How to Troubleshoot Half Wave Rectifier Failures?
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Rectifier Failure Analysis and Objectives
Half-wave rectifier failures can significantly impact the performance and reliability of electronic systems. This technical research report aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the challenges associated with troubleshooting these failures and establish clear objectives for addressing them. The evolution of rectifier technology has led to increasingly complex circuits, necessitating a deeper understanding of potential failure modes and their root causes.
The primary goal of this research is to develop a systematic approach to identifying, diagnosing, and resolving half-wave rectifier failures efficiently. By examining the historical progression of rectifier technology and current industry practices, we can establish a foundation for future advancements in troubleshooting methodologies. This analysis will encompass both theoretical and practical aspects of rectifier operation, focusing on the specific challenges posed by half-wave configurations.
One of the key objectives is to create a comprehensive catalog of common failure modes in half-wave rectifiers. This will involve an in-depth study of component degradation, circuit design flaws, and environmental factors that contribute to rectifier malfunction. By categorizing these failure modes, we can develop targeted diagnostic procedures and streamline the troubleshooting process.
Another crucial aspect of this research is to explore the latest advancements in diagnostic tools and techniques. This includes evaluating the effectiveness of various testing equipment, such as oscilloscopes, multimeters, and specialized rectifier analyzers. Additionally, we will investigate emerging technologies, like AI-driven fault detection systems and predictive maintenance algorithms, to assess their potential in enhancing rectifier failure analysis.
The research will also focus on developing a standardized troubleshooting protocol for half-wave rectifier failures. This protocol will incorporate best practices from industry experts, academic research, and real-world case studies. By establishing a systematic approach, we aim to reduce downtime, improve repair efficiency, and minimize the risk of recurring failures.
Furthermore, this study will address the challenges of troubleshooting rectifiers in diverse applications, ranging from consumer electronics to industrial power systems. Each application presents unique environmental conditions and operational requirements that can influence failure patterns and diagnostic approaches. By considering these variables, we can develop more robust and versatile troubleshooting strategies.
Lastly, the research will explore preventive measures and design improvements to mitigate the occurrence of half-wave rectifier failures. This proactive approach will involve analyzing current circuit designs, component selection criteria, and manufacturing processes to identify potential vulnerabilities. By addressing these issues at the design stage, we can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of rectifier failures in future applications.
The primary goal of this research is to develop a systematic approach to identifying, diagnosing, and resolving half-wave rectifier failures efficiently. By examining the historical progression of rectifier technology and current industry practices, we can establish a foundation for future advancements in troubleshooting methodologies. This analysis will encompass both theoretical and practical aspects of rectifier operation, focusing on the specific challenges posed by half-wave configurations.
One of the key objectives is to create a comprehensive catalog of common failure modes in half-wave rectifiers. This will involve an in-depth study of component degradation, circuit design flaws, and environmental factors that contribute to rectifier malfunction. By categorizing these failure modes, we can develop targeted diagnostic procedures and streamline the troubleshooting process.
Another crucial aspect of this research is to explore the latest advancements in diagnostic tools and techniques. This includes evaluating the effectiveness of various testing equipment, such as oscilloscopes, multimeters, and specialized rectifier analyzers. Additionally, we will investigate emerging technologies, like AI-driven fault detection systems and predictive maintenance algorithms, to assess their potential in enhancing rectifier failure analysis.
The research will also focus on developing a standardized troubleshooting protocol for half-wave rectifier failures. This protocol will incorporate best practices from industry experts, academic research, and real-world case studies. By establishing a systematic approach, we aim to reduce downtime, improve repair efficiency, and minimize the risk of recurring failures.
Furthermore, this study will address the challenges of troubleshooting rectifiers in diverse applications, ranging from consumer electronics to industrial power systems. Each application presents unique environmental conditions and operational requirements that can influence failure patterns and diagnostic approaches. By considering these variables, we can develop more robust and versatile troubleshooting strategies.
Lastly, the research will explore preventive measures and design improvements to mitigate the occurrence of half-wave rectifier failures. This proactive approach will involve analyzing current circuit designs, component selection criteria, and manufacturing processes to identify potential vulnerabilities. By addressing these issues at the design stage, we can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of rectifier failures in future applications.
