How Half Wave Rectifiers Influence Modern Electronics?
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Half Wave Rectifiers: Background and Objectives
Half wave rectifiers have played a pivotal role in the evolution of modern electronics, serving as a fundamental building block in power supply systems and signal processing circuits. The development of this technology can be traced back to the early 20th century when the need for converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) became increasingly important for various electronic applications.
The primary objective of half wave rectification is to convert AC input into a pulsating DC output by allowing current to flow in only one direction. This process is achieved through the use of diodes, which act as one-way valves for electrical current. As technology progressed, the efficiency and performance of half wave rectifiers have significantly improved, leading to their widespread adoption in numerous electronic devices and systems.
Throughout the years, half wave rectifiers have undergone several iterations and improvements. The initial designs utilized vacuum tube diodes, which were later replaced by solid-state semiconductor diodes. This transition marked a significant milestone in the miniaturization and increased reliability of electronic circuits. The advent of silicon-based diodes further enhanced the efficiency and power-handling capabilities of half wave rectifiers.
In modern electronics, half wave rectifiers continue to influence various applications, ranging from simple power supplies in household appliances to more complex systems in industrial and telecommunications equipment. Their simplicity and cost-effectiveness make them an attractive option for many low-power applications, while their ability to handle high voltages and currents ensures their relevance in high-power scenarios as well.
The ongoing technological advancements in semiconductor materials and manufacturing processes have led to the development of more efficient and compact half wave rectifier designs. These improvements have resulted in reduced power losses, increased thermal management capabilities, and enhanced overall performance of electronic systems incorporating half wave rectifiers.
As we look towards the future, the role of half wave rectifiers in modern electronics is expected to evolve further. With the growing emphasis on energy efficiency and miniaturization, researchers and engineers are exploring novel materials and circuit topologies to optimize the performance of half wave rectifiers. Additionally, the integration of smart control systems and advanced power management techniques is likely to expand the capabilities and applications of half wave rectifiers in emerging technologies such as renewable energy systems and electric vehicles.
The primary objective of half wave rectification is to convert AC input into a pulsating DC output by allowing current to flow in only one direction. This process is achieved through the use of diodes, which act as one-way valves for electrical current. As technology progressed, the efficiency and performance of half wave rectifiers have significantly improved, leading to their widespread adoption in numerous electronic devices and systems.
Throughout the years, half wave rectifiers have undergone several iterations and improvements. The initial designs utilized vacuum tube diodes, which were later replaced by solid-state semiconductor diodes. This transition marked a significant milestone in the miniaturization and increased reliability of electronic circuits. The advent of silicon-based diodes further enhanced the efficiency and power-handling capabilities of half wave rectifiers.
In modern electronics, half wave rectifiers continue to influence various applications, ranging from simple power supplies in household appliances to more complex systems in industrial and telecommunications equipment. Their simplicity and cost-effectiveness make them an attractive option for many low-power applications, while their ability to handle high voltages and currents ensures their relevance in high-power scenarios as well.
The ongoing technological advancements in semiconductor materials and manufacturing processes have led to the development of more efficient and compact half wave rectifier designs. These improvements have resulted in reduced power losses, increased thermal management capabilities, and enhanced overall performance of electronic systems incorporating half wave rectifiers.
As we look towards the future, the role of half wave rectifiers in modern electronics is expected to evolve further. With the growing emphasis on energy efficiency and miniaturization, researchers and engineers are exploring novel materials and circuit topologies to optimize the performance of half wave rectifiers. Additionally, the integration of smart control systems and advanced power management techniques is likely to expand the capabilities and applications of half wave rectifiers in emerging technologies such as renewable energy systems and electric vehicles.
Market Demand Analysis for Rectification Technologies
The market demand for rectification technologies, particularly half-wave rectifiers, has been steadily growing due to the increasing prevalence of electronic devices in various sectors. Half-wave rectifiers play a crucial role in converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), which is essential for powering modern electronics. The global power electronics market, which includes rectification technologies, is projected to reach significant growth in the coming years, driven by the rising demand for energy-efficient devices and the expansion of renewable energy systems.
In the consumer electronics sector, the proliferation of smartphones, laptops, and other portable devices has created a substantial demand for compact and efficient power supply units. Half-wave rectifiers are often used in these applications due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, especially in low-power devices. The automotive industry is another major driver of demand for rectification technologies. With the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), there is a growing need for high-performance rectifiers to manage power conversion in charging systems and onboard electronics.
