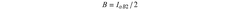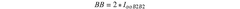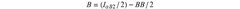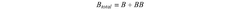Exploring Integration of Recycled Polypropylene in Home Product Design
JUL 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Recycled PP Integration Background and Objectives
The integration of recycled polypropylene (PP) in home product design represents a significant shift towards sustainable manufacturing practices in the consumer goods industry. This technological evolution is driven by increasing environmental concerns, regulatory pressures, and consumer demand for eco-friendly products. The journey of recycled PP in home products traces back to the early 2000s when recycling technologies for plastics began to mature, allowing for the reprocessing of post-consumer PP into usable raw materials.
As awareness of plastic pollution grew, the home products sector recognized the potential of recycled PP to reduce environmental impact while maintaining product quality. The initial focus was on incorporating small percentages of recycled content, gradually increasing as processing techniques improved. This progression has led to the current objective of maximizing recycled PP content in home products without compromising performance or aesthetics.
The primary goal of integrating recycled PP into home product design is to create a circular economy for plastics, reducing reliance on virgin materials and minimizing waste. This aligns with broader sustainability initiatives and supports companies in meeting their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) targets. Additionally, it aims to address consumer preferences for environmentally responsible products, potentially opening new market segments and enhancing brand reputation.
From a technical perspective, the objectives include developing processing methods that can handle the variability in recycled PP feedstock, ensuring consistent quality and performance in final products. This involves overcoming challenges such as color consistency, mechanical properties, and odor control associated with recycled materials. Research efforts are focused on improving sorting and cleaning technologies to produce higher quality recycled PP, as well as developing additives and compatibilizers to enhance the properties of recycled PP compounds.
The integration of recycled PP also aims to drive innovation in product design, encouraging the creation of products specifically engineered to utilize recycled materials effectively. This includes exploring new design paradigms that capitalize on the unique characteristics of recycled PP, such as textured surfaces or color variations that can be marketed as features rather than flaws.
Furthermore, there is a push to establish industry standards and certifications for recycled content in home products, providing transparency and credibility to consumers. This objective extends to developing robust supply chains for recycled PP, ensuring a steady and reliable source of high-quality recycled materials for manufacturers.
As awareness of plastic pollution grew, the home products sector recognized the potential of recycled PP to reduce environmental impact while maintaining product quality. The initial focus was on incorporating small percentages of recycled content, gradually increasing as processing techniques improved. This progression has led to the current objective of maximizing recycled PP content in home products without compromising performance or aesthetics.
The primary goal of integrating recycled PP into home product design is to create a circular economy for plastics, reducing reliance on virgin materials and minimizing waste. This aligns with broader sustainability initiatives and supports companies in meeting their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) targets. Additionally, it aims to address consumer preferences for environmentally responsible products, potentially opening new market segments and enhancing brand reputation.
From a technical perspective, the objectives include developing processing methods that can handle the variability in recycled PP feedstock, ensuring consistent quality and performance in final products. This involves overcoming challenges such as color consistency, mechanical properties, and odor control associated with recycled materials. Research efforts are focused on improving sorting and cleaning technologies to produce higher quality recycled PP, as well as developing additives and compatibilizers to enhance the properties of recycled PP compounds.
The integration of recycled PP also aims to drive innovation in product design, encouraging the creation of products specifically engineered to utilize recycled materials effectively. This includes exploring new design paradigms that capitalize on the unique characteristics of recycled PP, such as textured surfaces or color variations that can be marketed as features rather than flaws.
Furthermore, there is a push to establish industry standards and certifications for recycled content in home products, providing transparency and credibility to consumers. This objective extends to developing robust supply chains for recycled PP, ensuring a steady and reliable source of high-quality recycled materials for manufacturers.
Market Demand for Sustainable Home Products
The market demand for sustainable home products has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by growing environmental awareness and consumer preferences for eco-friendly options. This trend has created significant opportunities for integrating recycled polypropylene into home product design. Consumers are increasingly seeking products that align with their values of sustainability and environmental responsibility, leading to a shift in purchasing behaviors towards more sustainable alternatives.
