How Blockchain Technologies Can Enhance V12 Engine Supply Chains
AUG 5, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Blockchain in V12 Engine Supply Chains: Overview and Objectives
Blockchain technology has emerged as a transformative force across various industries, and its potential to revolutionize the V12 engine supply chain is particularly promising. This report aims to explore how blockchain can enhance the efficiency, transparency, and security of V12 engine supply chains, addressing key challenges and identifying opportunities for innovation.
The V12 engine, known for its power and prestige, represents a complex manufacturing process involving numerous suppliers, intricate logistics, and stringent quality control measures. As the automotive industry faces increasing pressure to improve traceability, reduce costs, and enhance sustainability, blockchain offers a compelling solution to streamline supply chain operations.
Historically, supply chain management in the automotive sector has relied on centralized systems, often resulting in information silos, delays in data sharing, and potential points of failure. Blockchain's decentralized nature and immutable ledger technology present an opportunity to overcome these limitations, creating a more resilient and responsive supply chain ecosystem for V12 engines.
The primary objectives of implementing blockchain in V12 engine supply chains are multifaceted. Firstly, it aims to enhance traceability by creating an unalterable record of each component's journey from raw material to finished product. This increased visibility can significantly reduce counterfeit parts, improve quality assurance, and facilitate more efficient recalls when necessary.
Secondly, blockchain technology seeks to optimize inventory management and logistics. By providing real-time data on parts availability and location, manufacturers can reduce stockouts, minimize excess inventory, and improve just-in-time manufacturing processes. This enhanced coordination can lead to substantial cost savings and improved production efficiency.
Thirdly, blockchain aims to streamline financial transactions within the supply chain. Smart contracts can automate payments, reducing administrative overhead and ensuring prompt settlement for suppliers. This can strengthen relationships across the supply chain and potentially unlock new financing options for smaller suppliers.
Lastly, the implementation of blockchain technology in V12 engine supply chains aligns with broader industry trends towards digitalization and Industry 4.0. By creating a digital twin of the supply chain, manufacturers can leverage advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to predict maintenance needs, optimize production schedules, and drive continuous improvement.
As we delve deeper into this report, we will explore the current state of blockchain adoption in automotive supply chains, analyze potential challenges, and evaluate the most promising use cases specific to V12 engine production. By understanding the intersection of blockchain capabilities and V12 engine supply chain needs, we can chart a course for future innovation and industry transformation.
The V12 engine, known for its power and prestige, represents a complex manufacturing process involving numerous suppliers, intricate logistics, and stringent quality control measures. As the automotive industry faces increasing pressure to improve traceability, reduce costs, and enhance sustainability, blockchain offers a compelling solution to streamline supply chain operations.
Historically, supply chain management in the automotive sector has relied on centralized systems, often resulting in information silos, delays in data sharing, and potential points of failure. Blockchain's decentralized nature and immutable ledger technology present an opportunity to overcome these limitations, creating a more resilient and responsive supply chain ecosystem for V12 engines.
The primary objectives of implementing blockchain in V12 engine supply chains are multifaceted. Firstly, it aims to enhance traceability by creating an unalterable record of each component's journey from raw material to finished product. This increased visibility can significantly reduce counterfeit parts, improve quality assurance, and facilitate more efficient recalls when necessary.
Secondly, blockchain technology seeks to optimize inventory management and logistics. By providing real-time data on parts availability and location, manufacturers can reduce stockouts, minimize excess inventory, and improve just-in-time manufacturing processes. This enhanced coordination can lead to substantial cost savings and improved production efficiency.
Thirdly, blockchain aims to streamline financial transactions within the supply chain. Smart contracts can automate payments, reducing administrative overhead and ensuring prompt settlement for suppliers. This can strengthen relationships across the supply chain and potentially unlock new financing options for smaller suppliers.
Lastly, the implementation of blockchain technology in V12 engine supply chains aligns with broader industry trends towards digitalization and Industry 4.0. By creating a digital twin of the supply chain, manufacturers can leverage advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to predict maintenance needs, optimize production schedules, and drive continuous improvement.
As we delve deeper into this report, we will explore the current state of blockchain adoption in automotive supply chains, analyze potential challenges, and evaluate the most promising use cases specific to V12 engine production. By understanding the intersection of blockchain capabilities and V12 engine supply chain needs, we can chart a course for future innovation and industry transformation.
