How Half Wave Rectifiers Improve System Reliability?
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Half Wave Rectifiers Background and Objectives
Half-wave rectifiers have played a crucial role in the evolution of power electronics and system reliability since their inception in the early 20th century. These devices, which convert alternating current (AC) to pulsating direct current (DC), have undergone significant improvements over the years, contributing to enhanced system reliability across various applications.
The development of half-wave rectifiers can be traced back to the invention of the vacuum tube diode by John Ambrose Fleming in 1904. This breakthrough laid the foundation for modern rectification technology. As electronic systems became more complex and demanding, the need for efficient and reliable power conversion methods grew, propelling further advancements in rectifier technology.
The primary objective of half-wave rectifiers in improving system reliability is to provide a stable and consistent power supply. By allowing current to flow in only one direction during each AC cycle, these devices help prevent reverse current flow, which can damage sensitive electronic components. This fundamental characteristic has made half-wave rectifiers indispensable in numerous applications, from simple household appliances to sophisticated industrial equipment.
Over time, the technology has evolved from vacuum tube diodes to solid-state semiconductor devices, such as silicon diodes and Schottky diodes. These advancements have led to significant improvements in efficiency, size reduction, and overall system reliability. Modern half-wave rectifiers offer faster switching speeds, lower forward voltage drops, and higher current-handling capabilities, all of which contribute to more robust and dependable electronic systems.
The ongoing technological trend in half-wave rectifiers focuses on further enhancing their performance and reliability. This includes the development of new materials and designs to minimize power losses, improve thermal management, and increase the overall lifespan of rectifier components. Additionally, researchers are exploring ways to integrate half-wave rectifiers with other power management technologies to create more comprehensive and efficient power conversion solutions.
As we look to the future, the objectives for half-wave rectifiers in system reliability continue to evolve. There is a growing emphasis on developing rectifiers that can handle higher frequencies and power levels while maintaining or improving efficiency. Furthermore, with the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources and the expansion of electric vehicle infrastructure, there is a pressing need for rectifiers that can operate reliably under diverse and challenging conditions.
The development of half-wave rectifiers can be traced back to the invention of the vacuum tube diode by John Ambrose Fleming in 1904. This breakthrough laid the foundation for modern rectification technology. As electronic systems became more complex and demanding, the need for efficient and reliable power conversion methods grew, propelling further advancements in rectifier technology.
The primary objective of half-wave rectifiers in improving system reliability is to provide a stable and consistent power supply. By allowing current to flow in only one direction during each AC cycle, these devices help prevent reverse current flow, which can damage sensitive electronic components. This fundamental characteristic has made half-wave rectifiers indispensable in numerous applications, from simple household appliances to sophisticated industrial equipment.
Over time, the technology has evolved from vacuum tube diodes to solid-state semiconductor devices, such as silicon diodes and Schottky diodes. These advancements have led to significant improvements in efficiency, size reduction, and overall system reliability. Modern half-wave rectifiers offer faster switching speeds, lower forward voltage drops, and higher current-handling capabilities, all of which contribute to more robust and dependable electronic systems.
The ongoing technological trend in half-wave rectifiers focuses on further enhancing their performance and reliability. This includes the development of new materials and designs to minimize power losses, improve thermal management, and increase the overall lifespan of rectifier components. Additionally, researchers are exploring ways to integrate half-wave rectifiers with other power management technologies to create more comprehensive and efficient power conversion solutions.
As we look to the future, the objectives for half-wave rectifiers in system reliability continue to evolve. There is a growing emphasis on developing rectifiers that can handle higher frequencies and power levels while maintaining or improving efficiency. Furthermore, with the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources and the expansion of electric vehicle infrastructure, there is a pressing need for rectifiers that can operate reliably under diverse and challenging conditions.
Market Demand Analysis for Reliable Power Systems
The demand for reliable power systems has been steadily increasing across various sectors, driven by the growing reliance on electronic devices and the critical nature of uninterrupted power supply in modern infrastructure. Half wave rectifiers play a crucial role in enhancing system reliability, making them a key component in power supply designs.
In the industrial sector, the market for reliable power systems is experiencing significant growth. Manufacturing facilities, data centers, and telecommunications infrastructure require robust power solutions to maintain continuous operations. The integration of half wave rectifiers in these systems helps mitigate power fluctuations and ensures a stable supply, reducing downtime and associated costs.