The industrial sector also contributes significantly to the market demand for rectification technologies. Factory automation, robotics, and industrial control systems rely heavily on power electronics, including half-wave rectifiers, for efficient operation. As industries continue to embrace Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing concepts, the demand for advanced rectification solutions is expected to rise further.
In the renewable energy sector, half-wave rectifiers are utilized in solar inverters and wind turbine systems to convert the generated AC power into usable DC power for grid integration or energy storage. The global push towards sustainable energy sources is driving substantial growth in this segment, consequently increasing the demand for rectification technologies.
The telecommunications industry is another key market for rectification technologies. With the ongoing rollout of 5G networks and the expansion of data centers, there is a growing need for efficient power conversion solutions to support the infrastructure. Half-wave rectifiers are often employed in power supply units for telecom equipment and data center servers.
Market trends indicate a shift towards more efficient and compact rectification solutions. While half-wave rectifiers remain relevant for certain applications, there is an increasing demand for full-wave and bridge rectifiers that offer higher efficiency and better power quality. This trend is particularly evident in high-power applications and industries where energy efficiency is a critical factor.
In the consumer electronics sector, the proliferation of smartphones, laptops, and other portable devices has created a substantial demand for compact and efficient power supply units. Half-wave rectifiers are often used in these applications due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, especially in low-power devices. The automotive industry is another major driver of demand for rectification technologies. With the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), there is a growing need for high-performance rectifiers to manage power conversion in charging systems and onboard electronics.
The industrial sector also contributes significantly to the market demand for rectification technologies. Factory automation, robotics, and industrial control systems rely heavily on power electronics, including half-wave rectifiers, for efficient operation. As industries continue to embrace Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing concepts, the demand for advanced rectification solutions is expected to rise further.
In the renewable energy sector, half-wave rectifiers are utilized in solar inverters and wind turbine systems to convert the generated AC power into usable DC power for grid integration or energy storage. The global push towards sustainable energy sources is driving substantial growth in this segment, consequently increasing the demand for rectification technologies.
The telecommunications industry is another key market for rectification technologies. With the ongoing rollout of 5G networks and the expansion of data centers, there is a growing need for efficient power conversion solutions to support the infrastructure. Half-wave rectifiers are often employed in power supply units for telecom equipment and data center servers.
Market trends indicate a shift towards more efficient and compact rectification solutions. While half-wave rectifiers remain relevant for certain applications, there is an increasing demand for full-wave and bridge rectifiers that offer higher efficiency and better power quality. This trend is particularly evident in high-power applications and industries where energy efficiency is a critical factor.
Current State and Challenges in Half Wave Rectification
Half wave rectification remains a fundamental process in modern electronics, serving as a crucial component in power supplies and signal processing circuits. The current state of this technology is characterized by its widespread use in various applications, ranging from simple household appliances to complex industrial systems. However, despite its ubiquity, half wave rectification faces several challenges that limit its efficiency and performance in certain scenarios.
One of the primary challenges in half wave rectification is the issue of power efficiency. By nature, half wave rectifiers only utilize one half of the AC input cycle, resulting in significant power loss. This inefficiency becomes particularly problematic in applications where energy conservation is critical, such as in battery-powered devices or renewable energy systems. Engineers and researchers are continually seeking ways to mitigate this inherent limitation, exploring circuit designs that can maximize the utilization of the input waveform.
Another significant challenge lies in the area of harmonic distortion. Half wave rectifiers introduce substantial harmonic content into the output signal, which can lead to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and compromise the overall system performance. This issue is especially pertinent in sensitive electronic equipment and communication systems, where signal integrity is paramount. Addressing this challenge requires sophisticated filtering techniques and circuit designs to minimize harmonic distortion and meet stringent EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) standards.
The ripple voltage associated with half wave rectification presents yet another hurdle. The pulsating DC output produced by half wave rectifiers necessitates substantial smoothing to achieve a stable DC voltage. This often requires large capacitors or complex filtering circuits, which can increase the size, cost, and complexity of the overall system. In applications where space is at a premium or where high-frequency operation is required, this limitation becomes particularly pronounced.
Thermal management is an additional concern in half wave rectification systems. The inefficient use of the input waveform can lead to increased heat generation, potentially compromising the reliability and lifespan of electronic components. This challenge is exacerbated in high-power applications, where thermal dissipation becomes a critical design consideration.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on enhancing the performance of half wave rectification systems. Innovations in semiconductor technology, such as the development of more efficient diodes with lower forward voltage drops, are helping to improve the overall efficiency of half wave rectifiers. Additionally, advancements in circuit design techniques, including the use of active rectification and synchronous rectification, are addressing some of the inherent limitations of traditional half wave rectification approaches.