Market Demand for Reliable Power Supplies
The market demand for reliable power supplies has been steadily increasing across various industries, driven by the growing reliance on electronic devices and systems in both consumer and industrial applications. Half-wave rectifiers, as fundamental components in power supply circuits, play a crucial role in converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). The reliability of these rectifiers directly impacts the performance and longevity of countless electronic devices, making their troubleshooting and maintenance a critical concern for manufacturers and end-users alike.
In the consumer electronics sector, the proliferation of smartphones, laptops, and smart home devices has created a substantial market for efficient and dependable power supplies. These devices require stable DC power for optimal operation, and any failures in the rectification process can lead to device malfunction or damage. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on improving the reliability of their power supply components, including half-wave rectifiers, to meet consumer expectations for long-lasting and trouble-free products.
The industrial sector presents an even more demanding market for reliable power supplies. In manufacturing environments, where continuous operation is crucial, any power supply failure can result in significant downtime and financial losses. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and telecommunications rely heavily on robust power systems to maintain their operations. The market demand in these sectors is not only for reliable rectifiers but also for advanced troubleshooting tools and techniques that can quickly identify and resolve issues in half-wave rectifier circuits.
The healthcare industry is another significant driver of demand for reliable power supplies. Medical equipment, from diagnostic devices to life-support systems, requires uninterrupted and stable power. The consequences of power supply failures in this context can be life-threatening, making the reliability of components like half-wave rectifiers a critical factor in equipment design and maintenance.
As renewable energy sources become more prevalent, the demand for reliable power conversion and rectification technologies is also growing. Solar and wind power systems often require efficient AC to DC conversion, creating new market opportunities for advanced rectifier technologies and troubleshooting solutions.
The global trend towards miniaturization and increased power efficiency in electronic devices is further shaping the market demand. Manufacturers are seeking compact, high-performance rectifier solutions that can deliver reliable power while minimizing heat generation and energy loss. This trend is particularly evident in the development of mobile devices and Internet of Things (IoT) applications, where power efficiency and reliability are paramount.
In the consumer electronics sector, the proliferation of smartphones, laptops, and smart home devices has created a substantial market for efficient and dependable power supplies. These devices require stable DC power for optimal operation, and any failures in the rectification process can lead to device malfunction or damage. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on improving the reliability of their power supply components, including half-wave rectifiers, to meet consumer expectations for long-lasting and trouble-free products.
The industrial sector presents an even more demanding market for reliable power supplies. In manufacturing environments, where continuous operation is crucial, any power supply failure can result in significant downtime and financial losses. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and telecommunications rely heavily on robust power systems to maintain their operations. The market demand in these sectors is not only for reliable rectifiers but also for advanced troubleshooting tools and techniques that can quickly identify and resolve issues in half-wave rectifier circuits.
The healthcare industry is another significant driver of demand for reliable power supplies. Medical equipment, from diagnostic devices to life-support systems, requires uninterrupted and stable power. The consequences of power supply failures in this context can be life-threatening, making the reliability of components like half-wave rectifiers a critical factor in equipment design and maintenance.
As renewable energy sources become more prevalent, the demand for reliable power conversion and rectification technologies is also growing. Solar and wind power systems often require efficient AC to DC conversion, creating new market opportunities for advanced rectifier technologies and troubleshooting solutions.
The global trend towards miniaturization and increased power efficiency in electronic devices is further shaping the market demand. Manufacturers are seeking compact, high-performance rectifier solutions that can deliver reliable power while minimizing heat generation and energy loss. This trend is particularly evident in the development of mobile devices and Internet of Things (IoT) applications, where power efficiency and reliability are paramount.
Current Challenges in Half Wave Rectifier Circuits
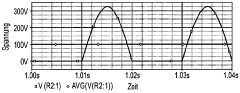
Half wave rectifier circuits, while fundamental in power electronics, face several challenges that can lead to failures and inefficiencies. One of the primary issues is the inherent inefficiency of the circuit design. By utilizing only one half of the AC waveform, half wave rectifiers waste a significant portion of the input power, resulting in lower overall efficiency compared to full wave rectifiers.
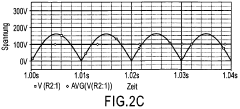
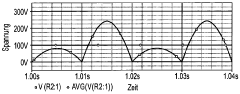
Voltage regulation presents another significant challenge. The output of a half wave rectifier is prone to fluctuations, especially under varying load conditions. This instability can lead to inconsistent power delivery and potential damage to connected devices. The pulsating nature of the output also contributes to a higher ripple factor, necessitating more extensive filtering to achieve a smoother DC output.
