How Carbolic Acid Functions in Food Preservation Technologies
JUL 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Carbolic Acid Preservation Background
Carbolic acid, also known as phenol, has a long and significant history in food preservation technologies. This organic compound was first isolated from coal tar in the 1830s and quickly gained prominence for its antiseptic properties. In the context of food preservation, carbolic acid's ability to inhibit microbial growth has made it a valuable tool in extending the shelf life of various food products.
The use of carbolic acid in food preservation can be traced back to the late 19th century when the principles of food microbiology were beginning to be understood. Its effectiveness against a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and yeasts, made it an attractive option for food manufacturers seeking to prevent spoilage and maintain product quality.
Carbolic acid functions primarily through its ability to denature proteins and disrupt cell membranes of microorganisms. This mechanism of action is particularly effective in preventing the growth of pathogenic bacteria that can cause foodborne illnesses. By interfering with the metabolic processes of these microorganisms, carbolic acid helps to maintain the safety and integrity of food products over extended periods.
In the early stages of its application, carbolic acid was used in relatively high concentrations, which sometimes led to concerns about its potential toxicity and impact on food flavor. However, as food preservation technologies advanced, more refined methods of applying carbolic acid were developed, allowing for its use in lower, safer concentrations while still maintaining its effectiveness.
The evolution of carbolic acid use in food preservation has been closely tied to regulatory developments in the food industry. As food safety standards became more stringent, the application of carbolic acid and other preservatives came under increased scrutiny. This led to more precise guidelines for its use, ensuring that it could be employed safely and effectively in various food products.
Today, carbolic acid continues to play a role in food preservation, albeit in a more limited capacity compared to its historical use. Modern food preservation techniques often combine carbolic acid with other preservatives or employ it as part of a multi-faceted approach to food safety and shelf-life extension. Its use is particularly notable in certain types of processed foods, where it helps to maintain product stability and prevent microbial contamination.
The ongoing research into carbolic acid and its derivatives has led to the development of more sophisticated preservation methods. These include the use of phenolic compounds in active packaging materials, where they can provide antimicrobial protection without direct contact with the food product. Such innovations demonstrate the continuing relevance of carbolic acid in the field of food preservation technologies, even as new alternatives emerge.
The use of carbolic acid in food preservation can be traced back to the late 19th century when the principles of food microbiology were beginning to be understood. Its effectiveness against a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and yeasts, made it an attractive option for food manufacturers seeking to prevent spoilage and maintain product quality.
Carbolic acid functions primarily through its ability to denature proteins and disrupt cell membranes of microorganisms. This mechanism of action is particularly effective in preventing the growth of pathogenic bacteria that can cause foodborne illnesses. By interfering with the metabolic processes of these microorganisms, carbolic acid helps to maintain the safety and integrity of food products over extended periods.
In the early stages of its application, carbolic acid was used in relatively high concentrations, which sometimes led to concerns about its potential toxicity and impact on food flavor. However, as food preservation technologies advanced, more refined methods of applying carbolic acid were developed, allowing for its use in lower, safer concentrations while still maintaining its effectiveness.
The evolution of carbolic acid use in food preservation has been closely tied to regulatory developments in the food industry. As food safety standards became more stringent, the application of carbolic acid and other preservatives came under increased scrutiny. This led to more precise guidelines for its use, ensuring that it could be employed safely and effectively in various food products.
Today, carbolic acid continues to play a role in food preservation, albeit in a more limited capacity compared to its historical use. Modern food preservation techniques often combine carbolic acid with other preservatives or employ it as part of a multi-faceted approach to food safety and shelf-life extension. Its use is particularly notable in certain types of processed foods, where it helps to maintain product stability and prevent microbial contamination.
The ongoing research into carbolic acid and its derivatives has led to the development of more sophisticated preservation methods. These include the use of phenolic compounds in active packaging materials, where they can provide antimicrobial protection without direct contact with the food product. Such innovations demonstrate the continuing relevance of carbolic acid in the field of food preservation technologies, even as new alternatives emerge.
