How isotonic solutions enhance oral rehydration solutions
AUG 19, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isotonic ORS Background
Oral rehydration solutions (ORS) have been a cornerstone in the treatment of dehydration, particularly in cases of acute diarrhea, for several decades. The concept of ORS was developed in the 1960s and gained widespread recognition in the 1970s as a simple, cost-effective method to combat dehydration-related mortality, especially in developing countries. The World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF have been instrumental in promoting the use of ORS globally.
Initially, ORS formulations were hypertonic, containing higher concentrations of glucose and electrolytes. However, research in the 1980s and 1990s revealed that isotonic solutions could be more effective and safer. Isotonic ORS, with an osmolarity similar to that of human plasma, emerged as an improved alternative to earlier hypertonic formulations.
The shift towards isotonic ORS was driven by the understanding that lower osmolarity solutions could enhance water absorption in the small intestine. This discovery was based on the principle of coupled transport, where sodium and glucose are co-transported across the intestinal epithelium, facilitating water absorption. Isotonic solutions, by maintaining a balance between solute concentration and body fluids, minimize the risk of adverse effects such as hypernatremia or fluid overload.
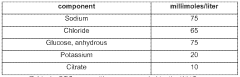
The development of isotonic ORS represented a significant advancement in oral rehydration therapy. These solutions typically contain sodium, potassium, chloride, citrate, and glucose in concentrations that closely match physiological levels. The reduced osmolarity (from about 311 mOsm/L in older formulations to 245 mOsm/L in newer ones) has been shown to decrease stool output, vomiting, and the need for intravenous fluid supplementation.
The evolution of ORS formulations has been guided by extensive clinical research and field studies. Large-scale trials in various countries have demonstrated the superiority of isotonic ORS in reducing the duration of diarrhea, decreasing stool volume, and improving overall outcomes in patients with acute gastroenteritis. These findings led to the WHO's recommendation in 2002 to adopt low osmolarity ORS as the global standard.
The success of isotonic ORS in managing dehydration has had a profound impact on global health, particularly in reducing childhood mortality due to diarrheal diseases. It has been hailed as one of the most important medical advancements of the 20th century, saving millions of lives worldwide. The simplicity and effectiveness of ORS have made it a crucial tool in both clinical settings and community-based health interventions.
Initially, ORS formulations were hypertonic, containing higher concentrations of glucose and electrolytes. However, research in the 1980s and 1990s revealed that isotonic solutions could be more effective and safer. Isotonic ORS, with an osmolarity similar to that of human plasma, emerged as an improved alternative to earlier hypertonic formulations.
The shift towards isotonic ORS was driven by the understanding that lower osmolarity solutions could enhance water absorption in the small intestine. This discovery was based on the principle of coupled transport, where sodium and glucose are co-transported across the intestinal epithelium, facilitating water absorption. Isotonic solutions, by maintaining a balance between solute concentration and body fluids, minimize the risk of adverse effects such as hypernatremia or fluid overload.
The development of isotonic ORS represented a significant advancement in oral rehydration therapy. These solutions typically contain sodium, potassium, chloride, citrate, and glucose in concentrations that closely match physiological levels. The reduced osmolarity (from about 311 mOsm/L in older formulations to 245 mOsm/L in newer ones) has been shown to decrease stool output, vomiting, and the need for intravenous fluid supplementation.
The evolution of ORS formulations has been guided by extensive clinical research and field studies. Large-scale trials in various countries have demonstrated the superiority of isotonic ORS in reducing the duration of diarrhea, decreasing stool volume, and improving overall outcomes in patients with acute gastroenteritis. These findings led to the WHO's recommendation in 2002 to adopt low osmolarity ORS as the global standard.
The success of isotonic ORS in managing dehydration has had a profound impact on global health, particularly in reducing childhood mortality due to diarrheal diseases. It has been hailed as one of the most important medical advancements of the 20th century, saving millions of lives worldwide. The simplicity and effectiveness of ORS have made it a crucial tool in both clinical settings and community-based health interventions.
Market Analysis ORS
The global market for Oral Rehydration Solutions (ORS) has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of the importance of hydration in treating diarrheal diseases and other conditions that lead to dehydration. The ORS market is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) expected to remain strong through the next decade.
Developing countries, particularly in regions such as Africa and South Asia, represent the largest market segments for ORS. These areas face high incidences of diarrheal diseases, especially among children under five years old, creating a substantial demand for effective rehydration solutions. The World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF have been instrumental in promoting the use of ORS in these regions, contributing to market expansion.