Recycled polypropylene, as a versatile and durable material, has gained traction in the home products sector due to its potential to reduce plastic waste and lower carbon footprints. The demand for sustainable home products spans various categories, including kitchenware, storage solutions, furniture, and decorative items. Market research indicates that consumers are willing to pay a premium for products made from recycled materials, with some studies suggesting a price tolerance of up to 20% higher for sustainable options.
The global market for sustainable home products has been expanding rapidly, with projections indicating continued growth in the coming years. This growth is fueled by both consumer demand and regulatory pressures aimed at reducing plastic waste and promoting circular economy principles. Major retailers and e-commerce platforms have responded to this trend by increasing their offerings of sustainable home products, further driving market expansion and accessibility.
In the context of recycled polypropylene, its integration into home product design addresses several key consumer concerns. These include reducing plastic waste, minimizing environmental impact, and supporting circular economy initiatives. Products made from recycled polypropylene often appeal to environmentally conscious consumers who seek to reduce their personal environmental footprint without compromising on product quality or functionality.
The market demand is further bolstered by the growing emphasis on transparency and traceability in product sourcing and manufacturing. Consumers are increasingly interested in understanding the origin of materials used in their home products and the environmental impact of their choices. This has led to a rise in eco-labeling and certification programs that highlight the use of recycled materials, including recycled polypropylene, in home products.
However, challenges remain in fully realizing the market potential for recycled polypropylene in home products. These include ensuring consistent quality and supply of recycled materials, addressing consumer perceptions about the aesthetics and durability of recycled products, and navigating the complex landscape of recycling regulations and standards across different regions. Overcoming these challenges will be crucial for manufacturers and designers looking to capitalize on the growing market demand for sustainable home products incorporating recycled polypropylene.
Recycled polypropylene, as a versatile and durable material, has gained traction in the home products sector due to its potential to reduce plastic waste and lower carbon footprints. The demand for sustainable home products spans various categories, including kitchenware, storage solutions, furniture, and decorative items. Market research indicates that consumers are willing to pay a premium for products made from recycled materials, with some studies suggesting a price tolerance of up to 20% higher for sustainable options.
The global market for sustainable home products has been expanding rapidly, with projections indicating continued growth in the coming years. This growth is fueled by both consumer demand and regulatory pressures aimed at reducing plastic waste and promoting circular economy principles. Major retailers and e-commerce platforms have responded to this trend by increasing their offerings of sustainable home products, further driving market expansion and accessibility.
In the context of recycled polypropylene, its integration into home product design addresses several key consumer concerns. These include reducing plastic waste, minimizing environmental impact, and supporting circular economy initiatives. Products made from recycled polypropylene often appeal to environmentally conscious consumers who seek to reduce their personal environmental footprint without compromising on product quality or functionality.
The market demand is further bolstered by the growing emphasis on transparency and traceability in product sourcing and manufacturing. Consumers are increasingly interested in understanding the origin of materials used in their home products and the environmental impact of their choices. This has led to a rise in eco-labeling and certification programs that highlight the use of recycled materials, including recycled polypropylene, in home products.
However, challenges remain in fully realizing the market potential for recycled polypropylene in home products. These include ensuring consistent quality and supply of recycled materials, addressing consumer perceptions about the aesthetics and durability of recycled products, and navigating the complex landscape of recycling regulations and standards across different regions. Overcoming these challenges will be crucial for manufacturers and designers looking to capitalize on the growing market demand for sustainable home products incorporating recycled polypropylene.
Recycled PP Technical Challenges in Home Design
The integration of recycled polypropylene (PP) in home product design presents several technical challenges that manufacturers and designers must overcome. One of the primary issues is the variability in the quality and composition of recycled PP. Unlike virgin PP, recycled materials often contain a mix of different grades and types of PP, as well as potential contaminants from previous use or the recycling process itself. This heterogeneity can lead to inconsistencies in the material properties, making it difficult to achieve uniform performance across batches.
