HDR10 vs Dolby Vision: Market Regulation Analysis
OCT 24, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HDR Technology Evolution and Objectives
High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology represents a significant advancement in visual display capabilities, evolving from the limitations of Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) to deliver enhanced contrast, brightness, and color accuracy. The journey began in the early 2000s with research into expanded luminance ranges, but commercial implementation only gained momentum around 2014 when the first HDR-capable displays entered the market.
The evolution of HDR technology has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, the focus was on increasing the peak brightness capabilities of displays from the standard 100 nits to over 1,000 nits. This was followed by developments in color gamut expansion, moving from the restricted Rec.709 color space to the more comprehensive Rec.2020 standard, enabling a significantly wider range of displayable colors.
HDR10, introduced in 2015, emerged as the first widely adopted open standard, establishing baseline specifications for HDR content delivery. Shortly thereafter, Dolby Vision entered the market as a proprietary alternative, offering dynamic metadata capabilities that HDR10 lacked. This technological divergence has shaped the current competitive landscape between these two dominant HDR formats.
The primary objective of HDR technology development has been to create more immersive and realistic viewing experiences by more closely replicating the human visual experience. This includes the ability to display both extremely bright highlights and detailed shadows simultaneously, a capability that conventional SDR technology cannot achieve due to its limited dynamic range.
Recent technological objectives have focused on addressing implementation challenges, including bandwidth requirements for transmission, backward compatibility with existing infrastructure, and the development of efficient compression algorithms to handle the increased data demands of HDR content.
The market has also witnessed the emergence of hybrid solutions like HDR10+, which aims to incorporate some of Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata advantages while maintaining an open standard approach. This represents an attempt to balance technological capabilities with market accessibility considerations.
Looking forward, the technical objectives for HDR technology include further increasing peak brightness capabilities, expanding color volume representation, improving tone mapping algorithms for various viewing environments, and developing more efficient encoding methods to reduce bandwidth requirements while maintaining visual quality. Additionally, there is growing emphasis on standardization efforts to ensure interoperability across different platforms and devices, addressing fragmentation concerns in the current market.
The evolution of HDR technology has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, the focus was on increasing the peak brightness capabilities of displays from the standard 100 nits to over 1,000 nits. This was followed by developments in color gamut expansion, moving from the restricted Rec.709 color space to the more comprehensive Rec.2020 standard, enabling a significantly wider range of displayable colors.
HDR10, introduced in 2015, emerged as the first widely adopted open standard, establishing baseline specifications for HDR content delivery. Shortly thereafter, Dolby Vision entered the market as a proprietary alternative, offering dynamic metadata capabilities that HDR10 lacked. This technological divergence has shaped the current competitive landscape between these two dominant HDR formats.
The primary objective of HDR technology development has been to create more immersive and realistic viewing experiences by more closely replicating the human visual experience. This includes the ability to display both extremely bright highlights and detailed shadows simultaneously, a capability that conventional SDR technology cannot achieve due to its limited dynamic range.
Recent technological objectives have focused on addressing implementation challenges, including bandwidth requirements for transmission, backward compatibility with existing infrastructure, and the development of efficient compression algorithms to handle the increased data demands of HDR content.
The market has also witnessed the emergence of hybrid solutions like HDR10+, which aims to incorporate some of Dolby Vision's dynamic metadata advantages while maintaining an open standard approach. This represents an attempt to balance technological capabilities with market accessibility considerations.
Looking forward, the technical objectives for HDR technology include further increasing peak brightness capabilities, expanding color volume representation, improving tone mapping algorithms for various viewing environments, and developing more efficient encoding methods to reduce bandwidth requirements while maintaining visual quality. Additionally, there is growing emphasis on standardization efforts to ensure interoperability across different platforms and devices, addressing fragmentation concerns in the current market.
Market Demand for Premium Video Standards
The demand for premium video standards has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by consumers' increasing appetite for high-quality visual experiences across various platforms. HDR10 and Dolby Vision, as leading High Dynamic Range technologies, have emerged as key differentiators in the premium content ecosystem, with distinct market adoption patterns and consumer preferences.
