How Half Wave Rectifier Design Affects Power Quality?
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Half Wave Rectifier Background and Objectives
Half wave rectifiers have been a fundamental component in power electronics since the early days of electrical engineering. Developed in the late 19th century, these devices played a crucial role in converting alternating current (AC) to pulsating direct current (DC). The evolution of half wave rectifiers has been closely tied to the advancement of power quality standards and the increasing demand for efficient energy conversion.
The primary objective of half wave rectifier design is to achieve optimal power conversion while minimizing negative impacts on power quality. This involves balancing factors such as efficiency, harmonic distortion, and power factor. As power systems have become more complex and sensitive to disturbances, the importance of understanding how half wave rectifier design affects power quality has grown significantly.
Over the years, the technology behind half wave rectifiers has progressed from simple diode-based designs to more sophisticated configurations incorporating advanced semiconductor devices. This evolution has been driven by the need to address power quality issues such as harmonic distortion, voltage fluctuations, and electromagnetic interference. The development of international standards for power quality, such as IEEE 519 and IEC 61000, has further emphasized the importance of optimizing rectifier design.
Recent technological trends in half wave rectifier design focus on improving power factor correction, reducing total harmonic distortion (THD), and enhancing overall system efficiency. Innovations in semiconductor materials and topologies have led to the development of high-frequency rectifiers capable of operating at elevated switching frequencies, thereby reducing the size of passive components and improving power density.
The impact of half wave rectifier design on power quality extends beyond the immediate point of conversion. It affects the entire power distribution system, influencing factors such as voltage stability, equipment lifespan, and energy efficiency. As renewable energy sources and smart grid technologies become more prevalent, the role of efficient and power quality-conscious rectifier designs becomes increasingly critical.
Looking ahead, the objectives for half wave rectifier design in relation to power quality include further reduction of harmonic content, improved dynamic response to load variations, and enhanced integration with digital control systems. There is also a growing emphasis on developing "smart" rectifiers capable of adapting to changing grid conditions and power quality requirements in real-time.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of half wave rectifier design in the context of power quality reflect a continuous journey of technological advancement and adaptation to evolving energy needs. As power systems become more complex and interconnected, the challenge of optimizing rectifier design to maintain and improve power quality remains at the forefront of power electronics research and development.
The primary objective of half wave rectifier design is to achieve optimal power conversion while minimizing negative impacts on power quality. This involves balancing factors such as efficiency, harmonic distortion, and power factor. As power systems have become more complex and sensitive to disturbances, the importance of understanding how half wave rectifier design affects power quality has grown significantly.
Over the years, the technology behind half wave rectifiers has progressed from simple diode-based designs to more sophisticated configurations incorporating advanced semiconductor devices. This evolution has been driven by the need to address power quality issues such as harmonic distortion, voltage fluctuations, and electromagnetic interference. The development of international standards for power quality, such as IEEE 519 and IEC 61000, has further emphasized the importance of optimizing rectifier design.
Recent technological trends in half wave rectifier design focus on improving power factor correction, reducing total harmonic distortion (THD), and enhancing overall system efficiency. Innovations in semiconductor materials and topologies have led to the development of high-frequency rectifiers capable of operating at elevated switching frequencies, thereby reducing the size of passive components and improving power density.
The impact of half wave rectifier design on power quality extends beyond the immediate point of conversion. It affects the entire power distribution system, influencing factors such as voltage stability, equipment lifespan, and energy efficiency. As renewable energy sources and smart grid technologies become more prevalent, the role of efficient and power quality-conscious rectifier designs becomes increasingly critical.
Looking ahead, the objectives for half wave rectifier design in relation to power quality include further reduction of harmonic content, improved dynamic response to load variations, and enhanced integration with digital control systems. There is also a growing emphasis on developing "smart" rectifiers capable of adapting to changing grid conditions and power quality requirements in real-time.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of half wave rectifier design in the context of power quality reflect a continuous journey of technological advancement and adaptation to evolving energy needs. As power systems become more complex and interconnected, the challenge of optimizing rectifier design to maintain and improve power quality remains at the forefront of power electronics research and development.
Power Quality Market Analysis
The power quality market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for reliable and efficient electrical power across various industries. This market encompasses a wide range of products and services designed to monitor, analyze, and improve the quality of electrical power supply. The global power quality equipment market is expected to reach substantial value in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) that reflects the growing importance of power quality in modern electrical systems.