Component stress is a critical concern in half wave rectifier circuits. The diode used in the rectification process experiences high peak inverse voltage (PIV) during the non-conducting half cycle. This stress can lead to premature diode failure, particularly in high-voltage applications. Additionally, the transformer in the circuit may suffer from core saturation due to the unidirectional current flow, potentially causing overheating and reduced efficiency.
Harmonic distortion is another challenge that plagues half wave rectifier circuits. The non-linear nature of the rectification process introduces harmonics into the power system, which can interfere with other electronic equipment and contribute to electromagnetic interference (EMI). This distortion not only affects the quality of the output but also may violate regulatory standards for power quality.
The limited current handling capacity of half wave rectifiers poses challenges in high-power applications. The circuit's inability to utilize the full AC cycle restricts the amount of power that can be efficiently converted, making it less suitable for applications requiring substantial current output. This limitation often necessitates the use of larger, more expensive components to achieve the desired power output.
Temperature management is a persistent challenge in half wave rectifier circuits. The intermittent nature of current flow can lead to thermal cycling, which stresses components and can accelerate wear. Proper heat dissipation becomes crucial, especially in compact designs where space for thermal management is limited.
Lastly, the reliability of half wave rectifier circuits in harsh environments presents ongoing challenges. Factors such as temperature extremes, humidity, and vibration can affect component performance and longevity. Ensuring robust operation under these conditions often requires additional design considerations and component selection, adding complexity and cost to the overall system.
Voltage regulation presents another significant challenge. The output of a half wave rectifier is prone to fluctuations, especially under varying load conditions. This instability can lead to inconsistent power delivery and potential damage to connected devices. The pulsating nature of the output also contributes to a higher ripple factor, necessitating more extensive filtering to achieve a smoother DC output.
Component stress is a critical concern in half wave rectifier circuits. The diode used in the rectification process experiences high peak inverse voltage (PIV) during the non-conducting half cycle. This stress can lead to premature diode failure, particularly in high-voltage applications. Additionally, the transformer in the circuit may suffer from core saturation due to the unidirectional current flow, potentially causing overheating and reduced efficiency.
Harmonic distortion is another challenge that plagues half wave rectifier circuits. The non-linear nature of the rectification process introduces harmonics into the power system, which can interfere with other electronic equipment and contribute to electromagnetic interference (EMI). This distortion not only affects the quality of the output but also may violate regulatory standards for power quality.
The limited current handling capacity of half wave rectifiers poses challenges in high-power applications. The circuit's inability to utilize the full AC cycle restricts the amount of power that can be efficiently converted, making it less suitable for applications requiring substantial current output. This limitation often necessitates the use of larger, more expensive components to achieve the desired power output.
Temperature management is a persistent challenge in half wave rectifier circuits. The intermittent nature of current flow can lead to thermal cycling, which stresses components and can accelerate wear. Proper heat dissipation becomes crucial, especially in compact designs where space for thermal management is limited.
Lastly, the reliability of half wave rectifier circuits in harsh environments presents ongoing challenges. Factors such as temperature extremes, humidity, and vibration can affect component performance and longevity. Ensuring robust operation under these conditions often requires additional design considerations and component selection, adding complexity and cost to the overall system.
Existing Troubleshooting Methods for Rectifiers
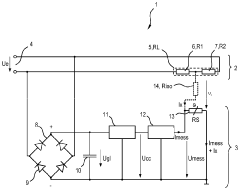
01 Circuit design and components
Half wave rectifiers typically consist of a diode and a transformer. The diode allows current to flow in only one direction, effectively converting AC to pulsating DC. The transformer is used to step down or step up the voltage as needed. This basic design can be modified with additional components like capacitors for improved performance.- Circuit design and components: Half wave rectifiers typically consist of a diode and transformer. The diode allows current to flow in only one direction, converting AC to pulsating DC. The transformer is used to step up or step down the input voltage as needed. Various circuit configurations and component selections can optimize performance for different applications.
- Efficiency improvements: Techniques to improve the efficiency of half wave rectifiers include using high-speed switching diodes, implementing snubber circuits to reduce switching losses, and optimizing the transformer design. Advanced control methods can also be employed to enhance overall system performance and reduce power losses.
- Applications in power supplies: Half wave rectifiers are commonly used in various power supply applications, including low-power electronic devices, battery chargers, and some industrial equipment. They can be integrated into more complex power conversion systems to provide specific voltage and current outputs for different loads.
