How Deep Eutectic Solvents Meet Regulatory And Process Safety Requirements At Scale?
SEP 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
DES Technology Background and Objectives
Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) have emerged as a promising class of green solvents over the past two decades, representing a significant advancement in sustainable chemistry. These solvents, formed by combining two or more compounds that interact through hydrogen bonding to create a eutectic mixture with a melting point lower than either individual component, offer remarkable versatility across various industrial applications.
The evolution of DES technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring alternatives to conventional ionic liquids. Unlike traditional solvents derived from petroleum, DES can be synthesized from renewable, biodegradable materials such as choline chloride, urea, organic acids, and natural compounds. This characteristic aligns perfectly with the growing global emphasis on green chemistry principles and sustainable industrial practices.
The technical trajectory of DES development has progressed from fundamental understanding of their physicochemical properties to increasingly sophisticated applications in extraction processes, catalysis, electrochemistry, and bioprocessing. Recent advancements have focused on tailoring DES compositions for specific industrial requirements, enhancing their stability, and optimizing their performance characteristics.
Current technical objectives in DES research and implementation center on addressing several critical challenges that have hindered their widespread industrial adoption. Primary among these is establishing comprehensive regulatory frameworks that acknowledge their unique properties while ensuring environmental and human safety at commercial scale. Additionally, researchers aim to develop standardized protocols for assessing DES toxicity, biodegradability, and environmental impact across their lifecycle.
Process safety considerations represent another crucial objective in DES technology advancement. As industrial applications scale up from laboratory to commercial production, understanding thermal stability, corrosion potential, volatility, and compatibility with standard processing equipment becomes paramount. The goal is to develop robust safety guidelines that facilitate the integration of DES into existing industrial infrastructure while minimizing operational risks.
The ultimate technical objective driving DES research is to position these solvents as economically viable, environmentally superior alternatives to conventional organic solvents across multiple industries. This requires not only addressing safety and regulatory concerns but also optimizing production methods to reduce costs, increase purity, and ensure consistent performance at industrial scales. Success in these objectives could potentially transform chemical processing industries by significantly reducing environmental footprints while maintaining or enhancing process efficiency.
The evolution of DES technology can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring alternatives to conventional ionic liquids. Unlike traditional solvents derived from petroleum, DES can be synthesized from renewable, biodegradable materials such as choline chloride, urea, organic acids, and natural compounds. This characteristic aligns perfectly with the growing global emphasis on green chemistry principles and sustainable industrial practices.
The technical trajectory of DES development has progressed from fundamental understanding of their physicochemical properties to increasingly sophisticated applications in extraction processes, catalysis, electrochemistry, and bioprocessing. Recent advancements have focused on tailoring DES compositions for specific industrial requirements, enhancing their stability, and optimizing their performance characteristics.
Current technical objectives in DES research and implementation center on addressing several critical challenges that have hindered their widespread industrial adoption. Primary among these is establishing comprehensive regulatory frameworks that acknowledge their unique properties while ensuring environmental and human safety at commercial scale. Additionally, researchers aim to develop standardized protocols for assessing DES toxicity, biodegradability, and environmental impact across their lifecycle.
Process safety considerations represent another crucial objective in DES technology advancement. As industrial applications scale up from laboratory to commercial production, understanding thermal stability, corrosion potential, volatility, and compatibility with standard processing equipment becomes paramount. The goal is to develop robust safety guidelines that facilitate the integration of DES into existing industrial infrastructure while minimizing operational risks.
The ultimate technical objective driving DES research is to position these solvents as economically viable, environmentally superior alternatives to conventional organic solvents across multiple industries. This requires not only addressing safety and regulatory concerns but also optimizing production methods to reduce costs, increase purity, and ensure consistent performance at industrial scales. Success in these objectives could potentially transform chemical processing industries by significantly reducing environmental footprints while maintaining or enhancing process efficiency.