The integration of digital control and monitoring systems is also playing a crucial role in optimizing half wave rectification processes. By employing sophisticated algorithms and real-time adjustment capabilities, these systems can adapt to varying load conditions and input fluctuations, thereby enhancing the overall performance and reliability of half wave rectification circuits.
One of the primary challenges in half wave rectification is the issue of power efficiency. By nature, half wave rectifiers only utilize one half of the AC input cycle, resulting in significant power loss. This inefficiency becomes particularly problematic in applications where energy conservation is critical, such as in battery-powered devices or renewable energy systems. Engineers and researchers are continually seeking ways to mitigate this inherent limitation, exploring circuit designs that can maximize the utilization of the input waveform.
Another significant challenge lies in the area of harmonic distortion. Half wave rectifiers introduce substantial harmonic content into the output signal, which can lead to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and compromise the overall system performance. This issue is especially pertinent in sensitive electronic equipment and communication systems, where signal integrity is paramount. Addressing this challenge requires sophisticated filtering techniques and circuit designs to minimize harmonic distortion and meet stringent EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) standards.
The ripple voltage associated with half wave rectification presents yet another hurdle. The pulsating DC output produced by half wave rectifiers necessitates substantial smoothing to achieve a stable DC voltage. This often requires large capacitors or complex filtering circuits, which can increase the size, cost, and complexity of the overall system. In applications where space is at a premium or where high-frequency operation is required, this limitation becomes particularly pronounced.
Thermal management is an additional concern in half wave rectification systems. The inefficient use of the input waveform can lead to increased heat generation, potentially compromising the reliability and lifespan of electronic components. This challenge is exacerbated in high-power applications, where thermal dissipation becomes a critical design consideration.
Despite these challenges, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on enhancing the performance of half wave rectification systems. Innovations in semiconductor technology, such as the development of more efficient diodes with lower forward voltage drops, are helping to improve the overall efficiency of half wave rectifiers. Additionally, advancements in circuit design techniques, including the use of active rectification and synchronous rectification, are addressing some of the inherent limitations of traditional half wave rectification approaches.