Another significant challenge is the degradation of mechanical properties in recycled PP. The polymer chains in PP can break down during the recycling process, resulting in a material with reduced strength, impact resistance, and durability compared to virgin PP. This degradation can be particularly problematic for home products that require high structural integrity or are subject to frequent use and stress.
Color consistency is also a major hurdle when working with recycled PP. The mixed sources of recycled materials often result in a grayish or off-white base color, which can be difficult to dye or pigment accurately. This limitation can restrict the aesthetic options for home product designs, potentially compromising the visual appeal that is crucial in consumer goods.
The presence of odors in recycled PP poses another challenge, especially for products used in close proximity to users, such as kitchenware or furniture. These odors can be a result of residual contaminants or the breakdown of additives during the recycling and reprocessing stages. Eliminating or masking these odors without using harmful chemicals is a complex task that requires innovative solutions.
Furthermore, the thermal stability of recycled PP can be compromised, affecting its processing window during manufacturing. This narrower processing range can lead to difficulties in molding and forming complex shapes, which are often required in home product design. It may also result in increased production costs due to the need for more precise temperature control and specialized equipment.
Lastly, ensuring the safety and regulatory compliance of products made from recycled PP is a significant challenge. Home products, especially those that come into contact with food or are used by children, must meet stringent safety standards. The potential presence of unknown additives or contaminants in recycled PP can make it challenging to guarantee consistent compliance with these regulations across all production batches.
Another significant challenge is the degradation of mechanical properties in recycled PP. The polymer chains in PP can break down during the recycling process, resulting in a material with reduced strength, impact resistance, and durability compared to virgin PP. This degradation can be particularly problematic for home products that require high structural integrity or are subject to frequent use and stress.
Color consistency is also a major hurdle when working with recycled PP. The mixed sources of recycled materials often result in a grayish or off-white base color, which can be difficult to dye or pigment accurately. This limitation can restrict the aesthetic options for home product designs, potentially compromising the visual appeal that is crucial in consumer goods.
The presence of odors in recycled PP poses another challenge, especially for products used in close proximity to users, such as kitchenware or furniture. These odors can be a result of residual contaminants or the breakdown of additives during the recycling and reprocessing stages. Eliminating or masking these odors without using harmful chemicals is a complex task that requires innovative solutions.
Furthermore, the thermal stability of recycled PP can be compromised, affecting its processing window during manufacturing. This narrower processing range can lead to difficulties in molding and forming complex shapes, which are often required in home product design. It may also result in increased production costs due to the need for more precise temperature control and specialized equipment.
Lastly, ensuring the safety and regulatory compliance of products made from recycled PP is a significant challenge. Home products, especially those that come into contact with food or are used by children, must meet stringent safety standards. The potential presence of unknown additives or contaminants in recycled PP can make it challenging to guarantee consistent compliance with these regulations across all production batches.
Current Solutions for Recycled PP Integration
01 Recycling processes for polypropylene
Various methods and processes for recycling polypropylene are developed to improve the quality and properties of recycled material. These processes may include sorting, cleaning, melting, and reforming the recycled polypropylene into new products or materials. Advanced techniques such as chemical recycling or compatibilization may be employed to enhance the recycled polypropylene's performance.- Recycling processes for polypropylene: Various methods and processes for recycling polypropylene are developed to improve the quality and properties of recycled material. These processes may include sorting, cleaning, melting, and reforming the recycled polypropylene into new products or materials. Advanced techniques such as chemical recycling or compatibilization may be employed to enhance the recycled polypropylene's performance.
- Blending recycled polypropylene with virgin materials: To improve the properties of recycled polypropylene, it is often blended with virgin polypropylene or other compatible materials. This approach helps to maintain or enhance the mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties of the final product. The blending ratios and techniques are optimized to achieve desired characteristics for specific applications.
- Additives and modifiers for recycled polypropylene: Various additives and modifiers are used to enhance the properties of recycled polypropylene. These may include stabilizers, compatibilizers, reinforcing agents, or impact modifiers. The additives help to improve the material's durability, processability, and overall performance, making it more suitable for a wider range of applications.