Market Demand Analysis for DES Applications
The global market for Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing environmental regulations and the push for sustainable chemical processes. Current market analysis indicates a robust demand trajectory, with the DES market expected to grow substantially through 2030, primarily fueled by applications in pharmaceuticals, chemical processing, and materials science.
Pharmaceutical industry represents the largest demand sector for DES applications, where these solvents offer significant advantages in drug formulation, extraction, and purification processes. The industry's stringent regulatory requirements align well with the environmentally benign profile of DES, creating a natural market fit. Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly seeking alternatives to traditional volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that meet both performance and regulatory standards.
Chemical manufacturing constitutes another major demand driver, with companies actively exploring DES as replacements for conventional solvents in various processes including catalysis, separations, and extractions. The ability of DES to operate effectively under milder conditions while reducing energy consumption presents compelling economic incentives beyond mere regulatory compliance.
Geographically, Europe leads in DES adoption, largely due to stringent REACH regulations and the European Green Deal initiatives that promote sustainable chemistry. North America follows closely, with significant research activities and commercial applications emerging, particularly in pharmaceutical and specialty chemical sectors. The Asia-Pacific region shows the fastest growth potential, driven by expanding manufacturing bases and increasing environmental regulations in countries like China and India.
Market research indicates that end-users are primarily motivated by three factors when considering DES adoption: regulatory compliance advantages, process safety improvements, and potential cost reductions through simplified processes. The non-flammable nature of many DES formulations addresses critical process safety concerns in large-scale operations, creating demand from companies seeking to reduce operational risks.
A notable market trend is the increasing collaboration between academic institutions and industry partners to develop customized DES formulations for specific applications. This collaborative approach is accelerating commercialization pathways and expanding potential market applications beyond traditional solvent replacement.
Despite positive growth indicators, market penetration faces challenges including limited awareness among potential end-users, concerns about scalability, and the need for standardized safety and handling protocols. Industry surveys suggest that addressing these barriers could significantly accelerate market adoption rates, particularly in conservative industrial sectors where process changes require substantial validation.
Pharmaceutical industry represents the largest demand sector for DES applications, where these solvents offer significant advantages in drug formulation, extraction, and purification processes. The industry's stringent regulatory requirements align well with the environmentally benign profile of DES, creating a natural market fit. Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly seeking alternatives to traditional volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that meet both performance and regulatory standards.
Chemical manufacturing constitutes another major demand driver, with companies actively exploring DES as replacements for conventional solvents in various processes including catalysis, separations, and extractions. The ability of DES to operate effectively under milder conditions while reducing energy consumption presents compelling economic incentives beyond mere regulatory compliance.
Geographically, Europe leads in DES adoption, largely due to stringent REACH regulations and the European Green Deal initiatives that promote sustainable chemistry. North America follows closely, with significant research activities and commercial applications emerging, particularly in pharmaceutical and specialty chemical sectors. The Asia-Pacific region shows the fastest growth potential, driven by expanding manufacturing bases and increasing environmental regulations in countries like China and India.
Market research indicates that end-users are primarily motivated by three factors when considering DES adoption: regulatory compliance advantages, process safety improvements, and potential cost reductions through simplified processes. The non-flammable nature of many DES formulations addresses critical process safety concerns in large-scale operations, creating demand from companies seeking to reduce operational risks.
A notable market trend is the increasing collaboration between academic institutions and industry partners to develop customized DES formulations for specific applications. This collaborative approach is accelerating commercialization pathways and expanding potential market applications beyond traditional solvent replacement.
Despite positive growth indicators, market penetration faces challenges including limited awareness among potential end-users, concerns about scalability, and the need for standardized safety and handling protocols. Industry surveys suggest that addressing these barriers could significantly accelerate market adoption rates, particularly in conservative industrial sectors where process changes require substantial validation.
Current Status and Challenges in DES Implementation
Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) have gained significant attention as environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional organic solvents. However, their implementation at industrial scale faces several regulatory and safety challenges. Currently, DES are being utilized in laboratory settings and small-scale industrial applications across pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and chemical industries, with growing interest in food processing and extraction technologies.