The integration of digital control and monitoring systems is also playing a crucial role in optimizing half wave rectification processes. By employing sophisticated algorithms and real-time adjustment capabilities, these systems can adapt to varying load conditions and input fluctuations, thereby enhancing the overall performance and reliability of half wave rectification circuits.
Existing Half Wave Rectifier Implementations
01 Circuit design for half-wave rectifiers
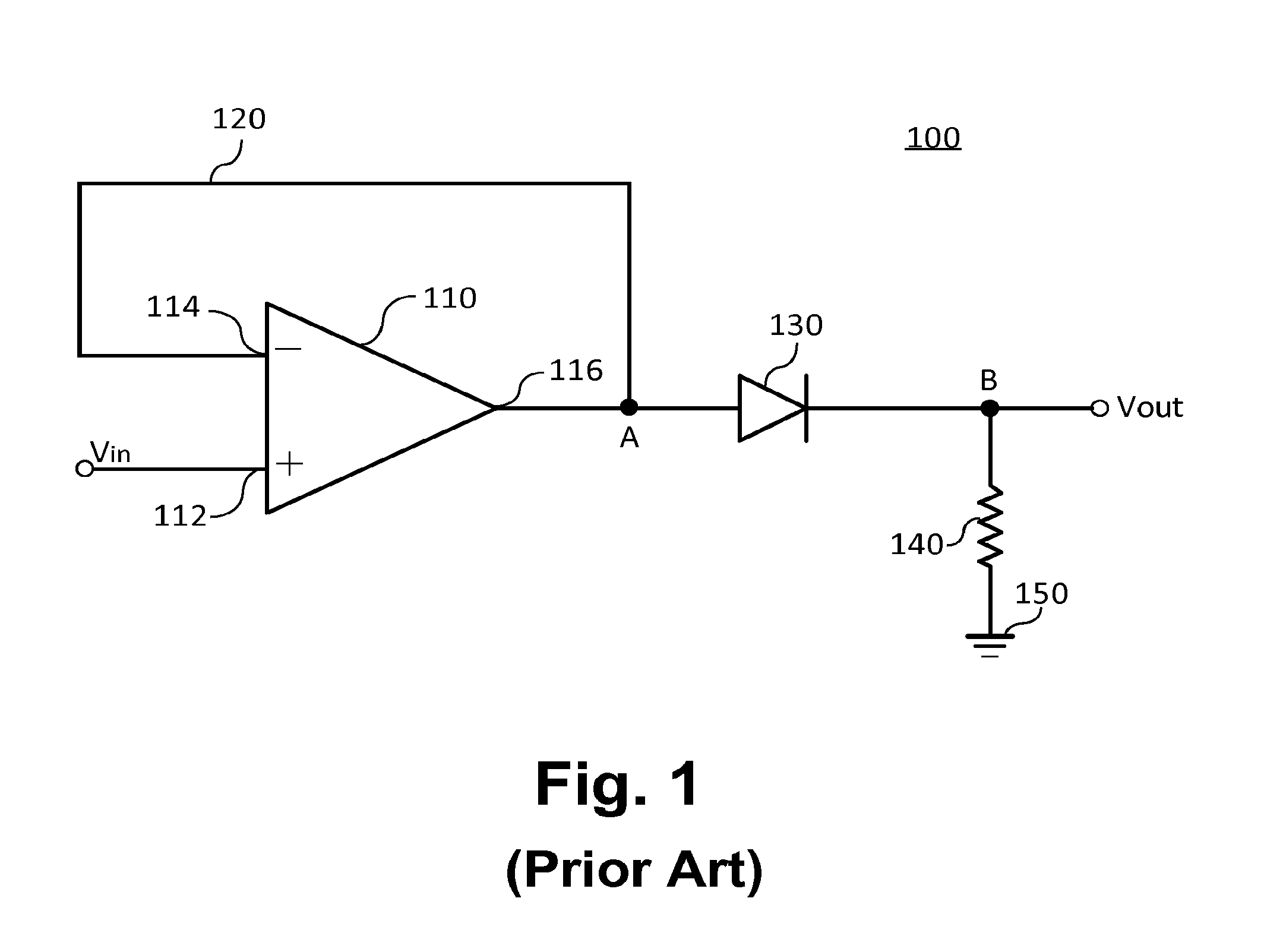
Half-wave rectifiers are designed to convert alternating current (AC) to pulsating direct current (DC) by allowing current flow in only one direction. The circuit typically includes a diode that conducts during the positive half-cycle of the AC input and blocks current during the negative half-cycle. This design is fundamental to power supply systems and various electronic applications.- Circuit design for half-wave rectifiers: Half-wave rectifiers are designed to convert alternating current (AC) to pulsating direct current (DC) by allowing current flow in only one direction. The circuit typically includes a diode that conducts during the positive half-cycle of the AC input and blocks current during the negative half-cycle. This design is fundamental to power supply systems and various electronic applications.
- Efficiency improvements in half-wave rectifiers: Advancements in half-wave rectifier designs focus on improving efficiency and reducing power losses. This includes the use of high-performance diodes, optimized circuit layouts, and advanced control techniques. Some designs incorporate additional components or novel configurations to minimize voltage drops and enhance overall system performance.
- Integration of half-wave rectifiers in power supply systems: Half-wave rectifiers are integral components in various power supply systems. They are used in voltage regulators, battery chargers, and power adapters. The integration of these rectifiers often involves considerations for smoothing capacitors, voltage stabilization, and protection circuits to ensure reliable and stable DC output for different applications.
- Half-wave rectifiers in specialized applications: Half-wave rectifiers find use in specialized applications beyond standard power supplies. These include RF signal detection, envelope tracking in communication systems, and certain types of sensor circuits. In these applications, the rectifier's ability to extract the envelope of an AC signal or provide peak detection is utilized for signal processing and measurement purposes.
- Miniaturization and integration of half-wave rectifiers: There is a trend towards miniaturization and integration of half-wave rectifiers in modern electronic designs. This includes the development of compact rectifier modules, integration into system-on-chip (SoC) designs, and the use of advanced packaging techniques. These efforts aim to reduce overall device size, improve thermal management, and enhance the reliability of electronic systems incorporating half-wave rectification.