Food Preservation Market Analysis
The global food preservation market has been experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for convenience foods, longer shelf life, and food safety. As of 2021, the market was valued at approximately $296 billion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.8% through 2026. This growth is attributed to several factors, including urbanization, changing lifestyles, and the need for extended food storage in both developed and developing economies.
The market for food preservation technologies can be segmented into various categories, including chemical preservatives, thermal processing, high-pressure processing, and irradiation. Among these, chemical preservatives, which include carbolic acid and its derivatives, hold a substantial market share due to their cost-effectiveness and wide applicability across different food products.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the food preservation market, accounting for over 60% of the global market share. This is primarily due to the presence of established food processing industries, stringent food safety regulations, and high consumer awareness regarding food quality and safety. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable incomes, and changing dietary habits.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the growth of the food preservation market. Consumers' heightened focus on food safety and the surge in demand for packaged and processed foods during lockdowns have created new opportunities for food preservation technologies. This trend is expected to continue in the post-pandemic era, as consumers maintain their preference for longer-lasting food products.
Key players in the food preservation market include multinational corporations such as Cargill, DuPont, and Kerry Group, as well as specialized preservative manufacturers. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to innovate new preservation techniques and improve existing ones, including those involving carbolic acid and its derivatives.
The market for carbolic acid in food preservation is influenced by factors such as regulatory approvals, consumer perception of chemical preservatives, and the growing trend towards natural and clean-label products. While carbolic acid and its derivatives continue to play a crucial role in food preservation, there is an increasing demand for alternative preservation methods that are perceived as more natural or less chemical-intensive.
The market for food preservation technologies can be segmented into various categories, including chemical preservatives, thermal processing, high-pressure processing, and irradiation. Among these, chemical preservatives, which include carbolic acid and its derivatives, hold a substantial market share due to their cost-effectiveness and wide applicability across different food products.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the food preservation market, accounting for over 60% of the global market share. This is primarily due to the presence of established food processing industries, stringent food safety regulations, and high consumer awareness regarding food quality and safety. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by rapid industrialization, increasing disposable incomes, and changing dietary habits.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the growth of the food preservation market. Consumers' heightened focus on food safety and the surge in demand for packaged and processed foods during lockdowns have created new opportunities for food preservation technologies. This trend is expected to continue in the post-pandemic era, as consumers maintain their preference for longer-lasting food products.
Key players in the food preservation market include multinational corporations such as Cargill, DuPont, and Kerry Group, as well as specialized preservative manufacturers. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to innovate new preservation techniques and improve existing ones, including those involving carbolic acid and its derivatives.
The market for carbolic acid in food preservation is influenced by factors such as regulatory approvals, consumer perception of chemical preservatives, and the growing trend towards natural and clean-label products. While carbolic acid and its derivatives continue to play a crucial role in food preservation, there is an increasing demand for alternative preservation methods that are perceived as more natural or less chemical-intensive.
Carbolic Acid Technology Status
Carbolic acid, also known as phenol, has been utilized in food preservation technologies for decades due to its potent antimicrobial properties. The current status of carbolic acid in food preservation is characterized by a balance between its effectiveness and safety concerns.
In recent years, the use of carbolic acid in direct food contact applications has been significantly restricted due to its potential toxicity. Regulatory bodies, such as the FDA in the United States and EFSA in Europe, have imposed strict limitations on its use in food-related applications. As a result, carbolic acid is primarily employed in indirect food preservation methods, such as sanitizing food processing equipment and surfaces.
The technology surrounding carbolic acid in food preservation has evolved to focus on developing safer derivatives and formulations. Researchers have been exploring modified versions of carbolic acid that retain its antimicrobial efficacy while reducing potential health risks. These efforts have led to the development of phenolic compounds with improved safety profiles, which are being tested for their applicability in food preservation.