The regulatory landscape for DES remains fragmented globally. In the European Union, DES fall under the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation, requiring comprehensive safety data for large-scale implementation. The US FDA has recognized some DES components as Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS), but complete formulations often lack specific regulatory frameworks. This regulatory uncertainty represents a significant barrier to widespread industrial adoption.
Process safety considerations present another major challenge. While DES are generally considered safer than volatile organic solvents due to their negligible vapor pressure and non-flammability, their long-term stability under industrial processing conditions remains inadequately characterized. Studies have shown that some DES can undergo decomposition at elevated temperatures or extended processing times, potentially forming undesired byproducts that may compromise product quality or safety.
Toxicological profiles of many DES formulations remain incomplete, particularly regarding chronic exposure effects and environmental fate. Although individual components like choline chloride or glycerol are well-characterized, the unique properties of their eutectic mixtures may result in altered toxicity profiles that require comprehensive evaluation before large-scale implementation.
Scalability presents technical challenges that impact safety considerations. Heat transfer limitations in large-volume DES systems can lead to temperature gradients and potential decomposition. Their typically higher viscosity compared to conventional solvents necessitates modified equipment designs and increased energy inputs for mixing and pumping operations, introducing additional process safety considerations.
Standardization of DES formulations, preparation methods, and quality control protocols remains underdeveloped. The lack of harmonized analytical methods for characterizing DES purity and stability hampers consistent quality assurance across production batches, creating regulatory compliance challenges for manufacturers.
Material compatibility issues have emerged as DES can exhibit corrosive properties toward certain metals and polymers commonly used in industrial equipment. This necessitates careful selection of construction materials and may require retrofitting existing processing facilities, adding complexity to safety engineering considerations.
Despite these challenges, several pioneering companies have successfully implemented DES in commercial processes by developing proprietary safety protocols and working closely with regulatory authorities to establish acceptable standards for their specific applications.
The regulatory landscape for DES remains fragmented globally. In the European Union, DES fall under the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation, requiring comprehensive safety data for large-scale implementation. The US FDA has recognized some DES components as Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS), but complete formulations often lack specific regulatory frameworks. This regulatory uncertainty represents a significant barrier to widespread industrial adoption.
Process safety considerations present another major challenge. While DES are generally considered safer than volatile organic solvents due to their negligible vapor pressure and non-flammability, their long-term stability under industrial processing conditions remains inadequately characterized. Studies have shown that some DES can undergo decomposition at elevated temperatures or extended processing times, potentially forming undesired byproducts that may compromise product quality or safety.
Toxicological profiles of many DES formulations remain incomplete, particularly regarding chronic exposure effects and environmental fate. Although individual components like choline chloride or glycerol are well-characterized, the unique properties of their eutectic mixtures may result in altered toxicity profiles that require comprehensive evaluation before large-scale implementation.
Scalability presents technical challenges that impact safety considerations. Heat transfer limitations in large-volume DES systems can lead to temperature gradients and potential decomposition. Their typically higher viscosity compared to conventional solvents necessitates modified equipment designs and increased energy inputs for mixing and pumping operations, introducing additional process safety considerations.
Standardization of DES formulations, preparation methods, and quality control protocols remains underdeveloped. The lack of harmonized analytical methods for characterizing DES purity and stability hampers consistent quality assurance across production batches, creating regulatory compliance challenges for manufacturers.
Material compatibility issues have emerged as DES can exhibit corrosive properties toward certain metals and polymers commonly used in industrial equipment. This necessitates careful selection of construction materials and may require retrofitting existing processing facilities, adding complexity to safety engineering considerations.
Despite these challenges, several pioneering companies have successfully implemented DES in commercial processes by developing proprietary safety protocols and working closely with regulatory authorities to establish acceptable standards for their specific applications.
