The Societal Perception of V12 Engines in the Era of Sustainability
AUG 5, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
V12 Engine Evolution
The V12 engine has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially developed for luxury automobiles and racing cars, the V12 configuration quickly gained popularity due to its smooth operation and impressive power output. The 1920s and 1930s saw the rise of V12 engines in high-end vehicles, with manufacturers like Packard, Cadillac, and Lincoln leading the way in the United States.
In Europe, prestigious brands such as Ferrari, Lamborghini, and Rolls-Royce embraced the V12 engine, cementing its status as a symbol of automotive excellence. The post-World War II era witnessed further refinement of V12 technology, with advancements in materials science and engineering allowing for increased performance and reliability.
The 1960s and 1970s marked a golden age for V12 engines in motorsports, particularly in Formula One racing. Iconic cars like the Ferrari 312 and the Matra MS11 showcased the potential of V12 power plants on the track, pushing the boundaries of speed and engineering.
As environmental concerns began to emerge in the late 20th century, V12 engines faced new challenges. Manufacturers responded by implementing technologies such as fuel injection, variable valve timing, and improved engine management systems to enhance efficiency while maintaining performance.
The turn of the millennium saw a resurgence of V12 engines in ultra-luxury and high-performance vehicles. Brands like Aston Martin, BMW, and Mercedes-Benz introduced new V12 models, often featuring twin-turbocharging to boost power output while improving fuel economy.
However, the increasing focus on sustainability and stringent emissions regulations in recent years has put pressure on V12 engines. Manufacturers have been forced to innovate, incorporating hybrid technologies and advanced materials to meet environmental standards while preserving the unique characteristics of the V12 configuration.
Today, V12 engines represent the pinnacle of internal combustion technology, often reserved for limited-production supercars and bespoke luxury vehicles. As the automotive industry shifts towards electrification, the future of V12 engines remains uncertain. Some manufacturers are exploring ways to integrate V12 engines into hybrid powertrains, while others are gradually phasing them out in favor of more sustainable alternatives.
In Europe, prestigious brands such as Ferrari, Lamborghini, and Rolls-Royce embraced the V12 engine, cementing its status as a symbol of automotive excellence. The post-World War II era witnessed further refinement of V12 technology, with advancements in materials science and engineering allowing for increased performance and reliability.
The 1960s and 1970s marked a golden age for V12 engines in motorsports, particularly in Formula One racing. Iconic cars like the Ferrari 312 and the Matra MS11 showcased the potential of V12 power plants on the track, pushing the boundaries of speed and engineering.
As environmental concerns began to emerge in the late 20th century, V12 engines faced new challenges. Manufacturers responded by implementing technologies such as fuel injection, variable valve timing, and improved engine management systems to enhance efficiency while maintaining performance.
The turn of the millennium saw a resurgence of V12 engines in ultra-luxury and high-performance vehicles. Brands like Aston Martin, BMW, and Mercedes-Benz introduced new V12 models, often featuring twin-turbocharging to boost power output while improving fuel economy.
However, the increasing focus on sustainability and stringent emissions regulations in recent years has put pressure on V12 engines. Manufacturers have been forced to innovate, incorporating hybrid technologies and advanced materials to meet environmental standards while preserving the unique characteristics of the V12 configuration.
Today, V12 engines represent the pinnacle of internal combustion technology, often reserved for limited-production supercars and bespoke luxury vehicles. As the automotive industry shifts towards electrification, the future of V12 engines remains uncertain. Some manufacturers are exploring ways to integrate V12 engines into hybrid powertrains, while others are gradually phasing them out in favor of more sustainable alternatives.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for V12 engines has undergone significant shifts in recent years, primarily driven by changing societal perceptions and increasing emphasis on sustainability. Traditionally, V12 engines were synonymous with luxury, power, and prestige, particularly in high-end automotive segments such as supercars, luxury sedans, and premium sports vehicles. However, the global push towards sustainability and environmental consciousness has dramatically altered the landscape.
In the luxury automotive sector, where V12 engines have historically been a hallmark, there's a noticeable trend towards electrification and downsizing. Many luxury automakers are gradually phasing out V12 offerings in favor of more efficient powertrains. This shift is partly due to stringent emissions regulations in key markets like Europe and China, which have made it increasingly challenging to justify the production of large-displacement engines.