The automotive industry represents another major market for reliable power systems incorporating half wave rectifiers. As vehicles become more electrified and autonomous, the demand for dependable power management solutions increases. Half wave rectifiers contribute to the overall reliability of automotive electrical systems, supporting critical functions such as engine management, safety features, and infotainment systems.
In the renewable energy sector, the market for reliable power systems is expanding rapidly. Solar and wind power installations require efficient power conversion and management to maximize energy output and grid stability. Half wave rectifiers play a vital role in these systems by improving the reliability of power conversion processes and enhancing overall system efficiency.
The healthcare industry also presents a significant market opportunity for reliable power systems. Medical equipment, life support systems, and diagnostic devices demand uninterrupted and stable power supply. The implementation of half wave rectifiers in healthcare power systems contributes to patient safety and the overall reliability of medical facilities.
Consumer electronics represent a vast market for reliable power systems. With the proliferation of smartphones, laptops, and smart home devices, there is a growing need for efficient and dependable power management solutions. Half wave rectifiers are integral components in chargers and power adapters, ensuring consistent power delivery and prolonging device lifespan.
The aerospace and defense sectors require highly reliable power systems for mission-critical applications. Aircraft, satellites, and military equipment depend on robust power management solutions to operate in challenging environments. Half wave rectifiers contribute to the reliability and longevity of these systems, making them essential components in aerospace and defense applications.
As smart cities and IoT technologies continue to evolve, the demand for reliable power systems in urban infrastructure is increasing. Street lighting, traffic management systems, and public safety networks all require dependable power solutions. Half wave rectifiers play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability of these systems, contributing to the overall efficiency and safety of smart city initiatives.
In the industrial sector, the market for reliable power systems is experiencing significant growth. Manufacturing facilities, data centers, and telecommunications infrastructure require robust power solutions to maintain continuous operations. The integration of half wave rectifiers in these systems helps mitigate power fluctuations and ensures a stable supply, reducing downtime and associated costs.
The automotive industry represents another major market for reliable power systems incorporating half wave rectifiers. As vehicles become more electrified and autonomous, the demand for dependable power management solutions increases. Half wave rectifiers contribute to the overall reliability of automotive electrical systems, supporting critical functions such as engine management, safety features, and infotainment systems.
In the renewable energy sector, the market for reliable power systems is expanding rapidly. Solar and wind power installations require efficient power conversion and management to maximize energy output and grid stability. Half wave rectifiers play a vital role in these systems by improving the reliability of power conversion processes and enhancing overall system efficiency.
The healthcare industry also presents a significant market opportunity for reliable power systems. Medical equipment, life support systems, and diagnostic devices demand uninterrupted and stable power supply. The implementation of half wave rectifiers in healthcare power systems contributes to patient safety and the overall reliability of medical facilities.
Consumer electronics represent a vast market for reliable power systems. With the proliferation of smartphones, laptops, and smart home devices, there is a growing need for efficient and dependable power management solutions. Half wave rectifiers are integral components in chargers and power adapters, ensuring consistent power delivery and prolonging device lifespan.
The aerospace and defense sectors require highly reliable power systems for mission-critical applications. Aircraft, satellites, and military equipment depend on robust power management solutions to operate in challenging environments. Half wave rectifiers contribute to the reliability and longevity of these systems, making them essential components in aerospace and defense applications.
As smart cities and IoT technologies continue to evolve, the demand for reliable power systems in urban infrastructure is increasing. Street lighting, traffic management systems, and public safety networks all require dependable power solutions. Half wave rectifiers play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability of these systems, contributing to the overall efficiency and safety of smart city initiatives.
Current Challenges in Half Wave Rectification
Half wave rectification, while a fundamental technique in power electronics, faces several challenges that impact its effectiveness and reliability in modern systems. One of the primary issues is the inherent inefficiency of the process. Half wave rectifiers only utilize one half of the AC waveform, effectively discarding 50% of the available power. This results in a lower overall power output and reduced energy efficiency, which is particularly problematic in applications where power conservation is crucial.
Another significant challenge is the presence of ripple in the output voltage. The pulsating nature of half wave rectification leads to a considerable amount of AC ripple superimposed on the DC output. This ripple can cause instability in sensitive electronic circuits and may require additional filtering components, increasing system complexity and cost. The ripple factor in half wave rectifiers is typically higher than in full wave rectifiers, making it less suitable for applications requiring smooth DC voltage.
Voltage regulation is also a concern with half wave rectifiers. The output voltage can vary significantly with changes in load or input voltage, making it difficult to maintain a stable DC supply. This poor voltage regulation can lead to inconsistent performance in connected devices and may necessitate the use of additional voltage regulation circuits, further complicating the system design.