One of the key factors driving the growth of the power quality market is the rising adoption of sensitive electronic equipment in industrial, commercial, and residential sectors. These devices require a stable and clean power supply to function optimally, making power quality solutions essential for their protection and longevity. Additionally, the increasing integration of renewable energy sources into the power grid has created new challenges for maintaining power quality, further fueling the demand for advanced power quality equipment and services.
The market for power quality solutions can be segmented based on equipment type, end-user industry, and geography. Equipment types include voltage regulators, harmonic filters, power conditioners, and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems. Among these, UPS systems hold a significant market share due to their widespread use in critical applications such as data centers, healthcare facilities, and industrial processes.
In terms of end-user industries, the manufacturing sector represents a major consumer of power quality solutions, followed by healthcare, IT and telecommunications, and transportation. The manufacturing industry's reliance on precision equipment and automated processes makes it particularly vulnerable to power quality issues, driving the adoption of power quality management systems.
Geographically, North America and Europe have traditionally been the largest markets for power quality equipment, owing to their well-established industrial sectors and stringent power quality regulations. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, fueled by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing investments in smart grid infrastructure.
The competitive landscape of the power quality market is characterized by the presence of several large multinational corporations as well as numerous smaller, specialized players. Key market players are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their market position and expand their product portfolios.
Looking ahead, the power quality market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by factors such as the increasing digitalization of industries, the growing importance of energy efficiency, and the rising awareness of the economic impacts of poor power quality. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning are also expected to play a significant role in the development of more advanced and predictive power quality management solutions.
One of the key factors driving the growth of the power quality market is the rising adoption of sensitive electronic equipment in industrial, commercial, and residential sectors. These devices require a stable and clean power supply to function optimally, making power quality solutions essential for their protection and longevity. Additionally, the increasing integration of renewable energy sources into the power grid has created new challenges for maintaining power quality, further fueling the demand for advanced power quality equipment and services.
The market for power quality solutions can be segmented based on equipment type, end-user industry, and geography. Equipment types include voltage regulators, harmonic filters, power conditioners, and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems. Among these, UPS systems hold a significant market share due to their widespread use in critical applications such as data centers, healthcare facilities, and industrial processes.
In terms of end-user industries, the manufacturing sector represents a major consumer of power quality solutions, followed by healthcare, IT and telecommunications, and transportation. The manufacturing industry's reliance on precision equipment and automated processes makes it particularly vulnerable to power quality issues, driving the adoption of power quality management systems.
Geographically, North America and Europe have traditionally been the largest markets for power quality equipment, owing to their well-established industrial sectors and stringent power quality regulations. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, fueled by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing investments in smart grid infrastructure.
The competitive landscape of the power quality market is characterized by the presence of several large multinational corporations as well as numerous smaller, specialized players. Key market players are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their market position and expand their product portfolios.
Looking ahead, the power quality market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, driven by factors such as the increasing digitalization of industries, the growing importance of energy efficiency, and the rising awareness of the economic impacts of poor power quality. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning are also expected to play a significant role in the development of more advanced and predictive power quality management solutions.
Current Challenges in Half Wave Rectifier Design
Half wave rectifiers, while simple in design, face several challenges that significantly impact power quality. One of the primary issues is the inherent inefficiency of these systems. By utilizing only half of the AC waveform, half wave rectifiers waste a substantial portion of the input power, leading to lower overall efficiency compared to full wave rectifiers.
The pulsating nature of the output from half wave rectifiers presents another significant challenge. This pulsation introduces a high ripple factor, which can cause instability in the DC output voltage. The ripple not only affects the quality of the power supplied to the load but also increases the stress on filtering components, potentially reducing their lifespan and reliability.
Harmonic distortion is a critical concern in half wave rectifier designs. The non-linear characteristics of these rectifiers generate harmonics in the AC supply system, particularly odd harmonics. These harmonics can propagate back into the power grid, causing electromagnetic interference and potentially damaging sensitive equipment connected to the same power source.
The poor power factor associated with half wave rectifiers is another challenge that designers must address. The discontinuous current draw from the AC source results in a low power factor, which can lead to increased power losses in the distribution system and higher electricity costs for industrial applications.
Voltage regulation in half wave rectifier circuits is often problematic. The output voltage tends to vary significantly with changes in load current, making it difficult to maintain a stable DC voltage without additional regulation circuitry. This voltage instability can be particularly troublesome in applications requiring precise voltage control.
Temperature sensitivity is another challenge faced by half wave rectifier designs. The performance of semiconductor components used in these rectifiers can vary with temperature fluctuations, affecting the overall reliability and consistency of the power supply. This sensitivity necessitates careful thermal management and component selection.