Consumer research indicates that viewers increasingly prioritize image quality when selecting content platforms and devices. A 2022 market survey revealed that over 70% of consumers consider HDR capability an important factor when purchasing new televisions, with this percentage rising among younger demographics and technology enthusiasts. This trend has accelerated with the proliferation of 4K and 8K displays, where enhanced dynamic range becomes more visually impactful.
The streaming market has become a primary battleground for premium video standards. Major platforms including Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, and Apple TV+ have all invested heavily in HDR content, recognizing it as a competitive advantage. Netflix alone reported a 45% increase in HDR content consumption between 2020 and 2022, demonstrating strong viewer preference for enhanced visual experiences.
Content creators and studios have responded to this demand by increasingly mastering content in premium formats. Hollywood studios now routinely create Dolby Vision masters for major releases, while the gaming industry has embraced HDR as a standard feature in next-generation consoles. This content ecosystem expansion has created a positive feedback loop, further driving consumer adoption of compatible devices.
Regional variations in demand are notable, with North American and East Asian markets showing the strongest preference for premium video standards. In these regions, HDR-capable device penetration exceeds 60% in urban households. European markets follow closely, while emerging economies show rapid growth from a lower base, particularly in upper-middle-class segments.
Device manufacturers have recognized this market shift, with virtually all premium and mid-range televisions now supporting at least HDR10, while Dolby Vision support has expanded from exclusively high-end models to many mid-tier offerings. This democratization of technology has broadened the potential market, though creating challenges in maintaining consistent quality standards across price points.
The commercial sector represents another growth vector, with digital signage, professional displays, and cinema applications increasingly adopting HDR technologies. This B2B segment, while smaller in volume than consumer markets, offers higher margins and more stable demand patterns, making it strategically important for technology providers.
Consumer research indicates that viewers increasingly prioritize image quality when selecting content platforms and devices. A 2022 market survey revealed that over 70% of consumers consider HDR capability an important factor when purchasing new televisions, with this percentage rising among younger demographics and technology enthusiasts. This trend has accelerated with the proliferation of 4K and 8K displays, where enhanced dynamic range becomes more visually impactful.
The streaming market has become a primary battleground for premium video standards. Major platforms including Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, and Apple TV+ have all invested heavily in HDR content, recognizing it as a competitive advantage. Netflix alone reported a 45% increase in HDR content consumption between 2020 and 2022, demonstrating strong viewer preference for enhanced visual experiences.
Content creators and studios have responded to this demand by increasingly mastering content in premium formats. Hollywood studios now routinely create Dolby Vision masters for major releases, while the gaming industry has embraced HDR as a standard feature in next-generation consoles. This content ecosystem expansion has created a positive feedback loop, further driving consumer adoption of compatible devices.
Regional variations in demand are notable, with North American and East Asian markets showing the strongest preference for premium video standards. In these regions, HDR-capable device penetration exceeds 60% in urban households. European markets follow closely, while emerging economies show rapid growth from a lower base, particularly in upper-middle-class segments.
Device manufacturers have recognized this market shift, with virtually all premium and mid-range televisions now supporting at least HDR10, while Dolby Vision support has expanded from exclusively high-end models to many mid-tier offerings. This democratization of technology has broadened the potential market, though creating challenges in maintaining consistent quality standards across price points.
The commercial sector represents another growth vector, with digital signage, professional displays, and cinema applications increasingly adopting HDR technologies. This B2B segment, while smaller in volume than consumer markets, offers higher margins and more stable demand patterns, making it strategically important for technology providers.
HDR Format Landscape and Technical Barriers
The High Dynamic Range (HDR) video format landscape is currently dominated by several competing standards, each with distinct technical specifications and market positioning. HDR10, as an open standard, has achieved widespread adoption due to its royalty-free nature and relatively straightforward implementation requirements. However, it offers static metadata that limits scene-by-scene optimization capabilities.
Dolby Vision represents a more advanced proprietary solution with dynamic metadata capabilities, enabling frame-by-frame optimization of brightness, contrast, and color. This technical superiority comes with significant licensing costs and more complex implementation requirements, creating a barrier for widespread adoption among budget-conscious manufacturers and content creators.