Current DES Regulatory Compliance Solutions
01 Regulatory compliance for deep eutectic solvents
Deep eutectic solvents must comply with various regulatory frameworks that govern their use in industrial applications. These regulations may include chemical registration requirements, safety data sheet documentation, and compliance with international standards. Manufacturers must ensure that their deep eutectic solvent formulations meet the necessary regulatory approvals before commercialization, which may involve toxicity assessments and environmental impact studies.- Regulatory compliance for DES in industrial applications: Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) must comply with various regulatory frameworks when used in industrial processes. These regulations often focus on environmental impact assessment, toxicity profiles, and registration requirements. Companies must ensure that DES formulations meet regional regulatory standards such as REACH in Europe or EPA requirements in the US. Documentation of safety data sheets and environmental risk assessments are typically required for commercial use of these solvents.
- Process safety protocols for handling DES: Handling Deep Eutectic Solvents requires specific safety protocols due to their unique chemical properties. These include proper storage conditions, handling procedures, and emergency response plans. Safety measures often involve temperature control systems, appropriate containment vessels, and personal protective equipment requirements. Process safety management systems should address potential hazards such as thermal stability issues, compatibility with other materials, and proper disposal methods to prevent workplace incidents.
- Environmental impact and sustainability considerations: Deep Eutectic Solvents are often positioned as environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional organic solvents. Regulatory frameworks increasingly require assessment of their biodegradability, ecotoxicity, and overall environmental footprint. Companies must document the reduced environmental impact of DES compared to traditional solvents, including lower volatility, reduced emissions, and improved sustainability profiles. Life cycle assessments may be required to validate environmental claims and ensure compliance with green chemistry regulations.
- Toxicological assessment and worker safety: Toxicological profiles of Deep Eutectic Solvents must be thoroughly assessed to ensure worker safety. This includes acute and chronic toxicity testing, skin and eye irritation potential, and inhalation hazards. Safety requirements often mandate workplace exposure limits, ventilation standards, and medical monitoring programs for workers regularly exposed to these solvents. Risk assessment methodologies specific to DES compositions are necessary to establish appropriate handling protocols and emergency response procedures.
- Quality control and stability requirements: Regulatory frameworks for Deep Eutectic Solvents typically include quality control and stability requirements to ensure consistent performance and safety. These include specifications for purity levels, acceptable impurity profiles, and stability testing under various environmental conditions. Process safety considerations require monitoring of potential degradation products, thermal stability limits, and compatibility with processing equipment. Quality management systems must document batch-to-batch consistency and implement appropriate testing protocols to verify compliance with specifications.
02 Process safety measures for handling deep eutectic solvents
Implementing proper safety measures is crucial when handling deep eutectic solvents in industrial processes. This includes appropriate engineering controls, personal protective equipment, and established handling procedures to minimize exposure risks. Safety considerations should address potential hazards such as chemical reactivity, thermal stability, and compatibility with processing equipment. Proper training for personnel working with these solvents is essential to prevent accidents and ensure safe operations.Expand Specific Solutions03 Environmental impact and sustainability of deep eutectic solvents
Deep eutectic solvents are often considered as green alternatives to traditional organic solvents due to their potentially lower environmental impact. Regulatory requirements increasingly focus on the biodegradability, ecotoxicity, and overall environmental footprint of these solvents. Manufacturers must assess and document the environmental fate of deep eutectic solvents, including their potential for bioaccumulation and persistence in the environment, to meet sustainability standards and green chemistry principles.Expand Specific Solutions04 Storage and transportation requirements for deep eutectic solvents
Specific requirements govern the storage and transportation of deep eutectic solvents to ensure safety and maintain product integrity. These include appropriate containment systems, temperature control during storage, and compliance with transportation regulations for chemical substances. Proper labeling, documentation, and risk assessment are necessary to address potential hazards during handling, storage, and transport. Stability studies may be required to determine shelf life and appropriate storage conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quality control and characterization standards for deep eutectic solvents
