formats.
The technical complexity difference between these workflows has significant implications for adoption rates, with smaller production houses often favoring HDR10's simpler implementation path despite Dolby Vision's superior technical capabilities and creative flexibility.
HDR10 employs a relatively straightforward workflow that utilizes static metadata throughout the entire content. Content creators establish key parameters such as maximum brightness, color primaries, and transfer characteristics once for the entire program. This approach offers simplicity and efficiency, particularly beneficial for productions with limited resources or tight deadlines. The mastering process typically involves color grading on HDR-capable monitors that support at least 1,000 nits of peak brightness, with the final output conforming to the HDR10 specification.
In contrast, Dolby Vision implements a more sophisticated dual-layer production pipeline. The workflow begins with creating a high-quality master that serves as the foundation for all deliverables. Unique to Dolby Vision is the dynamic metadata generation process, where scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame analysis occurs to optimize HDR presentation. This requires specialized tools like the Dolby Vision Content Mapping Unit (CMU) or software equivalents integrated into color grading systems.
Patent analysis reveals that Dolby holds significant intellectual property around dynamic metadata processing (US9685120B2, US9685139B2), which enables real-time content optimization based on display capabilities. HDR10, being an open standard, relies on fewer patented technologies, though Samsung and other manufacturers hold patents related to tone mapping implementations (US9961156B2).
The divergence in workflows creates notable production implications. Dolby Vision productions typically require 20-30% more time for post-production compared to HDR10-only workflows, primarily due to the additional metadata creation and quality control processes. However, this investment enables greater creative control and display-specific optimization.
For studios producing content for multiple distribution channels, the recommended approach has evolved toward a "single master" workflow. This involves creating a Dolby Vision master first, from which HDR10 versions can be automatically derived. This strategy, supported by patents like US10341632B2, allows content creators to maximize efficiency while maintaining quality across different HDR formats.
The technical complexity difference between these workflows has significant implications for adoption rates, with smaller production houses often favoring HDR10's simpler implementation path despite Dolby Vision's superior technical capabilities and creative flexibility.
Licensing Models and Cost Implications
The licensing landscape for HDR technologies represents a critical consideration for manufacturers and content creators navigating the HDR10 versus Dolby Vision decision. HDR10, as an open standard developed by the Consumer Technology Association, operates under a royalty-free licensing model. This approach significantly reduces implementation costs for manufacturers, as they can incorporate HDR10 capabilities into their devices without paying ongoing licensing fees to a specific technology owner.
In stark contrast, Dolby Vision employs a proprietary licensing model that requires manufacturers to pay both implementation fees and per-unit royalties. According to industry reports, these fees typically range between $2-3 per device, creating a substantial cost differential when scaled across mass-market production. For television manufacturers operating on thin margins, this additional expense can significantly impact product pricing strategies and overall profitability.
Content creators face a different set of licensing considerations. Studios producing content in Dolby Vision must invest in certified equipment and potentially pay content encoding fees. The Dolby Vision workflow requires specialized tools and quality control processes that add to production costs. Meanwhile, HDR10 content creation involves substantially lower licensing burdens, though it may require additional technical expertise to achieve optimal results without Dolby's automated tools.
The patent portfolios underlying these technologies reveal significant differences in protection scope. Dolby maintains a robust portfolio of over 100 patents specifically covering their Vision technology, creating a comprehensive protection framework that enables their premium pricing strategy. HDR10's open standard nature means its core technologies are either unpatented or covered by patents with reasonable and non-discriminatory (RAND) licensing terms.
For ecosystem participants, these licensing models create divergent incentives. The HDR10+ initiative, backed by Samsung and other manufacturers, emerged partly as a response to Dolby Vision's licensing costs. This alternative advanced HDR format maintains the royalty-free approach while adding some dynamic metadata capabilities similar to Dolby Vision.
The long-term cost implications extend beyond direct licensing fees. Manufacturers must consider certification costs, implementation engineering resources, and ongoing compliance requirements. Dolby Vision implementers must pass certification processes and maintain compatibility with Dolby's evolving specifications, representing hidden costs beyond the headline licensing fees.
In stark contrast, Dolby Vision employs a proprietary licensing model that requires manufacturers to pay both implementation fees and per-unit royalties. According to industry reports, these fees typically range between $2-3 per device, creating a substantial cost differential when scaled across mass-market production. For television manufacturers operating on thin margins, this additional expense can significantly impact product pricing strategies and overall profitability.
Content creators face a different set of licensing considerations. Studios producing content in Dolby Vision must invest in certified equipment and potentially pay content encoding fees. The Dolby Vision workflow requires specialized tools and quality control processes that add to production costs. Meanwhile, HDR10 content creation involves substantially lower licensing burdens, though it may require additional technical expertise to achieve optimal results without Dolby's automated tools.
The patent portfolios underlying these technologies reveal significant differences in protection scope. Dolby maintains a robust portfolio of over 100 patents specifically covering their Vision technology, creating a comprehensive protection framework that enables their premium pricing strategy. HDR10's open standard nature means its core technologies are either unpatented or covered by patents with reasonable and non-discriminatory (RAND) licensing terms.
For ecosystem participants, these licensing models create divergent incentives. The HDR10+ initiative, backed by Samsung and other manufacturers, emerged partly as a response to Dolby Vision's licensing costs. This alternative advanced HDR format maintains the royalty-free approach while adding some dynamic metadata capabilities similar to Dolby Vision.
The long-term cost implications extend beyond direct licensing fees. Manufacturers must consider certification costs, implementation engineering resources, and ongoing compliance requirements. Dolby Vision implementers must pass certification processes and maintain compatibility with Dolby's evolving specifications, representing hidden costs beyond the headline licensing fees.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!