HDR10+ emerged as Samsung's response to Dolby Vision, offering dynamic metadata capabilities without the substantial licensing fees. While technically comparable to Dolby Vision in many aspects, it faces challenges in gaining market traction due to its later market entry and more limited content ecosystem.
Hybrid Log-Gamma (HLG), developed by BBC and NHK, stands apart with its backward compatibility focus, allowing standard dynamic range (SDR) displays to show HDR content without metadata processing. This advantage is counterbalanced by its somewhat limited peak brightness capabilities compared to other formats.
The technical barriers in the HDR ecosystem are multifaceted. Content creation workflows require significant investment in compatible cameras, production monitors, and post-production software capable of handling the expanded color and brightness ranges. This creates a substantial entry barrier for smaller content producers.
Content distribution faces bandwidth challenges, as HDR formats typically require higher bitrates to preserve their enhanced visual information. This poses particular difficulties for streaming services operating in regions with bandwidth limitations and for broadcast television networks.
Device compatibility presents another significant barrier, with fragmentation across display technologies. Many older devices lack the necessary hardware to properly display HDR content, while even newer displays vary widely in their ability to accurately reproduce the expanded brightness and color ranges specified by different HDR standards.
Calibration and quality control represent ongoing challenges, as maintaining consistent visual experiences across different viewing environments and display technologies requires sophisticated color management systems and standardized measurement methodologies that are still evolving within the industry.
Dolby Vision represents a more advanced proprietary solution with dynamic metadata capabilities, enabling frame-by-frame optimization of brightness, contrast, and color. This technical superiority comes with significant licensing costs and more complex implementation requirements, creating a barrier for widespread adoption among budget-conscious manufacturers and content creators.
HDR10+ emerged as Samsung's response to Dolby Vision, offering dynamic metadata capabilities without the substantial licensing fees. While technically comparable to Dolby Vision in many aspects, it faces challenges in gaining market traction due to its later market entry and more limited content ecosystem.
Hybrid Log-Gamma (HLG), developed by BBC and NHK, stands apart with its backward compatibility focus, allowing standard dynamic range (SDR) displays to show HDR content without metadata processing. This advantage is counterbalanced by its somewhat limited peak brightness capabilities compared to other formats.
The technical barriers in the HDR ecosystem are multifaceted. Content creation workflows require significant investment in compatible cameras, production monitors, and post-production software capable of handling the expanded color and brightness ranges. This creates a substantial entry barrier for smaller content producers.
Content distribution faces bandwidth challenges, as HDR formats typically require higher bitrates to preserve their enhanced visual information. This poses particular difficulties for streaming services operating in regions with bandwidth limitations and for broadcast television networks.
Device compatibility presents another significant barrier, with fragmentation across display technologies. Many older devices lack the necessary hardware to properly display HDR content, while even newer displays vary widely in their ability to accurately reproduce the expanded brightness and color ranges specified by different HDR standards.
Calibration and quality control represent ongoing challenges, as maintaining consistent visual experiences across different viewing environments and display technologies requires sophisticated color management systems and standardized measurement methodologies that are still evolving within the industry.
Current HDR10 and Dolby Vision Implementation Approaches
01 HDR10 and Dolby Vision standards implementation
Implementation of HDR10 and Dolby Vision standards in display technologies involves specific technical requirements for content creation, transmission, and display. These standards define parameters for color gamut, brightness levels, and dynamic range that manufacturers must adhere to when developing compatible devices. The implementation includes hardware specifications and software algorithms that process high dynamic range content to deliver enhanced visual experiences.- HDR10 and Dolby Vision standards implementation: The implementation of HDR10 and Dolby Vision standards in display technologies requires specific technical configurations to ensure proper rendering of high dynamic range content. These standards define parameters for brightness, contrast, and color gamut that manufacturers must adhere to when developing compatible devices. The implementation involves hardware specifications and software algorithms that process and display HDR content according to these established standards.