Market Demand for Blockchain-Enhanced V12 Engine Supply Chains
The market demand for blockchain-enhanced V12 engine supply chains is driven by the increasing complexity and globalization of automotive manufacturing processes. As luxury and high-performance vehicle manufacturers seek to optimize their supply chain operations, blockchain technology offers a promising solution to address key challenges in transparency, traceability, and efficiency.
The automotive industry, particularly the high-end V12 engine segment, faces growing pressure to ensure the authenticity and quality of components. Blockchain technology can provide an immutable record of each part's journey through the supply chain, from raw material sourcing to final assembly. This level of transparency is highly valued by both manufacturers and consumers, as it helps combat counterfeit parts and ensures the integrity of the final product.
Supply chain disruptions and delays have become more frequent in recent years, impacting production schedules and increasing costs for V12 engine manufacturers. Blockchain-based systems can offer real-time visibility into inventory levels, production status, and logistics, enabling more agile and responsive supply chain management. This improved coordination can lead to reduced lead times, lower inventory costs, and enhanced production efficiency.
The demand for sustainable and ethically sourced components is also driving interest in blockchain-enhanced supply chains. Luxury car manufacturers are increasingly focused on demonstrating their commitment to environmental and social responsibility. Blockchain technology can provide verifiable proof of sustainable sourcing practices, ethical labor conditions, and compliance with environmental regulations throughout the supply chain.
Furthermore, the complexity of V12 engine production, with its numerous specialized components and precise manufacturing requirements, necessitates a high degree of coordination among multiple suppliers. Blockchain-based smart contracts can automate and streamline many aspects of supplier relationships, from order placement to payment processing, reducing administrative overhead and minimizing disputes.
As regulatory requirements become more stringent, particularly in areas such as emissions standards and safety certifications, blockchain technology offers a robust solution for maintaining comprehensive and tamper-proof compliance records. This capability is especially valuable for V12 engine manufacturers operating in multiple jurisdictions with varying regulatory landscapes.
The market for blockchain-enhanced V12 engine supply chains is still in its early stages, with adoption primarily driven by forward-thinking luxury and sports car manufacturers. However, as the technology matures and its benefits become more widely recognized, demand is expected to grow significantly across the automotive industry, potentially reshaping supply chain management practices for high-performance engines.
The automotive industry, particularly the high-end V12 engine segment, faces growing pressure to ensure the authenticity and quality of components. Blockchain technology can provide an immutable record of each part's journey through the supply chain, from raw material sourcing to final assembly. This level of transparency is highly valued by both manufacturers and consumers, as it helps combat counterfeit parts and ensures the integrity of the final product.
Supply chain disruptions and delays have become more frequent in recent years, impacting production schedules and increasing costs for V12 engine manufacturers. Blockchain-based systems can offer real-time visibility into inventory levels, production status, and logistics, enabling more agile and responsive supply chain management. This improved coordination can lead to reduced lead times, lower inventory costs, and enhanced production efficiency.
The demand for sustainable and ethically sourced components is also driving interest in blockchain-enhanced supply chains. Luxury car manufacturers are increasingly focused on demonstrating their commitment to environmental and social responsibility. Blockchain technology can provide verifiable proof of sustainable sourcing practices, ethical labor conditions, and compliance with environmental regulations throughout the supply chain.
Furthermore, the complexity of V12 engine production, with its numerous specialized components and precise manufacturing requirements, necessitates a high degree of coordination among multiple suppliers. Blockchain-based smart contracts can automate and streamline many aspects of supplier relationships, from order placement to payment processing, reducing administrative overhead and minimizing disputes.
As regulatory requirements become more stringent, particularly in areas such as emissions standards and safety certifications, blockchain technology offers a robust solution for maintaining comprehensive and tamper-proof compliance records. This capability is especially valuable for V12 engine manufacturers operating in multiple jurisdictions with varying regulatory landscapes.
The market for blockchain-enhanced V12 engine supply chains is still in its early stages, with adoption primarily driven by forward-thinking luxury and sports car manufacturers. However, as the technology matures and its benefits become more widely recognized, demand is expected to grow significantly across the automotive industry, potentially reshaping supply chain management practices for high-performance engines.
Current State and Challenges in V12 Engine Supply Chain Management
The V12 engine supply chain management currently faces several significant challenges and operates in a complex state. Traditional supply chain systems for V12 engines are often fragmented and lack transparency, leading to inefficiencies and potential disruptions. One of the primary issues is the difficulty in tracking and verifying the authenticity of components throughout the supply chain, which is crucial for maintaining the high-quality standards required for V12 engines.