The non-linear nature of half wave rectification introduces harmonic distortion into the power system. These harmonics can cause electromagnetic interference (EMI) and reduce power quality. In industrial settings, where multiple half wave rectifiers might be used, the cumulative effect of harmonics can lead to significant power system disturbances, potentially affecting other equipment connected to the same power source.
Component stress is another challenge in half wave rectification. The rectifying diode must handle the full reverse voltage of the AC supply during the non-conducting half cycle. This high peak inverse voltage (PIV) requirement can lead to increased component costs and potential reliability issues, especially in high-voltage applications.
Lastly, the unidirectional current flow in half wave rectifiers can cause DC saturation in transformers used in the power supply. This saturation can lead to increased core losses, reduced efficiency, and potential overheating of the transformer. In some cases, it may necessitate the use of larger, more expensive transformers to mitigate these effects.
These challenges collectively impact the overall reliability and performance of systems employing half wave rectification. Addressing these issues often requires trade-offs between simplicity, cost, and performance, making the design of efficient and reliable half wave rectifier systems a complex task in modern power electronics.
Another significant challenge is the presence of ripple in the output voltage. The pulsating nature of half wave rectification leads to a considerable amount of AC ripple superimposed on the DC output. This ripple can cause instability in sensitive electronic circuits and may require additional filtering components, increasing system complexity and cost. The ripple factor in half wave rectifiers is typically higher than in full wave rectifiers, making it less suitable for applications requiring smooth DC voltage.
Voltage regulation is also a concern with half wave rectifiers. The output voltage can vary significantly with changes in load or input voltage, making it difficult to maintain a stable DC supply. This poor voltage regulation can lead to inconsistent performance in connected devices and may necessitate the use of additional voltage regulation circuits, further complicating the system design.
The non-linear nature of half wave rectification introduces harmonic distortion into the power system. These harmonics can cause electromagnetic interference (EMI) and reduce power quality. In industrial settings, where multiple half wave rectifiers might be used, the cumulative effect of harmonics can lead to significant power system disturbances, potentially affecting other equipment connected to the same power source.
Component stress is another challenge in half wave rectification. The rectifying diode must handle the full reverse voltage of the AC supply during the non-conducting half cycle. This high peak inverse voltage (PIV) requirement can lead to increased component costs and potential reliability issues, especially in high-voltage applications.
Lastly, the unidirectional current flow in half wave rectifiers can cause DC saturation in transformers used in the power supply. This saturation can lead to increased core losses, reduced efficiency, and potential overheating of the transformer. In some cases, it may necessitate the use of larger, more expensive transformers to mitigate these effects.
These challenges collectively impact the overall reliability and performance of systems employing half wave rectification. Addressing these issues often requires trade-offs between simplicity, cost, and performance, making the design of efficient and reliable half wave rectifier systems a complex task in modern power electronics.
Existing Half Wave Rectifier Implementations
01 Improved circuit design for reliability
Enhanced circuit designs for half-wave rectifiers can significantly improve system reliability. These designs may include additional components or modified configurations to reduce stress on individual components, improve voltage regulation, and minimize power losses. Such improvements can lead to more stable and longer-lasting rectifier systems.- Improved circuit design for reliability: Enhanced circuit designs for half-wave rectifiers can significantly improve system reliability. These designs may include additional components or modified configurations to reduce stress on individual components, improve voltage regulation, and minimize power losses. Such improvements can lead to more stable and longer-lasting rectifier systems.
- Thermal management techniques: Implementing effective thermal management techniques is crucial for enhancing the reliability of half-wave rectifier systems. This may involve the use of heat sinks, improved cooling mechanisms, or thermal-resistant materials to dissipate heat more efficiently. Proper thermal management helps prevent component failure due to overheating and extends the overall system lifespan.
- Protection circuits and components: Incorporating protection circuits and components can significantly enhance the reliability of half-wave rectifier systems. These may include surge protectors, fuses, or voltage-limiting devices that safeguard the system against voltage spikes, overcurrent, and other electrical anomalies. Such protective measures help prevent damage to sensitive components and ensure consistent performance.
- Advanced control and monitoring systems: Implementing advanced control and monitoring systems can improve the reliability of half-wave rectifier systems. These may include microcontroller-based solutions, real-time monitoring of key parameters, and adaptive control algorithms. Such systems can detect potential issues early, adjust operating conditions as needed, and provide valuable diagnostic information for maintenance.