Lastly, the limited power handling capability of half wave rectifiers poses a challenge for high-power applications. The unidirectional current flow limits the amount of power that can be efficiently rectified, making these designs less suitable for scenarios requiring substantial power output.
Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches in circuit design, component selection, and filtering techniques. Engineers must balance the simplicity of half wave rectifiers against their inherent limitations to optimize power quality in specific applications.
The pulsating nature of the output from half wave rectifiers presents another significant challenge. This pulsation introduces a high ripple factor, which can cause instability in the DC output voltage. The ripple not only affects the quality of the power supplied to the load but also increases the stress on filtering components, potentially reducing their lifespan and reliability.
Harmonic distortion is a critical concern in half wave rectifier designs. The non-linear characteristics of these rectifiers generate harmonics in the AC supply system, particularly odd harmonics. These harmonics can propagate back into the power grid, causing electromagnetic interference and potentially damaging sensitive equipment connected to the same power source.
The poor power factor associated with half wave rectifiers is another challenge that designers must address. The discontinuous current draw from the AC source results in a low power factor, which can lead to increased power losses in the distribution system and higher electricity costs for industrial applications.
Voltage regulation in half wave rectifier circuits is often problematic. The output voltage tends to vary significantly with changes in load current, making it difficult to maintain a stable DC voltage without additional regulation circuitry. This voltage instability can be particularly troublesome in applications requiring precise voltage control.
Temperature sensitivity is another challenge faced by half wave rectifier designs. The performance of semiconductor components used in these rectifiers can vary with temperature fluctuations, affecting the overall reliability and consistency of the power supply. This sensitivity necessitates careful thermal management and component selection.
Lastly, the limited power handling capability of half wave rectifiers poses a challenge for high-power applications. The unidirectional current flow limits the amount of power that can be efficiently rectified, making these designs less suitable for scenarios requiring substantial power output.
Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches in circuit design, component selection, and filtering techniques. Engineers must balance the simplicity of half wave rectifiers against their inherent limitations to optimize power quality in specific applications.
Existing Half Wave Rectifier Design Solutions
01 Power factor correction in half-wave rectifiers
Implementing power factor correction techniques in half-wave rectifier circuits to improve power quality. This involves using active or passive components to reduce harmonic distortion and increase the power factor, resulting in more efficient power conversion and reduced stress on the power supply system.- Power factor correction in half-wave rectifiers: Implementing power factor correction techniques in half-wave rectifier circuits to improve power quality. This involves reducing harmonic distortion and improving the overall efficiency of the rectifier system.
- Harmonic reduction techniques: Employing various methods to reduce harmonics generated by half-wave rectifiers, such as using filters or advanced control strategies. This helps in minimizing the negative impact on power quality and meeting regulatory standards.
- Voltage regulation and stabilization: Incorporating voltage regulation and stabilization mechanisms in half-wave rectifier circuits to maintain consistent output voltage and improve overall power quality. This may include feedback control systems or voltage compensation techniques.
- EMI reduction in half-wave rectifiers: Implementing electromagnetic interference (EMI) reduction techniques in half-wave rectifier designs to minimize noise and improve power quality. This may involve shielding, filtering, or circuit layout optimizations.
- Efficiency improvement in half-wave rectification: Developing methods to enhance the efficiency of half-wave rectifier circuits, such as using advanced semiconductor devices or implementing energy recovery techniques. This leads to better power utilization and improved overall power quality.
02 Harmonic reduction techniques
Employing various methods to reduce harmonics generated by half-wave rectifiers, such as using filters, resonant circuits, or advanced control strategies. These techniques help to minimize the distortion in the output waveform and improve overall power quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Voltage regulation and stabilization
Incorporating voltage regulation and stabilization mechanisms in half-wave rectifier designs to maintain a consistent output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load conditions. This improves the reliability and performance of the power supply system.Expand Specific Solutions04 Efficiency improvement techniques
Implementing various methods to enhance the efficiency of half-wave rectifier circuits, such as using advanced semiconductor devices, optimizing circuit topology, or employing energy recovery techniques. These improvements result in reduced power losses and better overall power quality.Expand Specific Solutions05 Control and monitoring systems
Integrating advanced control and monitoring systems into half-wave rectifier circuits to optimize performance and maintain power quality. These systems may include microcontrollers, sensors, and feedback loops to adjust rectifier operation based on real-time conditions and ensure optimal power quality.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Power Electronics Industry
The half wave rectifier design's impact on power quality is a mature technology in the power electronics field, with ongoing research and development. The market for power quality solutions is substantial and growing, driven by increasing demand for reliable power in various industries. Key players like Mitsubishi Electric, NEC, and Huawei Technologies are actively involved in advancing rectifier technologies. These companies, along with others such as Energous Corp. and VICOR, Inc., are focusing on improving efficiency, reducing harmonics, and enhancing overall power quality. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established electronics giants and specialized power electronics firms, all striving to innovate in this critical area of power systems.
