HDR10 vs Dolby Vision: In-Depth Review of Patents and Designs
OCT 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HDR Technology Evolution and Objectives
High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology represents a significant advancement in visual display capabilities, evolving from the limitations of Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) displays. The journey began in the early 2000s when researchers started exploring methods to capture and display a wider range of luminance levels that more closely match human visual perception. By 2010, the first commercial HDR displays emerged, though with limited content availability and standardization.
The evolution accelerated around 2014-2015 with the introduction of HDR10, the first widely adopted open standard for HDR content. This milestone marked the beginning of mainstream HDR implementation, providing a foundation for enhanced contrast ratios and expanded color gamuts in consumer displays. HDR10 established a 10-bit color depth standard, supporting over a billion colors compared to the 16.7 million colors in traditional 8-bit displays.
Dolby Vision emerged shortly after as a proprietary alternative, introducing dynamic metadata capabilities that allow for frame-by-frame optimization of brightness, contrast, and color. This represented a significant technical advancement over HDR10's static metadata approach, which applies the same parameters across an entire piece of content.
The technical objectives driving HDR development focus on closing the gap between human visual capabilities and display technology limitations. The human eye can perceive approximately 20 stops of dynamic range, while traditional SDR displays could only reproduce about 6-8 stops. Modern HDR technologies aim to deliver 14-16 stops, dramatically improving the viewing experience.
Color accuracy represents another critical objective in HDR evolution. The transition from the limited Rec.709 color space used in HDTV to the expansive Rec.2020 color gamut supported by HDR technologies enables the reproduction of previously unachievable colors in consumer displays, approaching 75-80% of the visible color spectrum.
Peak brightness capabilities have also seen remarkable advancement, with HDR displays targeting 1,000-4,000 nits compared to the typical 100-300 nits of SDR displays. This enhancement allows for more realistic highlights and improved detail in both bright and dark scenes.
The ongoing technical evolution aims to address remaining challenges, including bandwidth limitations for content delivery, processing requirements for real-time HDR rendering, and the development of more energy-efficient display technologies capable of maintaining high brightness levels without excessive power consumption or heat generation.
The evolution accelerated around 2014-2015 with the introduction of HDR10, the first widely adopted open standard for HDR content. This milestone marked the beginning of mainstream HDR implementation, providing a foundation for enhanced contrast ratios and expanded color gamuts in consumer displays. HDR10 established a 10-bit color depth standard, supporting over a billion colors compared to the 16.7 million colors in traditional 8-bit displays.
Dolby Vision emerged shortly after as a proprietary alternative, introducing dynamic metadata capabilities that allow for frame-by-frame optimization of brightness, contrast, and color. This represented a significant technical advancement over HDR10's static metadata approach, which applies the same parameters across an entire piece of content.
The technical objectives driving HDR development focus on closing the gap between human visual capabilities and display technology limitations. The human eye can perceive approximately 20 stops of dynamic range, while traditional SDR displays could only reproduce about 6-8 stops. Modern HDR technologies aim to deliver 14-16 stops, dramatically improving the viewing experience.
Color accuracy represents another critical objective in HDR evolution. The transition from the limited Rec.709 color space used in HDTV to the expansive Rec.2020 color gamut supported by HDR technologies enables the reproduction of previously unachievable colors in consumer displays, approaching 75-80% of the visible color spectrum.
Peak brightness capabilities have also seen remarkable advancement, with HDR displays targeting 1,000-4,000 nits compared to the typical 100-300 nits of SDR displays. This enhancement allows for more realistic highlights and improved detail in both bright and dark scenes.
The ongoing technical evolution aims to address remaining challenges, including bandwidth limitations for content delivery, processing requirements for real-time HDR rendering, and the development of more energy-efficient display technologies capable of maintaining high brightness levels without excessive power consumption or heat generation.