Current applications of carbolic acid in food preservation technologies mainly revolve around its use as a disinfectant in food processing environments. It is particularly effective against a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. The compound's ability to disrupt cellular membranes and denature proteins makes it a powerful tool in maintaining hygienic conditions in food production facilities.
Despite its limitations in direct food contact, carbolic acid continues to play a crucial role in ensuring food safety through its application in cleaning and sanitizing processes. Its use in combination with other preservation methods, such as heat treatment or modified atmosphere packaging, has shown promising results in extending the shelf life of various food products.
Research is ongoing to explore novel applications of carbolic acid and its derivatives in food preservation. Some studies have investigated the potential of incorporating phenolic compounds into packaging materials to create active packaging systems. These systems aim to provide continuous antimicrobial protection throughout the food's storage and distribution.
The technology status of carbolic acid in food preservation is also influenced by the growing demand for natural and eco-friendly preservation methods. This has led to increased interest in plant-derived phenolic compounds that offer similar antimicrobial properties to synthetic carbolic acid but with potentially lower environmental and health impacts.
In conclusion, while the direct use of carbolic acid in food preservation has been limited due to safety concerns, its technological applications continue to evolve. The focus has shifted towards developing safer alternatives, optimizing its use in indirect preservation methods, and exploring innovative approaches to harness its antimicrobial properties in food safety and preservation.
In recent years, the use of carbolic acid in direct food contact applications has been significantly restricted due to its potential toxicity. Regulatory bodies, such as the FDA in the United States and EFSA in Europe, have imposed strict limitations on its use in food-related applications. As a result, carbolic acid is primarily employed in indirect food preservation methods, such as sanitizing food processing equipment and surfaces.
The technology surrounding carbolic acid in food preservation has evolved to focus on developing safer derivatives and formulations. Researchers have been exploring modified versions of carbolic acid that retain its antimicrobial efficacy while reducing potential health risks. These efforts have led to the development of phenolic compounds with improved safety profiles, which are being tested for their applicability in food preservation.
Current applications of carbolic acid in food preservation technologies mainly revolve around its use as a disinfectant in food processing environments. It is particularly effective against a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. The compound's ability to disrupt cellular membranes and denature proteins makes it a powerful tool in maintaining hygienic conditions in food production facilities.
Despite its limitations in direct food contact, carbolic acid continues to play a crucial role in ensuring food safety through its application in cleaning and sanitizing processes. Its use in combination with other preservation methods, such as heat treatment or modified atmosphere packaging, has shown promising results in extending the shelf life of various food products.
Research is ongoing to explore novel applications of carbolic acid and its derivatives in food preservation. Some studies have investigated the potential of incorporating phenolic compounds into packaging materials to create active packaging systems. These systems aim to provide continuous antimicrobial protection throughout the food's storage and distribution.
The technology status of carbolic acid in food preservation is also influenced by the growing demand for natural and eco-friendly preservation methods. This has led to increased interest in plant-derived phenolic compounds that offer similar antimicrobial properties to synthetic carbolic acid but with potentially lower environmental and health impacts.
In conclusion, while the direct use of carbolic acid in food preservation has been limited due to safety concerns, its technological applications continue to evolve. The focus has shifted towards developing safer alternatives, optimizing its use in indirect preservation methods, and exploring innovative approaches to harness its antimicrobial properties in food safety and preservation.
Current Carbolic Acid Solutions
01 Use of carbolic acid in preservation solutions
Carbolic acid, also known as phenol, is utilized in various preservation solutions due to its antimicrobial properties. These solutions are employed to protect materials, specimens, or products from microbial degradation, extending their shelf life and maintaining their integrity.- Use of carbolic acid in preservation solutions: Carbolic acid, also known as phenol, is utilized in various preservation solutions to prevent microbial growth and extend the shelf life of products. These solutions can be applied in different industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
- Carbolic acid in medical and healthcare applications: Carbolic acid is employed in medical and healthcare settings for its antiseptic properties. It is used in disinfectants, sterilization solutions, and as a preservative in pharmaceutical formulations to maintain product integrity and prevent contamination.