- Protection and filtering: To improve the quality of the output voltage and protect the circuit, various filtering and protection mechanisms can be incorporated. These may include capacitor filters to smooth the pulsating DC, voltage regulators to stabilize the output, and surge protection devices to guard against voltage spikes.
- Integration with other circuits: Half wave rectifiers can be integrated with other circuit elements to create more complex power conversion systems. This may include combining with inverters, voltage multipliers, or control circuits to achieve specific power conversion goals or to meet the requirements of particular applications.
02 Efficiency improvements
Various techniques are employed to improve the efficiency of half wave rectifiers. These may include using high-speed switching diodes, optimizing the transformer design, and implementing advanced control algorithms. Some designs incorporate power factor correction circuits to reduce harmonic distortion and improve overall system efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications in power supplies
Half wave rectifiers are commonly used in power supply circuits for various electronic devices. They can be found in low-power applications such as small household appliances, battery chargers, and some LED lighting systems. In these applications, the rectifier converts AC mains power to DC for use by the device's internal components.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration with other circuit elements
Half wave rectifiers are often integrated with other circuit elements to create more complex power conversion systems. This may include combining the rectifier with voltage regulators, filters, or inverters. Such integrated designs can provide more stable and reliable power output for sensitive electronic equipment.Expand Specific Solutions05 Miniaturization and packaging
Efforts are being made to miniaturize half wave rectifier circuits and improve their packaging for use in compact electronic devices. This includes the development of integrated circuit solutions that combine multiple functions in a single chip, as well as the use of advanced materials and manufacturing techniques to reduce size and improve heat dissipation.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Power Electronics Industry
The half wave rectifier troubleshooting landscape is characterized by a mature market with established players and well-understood technology. Companies like State Grid Corp. of China, Delta Electronics, and Panasonic Holdings Corp. are key players in this field, leveraging their extensive experience in power electronics. The market size is substantial, driven by the widespread use of rectifiers in various applications. Technologically, half wave rectifiers are well-developed, with ongoing innovations focusing on efficiency improvements and miniaturization. Research institutions like Zhejiang University and the Technical University of Denmark contribute to advancing rectifier technology through academic studies and industry collaborations.
Delta Electronics, Inc.
Technical Solution: Delta Electronics has developed advanced troubleshooting techniques for half-wave rectifier failures in power supplies. Their approach involves a systematic diagnostic process, including voltage and current waveform analysis using high-precision oscilloscopes. They employ thermal imaging to detect overheating components and utilize specialized software for circuit simulation to identify potential failure points. Delta's method also incorporates impedance measurement techniques to assess component degradation over time[1]. Their troubleshooting protocol includes checking for open or short circuits, verifying diode functionality, and analyzing ripple voltage levels. Additionally, they have implemented AI-driven predictive maintenance systems that can detect early signs of rectifier degradation, allowing for proactive replacement before failure occurs[3].
Strengths: Comprehensive diagnostic approach, advanced measurement techniques, and predictive maintenance capabilities. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment and trained personnel, potentially increasing troubleshooting costs.
Vertiv Corp.
Technical Solution: Vertiv has developed a multi-tiered approach to troubleshooting half-wave rectifier failures in their power distribution units and UPS systems. Their method begins with a visual inspection for obvious signs of damage, followed by electrical measurements using advanced power quality analyzers. Vertiv employs a proprietary algorithm that analyzes harmonic distortion patterns to identify specific types of rectifier failures[2]. They also utilize remote monitoring systems that can detect anomalies in rectifier performance in real-time, allowing for immediate intervention. Vertiv's troubleshooting process includes load testing to simulate various operational conditions and stress tests to identify intermittent faults. They have also developed a database of common failure modes and corresponding solutions, which is continuously updated based on field data[4].
Strengths: Real-time monitoring capabilities, extensive failure mode database, and advanced harmonic analysis. Weaknesses: May be overly complex for simple rectifier circuits, potentially leading to longer diagnostic times in some cases.
Core Innovations in Rectifier Diagnostics
Electric circuit and household appliance
PatentWO2010000767A1
Innovation
- The implementation of a half-wave rectifier in the DC circuit, which can include a single diode or triac, reduces or eliminates the influence of AC currents on measurement accuracy by minimizing leakage currents, and the use of a low-pass filter further enhances measurement precision by filtering out ripple effects.