Market Demand Analysis for High Dynamic Range Video
The high dynamic range (HDR) video market has experienced substantial growth since its commercial introduction in 2015, driven by increasing consumer demand for more immersive and realistic viewing experiences. Market research indicates that the global HDR TV market size was valued at approximately $25.6 billion in 2022, with projections to reach $72.8 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.2% during the forecast period.
Consumer adoption of HDR technology has been accelerating, with HDR-capable displays now present in over 60% of new television purchases in developed markets. This trend is supported by the growing availability of HDR content across streaming platforms, with major providers like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ offering extensive HDR libraries. Industry surveys reveal that 78% of consumers who have experienced HDR content express a preference for it over standard dynamic range (SDR) alternatives.
The market demand for HDR video technologies is segmented across various sectors. The consumer electronics segment dominates with approximately 65% market share, followed by the cinema and entertainment industry at 20%, and professional broadcasting at 15%. Within these segments, premium HDR formats like Dolby Vision are experiencing faster growth rates compared to the open standard HDR10, particularly in high-end consumer devices and professional content creation workflows.
Regional analysis shows North America leading the HDR market with 38% share, followed by Europe (27%), Asia-Pacific (25%), and rest of the world (10%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate over the next five years due to increasing disposable income and rapid adoption of advanced display technologies in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Content availability remains a critical driver for HDR adoption. The number of HDR titles available across major streaming platforms has increased by 320% since 2018, with approximately 40% of new premium content now being mastered in HDR formats. This trend is expected to continue as production costs decrease and consumer demand increases.
The competitive landscape between HDR10 and Dolby Vision reflects broader market dynamics. While HDR10 benefits from being an open standard with wider implementation across mid-range devices, Dolby Vision's superior technical capabilities have secured its position in the premium segment. Market research indicates that consumers are willing to pay a 15-20% premium for devices supporting advanced HDR formats like Dolby Vision, particularly in home theater setups and premium mobile devices.
Consumer adoption of HDR technology has been accelerating, with HDR-capable displays now present in over 60% of new television purchases in developed markets. This trend is supported by the growing availability of HDR content across streaming platforms, with major providers like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ offering extensive HDR libraries. Industry surveys reveal that 78% of consumers who have experienced HDR content express a preference for it over standard dynamic range (SDR) alternatives.
The market demand for HDR video technologies is segmented across various sectors. The consumer electronics segment dominates with approximately 65% market share, followed by the cinema and entertainment industry at 20%, and professional broadcasting at 15%. Within these segments, premium HDR formats like Dolby Vision are experiencing faster growth rates compared to the open standard HDR10, particularly in high-end consumer devices and professional content creation workflows.
Regional analysis shows North America leading the HDR market with 38% share, followed by Europe (27%), Asia-Pacific (25%), and rest of the world (10%). However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate over the next five years due to increasing disposable income and rapid adoption of advanced display technologies in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
Content availability remains a critical driver for HDR adoption. The number of HDR titles available across major streaming platforms has increased by 320% since 2018, with approximately 40% of new premium content now being mastered in HDR formats. This trend is expected to continue as production costs decrease and consumer demand increases.
The competitive landscape between HDR10 and Dolby Vision reflects broader market dynamics. While HDR10 benefits from being an open standard with wider implementation across mid-range devices, Dolby Vision's superior technical capabilities have secured its position in the premium segment. Market research indicates that consumers are willing to pay a 15-20% premium for devices supporting advanced HDR formats like Dolby Vision, particularly in home theater setups and premium mobile devices.
Current HDR Standards and Technical Challenges
The High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology landscape is currently dominated by several competing standards, each with distinct technical specifications and market positioning. HDR10, as an open standard, has achieved widespread adoption due to its non-proprietary nature and relatively straightforward implementation requirements. It utilizes static metadata and supports 10-bit color depth, providing significant improvements over Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) content. However, its static metadata approach means that brightness levels are set once for an entire piece of content, limiting scene-by-scene optimization.
Dolby Vision represents a more advanced implementation, supporting 12-bit color depth and dynamic metadata that allows for frame-by-frame brightness adjustments. This technical superiority comes with increased licensing costs and more complex implementation requirements, creating barriers to universal adoption despite its quality advantages. The proprietary nature of Dolby Vision has led to fragmented market support across devices and content platforms.