02 Efficiency improvements in half-wave rectifiers
Advancements in half-wave rectifier designs focus on improving efficiency and reducing power losses. This includes the use of high-performance diodes, optimized circuit layouts, and advanced control techniques. Some designs incorporate additional components or novel configurations to enhance the rectification process and minimize energy waste.Expand Specific Solutions03 Integration of half-wave rectifiers in power supply systems
Half-wave rectifiers are often integrated into larger power supply systems. These systems may include voltage regulators, filters, and other components to produce a stable DC output from an AC input. The integration of half-wave rectifiers in such systems requires careful consideration of factors like ripple voltage, load requirements, and overall system efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application-specific half-wave rectifier designs
Half-wave rectifiers are tailored for specific applications, such as battery charging, LED drivers, and small electronic devices. These designs may incorporate additional features like overcurrent protection, temperature compensation, or variable output control to meet the unique requirements of different applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Miniaturization and integration of half-wave rectifiers
There is a trend towards miniaturization and integration of half-wave rectifiers in electronic devices. This includes the development of compact rectifier modules, integrated circuits that incorporate rectifier functions, and the use of advanced packaging techniques to reduce the overall footprint of rectifier circuits in electronic products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Rectifier Manufacturing
The half wave rectifier technology market is in a mature stage, with a stable global demand driven by its widespread use in power supplies and signal processing. The market size is substantial, estimated in the billions of dollars annually, due to the technology's fundamental role in electronics. Technologically, half wave rectifiers are well-established, with ongoing incremental improvements in efficiency and miniaturization. Key players like TE Connectivity, Sanken Electric, and ON Semiconductor (Semiconductor Components Industries LLC) are focusing on enhancing performance and integrating rectifiers into more complex power management solutions. Universities such as the Technical University of Denmark and China Three Gorges University are contributing to research and development, potentially leading to future innovations in this field.