NEC Corp.
Technical Solution: NEC Corp. has developed an advanced half-wave rectifier design that incorporates active power factor correction (PFC) techniques. Their solution utilizes a microcontroller-based system to dynamically adjust the rectification process, minimizing harmonic distortion and improving overall power quality. The design implements a sophisticated control algorithm that monitors input voltage and current waveforms in real-time, allowing for adaptive switching of the rectifier components[1]. This approach significantly reduces the total harmonic distortion (THD) to less than 5%, compared to traditional half-wave rectifiers which can exhibit THD levels of 40% or higher[3]. Additionally, NEC's design incorporates a soft-start mechanism to limit inrush current, further enhancing power quality and reducing stress on the power supply components[5].
Strengths: Significantly reduced harmonic distortion, improved power factor, and enhanced overall power quality. Adaptive control allows for better performance across varying load conditions. Weaknesses: Increased complexity and cost due to the need for microcontroller and advanced control algorithms. May require more space in compact applications.
Mitsubishi Electric Corp.
Technical Solution: Mitsubishi Electric Corp. has innovated in half-wave rectifier design with a focus on power quality improvement for industrial applications. Their approach combines passive and active filtering techniques to mitigate the negative effects of half-wave rectification on power systems. The design incorporates a novel LC filter network that is tuned to attenuate specific harmonic frequencies generated by the rectification process[2]. This is complemented by an active harmonic injection system that introduces compensating currents to further reduce distortion. Mitsubishi's solution also features an advanced phase-locked loop (PLL) system for precise synchronization with the grid, ensuring optimal