- Applications of recycled polypropylene: Recycled polypropylene finds applications in various industries, including automotive, packaging, construction, and consumer goods. The material is used to manufacture products such as automotive parts, containers, furniture, and textiles. Ongoing research focuses on expanding the use of recycled polypropylene in high-value applications to promote circular economy principles.
- Quality control and characterization of recycled polypropylene: Techniques and methods for quality control and characterization of recycled polypropylene are developed to ensure consistent performance and properties. These may include advanced analytical methods, testing protocols, and standardization efforts to assess the material's mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties. Such measures help to increase confidence in the use of recycled polypropylene across various industries.
02 Blending recycled polypropylene with virgin materials
Recycled polypropylene is often blended with virgin polypropylene or other polymers to improve its mechanical properties and overall quality. This approach allows for the incorporation of recycled content while maintaining desired performance characteristics. The blending ratios and techniques are optimized to achieve specific material properties suitable for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Additives and compatibilizers for recycled polypropylene
Various additives and compatibilizers are used to enhance the properties of recycled polypropylene. These may include stabilizers, antioxidants, UV protectors, and coupling agents. Such additives help improve the mechanical strength, thermal stability, and overall performance of recycled polypropylene, making it more suitable for a wider range of applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Applications of recycled polypropylene
Recycled polypropylene finds applications in various industries, including automotive, packaging, construction, and consumer goods. It can be used to manufacture products such as automotive parts, containers, furniture, and textiles. The development of new applications for recycled polypropylene helps increase its demand and promotes a circular economy approach.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quality control and characterization of recycled polypropylene
Methods for quality control and characterization of recycled polypropylene are crucial for ensuring its suitability for different applications. These may include techniques for assessing mechanical properties, thermal behavior, molecular weight distribution, and contamination levels. Advanced analytical methods are employed to verify the consistency and reliability of recycled polypropylene materials.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Recycled PP Home Product Industry
The integration of recycled polypropylene in home product design is gaining traction in the mature plastics industry, driven by sustainability concerns and circular economy initiatives. The market for recycled plastics is expanding, with a projected global market size of $72.6 billion by 2026. Major players like SABIC, Borealis, and Total Petrochemicals are investing in advanced recycling technologies to improve the quality and performance of recycled polypropylene. Companies such as Electrolux and Gree Electric Appliances are exploring ways to incorporate recycled materials into their home appliances, while research institutions like the Indian Institute of Science are developing innovative recycling processes. The technology is advancing rapidly, with a focus on enhancing the properties of recycled polypropylene to match virgin materials, making it increasingly viable for high-quality home product applications.
SABIC Global Technologies BV
Technical Solution: SABIC has developed a pioneering technology for recycling polypropylene (PP) in home product design. Their TRUCIRCLE™ portfolio includes certified circular PP made from post-consumer recycled (PCR) content[1]. This technology uses advanced chemical recycling processes to break down plastic waste into its molecular components, which are then used to create new PP with properties identical to virgin material[2]. SABIC's process can handle mixed plastic waste streams, increasing the efficiency of recycling. The company has also implemented design for recyclability principles, ensuring that products made with their recycled PP can be easily recycled again at the end of their life[3].
Strengths: High-quality recycled PP comparable to virgin material, ability to handle mixed waste streams, closed-loop recycling potential. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to virgin PP, limited availability of suitable plastic waste feedstock.
Borealis AG
Technical Solution: Borealis has introduced its Borcycle™ technology, a state-of-the-art recycling technology for transforming plastic waste streams into value-added polyolefin products, including recycled PP for home product applications[4]. The process involves mechanical recycling combined with proprietary additives and compound formulations to enhance the properties of recycled PP. Borealis has also developed a range of PP compounds containing up to 50% post-consumer recycled content, suitable for various home products[5]. Their technology focuses on maintaining the mechanical properties and aesthetics of the recycled material, making it suitable for visible parts in home appliances and furniture[6].