- Component selection and quality assurance: Careful selection of high-quality components and rigorous quality assurance processes are essential for improving the reliability of half-wave rectifier systems. This includes using components with higher ratings, better tolerances, and proven reliability. Additionally, implementing thorough testing and burn-in procedures can help identify potential weaknesses before deployment, ensuring more reliable operation in the field.
02 Thermal management techniques
Implementing effective thermal management techniques is crucial for enhancing the reliability of half-wave rectifier systems. This may involve the use of heat sinks, improved cooling mechanisms, or thermal-resistant materials to dissipate heat more efficiently. Proper thermal management helps prevent component failure due to overheating and extends the overall system lifespan.Expand Specific Solutions03 Protection circuits and components
Incorporating protection circuits and components can significantly enhance the reliability of half-wave rectifier systems. These may include surge protectors, fuses, or voltage-limiting devices that safeguard the system against voltage spikes, overcurrent, and other electrical anomalies. Such protective measures help prevent damage to sensitive components and ensure consistent performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Advanced control and monitoring systems
Implementing advanced control and monitoring systems can improve the reliability of half-wave rectifier systems. These may include microcontroller-based solutions, real-time monitoring of key parameters, and adaptive control algorithms. Such systems can detect potential issues early, adjust operating conditions as needed, and provide valuable diagnostic information for maintenance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Component selection and quality assurance
Careful selection of high-quality components and rigorous quality assurance processes are essential for improving the reliability of half-wave rectifier systems. This includes using components with higher voltage and current ratings, selecting parts with proven reliability records, and implementing thorough testing procedures. These measures help ensure that the system can withstand operational stresses and maintain consistent performance over time.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Power Electronics Industry
The half wave rectifier technology market is in a mature stage, with a stable global market size estimated in the billions of dollars. Major players like Samsung Electronics, Mitsubishi Electric, and Toshiba have well-established positions, leveraging their expertise in power electronics and semiconductor manufacturing. The technology's reliability improvements have led to widespread adoption across various industries, including consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial applications. While innovation continues, particularly in efficiency and miniaturization, the core technology is well-understood and implemented by numerous companies, including Robert Bosch GmbH and TE Connectivity Solutions GmbH, indicating a high level of technical maturity and market saturation.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung Electronics has innovated in the field of half-wave rectifiers by integrating them into their power management integrated circuits (PMICs) for mobile and IoT devices. Their approach focuses on miniaturization and energy efficiency, utilizing advanced semiconductor processes to create rectifiers that operate at higher frequencies with minimal power loss[4]. Samsung's half-wave rectifiers incorporate adaptive voltage scaling techniques, which dynamically adjust the output voltage based on the system's power requirements, resulting in up to 15% improvement in overall device battery life[5]. Additionally, Samsung has developed a proprietary overvoltage protection mechanism that enhances the reliability of their rectifiers in fluctuating power environments, crucial for maintaining the longevity of sensitive electronic components[6].
Strengths: Highly integrated solution, excellent energy efficiency, and advanced protection features. Weaknesses: Primarily optimized for low-power applications, which may limit use in high-power scenarios.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Bosch has made significant strides in improving system reliability through their innovative half-wave rectifier designs, particularly in automotive applications. Their approach combines high-voltage silicon carbide (SiC) diodes with advanced packaging techniques to create rectifiers that can withstand the harsh environments found in modern vehicles[7]. Bosch's rectifiers feature a unique thermal interface material that improves heat dissipation by up to 40%, allowing for more compact designs and increased power density[8]. The company has also implemented a sophisticated current sensing mechanism within their rectifiers, enabling real-time monitoring and fault detection, which significantly enhances system reliability and safety in critical automotive systems[9].
Strengths: Robust design for harsh environments, excellent thermal management, and advanced fault detection capabilities. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost due to specialized components and may be overengineered for simpler applications.
Core Innovations in Rectifier Design
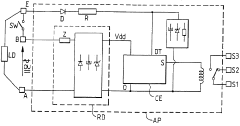
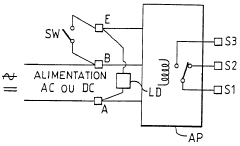
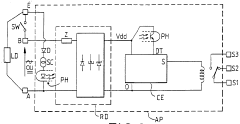
Electric apparatus with supply voltage control, operating in alternating or direct current
PatentWO2000016174A1
Innovation
- A control circuit using a half-wave rectifier and resistive divider bridge to generate a low DC voltage, with a microcontroller to detect the state of the control input signal, allowing operation across a wide range of supply voltages without the need for optocouplers, and maintaining detection accuracy even with external loads present.