The current state of V12 engine supply chains typically involves multiple tiers of suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. This complexity makes it challenging to maintain real-time visibility across the entire network, often resulting in inventory management issues, delayed deliveries, and increased costs. Moreover, the high-value nature of V12 engine components makes them susceptible to counterfeiting and theft, further complicating supply chain integrity.
Another significant challenge is the lack of standardized data sharing and communication protocols among different stakeholders in the supply chain. This leads to information silos, where critical data about production schedules, quality control, and logistics is not efficiently shared across the network. As a result, decision-making processes are often based on incomplete or outdated information, impacting overall supply chain performance.
The automotive industry's increasing focus on sustainability and environmental regulations also poses challenges for V12 engine supply chains. Tracking the environmental impact of production processes and ensuring compliance with various international standards across the supply chain is becoming increasingly complex and resource-intensive.
Furthermore, the global nature of V12 engine supply chains exposes them to geopolitical risks and trade uncertainties. Recent events such as the COVID-19 pandemic and trade disputes have highlighted the vulnerabilities in these complex international networks, emphasizing the need for more resilient and adaptable supply chain structures.
Quality control and traceability remain critical challenges in V12 engine supply chains. The high-performance nature of these engines demands stringent quality standards for all components. However, the current systems often struggle to provide a comprehensive and tamper-proof record of each component's journey through the supply chain, from raw material sourcing to final assembly.
Lastly, the integration of new technologies into existing supply chain infrastructures presents both opportunities and challenges. While innovations like IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics offer potential solutions, their implementation requires significant investment and organizational change, which can be slow and challenging in established supply chain networks.
The current state of V12 engine supply chains typically involves multiple tiers of suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. This complexity makes it challenging to maintain real-time visibility across the entire network, often resulting in inventory management issues, delayed deliveries, and increased costs. Moreover, the high-value nature of V12 engine components makes them susceptible to counterfeiting and theft, further complicating supply chain integrity.
Another significant challenge is the lack of standardized data sharing and communication protocols among different stakeholders in the supply chain. This leads to information silos, where critical data about production schedules, quality control, and logistics is not efficiently shared across the network. As a result, decision-making processes are often based on incomplete or outdated information, impacting overall supply chain performance.
The automotive industry's increasing focus on sustainability and environmental regulations also poses challenges for V12 engine supply chains. Tracking the environmental impact of production processes and ensuring compliance with various international standards across the supply chain is becoming increasingly complex and resource-intensive.
Furthermore, the global nature of V12 engine supply chains exposes them to geopolitical risks and trade uncertainties. Recent events such as the COVID-19 pandemic and trade disputes have highlighted the vulnerabilities in these complex international networks, emphasizing the need for more resilient and adaptable supply chain structures.
Quality control and traceability remain critical challenges in V12 engine supply chains. The high-performance nature of these engines demands stringent quality standards for all components. However, the current systems often struggle to provide a comprehensive and tamper-proof record of each component's journey through the supply chain, from raw material sourcing to final assembly.
Lastly, the integration of new technologies into existing supply chain infrastructures presents both opportunities and challenges. While innovations like IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics offer potential solutions, their implementation requires significant investment and organizational change, which can be slow and challenging in established supply chain networks.
Existing Blockchain Solutions for Automotive Supply Chains
01 Blockchain-based data management and security
This category focuses on using blockchain technology for secure data management, storage, and sharing. It includes methods for encrypting and decentralizing data, ensuring data integrity, and providing secure access control mechanisms. These solutions can be applied in various fields such as healthcare, finance, and supply chain management to enhance data security and privacy.- Blockchain-based data management and security: Blockchain technology is utilized for secure and efficient data management across various domains. It provides a decentralized and tamper-resistant ledger for storing and sharing information, enhancing data integrity and transparency. This approach is particularly useful in sectors requiring high levels of security and traceability, such as healthcare, finance, and supply chain management.
- Smart contract implementation and automation: Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with the terms directly written into code on the blockchain. They automate and enforce the execution of contractual terms without the need for intermediaries. This technology streamlines processes, reduces costs, and enhances trust in various applications, including financial transactions, property transfers, and digital asset management.