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Huawei has made significant strides in half-wave rectifier technology, particularly in the context of 5G base stations and energy-efficient mobile devices. Their approach focuses on high-frequency operation and miniaturization. Huawei's half-wave rectifiers are designed to operate efficiently at frequencies up to 100 MHz, enabling more compact power supply designs in their telecommunications equipment [6]. They have also developed multi-stage rectification techniques that combine half-wave and full-wave rectification to optimize efficiency across different load conditions. In their mobile devices, Huawei employs advanced half-wave rectifiers in conjunction with charge pump circuits to achieve highly efficient voltage conversion for various internal components [7].
Strengths: High-frequency operation, compact designs, optimized for telecommunications applications. Weaknesses: Potentially higher complexity, may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Panasonic Holdings Corp.
Technical Solution: Panasonic has focused on developing half-wave rectifiers for a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial power supplies. Their technology emphasizes reliability and efficiency across diverse operating conditions. Panasonic's half-wave rectifiers incorporate advanced thermal management techniques, allowing for stable operation in high-temperature environments up to 150°C [8]. They have also developed hybrid rectifier solutions that combine half-wave rectifiers with active switching elements to achieve higher efficiency in AC-DC conversion. In their automotive electronics, Panasonic utilizes half-wave rectifiers with integrated overvoltage protection, capable of handling transients up to 40V, enhancing reliability in vehicle electrical systems [9].
Strengths: Wide range of applications, high temperature tolerance, integrated protection features. Weaknesses: May not be as specialized for high-frequency applications as some competitors.
Core Innovations in Half Wave Rectification
Photosensor circuits including a switch mode power converter
PatentActiveEP2347635A2
Innovation
- A small, low-cost, efficient switch mode power converter circuit that utilizes a Darlington pair of transistors and a pulse width modulator to regulate the relay coil voltage, incorporating a phototransistor for light-level control and a half-wave rectifier for power conversion, reducing component count and heat generation.
AC to DC conversion circuit
PatentActiveUS7764528B2
Innovation
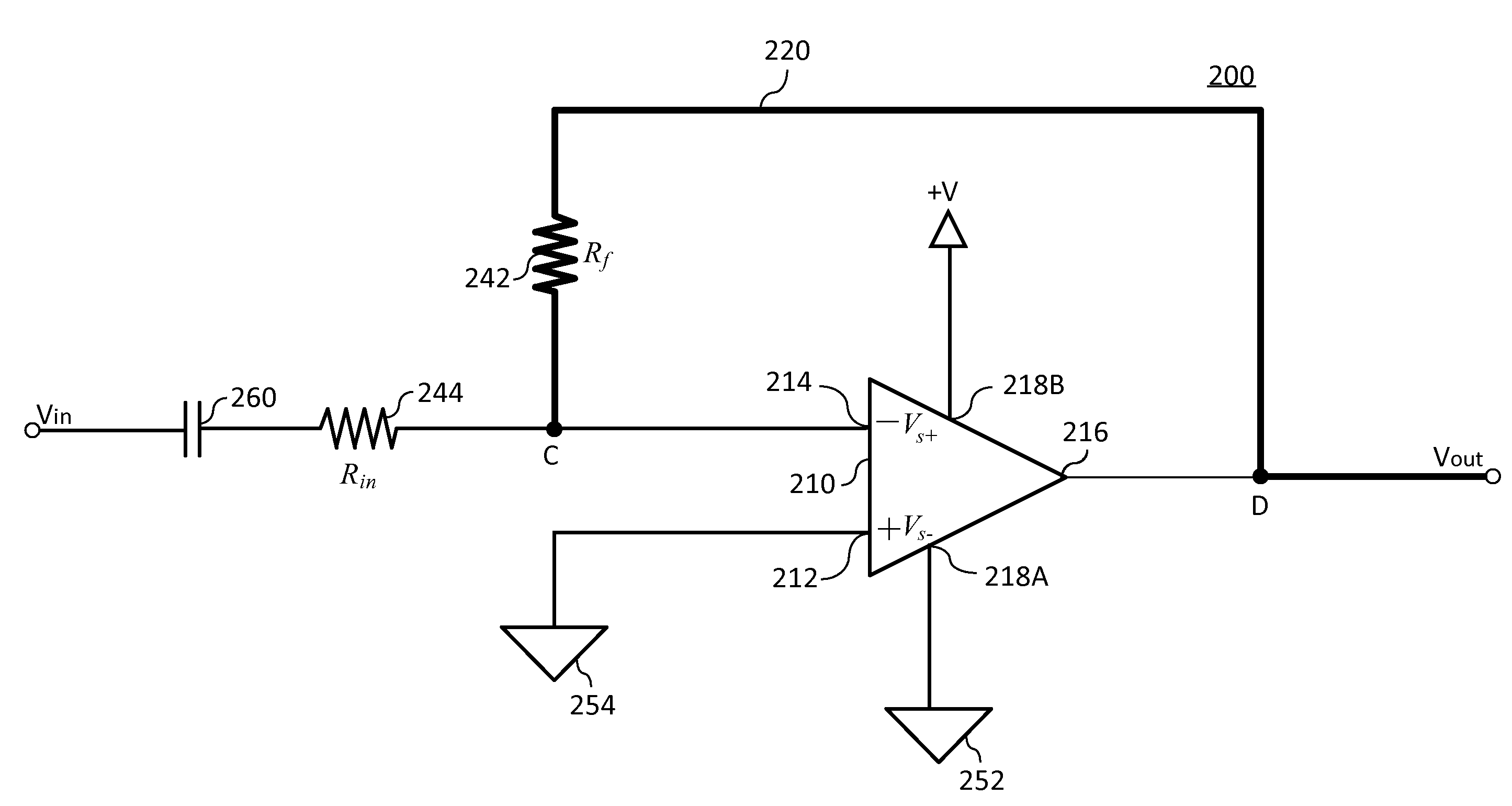
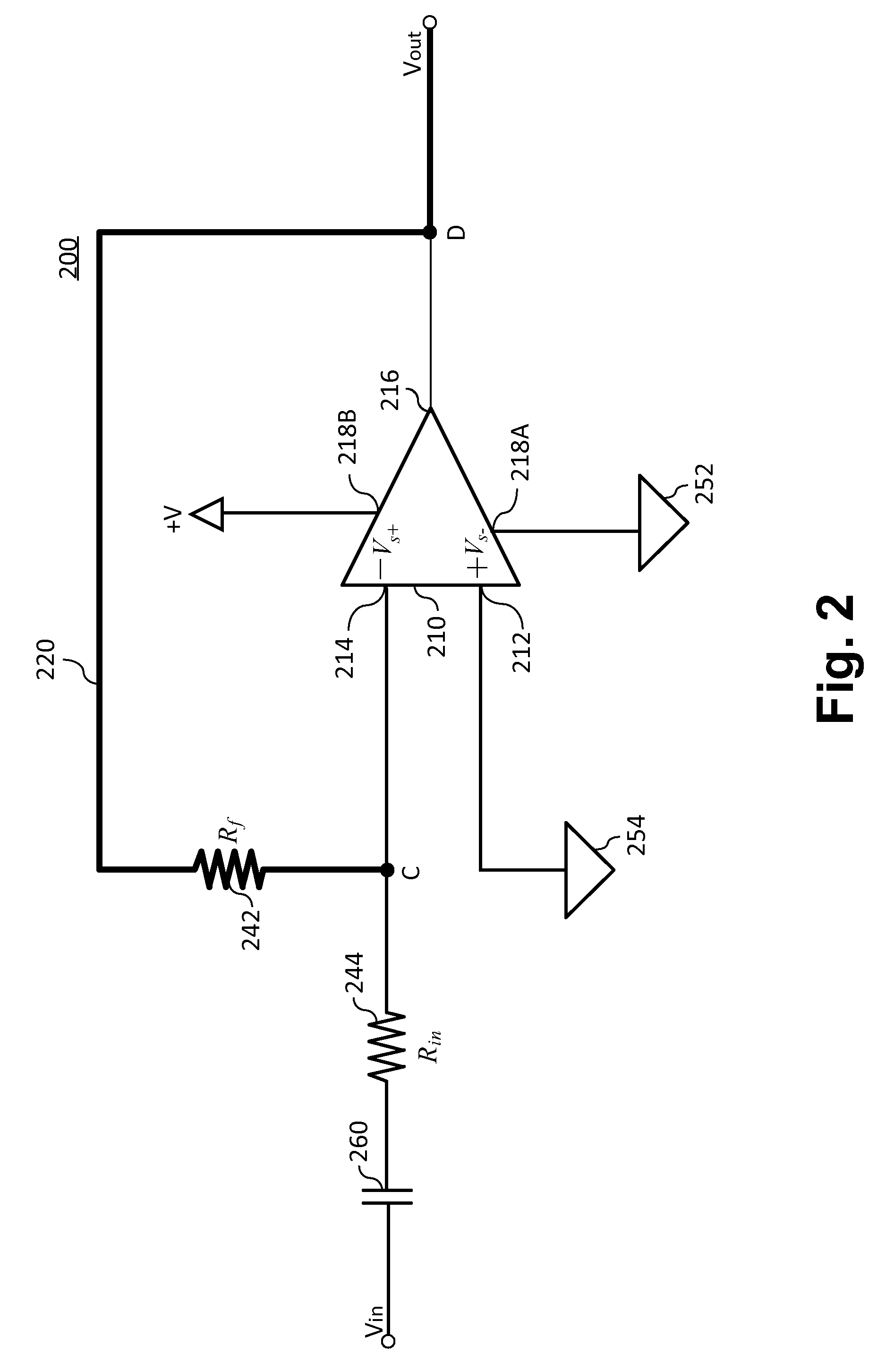
- A diode-less half-wave rectifier circuit utilizing an operational amplifier with a capacitor and resistors in a negative feedback loop, allowing low-level signals to be converted to half-wave rectified DC signals, thereby extending the dynamic range of rectification.
Efficiency Comparison: Half vs Full Wave Rectifiers