- Carbolic acid in water treatment and purification: Carbolic acid is utilized in water treatment processes to eliminate harmful microorganisms and improve water quality. It is incorporated into water purification systems and treatment methods for both industrial and domestic applications.
- Carbolic acid in industrial preservation: Carbolic acid is employed in various industrial preservation applications, including wood preservation, textile preservation, and as a component in protective coatings. It helps prevent decay, mold growth, and deterioration of materials in industrial settings.
- Carbolic acid in agricultural and pest control: Carbolic acid is used in agricultural applications for pest control and preservation of crops and seeds. It is incorporated into formulations for protecting plants from diseases and insects, as well as in storage solutions for agricultural products.
02 Carbolic acid in medical and pharmaceutical applications
Carbolic acid finds applications in medical and pharmaceutical fields for its antiseptic and disinfectant properties. It is used in the formulation of various medical products, including topical treatments and sterilization solutions for medical equipment.Expand Specific Solutions03 Carbolic acid in industrial preservation
In industrial settings, carbolic acid is employed as a preservative for various materials and products. It is particularly useful in preventing microbial growth and degradation in industrial processes, storage, and transportation of goods.Expand Specific Solutions04 Carbolic acid in water treatment and purification
Carbolic acid is utilized in water treatment and purification processes due to its ability to eliminate harmful microorganisms. It is incorporated into water treatment systems and purification methods to ensure the safety and quality of water for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Innovations in carbolic acid preservation techniques
Recent advancements in carbolic acid preservation techniques have led to improved efficacy and safety in its applications. These innovations include novel formulations, controlled release mechanisms, and combination with other preservatives to enhance its effectiveness while minimizing potential side effects.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Preservation
The food preservation technology utilizing carbolic acid is in a mature stage of development, with a well-established market and significant industry players. The global food preservatives market size is substantial, estimated to reach billions of dollars annually. Companies like LANXESS Deutschland GmbH, DSM IP Assets BV, and Chr. Hansen A/S are at the forefront of this technology, leveraging their expertise in chemical and bioscience solutions. These firms, along with others such as Arla Foods AmbA and Meiji Co., Ltd., have developed advanced formulations and applications of carbolic acid and related compounds for food preservation, demonstrating the high level of technical maturity in this field. The competitive landscape is characterized by ongoing research and development efforts to enhance efficacy and address evolving consumer preferences for natural preservatives.
LANXESS Deutschland GmbH
Technical Solution: LANXESS has developed advanced carbolic acid-based food preservation technologies. Their approach involves using phenol derivatives as antimicrobial agents in food packaging materials. The company has created a range of specialty chemicals that slowly release carbolic acid compounds, providing long-lasting protection against bacteria and fungi. This controlled-release technology ensures a consistent antimicrobial effect throughout the shelf life of the food product[1]. LANXESS has also formulated carbolic acid-based solutions for direct food application, particularly in meat and poultry processing, where the compounds act as surface sanitizers and preservatives[2].
Strengths: Expertise in specialty chemicals, controlled-release technology, and broad application range. Weaknesses: Potential consumer concerns about chemical preservatives, regulatory challenges in different markets.
DSM IP Assets BV
Technical Solution: DSM has innovated in the field of natural food preservation using carbolic acid derivatives. Their approach focuses on developing plant-based phenolic compounds that mimic the preservative effects of synthetic carbolic acid. DSM's technology utilizes green extraction methods to obtain these compounds from sources like rosemary and green tea[3]. The company has successfully incorporated these natural preservatives into a range of food products, including baked goods, dairy, and processed meats. DSM's preservatives work by inhibiting oxidation and microbial growth, extending shelf life while maintaining the "clean label" status desired by many consumers[4].
Strengths: Natural and clean label solutions, broad application in various food categories. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost compared to synthetic preservatives, variable efficacy depending on food matrix.