Photosensor circuits including a switch mode power converter, a driver transistor and a relay coil
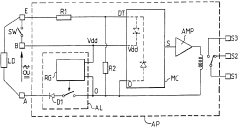
PatentActiveUS8026470B2
Innovation
- A photosensor circuit with a pulse width modulator and a Darlington pair of transistors that controls a relay coil to regulate AC power, using a half-wave rectifier and a phototransistor to generate a pulse width modulated signal responsive to light levels, reducing component count and improving efficiency.
Efficiency and Power Quality Considerations
Half-wave rectifiers play a crucial role in improving system reliability by enhancing efficiency and power quality in electrical systems. These devices convert alternating current (AC) to pulsating direct current (DC), which is essential for many applications in power electronics and electrical engineering.
The efficiency of half-wave rectifiers is a key consideration in their implementation. While they are not as efficient as full-wave rectifiers, they offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness in certain applications. Half-wave rectifiers typically achieve an efficiency of around 40.6%, which is sufficient for low-power applications or where power loss is not a critical concern. This efficiency is primarily due to the rectifier only utilizing one half of the AC waveform, resulting in some energy loss during the negative half-cycle.
Power quality is another significant aspect affected by half-wave rectifiers. These devices introduce harmonic distortion into the power system, which can impact the overall power quality. The harmonic content generated by half-wave rectifiers is characterized by odd harmonics, with the third harmonic being particularly prominent. This harmonic distortion can lead to increased losses in transformers and motors, as well as potential interference with sensitive electronic equipment.
To mitigate the power quality issues associated with half-wave rectifiers, various techniques can be employed. Filtering is a common approach, with the use of capacitors or inductors to smooth out the pulsating DC output. This helps reduce ripple and improve the overall quality of the rectified signal. Additionally, more advanced control techniques, such as pulse-width modulation (PWM), can be implemented to further enhance power quality and reduce harmonic distortion.
The impact of half-wave rectifiers on power factor is also an important consideration. Due to their non-linear characteristics, these devices can lead to a reduction in power factor, which affects the overall efficiency of the power distribution system. To address this issue, power factor correction techniques may be necessary, particularly in larger-scale applications where multiple half-wave rectifiers are used.
Despite these challenges, half-wave rectifiers continue to be valuable in improving system reliability in specific scenarios. Their simplicity and robustness make them suitable for applications where a basic level of AC to DC conversion is required, and where the trade-offs in efficiency and power quality are acceptable. By carefully considering the efficiency and power quality implications, engineers can effectively integrate half-wave rectifiers into systems to enhance overall reliability and performance.
The efficiency of half-wave rectifiers is a key consideration in their implementation. While they are not as efficient as full-wave rectifiers, they offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness in certain applications. Half-wave rectifiers typically achieve an efficiency of around 40.6%, which is sufficient for low-power applications or where power loss is not a critical concern. This efficiency is primarily due to the rectifier only utilizing one half of the AC waveform, resulting in some energy loss during the negative half-cycle.
Power quality is another significant aspect affected by half-wave rectifiers. These devices introduce harmonic distortion into the power system, which can impact the overall power quality. The harmonic content generated by half-wave rectifiers is characterized by odd harmonics, with the third harmonic being particularly prominent. This harmonic distortion can lead to increased losses in transformers and motors, as well as potential interference with sensitive electronic equipment.
To mitigate the power quality issues associated with half-wave rectifiers, various techniques can be employed. Filtering is a common approach, with the use of capacitors or inductors to smooth out the pulsating DC output. This helps reduce ripple and improve the overall quality of the rectified signal. Additionally, more advanced control techniques, such as pulse-width modulation (PWM), can be implemented to further enhance power quality and reduce harmonic distortion.
The impact of half-wave rectifiers on power factor is also an important consideration. Due to their non-linear characteristics, these devices can lead to a reduction in power factor, which affects the overall efficiency of the power distribution system. To address this issue, power factor correction techniques may be necessary, particularly in larger-scale applications where multiple half-wave rectifiers are used.
Despite these challenges, half-wave rectifiers continue to be valuable in improving system reliability in specific scenarios. Their simplicity and robustness make them suitable for applications where a basic level of AC to DC conversion is required, and where the trade-offs in efficiency and power quality are acceptable. By carefully considering the efficiency and power quality implications, engineers can effectively integrate half-wave rectifiers into systems to enhance overall reliability and performance.