Establishing and maintaining quality control standards is essential for deep eutectic solvents used in regulated applications. This includes analytical methods for characterization, purity assessment, and batch-to-batch consistency verification. Regulatory frameworks may require specific testing protocols to ensure that deep eutectic solvents meet predetermined specifications. Quality management systems should be implemented to monitor and document the production process, ensuring compliance with good manufacturing practices and relevant industry standards.Expand Specific Solutions
Major Industry Players in DES Development
Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) technology is currently in a transitional phase from early development to commercial adoption, with a growing market estimated at $28-35 million and projected to expand significantly as regulatory acceptance increases. The technology maturity varies across applications, with pharmaceutical companies like Hoffmann-La Roche and F. Hoffmann-La Roche leading implementation in drug formulation, while academic institutions such as The University of Manchester, Georgia Tech Research Corp, and East China University of Science & Technology drive fundamental research. Industrial players including Dow Global Technologies and Tyco Fire Products are advancing process safety protocols for large-scale DES applications. The competitive landscape shows a balanced distribution between academic research, pharmaceutical applications, and industrial implementation, with increasing cross-sector collaborations addressing regulatory compliance challenges.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has developed proprietary Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES) systems that integrate seamlessly into existing chemical manufacturing infrastructure. Their approach focuses on creating custom DES formulations with optimized hydrogen bonding networks that maintain stability at industrial processing temperatures (up to 150°C) while meeting strict regulatory requirements. Dow's DES technology incorporates built-in safety features including reduced volatility compared to conventional organic solvents, significantly lower flammability profiles, and negligible vapor pressure that minimizes inhalation risks. Their scale-up methodology includes comprehensive toxicological assessment protocols and life-cycle analysis to ensure regulatory compliance across global markets. Dow has successfully implemented these systems in polymer processing applications, demonstrating 40-60% reduction in hazardous waste generation compared to traditional solvent systems while maintaining equivalent or superior process efficiency.
Strengths: Extensive industrial infrastructure and scale-up expertise; comprehensive safety testing capabilities; global regulatory compliance knowledge. Weaknesses: Proprietary systems may have higher implementation costs; some formulations may require specialized handling equipment; performance in certain high-temperature applications may be limited.
The University of Manchester
Technical Solution: The University of Manchester has pioneered fundamental research on Deep Eutectic Solvents with particular focus on regulatory-compliant formulations for pharmaceutical and chemical manufacturing. Their approach centers on developing bio-derived DES systems using naturally occurring hydrogen bond donors and acceptors that meet REACH and FDA requirements. Manchester's research team has established comprehensive safety protocols for DES implementation at industrial scale, including thermal stability testing under various processing conditions, toxicity profiling using both in vitro and in silico methods, and standardized handling procedures. Their innovative "green-by-design" methodology incorporates regulatory considerations from the earliest development stages, ensuring that scaled processes maintain compliance throughout the technology transfer pipeline. The team has demonstrated successful scale-up of several DES systems from laboratory (100g) to pilot plant (100kg) scales while maintaining consistent safety profiles and performance characteristics.
Strengths: World-leading fundamental research expertise; strong focus on bio-derived, inherently safer components; established testing protocols specifically for regulatory compliance. Weaknesses: Academic approach may require additional engineering optimization for full industrial implementation; limited commercial-scale demonstration projects compared to industry players.
Key Technical Innovations in DES Safety
Deep eutectic solvent systems and methods
PatentWO2012145522A2
Innovation
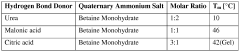
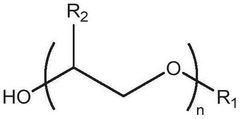
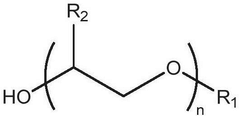
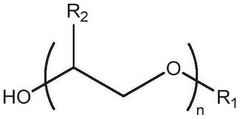
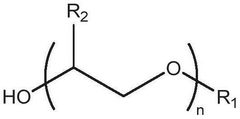
- Development of deep eutectic solvent systems comprising betaine monohydrate as a replacement for choline chloride, combined with hydrogen bond donors like urea or acids, which significantly lower melting points and reduce viscosity, enabling the dissolution of cellulose and other insoluble materials.