When comparing the efficiency of half-wave and full-wave rectifiers, several key factors come into play. Half-wave rectifiers, while simpler in design, generally exhibit lower efficiency compared to their full-wave counterparts. This efficiency disparity stems from the fundamental operational differences between the two types of rectifiers.
In half-wave rectification, only one half of the AC waveform is utilized, resulting in significant energy loss. During the negative half-cycle, the diode blocks current flow, effectively wasting half of the input power. This leads to a lower overall power output and reduced efficiency. Additionally, the pulsating nature of the half-wave rectified output requires more substantial filtering to achieve a smooth DC voltage, further impacting efficiency.
Full-wave rectifiers, on the other hand, make use of both positive and negative half-cycles of the AC input. This results in a more efficient conversion of AC to DC power. By utilizing the entire input waveform, full-wave rectifiers can deliver nearly twice the power output of half-wave rectifiers for the same input voltage. The smoother output waveform also requires less filtering, reducing power losses associated with smoothing capacitors and other filtering components.
The efficiency advantage of full-wave rectifiers becomes particularly pronounced in applications requiring higher power output or more stable DC voltages. In such scenarios, the improved power utilization and reduced ripple of full-wave rectifiers translate to significant energy savings and better overall system performance.
However, it's important to note that the efficiency gap between half-wave and full-wave rectifiers can vary depending on the specific application and circuit design. In low-power applications or where simplicity is paramount, the efficiency difference may be less critical, and half-wave rectifiers might still find use due to their simpler construction and lower component count.
Modern electronic design trends increasingly favor full-wave rectification, especially in power supplies and battery charging circuits, where energy efficiency is a key consideration. The superior efficiency of full-wave rectifiers aligns well with the growing emphasis on energy conservation and the need for more compact, high-performance electronic devices.
In half-wave rectification, only one half of the AC waveform is utilized, resulting in significant energy loss. During the negative half-cycle, the diode blocks current flow, effectively wasting half of the input power. This leads to a lower overall power output and reduced efficiency. Additionally, the pulsating nature of the half-wave rectified output requires more substantial filtering to achieve a smooth DC voltage, further impacting efficiency.