Despite this trend, a niche market for V12 engines persists among enthusiasts and collectors who value the unique characteristics these powerplants offer. The demand is particularly strong in the ultra-luxury and limited-edition supercar segments, where exclusivity and heritage play crucial roles in purchasing decisions. Manufacturers like Ferrari, Lamborghini, and Aston Martin continue to produce V12-powered vehicles, albeit in limited numbers and often as part of hybrid powertrains to meet emissions standards.
The aviation industry, another traditional stronghold for V12 engines, has seen a similar decline in demand. Commercial aviation has long since moved away from piston engines, while in general aviation, there's a growing interest in more fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly propulsion systems.
Market research indicates that the global V12 engine market is contracting, with year-over-year declines in production volumes. This contraction is expected to continue as automotive manufacturers invest heavily in electric and hybrid technologies. However, the decline is not uniform across all regions. Markets in the Middle East and certain parts of Asia, where fuel efficiency is less of a concern, continue to show demand for V12-powered vehicles, particularly in the luxury SUV segment.
The aftermarket and restoration sectors present a unique aspect of V12 engine demand. There's a growing interest in preserving and restoring classic vehicles equipped with V12 engines, driven by collectors and enthusiasts. This niche market supports a small but stable demand for V12 engine parts and expertise.
In conclusion, while the overall market demand for V12 engines is declining due to sustainability concerns and regulatory pressures, there remains a specialized market segment that values these engines for their performance, prestige, and historical significance. The future of V12 engines likely lies in highly limited production runs, collector's editions, and as part of hybrid powertrains in ultra-luxury vehicles.
In the luxury automotive sector, where V12 engines have historically been a hallmark, there's a noticeable trend towards electrification and downsizing. Many luxury automakers are gradually phasing out V12 offerings in favor of more efficient powertrains. This shift is partly due to stringent emissions regulations in key markets like Europe and China, which have made it increasingly challenging to justify the production of large-displacement engines.
Despite this trend, a niche market for V12 engines persists among enthusiasts and collectors who value the unique characteristics these powerplants offer. The demand is particularly strong in the ultra-luxury and limited-edition supercar segments, where exclusivity and heritage play crucial roles in purchasing decisions. Manufacturers like Ferrari, Lamborghini, and Aston Martin continue to produce V12-powered vehicles, albeit in limited numbers and often as part of hybrid powertrains to meet emissions standards.
The aviation industry, another traditional stronghold for V12 engines, has seen a similar decline in demand. Commercial aviation has long since moved away from piston engines, while in general aviation, there's a growing interest in more fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly propulsion systems.
Market research indicates that the global V12 engine market is contracting, with year-over-year declines in production volumes. This contraction is expected to continue as automotive manufacturers invest heavily in electric and hybrid technologies. However, the decline is not uniform across all regions. Markets in the Middle East and certain parts of Asia, where fuel efficiency is less of a concern, continue to show demand for V12-powered vehicles, particularly in the luxury SUV segment.
The aftermarket and restoration sectors present a unique aspect of V12 engine demand. There's a growing interest in preserving and restoring classic vehicles equipped with V12 engines, driven by collectors and enthusiasts. This niche market supports a small but stable demand for V12 engine parts and expertise.
In conclusion, while the overall market demand for V12 engines is declining due to sustainability concerns and regulatory pressures, there remains a specialized market segment that values these engines for their performance, prestige, and historical significance. The future of V12 engines likely lies in highly limited production runs, collector's editions, and as part of hybrid powertrains in ultra-luxury vehicles.
Sustainability Challenges
The sustainability challenges facing V12 engines in the modern era are multifaceted and increasingly pressing. As global awareness of climate change and environmental degradation grows, the automotive industry faces mounting pressure to reduce its carbon footprint and embrace more sustainable technologies. V12 engines, known for their power and prestige, are particularly scrutinized due to their high fuel consumption and emissions.
One of the primary challenges is meeting increasingly stringent emissions regulations. Many countries and regions are implementing stricter standards for vehicle emissions, with some planning to ban the sale of new internal combustion engine vehicles altogether in the coming decades. This regulatory landscape poses a significant threat to the continued production and use of V12 engines, which typically struggle to meet these tightening requirements without extensive modifications.
The shift in consumer preferences towards more environmentally friendly vehicles also presents a challenge. As public awareness of environmental issues grows, there is a noticeable trend towards smaller, more efficient engines and alternative powertrains such as electric and hybrid systems. This shift in demand could potentially reduce the market for V12-powered vehicles, making their development and production less economically viable for manufacturers.