Strengths: High recycled content achievable, maintained mechanical properties, suitable for visible applications. Weaknesses: Limited to mechanical recycling, which may not remove all contaminants, potential color limitations.
Innovations in Recycled PP Material Properties
Polymer Composition Comprising Recycled Polypropylene
PatentInactiveUS20200339795A1
Innovation
- A polymer composition comprising recycled polypropylene with up to 25% polyethylene and an ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer, which improves mechanical and optical properties by enhancing dispersion and compatibility.
Recyclate-containing polypropylene compositions with excellent surface quality
PatentPendingUS20250034383A1
Innovation
- A polypropylene composition is developed by blending a recyclate blend with two or more heterophasic propylene-ethylene copolymers, an ethylene-octene elastomer, a filler, and pigment/additive masterbatches, resulting in a balanced mechanical profile, low emissions, and excellent surface properties.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The integration of recycled polypropylene in home product design has significant environmental implications that warrant careful assessment. This approach aligns with circular economy principles, potentially reducing the environmental footprint of household items.
Recycling polypropylene conserves natural resources by decreasing the demand for virgin plastic production. This process typically requires less energy compared to manufacturing new plastic, resulting in reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Studies indicate that recycling polypropylene can save up to 88% of the energy needed for virgin material production.
However, the recycling process itself is not without environmental impacts. It involves collection, sorting, cleaning, and reprocessing, each step consuming energy and potentially generating emissions. The efficiency of these processes varies widely depending on local infrastructure and technologies employed.
Water usage is another critical factor to consider. While recycling generally uses less water than virgin plastic production, the cleaning phase of recycled polypropylene can still be water-intensive. Implementing water-efficient recycling technologies is crucial to mitigate this impact.
The use of recycled polypropylene in home products can significantly reduce waste sent to landfills or incineration. This not only conserves landfill space but also prevents the release of harmful chemicals and microplastics into the environment. However, the effectiveness of this waste reduction depends on the establishment of robust collection and recycling systems.
It's important to note that the quality of recycled polypropylene can degrade with each recycling cycle. This may limit the number of times the material can be reused, potentially leading to downcycling rather than true recycling. Innovations in recycling technologies and product design are necessary to address this challenge and extend the material's lifecycle.
The transportation involved in the recycling process also contributes to the overall environmental impact. Localized recycling facilities can help reduce these transportation-related emissions, but this requires significant infrastructure investment.
Lastly, the use of recycled polypropylene in home products may have indirect environmental benefits by raising consumer awareness about sustainability. This could lead to more environmentally conscious purchasing decisions and improved recycling habits, creating a positive feedback loop for environmental conservation.
Recycling polypropylene conserves natural resources by decreasing the demand for virgin plastic production. This process typically requires less energy compared to manufacturing new plastic, resulting in reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Studies indicate that recycling polypropylene can save up to 88% of the energy needed for virgin material production.
However, the recycling process itself is not without environmental impacts. It involves collection, sorting, cleaning, and reprocessing, each step consuming energy and potentially generating emissions. The efficiency of these processes varies widely depending on local infrastructure and technologies employed.
Water usage is another critical factor to consider. While recycling generally uses less water than virgin plastic production, the cleaning phase of recycled polypropylene can still be water-intensive. Implementing water-efficient recycling technologies is crucial to mitigate this impact.
The use of recycled polypropylene in home products can significantly reduce waste sent to landfills or incineration. This not only conserves landfill space but also prevents the release of harmful chemicals and microplastics into the environment. However, the effectiveness of this waste reduction depends on the establishment of robust collection and recycling systems.
It's important to note that the quality of recycled polypropylene can degrade with each recycling cycle. This may limit the number of times the material can be reused, potentially leading to downcycling rather than true recycling. Innovations in recycling technologies and product design are necessary to address this challenge and extend the material's lifecycle.
The transportation involved in the recycling process also contributes to the overall environmental impact. Localized recycling facilities can help reduce these transportation-related emissions, but this requires significant infrastructure investment.