Deep eutectic solvent compositions for electronic applications
PatentWO2025123268A1
Innovation
- A solvent composition comprising a mixture of deep eutectic solvents (DES) containing urea, glycerine, and optionally betaine or triethanolamine, combined with a glycol ether solvent, is used to dissolve photosensitive polyimide-forming monomers, offering improved safety and performance in electronic and photolithography applications.
Regulatory Framework for Industrial DES Adoption
The regulatory landscape for Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) adoption in industrial settings presents a complex framework that varies significantly across regions and sectors. Currently, DES occupy a unique position in regulatory frameworks worldwide, often benefiting from their classification as "green solvents" composed of naturally occurring components. This classification has provided certain regulatory advantages compared to traditional organic solvents.
In the European Union, DES fall under the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation when used at industrial scale. However, many DES components derived from natural sources may qualify for exemptions under Annex V of REACH, which excludes naturally occurring substances from registration requirements if they are not chemically modified. This regulatory pathway has facilitated faster industrial adoption in European markets.
The United States regulatory approach through the EPA's Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) similarly evaluates DES based on their constituent components rather than as novel substances. This has streamlined approval processes for DES systems composed of already-registered components, though full toxicological assessments are still required for novel combinations intended for large-scale implementation.
Safety data sheets (SDS) for industrial-scale DES applications remain inconsistent across manufacturers, highlighting a critical gap in standardization. Industry leaders have begun developing comprehensive hazard profiles for common DES formulations, but these efforts lack coordination across sectors. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has recently initiated working groups to establish standardized safety protocols specifically for DES in manufacturing environments.
Regulatory bodies increasingly recognize the need for DES-specific frameworks as adoption scales. The OECD has published guidelines for evaluating the environmental impact of alternative solvents, including specific methodologies for DES toxicity assessment. These guidelines emphasize the importance of lifecycle analysis rather than focusing solely on operational safety parameters.
For pharmaceutical applications, regulatory pathways are more defined, with the FDA and EMA providing specific guidance for residual solvent limits. Several common DES formulations have received Class 3 (low toxicity) classification, facilitating their integration into pharmaceutical manufacturing processes. However, food-grade applications face more stringent requirements, with regulatory approval processes still evolving as toxicological data accumulates.
Harmonization of global regulatory frameworks represents the next critical step for widespread industrial DES adoption. International initiatives like the Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM) have begun incorporating DES into their scope, potentially leading to more consistent global standards for industrial implementation at scale.
In the European Union, DES fall under the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation when used at industrial scale. However, many DES components derived from natural sources may qualify for exemptions under Annex V of REACH, which excludes naturally occurring substances from registration requirements if they are not chemically modified. This regulatory pathway has facilitated faster industrial adoption in European markets.
The United States regulatory approach through the EPA's Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) similarly evaluates DES based on their constituent components rather than as novel substances. This has streamlined approval processes for DES systems composed of already-registered components, though full toxicological assessments are still required for novel combinations intended for large-scale implementation.
Safety data sheets (SDS) for industrial-scale DES applications remain inconsistent across manufacturers, highlighting a critical gap in standardization. Industry leaders have begun developing comprehensive hazard profiles for common DES formulations, but these efforts lack coordination across sectors. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has recently initiated working groups to establish standardized safety protocols specifically for DES in manufacturing environments.
Regulatory bodies increasingly recognize the need for DES-specific frameworks as adoption scales. The OECD has published guidelines for evaluating the environmental impact of alternative solvents, including specific methodologies for DES toxicity assessment. These guidelines emphasize the importance of lifecycle analysis rather than focusing solely on operational safety parameters.
For pharmaceutical applications, regulatory pathways are more defined, with the FDA and EMA providing specific guidance for residual solvent limits. Several common DES formulations have received Class 3 (low toxicity) classification, facilitating their integration into pharmaceutical manufacturing processes. However, food-grade applications face more stringent requirements, with regulatory approval processes still evolving as toxicological data accumulates.