timing for the rectification process[4]. The company claims their design can achieve a power factor of 0.98 and reduce THD to less than 3% under typical operating conditions[6].
Strengths: Highly effective in reducing harmonic distortion and improving power factor in industrial settings. Robust design suitable for high-power applications. Weaknesses: Relatively high implementation cost. May require significant space for installation, limiting its use in compact systems.
Core Innovations in Half Wave Rectifier Technology
AC to DC conversion circuit
PatentActiveUS7764528B2
Innovation
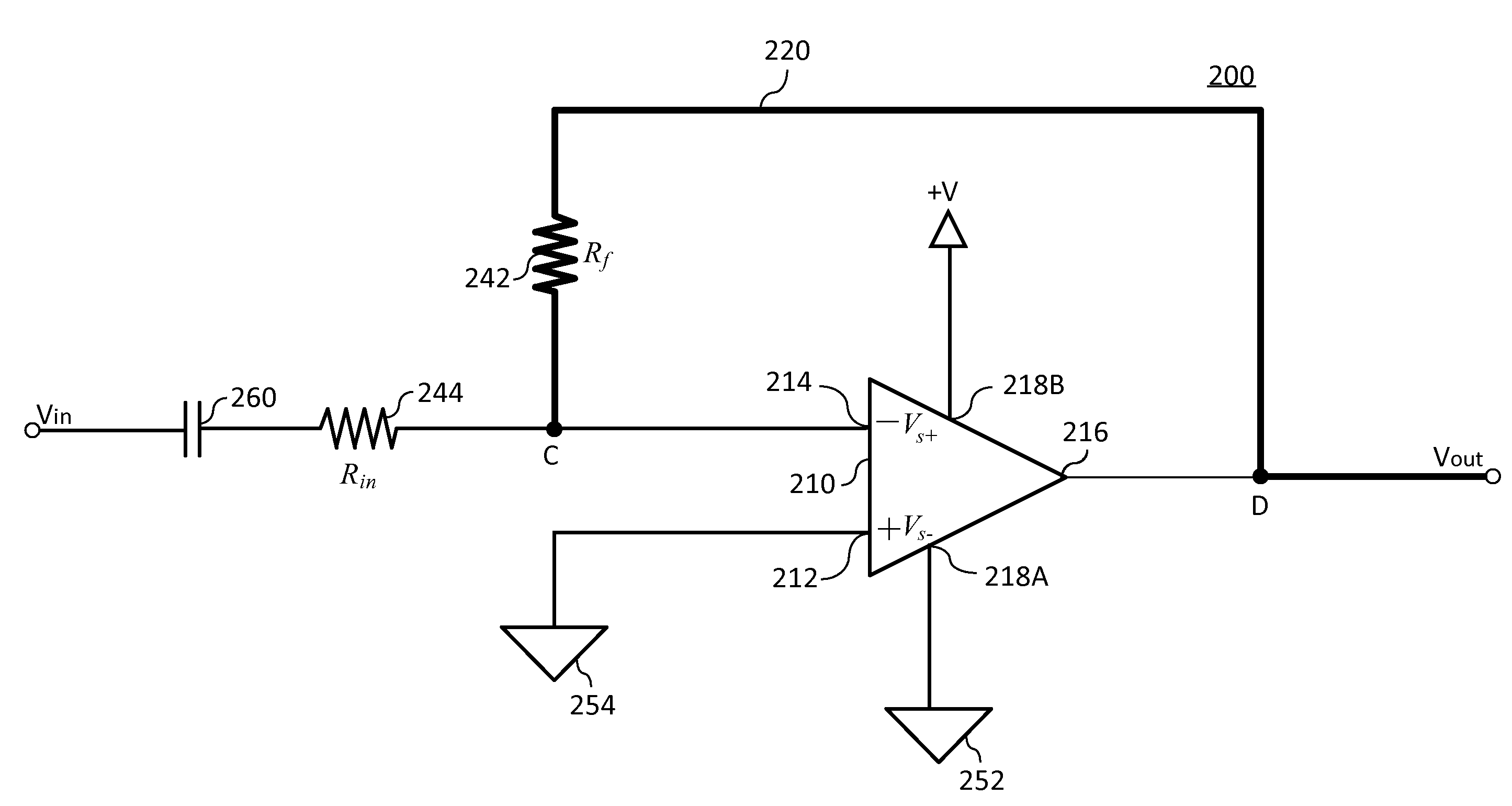
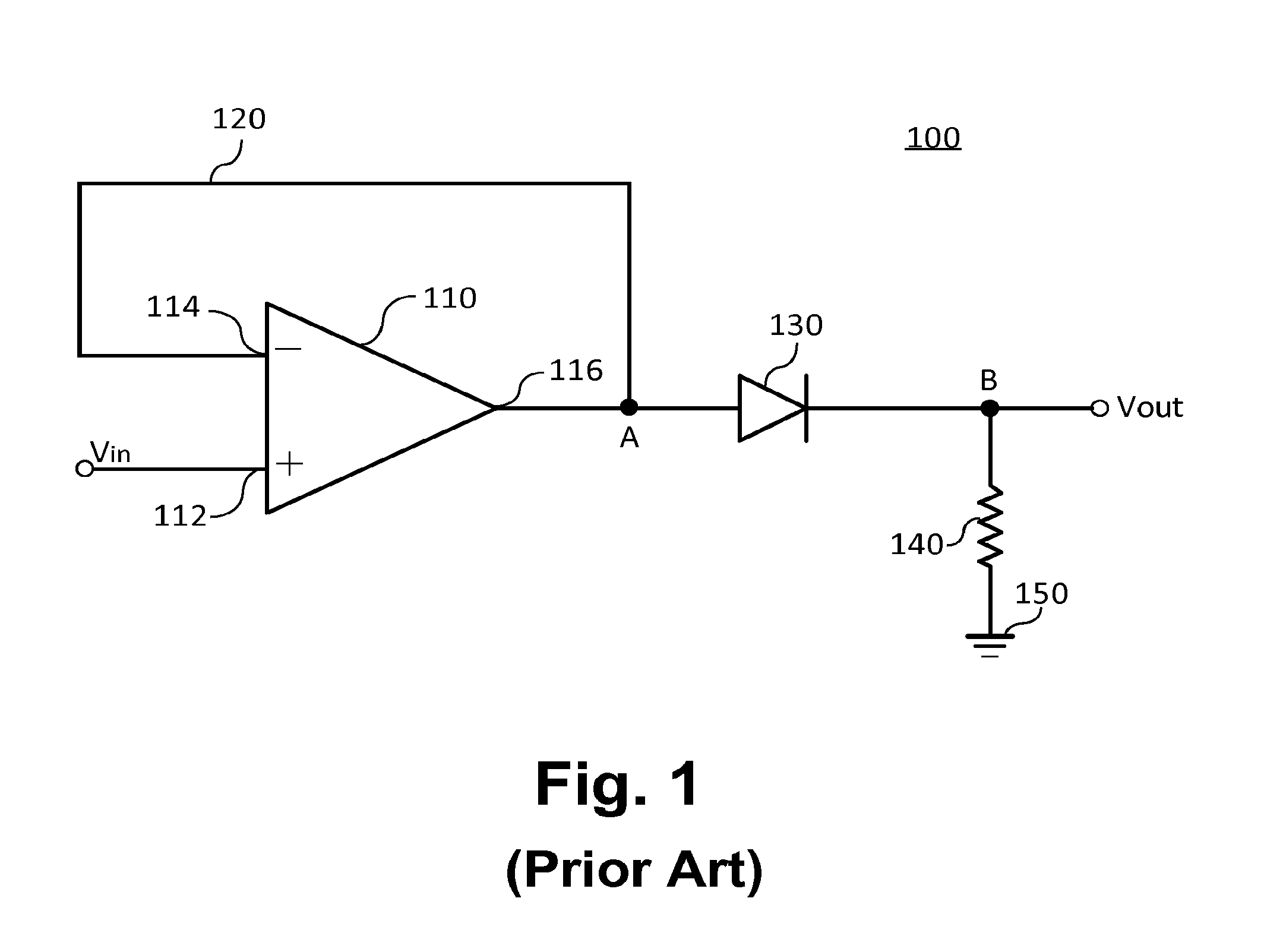
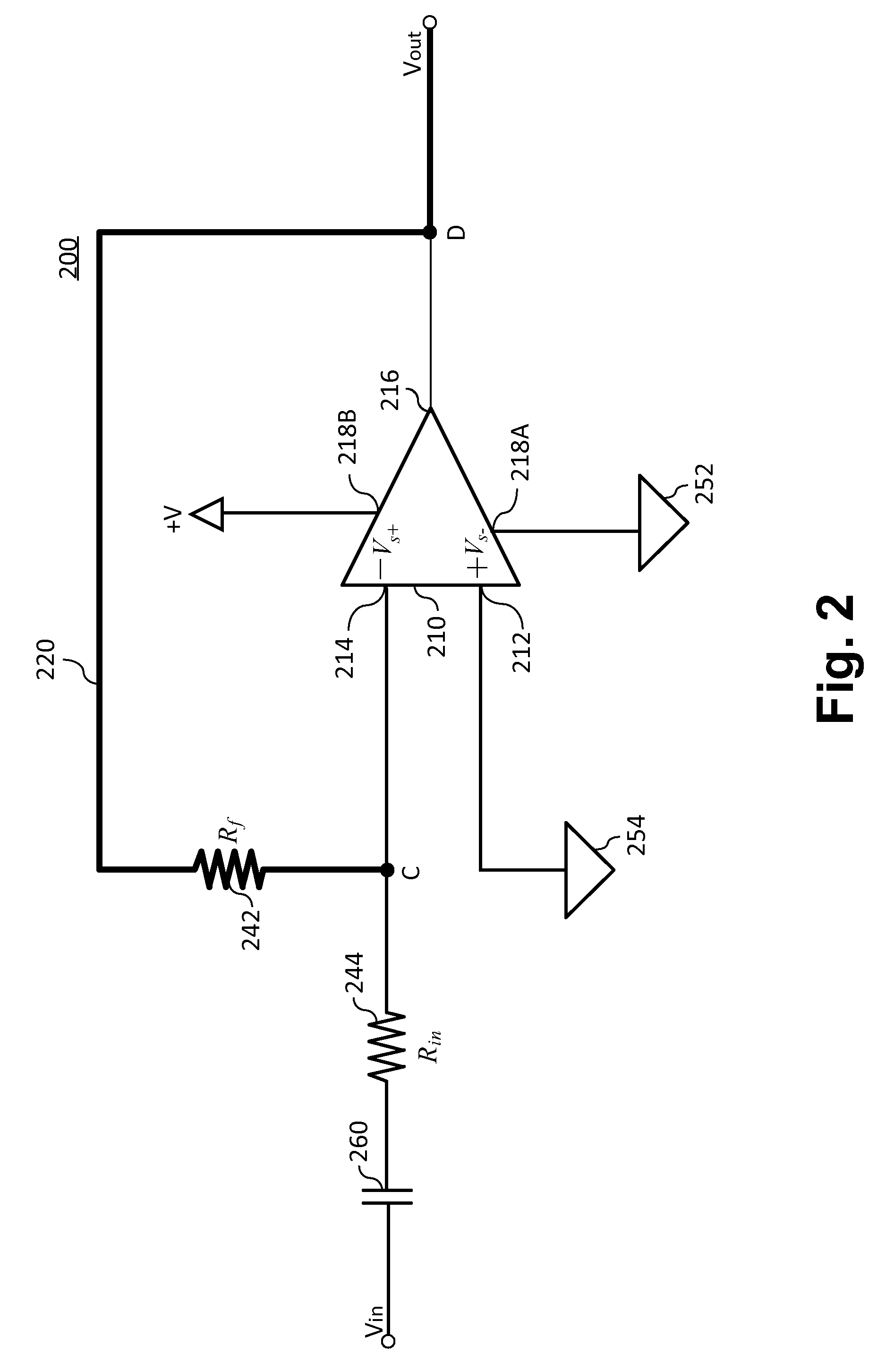
- A diode-less half-wave rectifier circuit utilizing an operational amplifier with a capacitor and resistors in a negative feedback loop, allowing low-level signals to be converted to half-wave rectified DC signals, thereby extending the dynamic range of rectification.