- Blockchain interoperability and cross-chain communication: Interoperability solutions enable different blockchain networks to communicate and share data seamlessly. This advancement allows for the creation of more comprehensive and interconnected blockchain ecosystems, facilitating the exchange of assets and information across diverse platforms. It enhances the overall utility and adoption of blockchain technology across various industries.
- Blockchain-based identity management and verification: Blockchain technology is applied to create secure and decentralized identity management systems. These systems allow individuals to have greater control over their personal data while providing a reliable method for identity verification. This approach enhances privacy, reduces identity fraud, and streamlines processes in areas such as digital authentication, access control, and know-your-customer (KYC) procedures.
- Scalability and performance improvements in blockchain networks: Innovations in blockchain architecture and consensus mechanisms aim to address scalability issues and improve network performance. These advancements include layer-2 solutions, sharding techniques, and novel consensus algorithms that enhance transaction throughput, reduce latency, and lower energy consumption. Such improvements are crucial for the widespread adoption of blockchain technology in high-volume applications and enterprise-level systems.
02 Smart contracts and automated transactions
This area covers the development and implementation of smart contracts on blockchain platforms. It includes methods for creating, executing, and managing self-executing contracts with predefined rules and conditions. These technologies enable automated, trustless transactions and can be applied in various industries to streamline processes, reduce intermediaries, and increase efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Blockchain interoperability and scalability
This category addresses the challenges of blockchain interoperability and scalability. It includes technologies for connecting different blockchain networks, facilitating cross-chain transactions, and improving the overall performance and throughput of blockchain systems. These solutions aim to enhance the adoption and practical application of blockchain technology across various sectors.Expand Specific Solutions04 Blockchain-based identity management and verification
This area focuses on using blockchain technology for secure and decentralized identity management and verification. It includes methods for creating self-sovereign identities, verifiable credentials, and secure authentication mechanisms. These solutions can be applied in various contexts, such as digital identity systems, access control, and Know Your Customer (KYC) processes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Blockchain integration with IoT and AI
This category explores the integration of blockchain technology with Internet of Things (IoT) devices and Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems. It includes methods for securing IoT data on the blockchain, enabling trustless communication between devices, and leveraging AI algorithms for blockchain optimization and decision-making. These technologies aim to enhance the security, efficiency, and intelligence of interconnected systems.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Blockchain and V12 Engine Manufacturing
The blockchain technology's application to V12 engine supply chains is in an early development stage, with a growing market potential as automotive manufacturers seek to enhance transparency and efficiency. The technology's maturity varies among key players, with established automakers like Toyota, Mercedes-Benz, and Ford exploring blockchain integration. Tech giants such as Tencent and Intel are also contributing to the field, leveraging their expertise in digital technologies. While the market size is expanding, widespread adoption is still emerging, as companies navigate the complexities of implementing blockchain solutions in traditional supply chain processes.
Toyota Motor Corp.
Technical Solution: Toyota is leveraging blockchain technology to enhance its V12 engine supply chain management. The company has implemented a distributed ledger system that tracks every component from manufacture to assembly, ensuring authenticity and reducing counterfeit parts[1]. This system provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, production schedules, and logistics, enabling more efficient just-in-time manufacturing[3]. Toyota's blockchain solution also incorporates smart contracts to automate payments and enforce compliance with quality standards and regulations[5]. The company is exploring the use of blockchain-based digital passports for each engine, containing its entire history and maintenance records, which can be accessed by authorized parties throughout the engine's lifecycle[2].
Strengths: Improved traceability, reduced counterfeiting, enhanced efficiency in supply chain operations. Weaknesses: High initial implementation costs, potential scalability issues with large-scale adoption.
Mercedes-Benz Group AG
Technical Solution: Mercedes-Benz is implementing a blockchain-based solution to optimize its V12 engine supply chain. The company has developed a decentralized platform that connects all suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics providers involved in the production process[4]. This system enables real-time tracking of parts and materials, from raw material sourcing to final assembly, ensuring transparency and reducing the risk of supply chain disruptions[6]. Mercedes-Benz's blockchain solution incorporates IoT sensors to monitor environmental conditions during transport, ensuring the quality of sensitive components[8]. The company is also using blockchain to create a tamper-proof record of each engine's production history, including quality control checks and test results, which can be accessed by authorized dealers and service centers[7].
Strengths: Enhanced transparency, improved quality control, streamlined warranty and recall processes. Weaknesses: Complexity in integrating legacy systems, potential resistance from traditional suppliers.