A method and system for driving a voice coil of a loudspeaker
PatentActiveGB2591767A
Innovation
- A voice coil driving system with segmented voice coil sections, where a centre voice coil section and auxiliary voice coil sections are driven by centre and auxiliary driving signals, respectively, with rectifying units attenuating or blocking currents in specific directions to minimize power consumption and heating by only powering sections within the air gap.
Thermal Management in Rectifier Circuits
Thermal management is a critical aspect of rectifier circuit design, particularly in half-wave rectifiers where power dissipation can lead to significant heat generation. Effective thermal management strategies are essential to ensure the reliable operation and longevity of rectifier circuits, especially when troubleshooting failures.
One of the primary thermal management techniques in rectifier circuits involves the use of heat sinks. These passive cooling devices increase the surface area available for heat dissipation, allowing for more efficient transfer of thermal energy from the rectifier components to the surrounding environment. The selection of an appropriate heat sink depends on factors such as the power rating of the rectifier, ambient temperature, and available space within the circuit enclosure.
Active cooling methods, such as forced-air cooling or liquid cooling systems, may be employed in high-power applications where passive cooling alone is insufficient. Forced-air cooling utilizes fans or blowers to increase air circulation around the rectifier components, enhancing convective heat transfer. Liquid cooling systems, while more complex, offer superior heat dissipation capabilities and are often used in industrial-scale rectifier applications.
Thermal interface materials (TIMs) play a crucial role in optimizing heat transfer between the rectifier components and heat sinks. These materials, such as thermal greases, pads, or adhesives, fill microscopic air gaps between surfaces, reducing thermal resistance and improving overall heat dissipation efficiency.
Proper component layout and PCB design are essential for effective thermal management. Placing heat-generating components away from temperature-sensitive elements and utilizing thermal vias to conduct heat through PCB layers can significantly improve heat distribution and dissipation.
Temperature monitoring and protection circuits are often integrated into rectifier designs to prevent thermal runaway and component failure. These may include temperature sensors, thermal shutdown circuits, or variable-speed fan controllers that adjust cooling based on real-time temperature measurements.
In the context of troubleshooting half-wave rectifier failures, thermal management issues can manifest as intermittent failures, reduced efficiency, or complete circuit breakdown. Identifying and addressing thermal-related problems often involves thermal imaging, temperature profiling, and careful analysis of component specifications and operating conditions.
By implementing comprehensive thermal management strategies and understanding their impact on rectifier performance, engineers can effectively diagnose and resolve thermal-related issues, ultimately improving the reliability and efficiency of half-wave rectifier circuits.
One of the primary thermal management techniques in rectifier circuits involves the use of heat sinks. These passive cooling devices increase the surface area available for heat dissipation, allowing for more efficient transfer of thermal energy from the rectifier components to the surrounding environment. The selection of an appropriate heat sink depends on factors such as the power rating of the rectifier, ambient temperature, and available space within the circuit enclosure.
Active cooling methods, such as forced-air cooling or liquid cooling systems, may be employed in high-power applications where passive cooling alone is insufficient. Forced-air cooling utilizes fans or blowers to increase air circulation around the rectifier components, enhancing convective heat transfer. Liquid cooling systems, while more complex, offer superior heat dissipation capabilities and are often used in industrial-scale rectifier applications.
Thermal interface materials (TIMs) play a crucial role in optimizing heat transfer between the rectifier components and heat sinks. These materials, such as thermal greases, pads, or adhesives, fill microscopic air gaps between surfaces, reducing thermal resistance and improving overall heat dissipation efficiency.
Proper component layout and PCB design are essential for effective thermal management. Placing heat-generating components away from temperature-sensitive elements and utilizing thermal vias to conduct heat through PCB layers can significantly improve heat distribution and dissipation.
Temperature monitoring and protection circuits are often integrated into rectifier designs to prevent thermal runaway and component failure. These may include temperature sensors, thermal shutdown circuits, or variable-speed fan controllers that adjust cooling based on real-time temperature measurements.
In the context of troubleshooting half-wave rectifier failures, thermal management issues can manifest as intermittent failures, reduced efficiency, or complete circuit breakdown. Identifying and addressing thermal-related problems often involves thermal imaging, temperature profiling, and careful analysis of component specifications and operating conditions.
By implementing comprehensive thermal management strategies and understanding their impact on rectifier performance, engineers can effectively diagnose and resolve thermal-related issues, ultimately improving the reliability and efficiency of half-wave rectifier circuits.