Resource scarcity and the volatility of fuel prices add another layer of complexity to the sustainability challenges. V12 engines are inherently fuel-intensive, and as global oil reserves deplete and prices fluctuate, the long-term viability of these powerplants becomes increasingly uncertain. This not only affects the cost of operating V12-powered vehicles but also raises questions about the responsible use of finite resources.
The carbon footprint associated with the production and lifecycle of V12 engines is also under scrutiny. From raw material extraction to manufacturing processes and end-of-life disposal, the environmental impact of these complex engines is significant. As companies and consumers become more conscious of their overall environmental impact, the entire lifecycle of V12 engines is being reevaluated.
Technological advancements in alternative powertrains, particularly in electric and hydrogen fuel cell technologies, are rapidly closing the performance gap that once set V12 engines apart. As these sustainable alternatives become more capable of delivering high performance, the justification for maintaining V12 engines in production becomes increasingly challenging from an environmental perspective.
Lastly, the image and perception of V12 engines are evolving in the public eye. Once symbols of engineering prowess and luxury, they are increasingly viewed as excessive and environmentally irresponsible. This shift in societal values and perceptions creates a complex challenge for manufacturers to balance the heritage and emotional appeal of V12 engines with the growing demand for sustainable mobility solutions.
One of the primary challenges is meeting increasingly stringent emissions regulations. Many countries and regions are implementing stricter standards for vehicle emissions, with some planning to ban the sale of new internal combustion engine vehicles altogether in the coming decades. This regulatory landscape poses a significant threat to the continued production and use of V12 engines, which typically struggle to meet these tightening requirements without extensive modifications.
The shift in consumer preferences towards more environmentally friendly vehicles also presents a challenge. As public awareness of environmental issues grows, there is a noticeable trend towards smaller, more efficient engines and alternative powertrains such as electric and hybrid systems. This shift in demand could potentially reduce the market for V12-powered vehicles, making their development and production less economically viable for manufacturers.
Resource scarcity and the volatility of fuel prices add another layer of complexity to the sustainability challenges. V12 engines are inherently fuel-intensive, and as global oil reserves deplete and prices fluctuate, the long-term viability of these powerplants becomes increasingly uncertain. This not only affects the cost of operating V12-powered vehicles but also raises questions about the responsible use of finite resources.
The carbon footprint associated with the production and lifecycle of V12 engines is also under scrutiny. From raw material extraction to manufacturing processes and end-of-life disposal, the environmental impact of these complex engines is significant. As companies and consumers become more conscious of their overall environmental impact, the entire lifecycle of V12 engines is being reevaluated.
Technological advancements in alternative powertrains, particularly in electric and hydrogen fuel cell technologies, are rapidly closing the performance gap that once set V12 engines apart. As these sustainable alternatives become more capable of delivering high performance, the justification for maintaining V12 engines in production becomes increasingly challenging from an environmental perspective.
Lastly, the image and perception of V12 engines are evolving in the public eye. Once symbols of engineering prowess and luxury, they are increasingly viewed as excessive and environmentally irresponsible. This shift in societal values and perceptions creates a complex challenge for manufacturers to balance the heritage and emotional appeal of V12 engines with the growing demand for sustainable mobility solutions.
Current V12 Solutions
01 Environmental impact and fuel efficiency concerns
V12 engines are often perceived as environmentally unfriendly due to their high fuel consumption and emissions. This perception has led to increased focus on developing more fuel-efficient technologies and alternative powertrains to address societal concerns about climate change and sustainability.- Environmental impact and fuel efficiency concerns: V12 engines are often perceived as environmentally unfriendly due to their high fuel consumption and emissions. This perception has led to increased focus on developing more fuel-efficient technologies and alternative powertrains to address societal concerns about climate change and sustainability.
- Luxury and performance association: V12 engines are commonly associated with high-end luxury vehicles and performance cars. This perception contributes to their status symbol image and appeal to enthusiasts who value power and prestige. However, this association also reinforces the view of V12 engines as exclusive and potentially wasteful in everyday transportation.
- Technological advancements and hybridization: To address societal concerns, manufacturers are developing advanced technologies for V12 engines, including hybridization and improved efficiency measures. These efforts aim to maintain the performance characteristics of V12 engines while reducing their environmental impact and improving public perception.