Core Innovations in Blockchain for V12 Engine Supply Chain Optimization
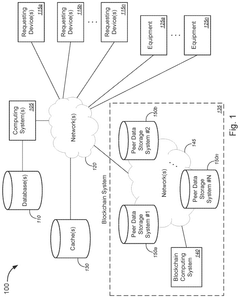
Data and source validation for equipment output data or equipment failure prediction using blockchains
PatentPendingUS20250168010A1
Innovation
- The use of blockchain technology to implement data and source validation for equipment output data and equipment failure prediction, as well as to securely track and store equipment configuration data through its immutable ledger functionality.
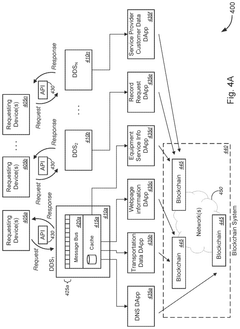
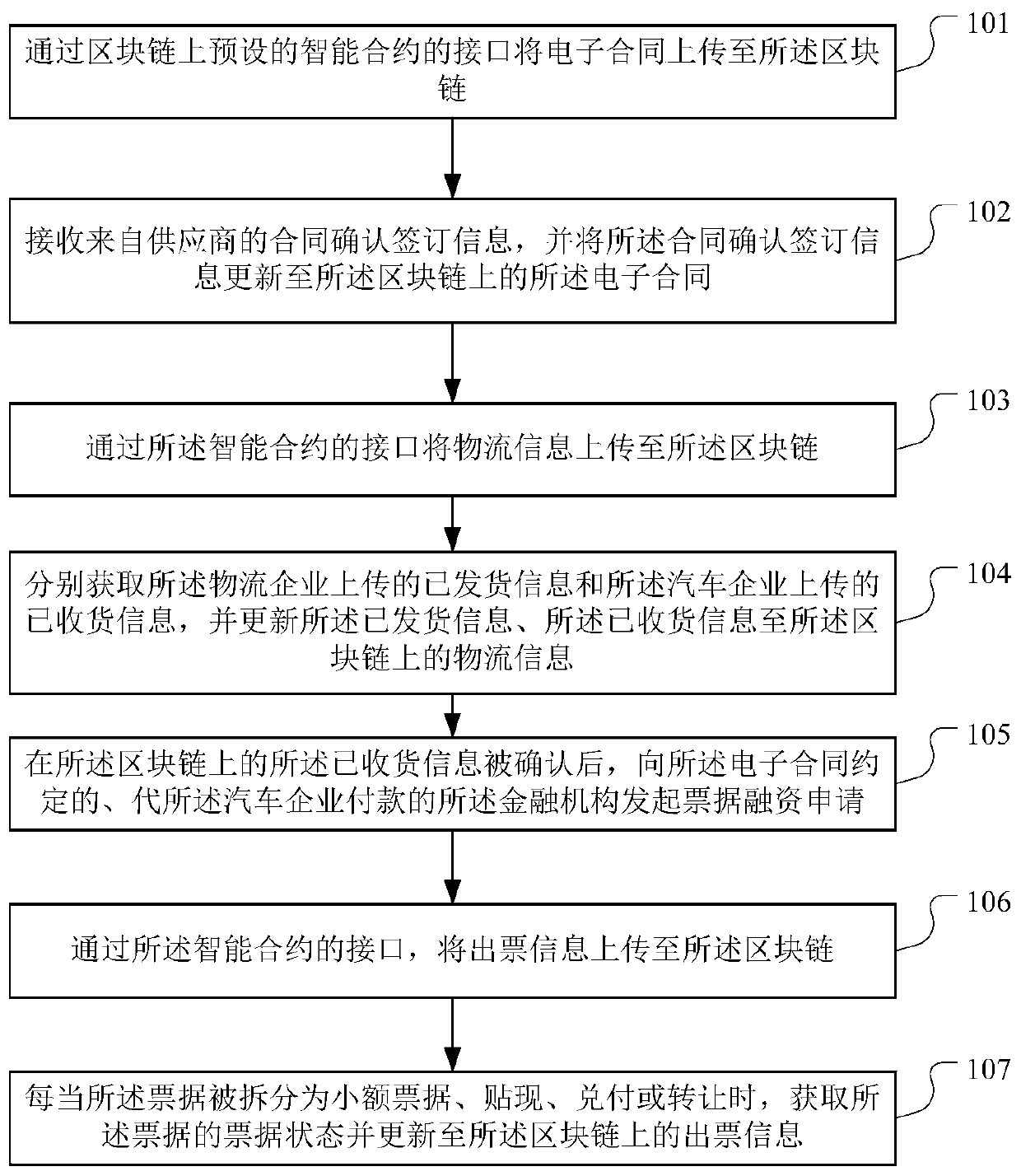
Supply process management and control method, device and equipment integrating bill financing and medium
PatentActiveCN109767214A
Innovation
- Through blockchain technology, smart contracts are preset to manage the supply chain transaction process of the automotive industry. Smart contracts on the blockchain are used to ensure the authenticity and traceability of the entire process data, improve information transparency, and achieve core corporate credit through bills. Transmission along the supply chain supports the splitting, transfer, discounting and redemption of bills to solve the financing problems of small and medium-sized enterprises.