HDR10+ emerged as Samsung's answer to Dolby Vision, incorporating dynamic metadata while maintaining an open standard approach with more favorable licensing terms. However, it has struggled to achieve the same level of content support as its competitors, particularly in streaming services beyond Amazon Prime Video and Samsung's ecosystem.
Hybrid Log-Gamma (HLG), developed by BBC and NHK, offers a broadcast-friendly solution with backward compatibility for SDR displays, but lacks the peak brightness capabilities of other standards. Its strength lies in live broadcasting applications where metadata management presents unique challenges.
Technical implementation challenges persist across all standards. Content mastering for multiple HDR formats requires significant resources, as each standard demands different color grading approaches and metadata management. This has created workflow inefficiencies throughout the production and distribution chain.
Device compatibility remains fragmented, with consumers often confused by inconsistent labeling and varying support across televisions, mobile devices, and streaming platforms. The absence of a universal HDR standard has complicated the consumer experience and slowed adoption rates.
Bandwidth constraints present another significant challenge, particularly for streaming services and broadcasters. HDR content typically requires higher bitrates to preserve quality, creating distribution challenges in regions with limited internet infrastructure or for services with bandwidth caps.
The technical evolution of display technologies further complicates the landscape, as advancements in mini-LED, micro-LED, and OLED technologies create varying capabilities for reproducing HDR content, resulting in inconsistent viewing experiences across different display types.
Dolby Vision represents a more advanced implementation, supporting 12-bit color depth and dynamic metadata that allows for frame-by-frame brightness adjustments. This technical superiority comes with increased licensing costs and more complex implementation requirements, creating barriers to universal adoption despite its quality advantages. The proprietary nature of Dolby Vision has led to fragmented market support across devices and content platforms.
HDR10+ emerged as Samsung's answer to Dolby Vision, incorporating dynamic metadata while maintaining an open standard approach with more favorable licensing terms. However, it has struggled to achieve the same level of content support as its competitors, particularly in streaming services beyond Amazon Prime Video and Samsung's ecosystem.
Hybrid Log-Gamma (HLG), developed by BBC and NHK, offers a broadcast-friendly solution with backward compatibility for SDR displays, but lacks the peak brightness capabilities of other standards. Its strength lies in live broadcasting applications where metadata management presents unique challenges.
Technical implementation challenges persist across all standards. Content mastering for multiple HDR formats requires significant resources, as each standard demands different color grading approaches and metadata management. This has created workflow inefficiencies throughout the production and distribution chain.
Device compatibility remains fragmented, with consumers often confused by inconsistent labeling and varying support across televisions, mobile devices, and streaming platforms. The absence of a universal HDR standard has complicated the consumer experience and slowed adoption rates.
Bandwidth constraints present another significant challenge, particularly for streaming services and broadcasters. HDR content typically requires higher bitrates to preserve quality, creating distribution challenges in regions with limited internet infrastructure or for services with bandwidth caps.
The technical evolution of display technologies further complicates the landscape, as advancements in mini-LED, micro-LED, and OLED technologies create varying capabilities for reproducing HDR content, resulting in inconsistent viewing experiences across different display types.
Technical Comparison of HDR10 and Dolby Vision
01 HDR display technology and implementation
High Dynamic Range (HDR) display technologies enable enhanced contrast ratios and color depth for more realistic visual experiences. These technologies involve specialized hardware designs and processing algorithms to handle the expanded luminance range and color gamut. Implementation includes methods for tone mapping, brightness control, and color space conversion to properly render HDR content on compatible displays.- HDR10 and Dolby Vision display technologies: High Dynamic Range (HDR) display technologies, including HDR10 and Dolby Vision, enhance visual experience by providing greater contrast, wider color gamut, and higher brightness levels. These technologies enable displays to show more detail in both bright and dark areas of an image, creating a more realistic viewing experience. The patents in this category cover various aspects of HDR display implementation, including hardware designs and signal processing methods.