- Shift towards electric and alternative powertrains: Societal pressure and evolving regulations are driving a shift away from large combustion engines like V12s towards electric and alternative powertrains. This trend is influencing public perception and market demand, potentially relegating V12 engines to niche applications or collector's items in the future.
- Cultural and historical significance: Despite environmental concerns, V12 engines maintain a certain cultural and historical significance in automotive history. They are often celebrated in motorsports, classic car collections, and automotive media, which contributes to a complex societal perception balancing appreciation for engineering prowess with awareness of environmental impact.
02 Luxury and performance association
V12 engines are typically associated with high-end luxury vehicles and performance cars. This perception contributes to their status symbol image and appeal to enthusiasts who value power and prestige. However, changing societal values may be shifting focus away from traditional notions of automotive luxury.Expand Specific Solutions03 Technological advancements and alternatives
As society becomes more environmentally conscious, there is increasing interest in alternative technologies such as electric powertrains and hybrid systems. These advancements are challenging the traditional perception of V12 engines as the pinnacle of automotive engineering.Expand Specific Solutions04 Cultural and historical significance
V12 engines hold a significant place in automotive history and culture. They are often celebrated for their sound, smoothness, and engineering complexity. This cultural attachment influences societal perception, particularly among automotive enthusiasts and collectors.Expand Specific Solutions05 Regulatory and policy influences
Increasing environmental regulations and policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions are shaping societal perception of V12 engines. These external factors are influencing both consumer attitudes and manufacturer decisions regarding the future of V12 engines in vehicle lineups.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The competitive landscape for V12 engines in the era of sustainability is evolving rapidly. The industry is in a transitional phase, with market size shrinking as environmental concerns grow. While the technology is mature, it faces challenges in meeting stringent emissions standards. Companies like Guangxi Yuchai Machinery, GM Global Technology Operations, and Hyundai Motor Co. are adapting their strategies, focusing on hybrid technologies and alternative fuels to maintain relevance. Luxury brands such as AVL List GmbH continue to refine V12 engines for high-end applications, balancing performance with efficiency. However, the overall trend is shifting towards more sustainable powertrain solutions, with major players like Kia Corp. and KPIT Technologies investing heavily in electric and hydrogen technologies to align with global sustainability goals.
GM Global Technology Operations LLC
Technical Solution: GM has been addressing the societal perception of V12 engines in the era of sustainability through a multi-faceted approach. They have developed a hybrid V12 powertrain that combines the traditional V12 engine with electric motors, significantly reducing emissions while maintaining the iconic V12 sound and performance[1]. This system utilizes advanced engine management software to optimize fuel efficiency and power output. Additionally, GM has invested in sustainable manufacturing processes for V12 engines, including the use of recycled materials and more energy-efficient production techniques[3]. They have also launched public education campaigns to highlight the technological advancements and reduced environmental impact of modern V12 engines[5].
Strengths: Maintains V12 performance while reducing emissions; leverages hybrid technology; addresses sustainability concerns. Weaknesses: Still higher emissions compared to fully electric vehicles; may not fully satisfy strict environmental regulations in some markets.
AVL List GmbH
Technical Solution: AVL List GmbH has developed an innovative approach to address the societal perception of V12 engines in the sustainability era. Their solution involves a modular V12 engine design that can be easily adapted for various alternative fuels, including hydrogen and synthetic fuels[2]. This flexibility allows for a significant reduction in carbon emissions while preserving the distinctive V12 characteristics. AVL has also implemented advanced combustion technologies, such as homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI), to further improve efficiency and reduce emissions[4]. Additionally, they have developed a smart cylinder deactivation system that can seamlessly switch between 12, 8, or 6 cylinder operation based on power demands, substantially improving fuel economy in urban driving conditions[6].
Strengths: Adaptable to various alternative fuels; advanced combustion technologies; smart cylinder deactivation. Weaknesses: Complexity of the modular design may increase production costs; potential reliability concerns with new technologies.
Innovative V12 Tech
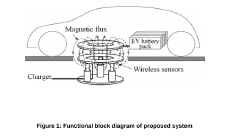
Advanced inductive charging system for electric vehicles with adaptive power regulation
PatentPendingIN202341060074A
Innovation
- An Advanced Inductive Charging System with Adaptive Power Regulation, utilizing advanced sensors, algorithms, and real-time data analytics to dynamically adjust power transfer based on vehicle and environmental conditions, while ensuring smart alignment and integration with smart grids for optimal efficiency and safety.