Carbolic Acid Innovations
Method for separation of proteins from phenolic compounds
PatentPendingUS20240010676A1
Innovation
- A method involving cross-flow membrane filtration followed by diafiltration with increased ionic strength and pH control, allowing phenolic compounds to permeate while retaining proteins, and subsequent recycling of salts to enhance permeability and reduce fouling, thereby isolating phenolic compounds in a purified state.
Phenolic compounds and uses thereof
PatentWO1996019435A1
Innovation
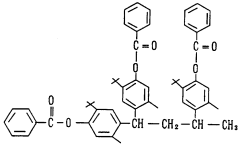
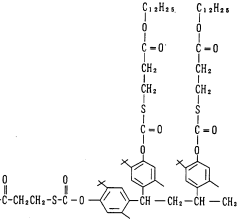
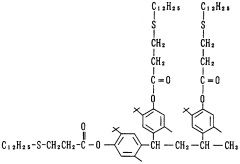
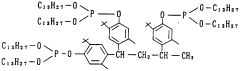
- A phenol compound with a phenyl ester structure, represented by the general formula [1], is designed to prevent oxidation deterioration in organic materials, even in the presence of water or hot water, by maintaining its antioxidant effect through chemical structure modifications that produce a new compound with anti-oxidative properties upon degradation.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding the use of carbolic acid in food preservation technologies is complex and multifaceted, involving various national and international bodies. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating food additives and preservatives. The FDA has established specific guidelines for the use of carbolic acid, also known as phenol, in food preservation. These regulations outline permissible concentrations, application methods, and safety requirements for its use in food products.
At the international level, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides global standards for food safety and quality. The Codex has set maximum residue limits for carbolic acid in various food categories, ensuring a harmonized approach to its use across different countries.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also conducted extensive assessments on the safety of carbolic acid in food preservation. Their scientific opinions inform the European Union's regulations on food additives, including specific provisions for carbolic acid usage in food processing and preservation.
In addition to these overarching regulatory bodies, individual countries often have their own regulatory agencies that oversee the use of food preservatives. For instance, Health Canada regulates food additives through the Food and Drug Regulations, while the Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ) sets standards for both countries.
These regulatory frameworks typically address several key aspects of carbolic acid use in food preservation. These include maximum allowable concentrations, approved food categories for application, labeling requirements, and safety assessment protocols. Many regulations also mandate regular reviews of scientific evidence to ensure that safety standards remain up-to-date with the latest research findings.
Compliance with these regulations often requires food manufacturers to implement rigorous quality control measures and conduct regular testing to ensure that carbolic acid levels in their products remain within prescribed limits. Additionally, many regulatory bodies require manufacturers to demonstrate the technological need for using carbolic acid as a preservative, ensuring that its use is justified and not merely for convenience.
As scientific understanding of food preservation technologies evolves, regulatory frameworks are periodically updated to reflect new findings. This dynamic nature of food safety regulations necessitates ongoing vigilance from both regulators and food manufacturers to ensure that the use of carbolic acid in food preservation remains safe and effective.
At the international level, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides global standards for food safety and quality. The Codex has set maximum residue limits for carbolic acid in various food categories, ensuring a harmonized approach to its use across different countries.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also conducted extensive assessments on the safety of carbolic acid in food preservation. Their scientific opinions inform the European Union's regulations on food additives, including specific provisions for carbolic acid usage in food processing and preservation.
In addition to these overarching regulatory bodies, individual countries often have their own regulatory agencies that oversee the use of food preservatives. For instance, Health Canada regulates food additives through the Food and Drug Regulations, while the Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ) sets standards for both countries.
These regulatory frameworks typically address several key aspects of carbolic acid use in food preservation. These include maximum allowable concentrations, approved food categories for application, labeling requirements, and safety assessment protocols. Many regulations also mandate regular reviews of scientific evidence to ensure that safety standards remain up-to-date with the latest research findings.