- HDR image processing and encoding methods: This category encompasses patents related to processing and encoding methods for HDR content. These methods include algorithms for tone mapping, color grading, and dynamic range adjustment to optimize HDR content for different display capabilities. The technologies enable efficient compression and transmission of HDR signals while preserving the enhanced visual quality that HDR provides.
- Content protection and digital rights management for HDR: Patents in this category focus on protecting HDR content through various digital rights management (DRM) systems. These technologies ensure that premium HDR content, such as movies and TV shows in Dolby Vision or HDR10 format, can be securely distributed while preventing unauthorized copying or viewing. The solutions include encryption methods, authentication protocols, and secure playback mechanisms specifically designed for high-value HDR content.
- HDR-compatible devices and hardware designs: This category covers hardware implementations and device designs that support HDR10 and Dolby Vision technologies. The patents include designs for televisions, monitors, projectors, and mobile devices capable of displaying HDR content. These hardware solutions address challenges such as achieving sufficient brightness levels, managing heat dissipation, and implementing the necessary processing capabilities to render HDR content correctly.
- HDR metadata handling and transmission systems: Patents related to the handling and transmission of HDR metadata, which is crucial for proper rendering of HDR content. This metadata includes information about brightness levels, color mapping, and dynamic range that helps displays correctly interpret and present HDR content. The technologies cover methods for embedding metadata in video streams, transmitting it through various interfaces (like HDMI), and processing it at the receiving end to optimize the viewing experience.
02 Dolby Vision encoding and processing methods
Dolby Vision technology employs advanced encoding methods to deliver enhanced dynamic range and color accuracy. These methods include frame-by-frame metadata processing, content-adaptive mapping algorithms, and specialized color grading techniques. The technology enables content creators to preserve their creative intent across different display capabilities while maintaining optimal visual quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 HDR10 and Dolby Vision compatible hardware designs
Hardware designs specifically engineered to support HDR10 and Dolby Vision standards include specialized display panels, processing chips, and interface components. These designs incorporate features such as enhanced backlight systems, improved color filters, and dedicated processing units to handle the expanded dynamic range and color information. The hardware must be capable of interpreting and correctly displaying the metadata associated with HDR content.Expand Specific Solutions04 Signal processing for HDR content delivery
Signal processing techniques for HDR content delivery involve methods for efficiently transmitting and receiving high dynamic range video signals. These techniques include compression algorithms optimized for HDR data, metadata handling protocols, and signal conversion methods for compatibility with various display technologies. Advanced processing ensures minimal loss of dynamic range and color information during transmission while maintaining bandwidth efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions05 Content management systems for HDR media
Content management systems designed for HDR media facilitate the creation, storage, distribution, and playback of high dynamic range content. These systems include specialized workflows for content creators, digital rights management solutions, and adaptive delivery mechanisms that optimize the viewing experience based on display capabilities. They enable efficient handling of the larger data requirements associated with HDR content while ensuring proper presentation across different devices.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in HDR Ecosystem
The HDR10 vs Dolby Vision competitive landscape is currently in a mature growth phase, with the global HDR market expected to reach significant scale as 4K and 8K displays proliferate. Dolby Laboratories maintains leadership in premium HDR technology through its proprietary Dolby Vision format, while Samsung, Sony, and LG Display champion the open-source HDR10/HDR10+ standards. The ecosystem includes diverse players across the value chain: content creators (Sony Group), chip manufacturers (MediaTek, NVIDIA), display manufacturers (BOE Technology, LG Display), and device makers (Huawei, Microsoft). Technology maturity varies, with Dolby Vision offering advanced dynamic metadata capabilities versus HDR10's static approach, though HDR10+ has narrowed this gap. Major technology companies like Google and Apple have implemented support for both standards, indicating market stabilization around dual-format compatibility.
Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp.