In developed countries, the ORS market is evolving beyond its traditional use for treating diarrheal diseases. There is a growing trend towards using ORS for general hydration purposes, including sports recovery and hangover relief. This diversification of applications has opened new market opportunities and attracted interest from major beverage companies looking to expand their product portfolios.
The market is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and newer entrants specializing in hydration products. Key players in the global ORS market include Abbott Laboratories, Sanofi, Johnson & Johnson, and local manufacturers in various countries. These companies are investing in research and development to improve the efficacy and palatability of ORS formulations, with a focus on creating isotonic solutions that enhance absorption rates.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards more palatable and convenient ORS products. This has led to the development of flavored variants and ready-to-drink formulations, which are gaining popularity, especially in urban areas and among younger demographics. The trend towards natural and organic ingredients is also influencing product development in the ORS market.
E-commerce and direct-to-consumer channels are becoming increasingly important for ORS distribution, particularly in developed markets. These channels offer convenience and the ability to reach consumers directly, bypassing traditional retail outlets. In developing countries, however, government programs and NGO initiatives remain crucial for ORS distribution, especially in rural and underserved areas.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the ORS market. While it has increased awareness of health and hydration, supply chain disruptions have posed challenges for manufacturers and distributors. As the global health situation stabilizes, the ORS market is expected to benefit from heightened health consciousness and increased investment in healthcare infrastructure in many countries.
Developing countries, particularly in regions such as Africa and South Asia, represent the largest market segments for ORS. These areas face high incidences of diarrheal diseases, especially among children under five years old, creating a substantial demand for effective rehydration solutions. The World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF have been instrumental in promoting the use of ORS in these regions, contributing to market expansion.
In developed countries, the ORS market is evolving beyond its traditional use for treating diarrheal diseases. There is a growing trend towards using ORS for general hydration purposes, including sports recovery and hangover relief. This diversification of applications has opened new market opportunities and attracted interest from major beverage companies looking to expand their product portfolios.
The market is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and newer entrants specializing in hydration products. Key players in the global ORS market include Abbott Laboratories, Sanofi, Johnson & Johnson, and local manufacturers in various countries. These companies are investing in research and development to improve the efficacy and palatability of ORS formulations, with a focus on creating isotonic solutions that enhance absorption rates.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards more palatable and convenient ORS products. This has led to the development of flavored variants and ready-to-drink formulations, which are gaining popularity, especially in urban areas and among younger demographics. The trend towards natural and organic ingredients is also influencing product development in the ORS market.
E-commerce and direct-to-consumer channels are becoming increasingly important for ORS distribution, particularly in developed markets. These channels offer convenience and the ability to reach consumers directly, bypassing traditional retail outlets. In developing countries, however, government programs and NGO initiatives remain crucial for ORS distribution, especially in rural and underserved areas.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the ORS market. While it has increased awareness of health and hydration, supply chain disruptions have posed challenges for manufacturers and distributors. As the global health situation stabilizes, the ORS market is expected to benefit from heightened health consciousness and increased investment in healthcare infrastructure in many countries.
Challenges in ORS
Despite the proven effectiveness of oral rehydration solutions (ORS) in treating dehydration, several challenges persist in their widespread adoption and optimal use. One significant issue is the palatability of traditional ORS formulations. Many patients, especially children, find the taste unpleasant, leading to poor compliance and reduced effectiveness. This taste barrier often results in incomplete consumption of the prescribed ORS, compromising its therapeutic benefits.
Another challenge lies in the osmolarity of conventional ORS. While designed to match the body's electrolyte balance, some formulations can have higher osmolarity than optimal, potentially leading to osmotic diarrhea in certain cases. This paradoxical effect can exacerbate the very condition ORS is meant to treat, particularly in vulnerable populations such as young children and the elderly.
The stability and shelf life of ORS present additional hurdles. In many resource-limited settings, where ORS is most critically needed, environmental factors like high temperature and humidity can degrade the quality of pre-packaged solutions. This degradation not only affects the efficacy of the treatment but also raises concerns about potential contamination and safety.
Variability in electrolyte composition across different ORS formulations poses another challenge. While the World Health Organization (WHO) provides standard guidelines, regional variations and proprietary formulations can lead to inconsistencies in treatment outcomes. This variability complicates the standardization of treatment protocols and can confuse healthcare providers and patients alike.
The correct preparation of ORS from powder formulations remains a persistent issue, particularly in home settings. Inaccurate mixing, often due to lack of proper measuring tools or understanding, can result in solutions that are too concentrated or too dilute. Both scenarios can compromise the effectiveness of the treatment and potentially worsen the patient's condition.