Compliance with these regulations often requires food manufacturers to implement rigorous quality control measures and conduct regular testing to ensure that carbolic acid levels in their products remain within prescribed limits. Additionally, many regulatory bodies require manufacturers to demonstrate the technological need for using carbolic acid as a preservative, ensuring that its use is justified and not merely for convenience.
As scientific understanding of food preservation technologies evolves, regulatory frameworks are periodically updated to reflect new findings. This dynamic nature of food safety regulations necessitates ongoing vigilance from both regulators and food manufacturers to ensure that the use of carbolic acid in food preservation remains safe and effective.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The use of carbolic acid (phenol) in food preservation technologies has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. While effective in inhibiting microbial growth and extending food shelf life, the widespread application of carbolic acid raises concerns about its potential ecological impact.
One primary environmental concern is the release of carbolic acid residues into water systems through food processing effluents. These residues can persist in aquatic environments, potentially harming aquatic organisms and disrupting ecosystem balance. Studies have shown that even low concentrations of phenol can be toxic to fish, invertebrates, and algae, leading to reduced biodiversity in affected water bodies.
Soil contamination is another environmental risk associated with carbolic acid use in food preservation. Improper disposal of treated food products or packaging materials can result in soil pollution, affecting soil microorganisms and plant growth. This contamination may persist in the soil for extended periods, potentially entering the food chain through crops grown in affected areas.
The production and disposal of carbolic acid also contribute to air pollution. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released during manufacturing processes and waste incineration can contribute to smog formation and air quality degradation. Additionally, the carbon footprint associated with the production and transportation of carbolic acid adds to overall greenhouse gas emissions.
From a sustainability perspective, the reliance on synthetic chemical preservatives like carbolic acid raises questions about long-term environmental sustainability in food preservation practices. There is growing interest in developing more environmentally friendly alternatives, such as natural antimicrobials derived from plant extracts or biopreservation techniques using beneficial microorganisms.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented strict guidelines for the use and disposal of carbolic acid in food preservation to mitigate its environmental impact. These regulations often include limits on residue levels in food products, proper waste management protocols, and requirements for treatment of industrial effluents containing phenolic compounds.
As the food industry continues to evolve, there is an increasing focus on developing more sustainable preservation technologies that minimize environmental impact while maintaining food safety and quality. This includes research into green chemistry approaches for synthesizing less harmful preservatives and exploring novel preservation methods that reduce reliance on chemical additives altogether.
One primary environmental concern is the release of carbolic acid residues into water systems through food processing effluents. These residues can persist in aquatic environments, potentially harming aquatic organisms and disrupting ecosystem balance. Studies have shown that even low concentrations of phenol can be toxic to fish, invertebrates, and algae, leading to reduced biodiversity in affected water bodies.
Soil contamination is another environmental risk associated with carbolic acid use in food preservation. Improper disposal of treated food products or packaging materials can result in soil pollution, affecting soil microorganisms and plant growth. This contamination may persist in the soil for extended periods, potentially entering the food chain through crops grown in affected areas.
The production and disposal of carbolic acid also contribute to air pollution. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released during manufacturing processes and waste incineration can contribute to smog formation and air quality degradation. Additionally, the carbon footprint associated with the production and transportation of carbolic acid adds to overall greenhouse gas emissions.
From a sustainability perspective, the reliance on synthetic chemical preservatives like carbolic acid raises questions about long-term environmental sustainability in food preservation practices. There is growing interest in developing more environmentally friendly alternatives, such as natural antimicrobials derived from plant extracts or biopreservation techniques using beneficial microorganisms.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have implemented strict guidelines for the use and disposal of carbolic acid in food preservation to mitigate its environmental impact. These regulations often include limits on residue levels in food products, proper waste management protocols, and requirements for treatment of industrial effluents containing phenolic compounds.
As the food industry continues to evolve, there is an increasing focus on developing more sustainable preservation technologies that minimize environmental impact while maintaining food safety and quality. This includes research into green chemistry approaches for synthesizing less harmful preservatives and exploring novel preservation methods that reduce reliance on chemical additives altogether.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!