Technical Solution: Dolby Vision represents Dolby's proprietary HDR technology that utilizes dynamic metadata to optimize content on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis. The technology supports up to 12-bit color depth, allowing for 68.7 billion colors, significantly more than HDR10's 10-bit capability (1.07 billion colors). Dolby Vision's patents cover its unique perceptual quantizer (PQ) curve that maps content to display capabilities more effectively than standard gamma curves. The technology incorporates sophisticated tone mapping algorithms that dynamically adjust brightness, contrast, and color saturation based on the specific capabilities of the display device and the creative intent of content producers. Dolby Vision also includes patents for backward compatibility with SDR displays and integration with various content delivery systems, ensuring seamless implementation across the content ecosystem[1][3]. The technology supports peak brightness levels up to 10,000 nits, though current displays typically max out at 1,000-4,000 nits.
Strengths: Superior image quality through dynamic metadata; greater color depth; better adaptation to different display capabilities; consistent experience across devices. Weaknesses: Requires licensing fees for manufacturers; more complex implementation; higher processing requirements; limited content availability compared to open standards.
Sony Group Corp.
Technical Solution: Sony has developed proprietary HDR technologies that work with both HDR10 and Dolby Vision standards while adding their own enhancements. Their X1 Ultimate and Cognitive Processors incorporate advanced HDR remastering that analyzes and optimizes each object in a scene individually. Sony's approach includes patents for object-based HDR processing that identifies and enhances specific elements within frames rather than applying uniform adjustments. Their TRILUMINOS display technology expands the color gamut beyond standard RGB configurations to reproduce more natural and precise colors in HDR content. Sony has also patented dynamic tone mapping algorithms that analyze incoming HDR signals and optimize them for their specific display capabilities, particularly important for their BRAVIA OLED and LED lineup. Additionally, Sony has developed dual database processing that uses pattern matching from thousands of reference images to reduce noise and upscale content to HDR quality[2][5]. Their technology includes compatibility layers that allow optimal presentation of both HDR10 and Dolby Vision content.
Strengths: Object-based processing provides more precise image enhancement; excellent upscaling of non-HDR content; strong integration between hardware and software; compatibility with multiple HDR standards. Weaknesses: Premium pricing; some technologies limited to high-end models; proprietary nature can limit interoperability with third-party devices.
Patent Analysis of HDR10 and Dolby Vision
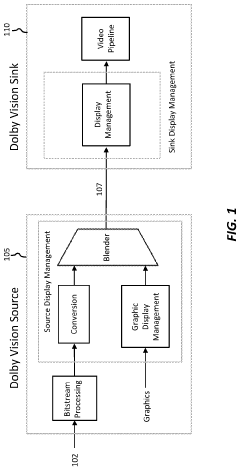
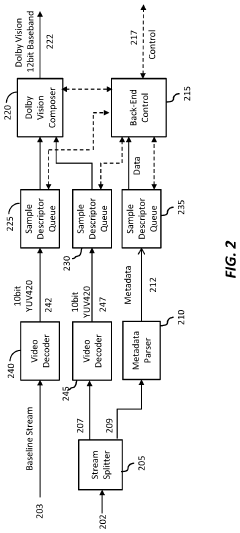
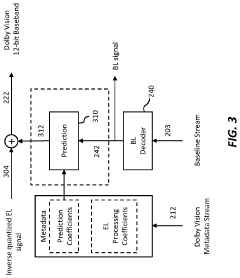
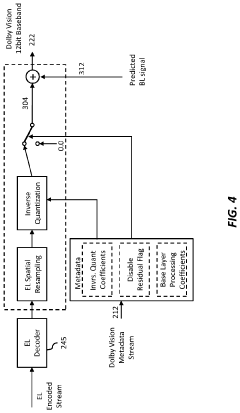
Layered representation and delivery of high dynamic range video
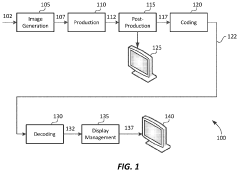
PatentActiveUS20190373290A1
Innovation
- The implementation of a layered representation and delivery system for HDR video, utilizing Dolby Vision technology, which includes a base layer and enhancement layer, along with metadata processing to reconstruct HDR signals, ensuring seamless playback on compatible displays.