Environmental Impact of Blockchain-Enhanced V12 Engine Supply Chains
The integration of blockchain technologies into V12 engine supply chains presents both opportunities and challenges for environmental sustainability. By enhancing transparency, traceability, and efficiency, blockchain can potentially reduce waste, optimize resource utilization, and minimize the carbon footprint associated with V12 engine production and distribution.
One of the primary environmental benefits of blockchain-enhanced supply chains is the reduction of overproduction and excess inventory. Through real-time tracking and demand forecasting, manufacturers can more accurately align production with market needs, thereby minimizing the energy and resources expended on unnecessary production. This optimization can lead to significant reductions in raw material consumption, energy usage, and associated greenhouse gas emissions.
Blockchain's ability to provide immutable and transparent records of each component's journey through the supply chain can also contribute to improved lifecycle management of V12 engines. This enhanced traceability enables more efficient maintenance, repair, and recycling processes, potentially extending the lifespan of engines and reducing the environmental impact of premature replacements.
Furthermore, the technology can facilitate the verification and tracking of sustainable practices throughout the supply chain. By recording and validating sustainability certifications, emissions data, and compliance with environmental regulations, blockchain can help ensure that all participants in the V12 engine supply chain adhere to agreed-upon environmental standards. This increased accountability can drive the adoption of more sustainable practices industry-wide.
However, it is crucial to consider the environmental costs associated with implementing and maintaining blockchain systems. The energy-intensive nature of some blockchain networks, particularly those using proof-of-work consensus mechanisms, could potentially offset some of the environmental gains achieved through supply chain optimization. To mitigate this, the adoption of more energy-efficient blockchain protocols and the use of renewable energy sources for blockchain operations should be prioritized.
Additionally, the digitization of supply chain processes enabled by blockchain can lead to reduced paper usage and decreased reliance on physical documentation. This shift towards digital record-keeping can contribute to forest conservation efforts and reduce the carbon footprint associated with document transportation and storage.
In conclusion, while blockchain technology offers significant potential for enhancing the environmental sustainability of V12 engine supply chains, its implementation must be carefully managed to ensure that the benefits outweigh the potential environmental costs. As the technology continues to evolve, ongoing research and development efforts should focus on maximizing its positive environmental impact while minimizing its energy consumption and associated emissions.
One of the primary environmental benefits of blockchain-enhanced supply chains is the reduction of overproduction and excess inventory. Through real-time tracking and demand forecasting, manufacturers can more accurately align production with market needs, thereby minimizing the energy and resources expended on unnecessary production. This optimization can lead to significant reductions in raw material consumption, energy usage, and associated greenhouse gas emissions.
Blockchain's ability to provide immutable and transparent records of each component's journey through the supply chain can also contribute to improved lifecycle management of V12 engines. This enhanced traceability enables more efficient maintenance, repair, and recycling processes, potentially extending the lifespan of engines and reducing the environmental impact of premature replacements.
Furthermore, the technology can facilitate the verification and tracking of sustainable practices throughout the supply chain. By recording and validating sustainability certifications, emissions data, and compliance with environmental regulations, blockchain can help ensure that all participants in the V12 engine supply chain adhere to agreed-upon environmental standards. This increased accountability can drive the adoption of more sustainable practices industry-wide.