Full-wave rectifiers, on the other hand, make use of both positive and negative half-cycles of the AC input. This results in a more efficient conversion of AC to DC power. By utilizing the entire input waveform, full-wave rectifiers can deliver nearly twice the power output of half-wave rectifiers for the same input voltage. The smoother output waveform also requires less filtering, reducing power losses associated with smoothing capacitors and other filtering components.
The efficiency advantage of full-wave rectifiers becomes particularly pronounced in applications requiring higher power output or more stable DC voltages. In such scenarios, the improved power utilization and reduced ripple of full-wave rectifiers translate to significant energy savings and better overall system performance.
However, it's important to note that the efficiency gap between half-wave and full-wave rectifiers can vary depending on the specific application and circuit design. In low-power applications or where simplicity is paramount, the efficiency difference may be less critical, and half-wave rectifiers might still find use due to their simpler construction and lower component count.
Modern electronic design trends increasingly favor full-wave rectification, especially in power supplies and battery charging circuits, where energy efficiency is a key consideration. The superior efficiency of full-wave rectifiers aligns well with the growing emphasis on energy conservation and the need for more compact, high-performance electronic devices.
Applications of Half Wave Rectifiers in Modern Electronics
Half wave rectifiers play a crucial role in modern electronics, finding applications across various sectors. In power supplies, these devices are instrumental in converting alternating current (AC) to pulsating direct current (DC), which is essential for many electronic devices. This conversion process is particularly useful in low-power applications where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are prioritized over efficiency.
In the field of signal processing, half wave rectifiers are employed to modify waveforms, particularly in audio and radio frequency circuits. They effectively remove the negative portion of an AC signal, resulting in a unidirectional current flow. This characteristic makes them valuable in amplitude modulation (AM) radio receivers, where they help extract the audio signal from the carrier wave.
The automotive industry also benefits from half wave rectifiers. They are used in vehicle charging systems, particularly in older models, to convert the AC output from the alternator into DC for battery charging and powering the vehicle's electrical systems. While less efficient than full wave rectifiers, their simplicity and lower component count can be advantageous in certain designs.
In renewable energy systems, half wave rectifiers find application in small-scale solar and wind power installations. They assist in converting the variable output from these sources into a more usable form of electricity, albeit with some limitations in efficiency compared to more advanced rectification methods.
The telecommunications sector utilizes half wave rectifiers in various signal processing applications. They are particularly useful in peak detection circuits, which are essential for analyzing and interpreting communication signals. In this context, the rectifier's ability to pass only positive or negative portions of a signal is leveraged to extract specific information from complex waveforms.
Consumer electronics also incorporate half wave rectifiers, especially in low-power devices where full wave rectification would be overkill. Examples include simple battery chargers, LED drivers, and some types of voltage regulators in small appliances. The simplicity of half wave rectifiers makes them a cost-effective solution for these applications.
In scientific and medical instrumentation, half wave rectifiers are used in specialized measurement and analysis equipment. They can be found in oscilloscopes, spectrum analyzers, and certain types of medical imaging devices, where their signal-shaping properties are valuable for precise measurements and data interpretation.
In the field of signal processing, half wave rectifiers are employed to modify waveforms, particularly in audio and radio frequency circuits. They effectively remove the negative portion of an AC signal, resulting in a unidirectional current flow. This characteristic makes them valuable in amplitude modulation (AM) radio receivers, where they help extract the audio signal from the carrier wave.
The automotive industry also benefits from half wave rectifiers. They are used in vehicle charging systems, particularly in older models, to convert the AC output from the alternator into DC for battery charging and powering the vehicle's electrical systems. While less efficient than full wave rectifiers, their simplicity and lower component count can be advantageous in certain designs.
In renewable energy systems, half wave rectifiers find application in small-scale solar and wind power installations. They assist in converting the variable output from these sources into a more usable form of electricity, albeit with some limitations in efficiency compared to more advanced rectification methods.
The telecommunications sector utilizes half wave rectifiers in various signal processing applications. They are particularly useful in peak detection circuits, which are essential for analyzing and interpreting communication signals. In this context, the rectifier's ability to pass only positive or negative portions of a signal is leveraged to extract specific information from complex waveforms.
Consumer electronics also incorporate half wave rectifiers, especially in low-power devices where full wave rectification would be overkill. Examples include simple battery chargers, LED drivers, and some types of voltage regulators in small appliances. The simplicity of half wave rectifiers makes them a cost-effective solution for these applications.
In scientific and medical instrumentation, half wave rectifiers are used in specialized measurement and analysis equipment. They can be found in oscilloscopes, spectrum analyzers, and certain types of medical imaging devices, where their signal-shaping properties are valuable for precise measurements and data interpretation.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!