Video coding using reference picture resampling supporting region of interest
PatentActiveUS20220286667A1
Innovation
- The implementation of reference picture resampling (RPR) with support for region of interest (ROI) in video coding, allowing for flexible scaling and decoding of specific regions within a video frame, enabling scalable distribution of HDR content compatible with various display resolutions and devices.
Content Creation Pipeline for HDR Formats
The content creation pipeline for HDR formats represents a critical workflow that determines how effectively high dynamic range content can be captured, processed, and delivered to end viewers. For HDR10, the pipeline begins with capture devices capable of recording wider brightness ranges, typically using cameras with at least 10-bit color depth. The raw footage undergoes color grading in a post-production environment where colorists manually set static metadata, including the content's maximum brightness level and color primaries according to the BT.2020 color space.
HDR10 content creation relies heavily on standardized tools and workflows, with metadata remaining consistent throughout the entire content. This approach offers simplicity but lacks scene-by-scene optimization. The static metadata approach means that creative decisions must accommodate the limitations of the least capable display in the distribution chain.
In contrast, Dolby Vision implements a more sophisticated pipeline that begins with capture at 12-bit color depth. Its distinguishing feature is the creation of a content master at up to 10,000 nits brightness, serving as a "golden reference" that preserves the creator's true intent. During post-production, Dolby's proprietary tools generate dynamic metadata that carries frame-by-frame or scene-by-scene brightness and color mapping instructions.
This dynamic approach allows Dolby Vision content to adapt intelligently to the capabilities of each display device. The pipeline includes the creation of trim passes—specific instructions for how content should appear on displays with different capabilities—ensuring consistent creative intent across viewing environments.
Patent analysis reveals Dolby's significant intellectual property around this adaptive mapping process, with key patents covering the generation and application of dynamic metadata (US9685120B2, US9685139B2). HDR10's pipeline is less encumbered by patents, relying more on open standards defined by organizations like SMPTE.
The technical complexity difference between these pipelines directly impacts production costs and workflows. Dolby Vision requires specialized tools, training, and certification, creating a higher barrier to entry but potentially delivering superior visual results. HDR10 offers a more accessible pipeline with lower licensing costs, explaining its broader adoption despite potential quality compromises.
Recent developments show convergence in these pipelines, with HDR10+ introducing some dynamic metadata capabilities while maintaining a more open approach than Dolby Vision's fully proprietary system.
HDR10 content creation relies heavily on standardized tools and workflows, with metadata remaining consistent throughout the entire content. This approach offers simplicity but lacks scene-by-scene optimization. The static metadata approach means that creative decisions must accommodate the limitations of the least capable display in the distribution chain.
In contrast, Dolby Vision implements a more sophisticated pipeline that begins with capture at 12-bit color depth. Its distinguishing feature is the creation of a content master at up to 10,000 nits brightness, serving as a "golden reference" that preserves the creator's true intent. During post-production, Dolby's proprietary tools generate dynamic metadata that carries frame-by-frame or scene-by-scene brightness and color mapping instructions.
This dynamic approach allows Dolby Vision content to adapt intelligently to the capabilities of each display device. The pipeline includes the creation of trim passes—specific instructions for how content should appear on displays with different capabilities—ensuring consistent creative intent across viewing environments.
Patent analysis reveals Dolby's significant intellectual property around this adaptive mapping process, with key patents covering the generation and application of dynamic metadata (US9685120B2, US9685139B2). HDR10's pipeline is less encumbered by patents, relying more on open standards defined by organizations like SMPTE.
The technical complexity difference between these pipelines directly impacts production costs and workflows. Dolby Vision requires specialized tools, training, and certification, creating a higher barrier to entry but potentially delivering superior visual results. HDR10 offers a more accessible pipeline with lower licensing costs, explaining its broader adoption despite potential quality compromises.