EMI Considerations for Half Wave Rectifiers
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) is a critical consideration in the design and operation of half wave rectifiers. These devices, while essential in power conversion, can be significant sources of electromagnetic noise, potentially affecting nearby electronic systems and compromising overall circuit performance.
The primary source of EMI in half wave rectifiers stems from the abrupt switching action during the rectification process. As the diode alternates between conducting and non-conducting states, it generates high-frequency harmonics that can propagate through both conducted and radiated paths. These harmonics, if left unmitigated, can interfere with sensitive electronic equipment, causing malfunctions or degraded performance in nearby systems.
To address EMI concerns, several strategies can be employed. Proper shielding is paramount, involving the use of conductive enclosures or barriers to contain electromagnetic emissions. This approach helps to prevent the radiated EMI from affecting surrounding circuits. Additionally, implementing effective grounding techniques is crucial. A well-designed ground plane can significantly reduce common-mode noise and provide a low-impedance path for high-frequency currents.
Filtering is another key aspect of EMI mitigation in half wave rectifiers. Input and output filters, such as LC (inductor-capacitor) networks, can attenuate high-frequency noise components. Specifically, input filters help to prevent noise from propagating back into the power source, while output filters smooth the rectified waveform and reduce ripple, which is a common source of EMI.
Component selection and layout also play vital roles in EMI reduction. Using high-quality diodes with fast switching characteristics can minimize the generation of high-frequency noise. Careful PCB layout, including the use of short, direct traces and strategic component placement, can significantly reduce EMI by minimizing loop areas and parasitic inductances.
In more demanding applications, advanced techniques such as soft switching or resonant topologies may be employed. These methods aim to reduce the abruptness of the switching transitions, thereby lowering the high-frequency content of the EMI spectrum.
Compliance with regulatory standards, such as FCC regulations in the United States or CE marking requirements in Europe, often necessitates comprehensive EMI mitigation strategies. This may involve extensive testing and iterative design improvements to ensure that the half wave rectifier meets specified emission limits across various frequency bands.
As technology advances, the importance of EMI considerations in half wave rectifier design continues to grow. With the increasing prevalence of sensitive electronic devices and the push towards higher power densities, effective EMI management becomes not just a regulatory requirement but a critical factor in ensuring the reliability and performance of electronic systems incorporating half wave rectifiers.
The primary source of EMI in half wave rectifiers stems from the abrupt switching action during the rectification process. As the diode alternates between conducting and non-conducting states, it generates high-frequency harmonics that can propagate through both conducted and radiated paths. These harmonics, if left unmitigated, can interfere with sensitive electronic equipment, causing malfunctions or degraded performance in nearby systems.
To address EMI concerns, several strategies can be employed. Proper shielding is paramount, involving the use of conductive enclosures or barriers to contain electromagnetic emissions. This approach helps to prevent the radiated EMI from affecting surrounding circuits. Additionally, implementing effective grounding techniques is crucial. A well-designed ground plane can significantly reduce common-mode noise and provide a low-impedance path for high-frequency currents.
Filtering is another key aspect of EMI mitigation in half wave rectifiers. Input and output filters, such as LC (inductor-capacitor) networks, can attenuate high-frequency noise components. Specifically, input filters help to prevent noise from propagating back into the power source, while output filters smooth the rectified waveform and reduce ripple, which is a common source of EMI.
Component selection and layout also play vital roles in EMI reduction. Using high-quality diodes with fast switching characteristics can minimize the generation of high-frequency noise. Careful PCB layout, including the use of short, direct traces and strategic component placement, can significantly reduce EMI by minimizing loop areas and parasitic inductances.
In more demanding applications, advanced techniques such as soft switching or resonant topologies may be employed. These methods aim to reduce the abruptness of the switching transitions, thereby lowering the high-frequency content of the EMI spectrum.
Compliance with regulatory standards, such as FCC regulations in the United States or CE marking requirements in Europe, often necessitates comprehensive EMI mitigation strategies. This may involve extensive testing and iterative design improvements to ensure that the half wave rectifier meets specified emission limits across various frequency bands.
As technology advances, the importance of EMI considerations in half wave rectifier design continues to grow. With the increasing prevalence of sensitive electronic devices and the push towards higher power densities, effective EMI management becomes not just a regulatory requirement but a critical factor in ensuring the reliability and performance of electronic systems incorporating half wave rectifiers.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!