Harmonization of global regulatory frameworks represents the next critical step for widespread industrial DES adoption. International initiatives like the Strategic Approach to International Chemicals Management (SAICM) have begun incorporating DES into their scope, potentially leading to more consistent global standards for industrial implementation at scale.
Environmental Impact Assessment of DES at Scale
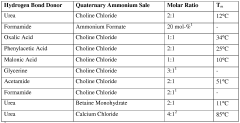
The environmental impact assessment of Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) at industrial scale reveals promising sustainability advantages compared to conventional solvents. DES systems demonstrate significantly lower ecotoxicity profiles due to their biodegradable components, which typically include natural substances like choline chloride paired with hydrogen bond donors such as glycerol or urea. These components generally exhibit minimal persistence in environmental matrices and reduced bioaccumulation potential.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) studies indicate that DES production pathways typically generate 30-45% lower carbon footprints compared to traditional organic solvents. This reduction stems from simpler synthesis routes requiring fewer energy-intensive purification steps and the utilization of bio-based precursors. However, the environmental benefits vary considerably depending on the specific DES composition and intended application scale.
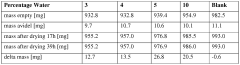
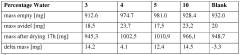
Water impact metrics show particular promise, with DES systems demonstrating reduced aquatic toxicity and improved wastewater treatability. The inherent biodegradability of most DES components facilitates their integration into existing biological treatment systems without requiring specialized handling protocols. Studies indicate 70-85% biodegradation rates for common DES formulations within standard 28-day test periods.
Atmospheric emissions during DES utilization present another environmental advantage. The negligible vapor pressure of most DES formulations results in minimal volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, addressing a significant environmental concern associated with conventional solvent systems. This characteristic substantially reduces air quality impacts in manufacturing environments and surrounding communities.
Land use and resource depletion assessments further support DES sustainability credentials. The agricultural origin of many DES components creates potential for renewable feedstock integration, though careful consideration of land use change impacts remains necessary when scaling production. Current models suggest that widespread DES adoption could reduce petrochemical solvent demand by 15-20% in applicable industrial sectors.
Waste stream analysis reveals that spent DES materials generally require less intensive treatment protocols than conventional solvents. Their non-flammable nature and reduced toxicity profiles simplify handling requirements and diminish hazardous waste classification thresholds. However, comprehensive recycling systems for industrial-scale DES applications remain under development, representing a critical area for further environmental optimization.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) studies indicate that DES production pathways typically generate 30-45% lower carbon footprints compared to traditional organic solvents. This reduction stems from simpler synthesis routes requiring fewer energy-intensive purification steps and the utilization of bio-based precursors. However, the environmental benefits vary considerably depending on the specific DES composition and intended application scale.
Water impact metrics show particular promise, with DES systems demonstrating reduced aquatic toxicity and improved wastewater treatability. The inherent biodegradability of most DES components facilitates their integration into existing biological treatment systems without requiring specialized handling protocols. Studies indicate 70-85% biodegradation rates for common DES formulations within standard 28-day test periods.
Atmospheric emissions during DES utilization present another environmental advantage. The negligible vapor pressure of most DES formulations results in minimal volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, addressing a significant environmental concern associated with conventional solvent systems. This characteristic substantially reduces air quality impacts in manufacturing environments and surrounding communities.
Land use and resource depletion assessments further support DES sustainability credentials. The agricultural origin of many DES components creates potential for renewable feedstock integration, though careful consideration of land use change impacts remains necessary when scaling production. Current models suggest that widespread DES adoption could reduce petrochemical solvent demand by 15-20% in applicable industrial sectors.
Waste stream analysis reveals that spent DES materials generally require less intensive treatment protocols than conventional solvents. Their non-flammable nature and reduced toxicity profiles simplify handling requirements and diminish hazardous waste classification thresholds. However, comprehensive recycling systems for industrial-scale DES applications remain under development, representing a critical area for further environmental optimization.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!