Methods and apparatus for three-phase rectifier with lower voltage switches
PatentWO2008134206A2
Innovation
- The use of series-coupled switches in a three-phase rectifier circuit allows the DC output voltage to be apportioned among multiple load capacitors, reducing the required power rating of the switches and enabling the use of lower voltage-rated switches, such as 6500 Volts IGBTs, to achieve the same output.
Regulatory Standards for Power Quality
Power quality is a critical aspect of electrical systems, and regulatory standards play a crucial role in ensuring its maintenance. These standards are established by various national and international organizations to define acceptable levels of power quality and provide guidelines for compliance.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed several standards related to power quality, including IEC 61000-3-2 and IEC 61000-3-4, which address harmonic limits for equipment connected to low-voltage power systems. These standards are particularly relevant to half-wave rectifier designs, as they can introduce significant harmonic distortion into the power system.
In the United States, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) has established IEEE 519-2014, which sets limits on harmonic distortion in power systems. This standard provides guidelines for both voltage and current distortion, taking into account the size of the load relative to the system capacity.
The European Union has implemented the EN 50160 standard, which specifies voltage characteristics of electricity supplied by public distribution networks. This standard addresses various power quality parameters, including frequency variations, voltage fluctuations, and harmonic distortion.
Regulatory bodies often require compliance with these standards for equipment manufacturers and power system operators. For instance, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) in the United States enforces power quality standards to ensure the reliability and stability of the national power grid.
Many countries have adopted or adapted these international standards to suit their specific needs. For example, Australia and New Zealand follow the AS/NZS 61000 series of standards, which are based on the IEC standards but tailored to local requirements.
Compliance with these regulatory standards often necessitates the implementation of power quality improvement techniques in half-wave rectifier designs. This may include the use of passive or active filtering, power factor correction circuits, or more advanced rectifier topologies to mitigate harmonic distortion and improve overall power quality.
As technology advances and power systems become more complex, regulatory standards continue to evolve. For instance, the increasing integration of renewable energy sources and power electronic devices has led to the development of new standards addressing issues such as voltage ride-through capabilities and grid stability under varying conditions.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed several standards related to power quality, including IEC 61000-3-2 and IEC 61000-3-4, which address harmonic limits for equipment connected to low-voltage power systems. These standards are particularly relevant to half-wave rectifier designs, as they can introduce significant harmonic distortion into the power system.
In the United States, the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) has established IEEE 519-2014, which sets limits on harmonic distortion in power systems. This standard provides guidelines for both voltage and current distortion, taking into account the size of the load relative to the system capacity.
The European Union has implemented the EN 50160 standard, which specifies voltage characteristics of electricity supplied by public distribution networks. This standard addresses various power quality parameters, including frequency variations, voltage fluctuations, and harmonic distortion.
Regulatory bodies often require compliance with these standards for equipment manufacturers and power system operators. For instance, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) in the United States enforces power quality standards to ensure the reliability and stability of the national power grid.
Many countries have adopted or adapted these international standards to suit their specific needs. For example, Australia and New Zealand follow the AS/NZS 61000 series of standards, which are based on the IEC standards but tailored to local requirements.
Compliance with these regulatory standards often necessitates the implementation of power quality improvement techniques in half-wave rectifier designs. This may include the use of passive or active filtering, power factor correction circuits, or more advanced rectifier topologies to mitigate harmonic distortion and improve overall power quality.