- Licensing and certification requirements: Market regulations for HDR technologies include licensing frameworks and certification processes that manufacturers must follow to legally implement HDR10 and Dolby Vision in their products. These requirements ensure that devices meet the technical specifications and performance standards established by the technology developers. Certification programs verify compliance with these standards and authorize the use of official logos and branding on compatible products.
- Content protection and digital rights management: Regulations governing HDR content delivery include content protection mechanisms and digital rights management systems designed to prevent unauthorized copying or distribution of premium HDR content. These protection schemes are mandatory for devices that display HDR10 and Dolby Vision content from commercial streaming services or physical media. The regulations specify encryption methods, authentication protocols, and secure playback pathways to maintain content security throughout the distribution chain.
- Interoperability and compatibility standards: Market regulations address interoperability issues between different HDR formats and devices to ensure consistent user experience across the ecosystem. These standards define how HDR10 and Dolby Vision content should be handled when displayed on devices with varying capabilities, including fallback mechanisms for displaying HDR content on non-HDR displays. The regulations promote seamless integration between content sources, distribution platforms, and display devices.
- Energy efficiency and environmental regulations: HDR display technologies must comply with energy efficiency standards and environmental regulations that govern power consumption and materials usage. These regulations balance the higher power requirements of HDR displays against energy conservation goals. Manufacturers must design HDR10 and Dolby Vision compatible devices that meet regional energy efficiency certifications while still delivering the enhanced brightness and contrast that HDR technologies require.
02 Regulatory compliance for HDR technologies
Regulatory frameworks govern the implementation and market distribution of HDR technologies including HDR10 and Dolby Vision. These regulations address aspects such as technical specifications, interoperability requirements, and certification processes that manufacturers must follow. Compliance with these regulations ensures that devices meet minimum performance standards and can properly display HDR content while maintaining compatibility across different platforms and devices.Expand Specific Solutions03 Licensing and intellectual property management
The HDR10 and Dolby Vision ecosystems involve complex licensing structures and intellectual property considerations. Companies must navigate patent licensing agreements to implement these technologies in their products. Dolby Vision, as a proprietary technology, requires specific licensing arrangements, while HDR10 operates under different intellectual property frameworks. These licensing models impact market entry barriers and influence how manufacturers incorporate HDR technologies into their product lines.Expand Specific Solutions04 Content protection and digital rights management
HDR content delivery systems incorporate protection mechanisms to prevent unauthorized copying and distribution. These systems include encryption protocols, digital rights management solutions, and secure transmission methods specifically designed for high-value HDR content. The regulatory framework addresses how content creators, distributors, and device manufacturers must implement these protection measures while ensuring legitimate consumer access to HDR10 and Dolby Vision content.Expand Specific Solutions05 Market standardization and interoperability requirements
Regulations governing HDR technologies focus on ensuring interoperability between different devices and platforms. These standards define how HDR10 and Dolby Vision content should be encoded, transmitted, and displayed across various consumer electronics. The regulatory framework promotes consistency in implementation while allowing for technological innovation, addressing aspects such as metadata handling, color space conversion, and brightness mapping to ensure consistent viewing experiences.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in HDR Ecosystem
The HDR10 vs Dolby Vision market presents a competitive landscape in the maturing high dynamic range video technology sector. Currently in a growth phase, the market is expanding rapidly with an estimated value exceeding $13 billion globally. Dolby Vision, championed by Dolby Laboratories, offers a premium proprietary solution with dynamic metadata, while HDR10, supported by Samsung, Sony, and Philips, provides an open standard alternative. The technology ecosystem shows varying maturity levels: Dolby maintains strong licensing control over its ecosystem, while major electronics manufacturers like Samsung, LG, and Huawei have strategically aligned with HDR10+. Content providers and streaming platforms increasingly support both standards, creating a complex regulatory environment balancing proprietary innovation against open standard accessibility.
Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corp.