Thermal Management in Rectifier Systems
Thermal management is a critical aspect of rectifier systems, particularly in half-wave rectifiers, which play a significant role in improving system reliability. The conversion of AC to DC power in rectifiers generates heat as a byproduct, and effective thermal management is essential to maintain optimal performance and extend the lifespan of the system components.
Half-wave rectifiers, while simpler in design compared to full-wave rectifiers, present unique thermal challenges. The pulsating nature of the output current in half-wave rectification can lead to uneven heat distribution across the rectifier components. This uneven heating can cause thermal stress and potentially lead to premature failure of sensitive electronic components if not properly managed.
To address these thermal concerns, several strategies are employed in half-wave rectifier systems. Heat sinks are commonly used to dissipate excess heat from semiconductor devices such as diodes. These heat sinks increase the surface area for heat transfer, allowing for more efficient cooling through natural convection or forced air cooling. The design and material selection of heat sinks are crucial factors in their effectiveness, with materials like aluminum and copper being popular choices due to their high thermal conductivity.
Active cooling methods, such as fans or liquid cooling systems, may be implemented in high-power applications where passive cooling is insufficient. These active cooling solutions can significantly enhance heat dissipation, allowing for higher power handling capabilities and improved system reliability. However, they also introduce additional complexity and potential points of failure, requiring careful consideration in system design.
Thermal interface materials (TIMs) play a vital role in improving heat transfer between the rectifier components and heat sinks. These materials, which can include thermal greases, pads, or phase-change materials, help to fill microscopic air gaps and ensure efficient heat conduction. The selection of appropriate TIMs is critical, as their thermal conductivity and long-term stability directly impact the overall thermal management effectiveness.
Temperature monitoring and control systems are often integrated into rectifier designs to ensure optimal thermal performance. These systems may include temperature sensors, thermal shutdown circuits, and variable speed fan controls. By continuously monitoring component temperatures and adjusting cooling mechanisms accordingly, these systems can prevent thermal runaway and maintain safe operating conditions.
In the context of system reliability, effective thermal management in half-wave rectifiers contributes to several key benefits. By maintaining components within their specified temperature ranges, thermal management systems help to prevent thermal-induced failures, such as semiconductor junction breakdown or electrolytic capacitor degradation. This, in turn, leads to extended component lifespans and reduced maintenance requirements, ultimately enhancing the overall reliability and availability of the rectifier system.
Half-wave rectifiers, while simpler in design compared to full-wave rectifiers, present unique thermal challenges. The pulsating nature of the output current in half-wave rectification can lead to uneven heat distribution across the rectifier components. This uneven heating can cause thermal stress and potentially lead to premature failure of sensitive electronic components if not properly managed.
To address these thermal concerns, several strategies are employed in half-wave rectifier systems. Heat sinks are commonly used to dissipate excess heat from semiconductor devices such as diodes. These heat sinks increase the surface area for heat transfer, allowing for more efficient cooling through natural convection or forced air cooling. The design and material selection of heat sinks are crucial factors in their effectiveness, with materials like aluminum and copper being popular choices due to their high thermal conductivity.
Active cooling methods, such as fans or liquid cooling systems, may be implemented in high-power applications where passive cooling is insufficient. These active cooling solutions can significantly enhance heat dissipation, allowing for higher power handling capabilities and improved system reliability. However, they also introduce additional complexity and potential points of failure, requiring careful consideration in system design.
Thermal interface materials (TIMs) play a vital role in improving heat transfer between the rectifier components and heat sinks. These materials, which can include thermal greases, pads, or phase-change materials, help to fill microscopic air gaps and ensure efficient heat conduction. The selection of appropriate TIMs is critical, as their thermal conductivity and long-term stability directly impact the overall thermal management effectiveness.
Temperature monitoring and control systems are often integrated into rectifier designs to ensure optimal thermal performance. These systems may include temperature sensors, thermal shutdown circuits, and variable speed fan controls. By continuously monitoring component temperatures and adjusting cooling mechanisms accordingly, these systems can prevent thermal runaway and maintain safe operating conditions.
In the context of system reliability, effective thermal management in half-wave rectifiers contributes to several key benefits. By maintaining components within their specified temperature ranges, thermal management systems help to prevent thermal-induced failures, such as semiconductor junction breakdown or electrolytic capacitor degradation. This, in turn, leads to extended component lifespans and reduced maintenance requirements, ultimately enhancing the overall reliability and availability of the rectifier system.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!