Lastly, there's the challenge of educating both healthcare providers and the general public about the importance and correct use of ORS. Misconceptions about the effectiveness of ORS compared to other interventions, such as intravenous fluids or antibiotics, can lead to underutilization of this life-saving treatment. Overcoming these educational barriers is crucial for maximizing the potential of ORS in combating dehydration globally.
Another challenge lies in the osmolarity of conventional ORS. While designed to match the body's electrolyte balance, some formulations can have higher osmolarity than optimal, potentially leading to osmotic diarrhea in certain cases. This paradoxical effect can exacerbate the very condition ORS is meant to treat, particularly in vulnerable populations such as young children and the elderly.
The stability and shelf life of ORS present additional hurdles. In many resource-limited settings, where ORS is most critically needed, environmental factors like high temperature and humidity can degrade the quality of pre-packaged solutions. This degradation not only affects the efficacy of the treatment but also raises concerns about potential contamination and safety.
Variability in electrolyte composition across different ORS formulations poses another challenge. While the World Health Organization (WHO) provides standard guidelines, regional variations and proprietary formulations can lead to inconsistencies in treatment outcomes. This variability complicates the standardization of treatment protocols and can confuse healthcare providers and patients alike.
The correct preparation of ORS from powder formulations remains a persistent issue, particularly in home settings. Inaccurate mixing, often due to lack of proper measuring tools or understanding, can result in solutions that are too concentrated or too dilute. Both scenarios can compromise the effectiveness of the treatment and potentially worsen the patient's condition.
Lastly, there's the challenge of educating both healthcare providers and the general public about the importance and correct use of ORS. Misconceptions about the effectiveness of ORS compared to other interventions, such as intravenous fluids or antibiotics, can lead to underutilization of this life-saving treatment. Overcoming these educational barriers is crucial for maximizing the potential of ORS in combating dehydration globally.
Current Isotonic ORS
01 Electrolyte balance optimization
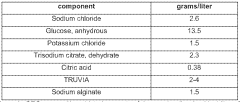
Enhancing isotonic solutions by optimizing the balance of electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and chloride. This approach aims to closely mimic the body's natural fluid composition, improving hydration and cellular function.- Electrolyte composition optimization: Enhancing isotonic solutions by optimizing the electrolyte composition. This involves carefully balancing various ions such as sodium, potassium, and chloride to match the body's natural fluid composition. The improved formulation can lead to better hydration and cellular function.
- Osmolality adjustment techniques: Developing methods to precisely adjust the osmolality of isotonic solutions. This includes using specific additives or advanced measurement techniques to ensure the solution maintains the correct osmotic pressure, improving its effectiveness and reducing potential side effects.
- Incorporation of bioactive compounds: Enhancing isotonic solutions by incorporating bioactive compounds such as amino acids, vitamins, or antioxidants. These additions can provide additional benefits beyond hydration, such as improved cellular function or faster recovery in medical applications.
- Stability and shelf-life improvement: Developing techniques to improve the stability and shelf-life of isotonic solutions. This includes using novel preservatives, packaging innovations, or formulation adjustments to maintain the solution's efficacy over extended periods without compromising its isotonic properties.
- Delivery system optimization: Enhancing the delivery systems for isotonic solutions to improve their effectiveness. This involves developing new administration methods, such as specialized infusion devices or novel packaging, to ensure accurate dosing and maintain the solution's isotonic properties during administration.
02 Osmolality adjustment techniques
Developing methods to precisely adjust the osmolality of isotonic solutions, ensuring they match the osmotic pressure of body fluids. This may involve using specific solutes or advanced measurement techniques to achieve optimal isotonicity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Incorporation of beneficial additives
Enhancing isotonic solutions by incorporating additives such as vitamins, minerals, or amino acids. These additions aim to provide additional nutritional or therapeutic benefits while maintaining isotonicity.Expand Specific Solutions04 Stability and shelf-life improvement
Developing techniques to improve the stability and extend the shelf-life of isotonic solutions. This may include using specific preservatives, packaging innovations, or formulation adjustments to maintain efficacy over time.Expand Specific Solutions05 Delivery system optimization
Enhancing the delivery systems for isotonic solutions, such as improved infusion devices or novel packaging designs. These innovations aim to ensure accurate dosing, prevent contamination, and enhance user convenience.Expand Specific Solutions
Key ORS Manufacturers
The market for isotonic solutions in oral rehydration is in a growth phase, driven by increasing awareness of hydration's importance and the rising prevalence of conditions requiring rehydration. The global oral rehydration solution market is expanding, with a projected CAGR of 3.5% from 2021 to 2028. Technologically, the field is moderately mature, with ongoing innovations focused on improving efficacy and palatability. Key players like Abbott Laboratories, Novartis AG, and Procter & Gamble Co. are investing in R&D to enhance their product offerings, while newer entrants such as Six Sigma Laboratories LLC are introducing novel formulations. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and specialized hydration-focused firms, indicating a dynamic and evolving market.