As technology advances and power systems become more complex, regulatory standards continue to evolve. For instance, the increasing integration of renewable energy sources and power electronic devices has led to the development of new standards addressing issues such as voltage ride-through capabilities and grid stability under varying conditions.
Environmental Impact of Rectifier Designs
The environmental impact of rectifier designs, particularly half-wave rectifiers, is a critical consideration in the context of power quality and sustainability. Half-wave rectifiers, while simple in design, can have significant implications for energy efficiency and environmental footprint.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with half-wave rectifier designs is their relatively low power efficiency. By utilizing only one half of the AC cycle, these rectifiers waste a substantial amount of energy, converting it into heat rather than usable DC power. This inefficiency leads to increased power consumption, which in turn results in higher greenhouse gas emissions from power generation facilities.
The harmonics introduced by half-wave rectifiers into the power system also contribute to environmental issues. These harmonics cause distortions in the voltage and current waveforms, leading to increased losses in transmission and distribution systems. As a result, more energy is required to compensate for these losses, further exacerbating the environmental impact through increased fuel consumption and emissions.
Moreover, the poor power quality resulting from half-wave rectifier designs can lead to premature failure of electrical equipment. This not only increases electronic waste but also necessitates more frequent replacements, contributing to resource depletion and manufacturing-related environmental impacts.
The electromagnetic interference (EMI) generated by half-wave rectifiers can also have indirect environmental consequences. EMI can affect sensitive electronic equipment and wildlife, potentially disrupting ecosystems and biodiversity in areas near power infrastructure.
From a lifecycle perspective, the simplicity of half-wave rectifier designs may initially seem advantageous due to fewer components. However, their inefficiency often necessitates larger cooling systems and more robust power supply components, which can increase the overall material footprint and embodied energy of the devices they are used in.
In the context of renewable energy integration, the poor power quality associated with half-wave rectifiers can pose challenges. As the grid incorporates more intermittent renewable sources, maintaining power quality becomes crucial. The harmonics and inefficiencies introduced by half-wave rectifiers can complicate this integration, potentially leading to increased reliance on fossil fuel-based backup power sources.
Addressing these environmental concerns has led to the development of more efficient rectifier designs, such as full-wave and bridge rectifiers. These alternatives offer improved power quality and efficiency, reducing energy waste and associated environmental impacts. As the focus on sustainability intensifies, the shift towards more environmentally friendly rectifier designs becomes increasingly important in mitigating the ecological footprint of power electronics.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with half-wave rectifier designs is their relatively low power efficiency. By utilizing only one half of the AC cycle, these rectifiers waste a substantial amount of energy, converting it into heat rather than usable DC power. This inefficiency leads to increased power consumption, which in turn results in higher greenhouse gas emissions from power generation facilities.
The harmonics introduced by half-wave rectifiers into the power system also contribute to environmental issues. These harmonics cause distortions in the voltage and current waveforms, leading to increased losses in transmission and distribution systems. As a result, more energy is required to compensate for these losses, further exacerbating the environmental impact through increased fuel consumption and emissions.
Moreover, the poor power quality resulting from half-wave rectifier designs can lead to premature failure of electrical equipment. This not only increases electronic waste but also necessitates more frequent replacements, contributing to resource depletion and manufacturing-related environmental impacts.
The electromagnetic interference (EMI) generated by half-wave rectifiers can also have indirect environmental consequences. EMI can affect sensitive electronic equipment and wildlife, potentially disrupting ecosystems and biodiversity in areas near power infrastructure.
From a lifecycle perspective, the simplicity of half-wave rectifier designs may initially seem advantageous due to fewer components. However, their inefficiency often necessitates larger cooling systems and more robust power supply components, which can increase the overall material footprint and embodied energy of the devices they are used in.
In the context of renewable energy integration, the poor power quality associated with half-wave rectifiers can pose challenges. As the grid incorporates more intermittent renewable sources, maintaining power quality becomes crucial. The harmonics and inefficiencies introduced by half-wave rectifiers can complicate this integration, potentially leading to increased reliance on fossil fuel-based backup power sources.
Addressing these environmental concerns has led to the development of more efficient rectifier designs, such as full-wave and bridge rectifiers. These alternatives offer improved power quality and efficiency, reducing energy waste and associated environmental impacts. As the focus on sustainability intensifies, the shift towards more environmentally friendly rectifier designs becomes increasingly important in mitigating the ecological footprint of power electronics.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!