However, it is crucial to consider the environmental costs associated with implementing and maintaining blockchain systems. The energy-intensive nature of some blockchain networks, particularly those using proof-of-work consensus mechanisms, could potentially offset some of the environmental gains achieved through supply chain optimization. To mitigate this, the adoption of more energy-efficient blockchain protocols and the use of renewable energy sources for blockchain operations should be prioritized.
Additionally, the digitization of supply chain processes enabled by blockchain can lead to reduced paper usage and decreased reliance on physical documentation. This shift towards digital record-keeping can contribute to forest conservation efforts and reduce the carbon footprint associated with document transportation and storage.
In conclusion, while blockchain technology offers significant potential for enhancing the environmental sustainability of V12 engine supply chains, its implementation must be carefully managed to ensure that the benefits outweigh the potential environmental costs. As the technology continues to evolve, ongoing research and development efforts should focus on maximizing its positive environmental impact while minimizing its energy consumption and associated emissions.
Regulatory Considerations for Blockchain in Automotive Industry
The integration of blockchain technology in the automotive industry, particularly in V12 engine supply chains, brings forth a complex regulatory landscape that manufacturers and suppliers must navigate. As blockchain adoption increases, regulatory bodies are developing new frameworks to address the unique challenges posed by this technology.
One of the primary regulatory considerations is data privacy and protection. The European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and similar laws worldwide have significant implications for blockchain implementations in automotive supply chains. These regulations require careful management of personal data, including the right to erasure, which can be challenging given blockchain's immutable nature. Automotive companies must design their blockchain solutions with privacy-by-design principles to ensure compliance.
Security regulations also play a crucial role in blockchain adoption for V12 engine supply chains. The automotive industry is subject to stringent cybersecurity standards, such as the UN Regulation No. 155 on Cyber Security and Cyber Security Management System. Blockchain implementations must adhere to these regulations, ensuring robust security measures to protect against potential cyber threats and unauthorized access to sensitive supply chain data.
Traceability and provenance regulations are becoming increasingly important in the automotive sector. The implementation of blockchain in V12 engine supply chains can help meet these requirements by providing an immutable record of parts and materials throughout the supply chain. However, companies must ensure their blockchain solutions comply with regulations such as the EU's End-of-Life Vehicles Directive, which mandates the traceability of certain materials and components.
Cross-border data transfer regulations present another challenge for blockchain adoption in global V12 engine supply chains. Different jurisdictions have varying requirements for data localization and transfer, such as the EU-US Privacy Shield framework. Automotive companies must carefully consider these regulations when designing their blockchain networks to ensure compliance across all operating regions.
Smart contract regulations are an emerging area of concern for blockchain implementations in the automotive industry. As smart contracts become more prevalent in supply chain management, regulators are beginning to scrutinize their legal status and enforceability. Automotive companies must stay abreast of developments in this area to ensure their blockchain-based smart contracts are legally valid and enforceable across different jurisdictions.
One of the primary regulatory considerations is data privacy and protection. The European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and similar laws worldwide have significant implications for blockchain implementations in automotive supply chains. These regulations require careful management of personal data, including the right to erasure, which can be challenging given blockchain's immutable nature. Automotive companies must design their blockchain solutions with privacy-by-design principles to ensure compliance.
Security regulations also play a crucial role in blockchain adoption for V12 engine supply chains. The automotive industry is subject to stringent cybersecurity standards, such as the UN Regulation No. 155 on Cyber Security and Cyber Security Management System. Blockchain implementations must adhere to these regulations, ensuring robust security measures to protect against potential cyber threats and unauthorized access to sensitive supply chain data.
Traceability and provenance regulations are becoming increasingly important in the automotive sector. The implementation of blockchain in V12 engine supply chains can help meet these requirements by providing an immutable record of parts and materials throughout the supply chain. However, companies must ensure their blockchain solutions comply with regulations such as the EU's End-of-Life Vehicles Directive, which mandates the traceability of certain materials and components.
Cross-border data transfer regulations present another challenge for blockchain adoption in global V12 engine supply chains. Different jurisdictions have varying requirements for data localization and transfer, such as the EU-US Privacy Shield framework. Automotive companies must carefully consider these regulations when designing their blockchain networks to ensure compliance across all operating regions.
Smart contract regulations are an emerging area of concern for blockchain implementations in the automotive industry. As smart contracts become more prevalent in supply chain management, regulators are beginning to scrutinize their legal status and enforceability. Automotive companies must stay abreast of developments in this area to ensure their blockchain-based smart contracts are legally valid and enforceable across different jurisdictions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!