Technical Solution: Dolby Vision represents Dolby's premium HDR technology that provides a 12-bit color depth (compared to HDR10's 10-bit), enabling up to 68 billion colors versus HDR10's 1 billion. The technology incorporates dynamic metadata that allows frame-by-frame optimization of brightness, contrast, and color, resulting in more precise image rendering across various content types. Dolby Vision supports peak brightness levels up to 10,000 nits (though current displays typically max out at 4,000 nits), significantly exceeding HDR10's typical 1,000 nits capability. Additionally, Dolby Vision implements a sophisticated content mapping technology that ensures optimal performance across different display capabilities, automatically adjusting content parameters to match the specific display's capabilities[1][3]. The technology has been widely adopted across the entertainment ecosystem, from content creation to distribution and display manufacturing.
Strengths: Superior technical specifications with 12-bit color depth and dynamic metadata enabling more precise image optimization; comprehensive ecosystem support from production to display; better cross-device consistency through dynamic mapping technology. Weaknesses: Requires licensing fees which increases implementation costs; proprietary nature creates market fragmentation; requires more processing power which can impact device performance and battery life in mobile applications.
Koninklijke Philips NV
Technical Solution: Philips, as one of the founding members of the HDR10 standard, has developed a technical approach focused on open standards and broad compatibility. Their HDR10 implementation provides a 10-bit color depth supporting approximately 1 billion colors and uses static metadata that remains consistent throughout content playback. Philips has further contributed to the development of HDR10+, an enhanced version that incorporates dynamic metadata similar to Dolby Vision but maintains an open, royalty-free licensing model. The company's displays typically support peak brightness levels of 1,000-1,500 nits for HDR content. Philips has integrated their Ambilight technology with HDR rendering to create an expanded visual experience that projects colors beyond the screen edges, enhancing perceived contrast and immersion when displaying HDR content[2]. Their approach emphasizes compatibility across different content sources while maintaining reasonable implementation costs for manufacturers.
Strengths: Open standard approach reduces implementation barriers; HDR10+ offers improved performance while maintaining backward compatibility; integration with proprietary Ambilight technology creates differentiated viewing experience. Weaknesses: Base HDR10 offers lower technical specifications than Dolby Vision with fewer colors and less precise tone mapping; static metadata provides less optimization capability for varying content; market position less dominant than some competitors in the premium segment.
Core Patents and Technical Specifications Analysis
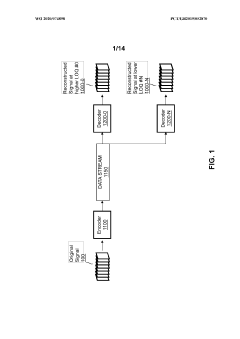
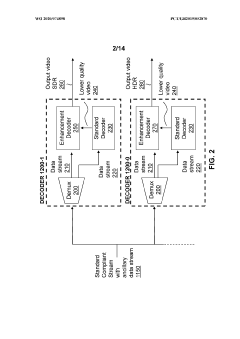
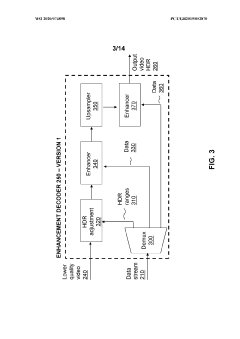
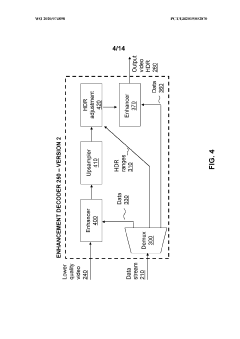
Enhancement decoder for video signals with multi-level enhancement and coding format adjustment
PatentWO2020074898A1
Innovation
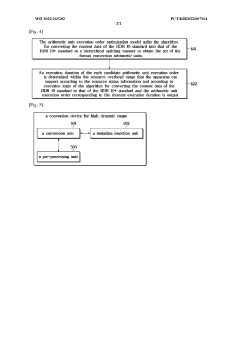
- A hierarchical coding scheme that allows for the encoding and decoding of HDR-type signals to be compatible with both HDR and SDR displays, using an enhancement decoder that includes an interface for receiving video streams, de-multiplexing enhancement data, and a coding format adjustment module to convert between different bit lengths and resolutions, ensuring backwards compatibility and flexibility in signal processing.