Lastly, the use of recycled polypropylene in home products may have indirect environmental benefits by raising consumer awareness about sustainability. This could lead to more environmentally conscious purchasing decisions and improved recycling habits, creating a positive feedback loop for environmental conservation.
Consumer Acceptance and Education Strategies
Consumer acceptance and education strategies play a crucial role in the successful integration of recycled polypropylene in home product design. As consumers become increasingly environmentally conscious, there is a growing demand for sustainable products. However, misconceptions and lack of awareness about recycled materials can hinder their adoption in everyday household items.
To address these challenges, companies must develop comprehensive consumer education campaigns. These initiatives should focus on highlighting the benefits of recycled polypropylene, such as its reduced environmental impact and comparable performance to virgin materials. Clear and transparent communication about the recycling process, quality control measures, and safety standards can help alleviate concerns about the material's integrity and reliability.
Product labeling and packaging present excellent opportunities to educate consumers at the point of purchase. Implementing easy-to-understand eco-labels and providing concise information about the recycled content can empower consumers to make informed decisions. Additionally, leveraging digital platforms and social media can extend the reach of educational efforts, allowing for more in-depth explanations and interactive content.
Collaborations with environmental organizations and influencers can lend credibility to the use of recycled polypropylene in home products. These partnerships can help disseminate information through trusted channels and potentially influence consumer perceptions positively. Hosting workshops, webinars, and community events centered around sustainability and recycled materials can further engage consumers and foster a sense of environmental responsibility.
To enhance consumer acceptance, companies should consider implementing trial programs or money-back guarantees for products made with recycled polypropylene. This approach can lower the perceived risk for consumers and encourage them to experience the quality of recycled materials firsthand. Positive user experiences can lead to word-of-mouth recommendations, further driving acceptance within consumer networks.
Addressing potential concerns about the aesthetics of recycled polypropylene products is also essential. Showcasing innovative designs that highlight the material's unique properties can help shift perceptions from "recycled" to "desirable." Emphasizing the material's versatility and its ability to create visually appealing and functional home products can attract design-conscious consumers.
Lastly, integrating recycled polypropylene into well-known and trusted product lines can leverage existing brand loyalty to promote acceptance. Gradually introducing recycled content into familiar products allows consumers to experience the benefits of sustainable materials within the context of brands they already trust and use regularly.
To address these challenges, companies must develop comprehensive consumer education campaigns. These initiatives should focus on highlighting the benefits of recycled polypropylene, such as its reduced environmental impact and comparable performance to virgin materials. Clear and transparent communication about the recycling process, quality control measures, and safety standards can help alleviate concerns about the material's integrity and reliability.
Product labeling and packaging present excellent opportunities to educate consumers at the point of purchase. Implementing easy-to-understand eco-labels and providing concise information about the recycled content can empower consumers to make informed decisions. Additionally, leveraging digital platforms and social media can extend the reach of educational efforts, allowing for more in-depth explanations and interactive content.
Collaborations with environmental organizations and influencers can lend credibility to the use of recycled polypropylene in home products. These partnerships can help disseminate information through trusted channels and potentially influence consumer perceptions positively. Hosting workshops, webinars, and community events centered around sustainability and recycled materials can further engage consumers and foster a sense of environmental responsibility.
To enhance consumer acceptance, companies should consider implementing trial programs or money-back guarantees for products made with recycled polypropylene. This approach can lower the perceived risk for consumers and encourage them to experience the quality of recycled materials firsthand. Positive user experiences can lead to word-of-mouth recommendations, further driving acceptance within consumer networks.
Addressing potential concerns about the aesthetics of recycled polypropylene products is also essential. Showcasing innovative designs that highlight the material's unique properties can help shift perceptions from "recycled" to "desirable." Emphasizing the material's versatility and its ability to create visually appealing and functional home products can attract design-conscious consumers.
Lastly, integrating recycled polypropylene into well-known and trusted product lines can leverage existing brand loyalty to promote acceptance. Gradually introducing recycled content into familiar products allows consumers to experience the benefits of sustainable materials within the context of brands they already trust and use regularly.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!