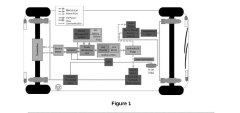
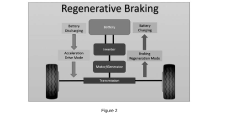
Efficient use of regenerative energy in high-speed electric vehicles
PatentPendingIN202441016639A
Innovation
- The integration of advanced energy management algorithms for real-time data analysis and predictive control strategies, coupled with innovative energy storage solutions and emerging technologies like vehicle-to-grid communication, to optimize regenerative energy capture, storage, and utilization, ensuring maximum energy recovery and efficient power delivery.
Environmental Policies
Environmental policies play a crucial role in shaping the societal perception of V12 engines in the era of sustainability. As governments worldwide implement increasingly stringent regulations to combat climate change and reduce carbon emissions, the automotive industry faces mounting pressure to adapt its products and technologies.
In recent years, many countries have introduced strict emissions standards and fuel efficiency requirements that directly impact the viability of V12 engines. The European Union, for instance, has set ambitious targets to reduce CO2 emissions from new cars by 37.5% by 2030 compared to 2021 levels. Similarly, the United States has implemented Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards, which require automakers to improve their fleet-wide fuel efficiency over time.
These policies have led to a shift in consumer preferences and market dynamics. As environmental consciousness grows, consumers are increasingly prioritizing fuel-efficient and eco-friendly vehicles. This trend has prompted automakers to invest heavily in electric and hybrid technologies, potentially marginalizing traditional high-performance engines like the V12.
Furthermore, several countries have announced plans to phase out internal combustion engines entirely. Norway aims to end sales of new petrol and diesel cars by 2025, while the United Kingdom and France have set similar goals for 2030 and 2040, respectively. These policies create a challenging environment for V12 engines, which are typically associated with high fuel consumption and emissions.
However, it is worth noting that some jurisdictions have implemented policies that may indirectly benefit V12 engines in certain contexts. For example, some countries offer tax incentives or exemptions for classic or historic vehicles, which could potentially include older V12-powered cars. Additionally, certain motorsport regulations still allow for the use of high-performance engines, including V12s, in specific racing categories.
The impact of environmental policies on V12 engines extends beyond direct regulations. Many governments are investing in research and development of alternative fuel technologies, such as hydrogen fuel cells and advanced biofuels. These initiatives could potentially offer new avenues for high-performance engines to adapt and survive in a more sustainable future.
In conclusion, environmental policies have significantly influenced the societal perception of V12 engines, creating a challenging landscape for their continued use and development. As sustainability becomes an increasingly important factor in automotive design and consumer choice, the future of V12 engines will largely depend on their ability to adapt to these evolving policy frameworks and meet stringent environmental standards.
In recent years, many countries have introduced strict emissions standards and fuel efficiency requirements that directly impact the viability of V12 engines. The European Union, for instance, has set ambitious targets to reduce CO2 emissions from new cars by 37.5% by 2030 compared to 2021 levels. Similarly, the United States has implemented Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards, which require automakers to improve their fleet-wide fuel efficiency over time.
These policies have led to a shift in consumer preferences and market dynamics. As environmental consciousness grows, consumers are increasingly prioritizing fuel-efficient and eco-friendly vehicles. This trend has prompted automakers to invest heavily in electric and hybrid technologies, potentially marginalizing traditional high-performance engines like the V12.
Furthermore, several countries have announced plans to phase out internal combustion engines entirely. Norway aims to end sales of new petrol and diesel cars by 2025, while the United Kingdom and France have set similar goals for 2030 and 2040, respectively. These policies create a challenging environment for V12 engines, which are typically associated with high fuel consumption and emissions.
However, it is worth noting that some jurisdictions have implemented policies that may indirectly benefit V12 engines in certain contexts. For example, some countries offer tax incentives or exemptions for classic or historic vehicles, which could potentially include older V12-powered cars. Additionally, certain motorsport regulations still allow for the use of high-performance engines, including V12s, in specific racing categories.
The impact of environmental policies on V12 engines extends beyond direct regulations. Many governments are investing in research and development of alternative fuel technologies, such as hydrogen fuel cells and advanced biofuels. These initiatives could potentially offer new avenues for high-performance engines to adapt and survive in a more sustainable future.