Conversion method and device for high dynamic range format
PatentWO2022265282A1
Innovation
- A conversion method and device that split the HDR10 to HDR10+ algorithm into hierarchical arithmetic units and determine an execution order to minimize processing duration, allowing for concurrent processing and reduced power consumption.
Regulatory Framework for Content Distribution
The regulatory landscape governing HDR content distribution is complex and varies significantly across global markets. In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has established technical standards for broadcast television that accommodate HDR formats, but has not mandated specific HDR technologies. This technology-neutral approach allows broadcasters and content providers to choose between HDR10 and Dolby Vision based on market considerations rather than regulatory requirements.
The European Union, through the Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) consortium, has developed specifications that support both HDR10 and Dolby Vision in broadcast standards. The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) has incorporated these specifications into formal standards, creating a framework that acknowledges both formats while maintaining technological neutrality. This approach has facilitated market-driven adoption rather than regulatory prescription.
In Asia, regulatory approaches diverge significantly. Japan's Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications has endorsed both formats for 4K/8K broadcasting, while China's National Radio and Television Administration has shown preference for HDR10+ in its standards development, potentially influencing market dynamics in the region. South Korea has adopted a similar technology-neutral stance to the United States.
Content licensing regulations also impact HDR format distribution. Dolby Vision requires licensing fees from both content creators and device manufacturers, subjecting it to additional regulatory scrutiny in markets with strong anti-monopoly frameworks. Several jurisdictions have examined whether these licensing requirements create unfair market advantages, though no major regulatory actions have resulted to date.
Copyright protection frameworks intersect with HDR technology implementation, as both formats incorporate digital rights management (DRM) systems. The legal requirements for content protection vary by jurisdiction, with the EU's Copyright Directive and the US Digital Millennium Copyright Act establishing different parameters for how HDR content can be protected and distributed.
International standards bodies, including the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), have developed recommendations for HDR implementation that influence regulatory approaches. The ITU-R BT.2100 recommendation acknowledges both HDR10 and Dolby Vision parameters, providing a technical foundation that many national regulators reference in their frameworks.
Consumer protection regulations increasingly address display technology claims, with several countries implementing rules about how HDR capabilities can be advertised. These regulations aim to prevent misleading marketing claims about display performance, indirectly influencing how HDR formats compete in the marketplace.
The European Union, through the Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) consortium, has developed specifications that support both HDR10 and Dolby Vision in broadcast standards. The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) has incorporated these specifications into formal standards, creating a framework that acknowledges both formats while maintaining technological neutrality. This approach has facilitated market-driven adoption rather than regulatory prescription.
In Asia, regulatory approaches diverge significantly. Japan's Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications has endorsed both formats for 4K/8K broadcasting, while China's National Radio and Television Administration has shown preference for HDR10+ in its standards development, potentially influencing market dynamics in the region. South Korea has adopted a similar technology-neutral stance to the United States.
Content licensing regulations also impact HDR format distribution. Dolby Vision requires licensing fees from both content creators and device manufacturers, subjecting it to additional regulatory scrutiny in markets with strong anti-monopoly frameworks. Several jurisdictions have examined whether these licensing requirements create unfair market advantages, though no major regulatory actions have resulted to date.
Copyright protection frameworks intersect with HDR technology implementation, as both formats incorporate digital rights management (DRM) systems. The legal requirements for content protection vary by jurisdiction, with the EU's Copyright Directive and the US Digital Millennium Copyright Act establishing different parameters for how HDR content can be protected and distributed.
International standards bodies, including the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), have developed recommendations for HDR implementation that influence regulatory approaches. The ITU-R BT.2100 recommendation acknowledges both HDR10 and Dolby Vision parameters, providing a technical foundation that many national regulators reference in their frameworks.
Consumer protection regulations increasingly address display technology claims, with several countries implementing rules about how HDR capabilities can be advertised. These regulations aim to prevent misleading marketing claims about display performance, indirectly influencing how HDR formats compete in the marketplace.