Recent developments show convergence in these pipelines, with HDR10+ introducing some dynamic metadata capabilities while maintaining a more open approach than Dolby Vision's fully proprietary system.
Licensing Models and Implementation Costs
The licensing models for HDR10 and Dolby Vision represent significantly different approaches to market penetration and revenue generation in the high dynamic range display technology sector. HDR10, as an open standard developed by the Consumer Technology Association, operates on a royalty-free basis, allowing manufacturers to implement the technology without direct licensing fees. This open approach has facilitated widespread adoption across the industry, particularly among budget and mid-range device manufacturers seeking to offer HDR capabilities without incurring substantial licensing costs.
In contrast, Dolby Vision employs a proprietary licensing model that requires manufacturers to pay both upfront implementation fees and ongoing royalties. These fees typically range from $2-3 per device, though exact figures vary based on production volume and negotiated agreements. The licensing structure includes separate components for hardware implementation and content creation, creating multiple revenue streams for Dolby Laboratories.
Implementation costs extend beyond licensing fees for both technologies. For HDR10, manufacturers face relatively modest implementation expenses, primarily involving firmware updates and quality control testing to ensure compatibility with the standard. The hardware requirements are minimal, as most modern display processors can handle the 10-bit color depth and static metadata processing without significant modifications.
Dolby Vision implementation demands more substantial investment in both hardware and software. Manufacturers must integrate specialized chips capable of processing dynamic metadata and 12-bit color depth, increasing component costs by approximately $10-15 per unit. Additionally, manufacturers must undergo Dolby's certification process, which involves rigorous testing and quality assurance procedures that can extend development timelines by 3-6 months.
For content creators, the cost differential is equally significant. HDR10 content creation requires standard color grading equipment with 10-bit processing capabilities, while Dolby Vision necessitates specialized tools and software licenses that can cost studios $50,000-100,000 annually. This higher barrier to entry for content creation has influenced adoption rates in different market segments.
The contrasting licensing approaches have shaped market dynamics, with HDR10 achieving broader implementation across price points while Dolby Vision has established itself as a premium offering with higher perceived value. This dichotomy has led many manufacturers to adopt a tiered strategy, implementing HDR10 across their entire product range while reserving Dolby Vision for premium models where higher retail prices can offset the additional licensing and implementation costs.
In contrast, Dolby Vision employs a proprietary licensing model that requires manufacturers to pay both upfront implementation fees and ongoing royalties. These fees typically range from $2-3 per device, though exact figures vary based on production volume and negotiated agreements. The licensing structure includes separate components for hardware implementation and content creation, creating multiple revenue streams for Dolby Laboratories.
Implementation costs extend beyond licensing fees for both technologies. For HDR10, manufacturers face relatively modest implementation expenses, primarily involving firmware updates and quality control testing to ensure compatibility with the standard. The hardware requirements are minimal, as most modern display processors can handle the 10-bit color depth and static metadata processing without significant modifications.
Dolby Vision implementation demands more substantial investment in both hardware and software. Manufacturers must integrate specialized chips capable of processing dynamic metadata and 12-bit color depth, increasing component costs by approximately $10-15 per unit. Additionally, manufacturers must undergo Dolby's certification process, which involves rigorous testing and quality assurance procedures that can extend development timelines by 3-6 months.
For content creators, the cost differential is equally significant. HDR10 content creation requires standard color grading equipment with 10-bit processing capabilities, while Dolby Vision necessitates specialized tools and software licenses that can cost studios $50,000-100,000 annually. This higher barrier to entry for content creation has influenced adoption rates in different market segments.
The contrasting licensing approaches have shaped market dynamics, with HDR10 achieving broader implementation across price points while Dolby Vision has established itself as a premium offering with higher perceived value. This dichotomy has led many manufacturers to adopt a tiered strategy, implementing HDR10 across their entire product range while reserving Dolby Vision for premium models where higher retail prices can offset the additional licensing and implementation costs.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!