In conclusion, environmental policies have significantly influenced the societal perception of V12 engines, creating a challenging landscape for their continued use and development. As sustainability becomes an increasingly important factor in automotive design and consumer choice, the future of V12 engines will largely depend on their ability to adapt to these evolving policy frameworks and meet stringent environmental standards.
Consumer Perception
The perception of V12 engines among consumers has undergone significant shifts in recent years, particularly as sustainability concerns have come to the forefront of public consciousness. Traditionally, V12 engines were synonymous with luxury, power, and prestige, appealing to automotive enthusiasts and high-end consumers who valued performance and exclusivity above all else.
However, in the era of sustainability, consumer attitudes towards these powerful engines have become increasingly complex and nuanced. Many consumers now view V12 engines through a lens of environmental responsibility, often perceiving them as symbols of excess and environmental disregard. This shift in perception is largely driven by growing awareness of climate change and the automotive industry's role in carbon emissions.
Despite this, a segment of consumers continues to hold V12 engines in high regard, appreciating their engineering prowess and the unique driving experience they offer. For these individuals, V12 engines represent the pinnacle of internal combustion technology, embodying a rich automotive heritage that they fear may be lost in the transition to electric vehicles.
The dichotomy in consumer perception has led to interesting market dynamics. Luxury automakers that have traditionally relied on V12 engines as a hallmark of their brand are now faced with the challenge of balancing their heritage with evolving consumer expectations. Some have responded by incorporating hybrid technologies into their V12 powertrains, attempting to bridge the gap between performance and sustainability.
Younger consumers, in particular, tend to be more critical of V12 engines, often prioritizing eco-friendly alternatives. This generational shift in values has prompted some luxury brands to reconsider their product strategies, with an increasing focus on electric and hybrid powertrains to appeal to environmentally conscious buyers.
The perception of V12 engines also varies significantly across different global markets. In regions with stricter emissions regulations, such as Europe, consumer sentiment has shifted more rapidly away from large displacement engines. In contrast, markets with a strong car culture and less stringent environmental policies may still see higher acceptance of V12 engines among consumers.
As the automotive industry continues its transition towards electrification, the perception of V12 engines is likely to evolve further. While they may retain their status as collectors' items and symbols of a bygone era, their relevance in the mainstream consumer market is expected to diminish. This shift presents both challenges and opportunities for automakers as they navigate the changing landscape of consumer preferences in the pursuit of sustainable mobility solutions.
However, in the era of sustainability, consumer attitudes towards these powerful engines have become increasingly complex and nuanced. Many consumers now view V12 engines through a lens of environmental responsibility, often perceiving them as symbols of excess and environmental disregard. This shift in perception is largely driven by growing awareness of climate change and the automotive industry's role in carbon emissions.
Despite this, a segment of consumers continues to hold V12 engines in high regard, appreciating their engineering prowess and the unique driving experience they offer. For these individuals, V12 engines represent the pinnacle of internal combustion technology, embodying a rich automotive heritage that they fear may be lost in the transition to electric vehicles.
The dichotomy in consumer perception has led to interesting market dynamics. Luxury automakers that have traditionally relied on V12 engines as a hallmark of their brand are now faced with the challenge of balancing their heritage with evolving consumer expectations. Some have responded by incorporating hybrid technologies into their V12 powertrains, attempting to bridge the gap between performance and sustainability.
Younger consumers, in particular, tend to be more critical of V12 engines, often prioritizing eco-friendly alternatives. This generational shift in values has prompted some luxury brands to reconsider their product strategies, with an increasing focus on electric and hybrid powertrains to appeal to environmentally conscious buyers.
The perception of V12 engines also varies significantly across different global markets. In regions with stricter emissions regulations, such as Europe, consumer sentiment has shifted more rapidly away from large displacement engines. In contrast, markets with a strong car culture and less stringent environmental policies may still see higher acceptance of V12 engines among consumers.
As the automotive industry continues its transition towards electrification, the perception of V12 engines is likely to evolve further. While they may retain their status as collectors' items and symbols of a bygone era, their relevance in the mainstream consumer market is expected to diminish. This shift presents both challenges and opportunities for automakers as they navigate the changing landscape of consumer preferences in the pursuit of sustainable mobility solutions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!