Licensing Models and Cost Structure Comparison
The licensing models for HDR10 and Dolby Vision represent fundamentally different approaches to market penetration and revenue generation in the high dynamic range video technology space. HDR10, as an open standard, operates on a royalty-free basis, requiring no licensing fees for implementation in displays, content creation tools, or distribution platforms. This open approach has facilitated widespread adoption across the industry, particularly among budget and mid-range device manufacturers who seek to offer HDR capabilities without incurring additional licensing costs.
In contrast, Dolby Vision employs a multi-tiered proprietary licensing structure that generates revenue at multiple points in the content delivery chain. Content creators must license Dolby Vision encoding tools, device manufacturers pay per-unit royalties for implementation in their hardware, and in some cases, distribution platforms may incur fees for delivering Dolby Vision content. Industry reports suggest that manufacturer licensing fees range from $2-3 per television unit, with higher fees for premium devices and professional equipment.
The cost implications extend beyond direct licensing fees. HDR10 implementation typically requires minimal additional hardware investment beyond basic HDR capability, with most processing handled by standard components. Dolby Vision, however, often necessitates dedicated processing chips or enhanced hardware specifications to support its dynamic metadata processing requirements, increasing the bill of materials for manufacturers by an estimated $5-15 per unit depending on device category.
For content creators, the cost differential is equally significant. HDR10 mastering can be accomplished with standard color grading tools with HDR support, while Dolby Vision mastering requires specialized equipment and software licenses that can add $10,000-50,000 to post-production facility setup costs, plus ongoing subscription or per-project fees.
These divergent licensing approaches have created distinct market segments. Premium consumer electronics brands have embraced Dolby Vision's licensing costs as a means of differentiation and value-added positioning, while budget manufacturers have rallied around HDR10 to deliver competitive HDR capabilities at lower price points. The content production ecosystem reflects similar stratification, with major studios and premium streaming platforms investing in Dolby Vision workflows while independent producers and smaller platforms predominantly utilize HDR10.
The regulatory implications of these licensing models have attracted increasing scrutiny from market competition authorities, particularly in the EU and South Korea, where concerns about market access barriers and technology lock-in have been raised. Several regulatory reviews have examined whether Dolby's licensing practices constitute an unfair competitive advantage against open standards like HDR10.
In contrast, Dolby Vision employs a multi-tiered proprietary licensing structure that generates revenue at multiple points in the content delivery chain. Content creators must license Dolby Vision encoding tools, device manufacturers pay per-unit royalties for implementation in their hardware, and in some cases, distribution platforms may incur fees for delivering Dolby Vision content. Industry reports suggest that manufacturer licensing fees range from $2-3 per television unit, with higher fees for premium devices and professional equipment.
The cost implications extend beyond direct licensing fees. HDR10 implementation typically requires minimal additional hardware investment beyond basic HDR capability, with most processing handled by standard components. Dolby Vision, however, often necessitates dedicated processing chips or enhanced hardware specifications to support its dynamic metadata processing requirements, increasing the bill of materials for manufacturers by an estimated $5-15 per unit depending on device category.
For content creators, the cost differential is equally significant. HDR10 mastering can be accomplished with standard color grading tools with HDR support, while Dolby Vision mastering requires specialized equipment and software licenses that can add $10,000-50,000 to post-production facility setup costs, plus ongoing subscription or per-project fees.
These divergent licensing approaches have created distinct market segments. Premium consumer electronics brands have embraced Dolby Vision's licensing costs as a means of differentiation and value-added positioning, while budget manufacturers have rallied around HDR10 to deliver competitive HDR capabilities at lower price points. The content production ecosystem reflects similar stratification, with major studios and premium streaming platforms investing in Dolby Vision workflows while independent producers and smaller platforms predominantly utilize HDR10.
The regulatory implications of these licensing models have attracted increasing scrutiny from market competition authorities, particularly in the EU and South Korea, where concerns about market access barriers and technology lock-in have been raised. Several regulatory reviews have examined whether Dolby's licensing practices constitute an unfair competitive advantage against open standards like HDR10.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!