Abbott Laboratories
Technical Solution: Abbott Laboratories has developed an advanced oral rehydration solution (ORS) that incorporates isotonic technology to enhance fluid absorption. Their formulation includes a balanced mixture of electrolytes and glucose, carefully designed to match the osmolarity of body fluids. This isotonic composition facilitates rapid absorption in the small intestine, promoting efficient rehydration[1]. Abbott's ORS also includes zinc supplementation, which has been shown to reduce the duration and severity of diarrheal episodes[3]. The company has conducted extensive clinical trials to optimize the ratio of sodium to glucose, ensuring maximum effectiveness in treating dehydration caused by various conditions, including acute gastroenteritis[5].
Strengths: Scientifically optimized formulation, inclusion of zinc for additional health benefits, extensive clinical validation. Weaknesses: May be more expensive than basic ORS formulations, potential for over-reliance on ORS instead of addressing underlying causes of dehydration.
Novartis AG
Technical Solution: Novartis AG has developed a novel approach to enhancing oral rehydration solutions using isotonic principles. Their formulation incorporates a proprietary blend of electrolytes and low-osmolarity carbohydrates, designed to match the body's physiological fluids closely. This isotonic solution facilitates rapid absorption through the intestinal walls, promoting efficient rehydration[2]. Novartis has also integrated specific amino acids into their ORS, which have been shown to enhance sodium and water absorption in the small intestine[4]. The company's research has focused on optimizing the solution's taste without compromising its isotonic properties, addressing a common barrier to ORS compliance, especially in pediatric populations[6].
Strengths: Innovative amino acid integration, focus on palatability to improve compliance, strong research backing. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs, may require more consumer education on benefits compared to traditional ORS.
Isotonic Innovations
Oral rehydration solution with improved taste
PatentWO2014200555A1
Innovation
- Development of an ORS comprising a non-starch viscosity enhancing polymer, sodium salt, potassium salt, glucose, citrate salt, and a sweetener, with specific concentrations of sodium, potassium, and citrate, along with pH adjustment to mask saltiness and improve palatability, while maintaining the optimal glucose-to-sodium ratio.
Oral rehydration compositions containing liposomes
PatentInactiveUS20050008685A1
Innovation
- Encapsulating a portion of electrolytes in liposomes, along with optional nutraceuticals, to provide an alternative absorption mechanism and improve taste acceptability, while maintaining low osmolarity through the use of liposomed electrolytes and minimal carbohydrates, allowing for enhanced absorption and delivery of other compounds like vaccines and drugs.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding oral rehydration solutions (ORS) and isotonic solutions plays a crucial role in ensuring their safety, efficacy, and accessibility. In many countries, ORS are classified as over-the-counter (OTC) medications, subject to specific regulations governing their composition, manufacturing, and distribution.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has established guidelines for the formulation of ORS, which serve as a global standard. These guidelines specify the optimal concentrations of glucose, sodium, potassium, chloride, and citrate to achieve isotonicity and maximize rehydration efficacy. Regulatory bodies in various countries often adopt or adapt these guidelines when setting their own standards for ORS.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates ORS as OTC drugs. The FDA has established specific requirements for the labeling, packaging, and marketing of ORS products. These regulations ensure that consumers receive accurate information about the product's intended use, dosage, and potential side effects.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees the regulation of ORS in the European Union. The EMA has established harmonized standards for ORS composition and quality across member states, facilitating their free movement within the EU market. These standards also address the use of isotonic solutions in ORS formulations.
In developing countries, where diarrheal diseases pose a significant public health challenge, regulatory frameworks often focus on ensuring widespread access to ORS. Many governments have implemented policies to promote the availability of ORS through public health programs and subsidized distribution channels.
Regulatory bodies also monitor the quality and safety of ORS products through post-market surveillance. This includes periodic testing of marketed products to ensure compliance with established standards and investigation of any adverse event reports related to ORS use.
As research continues to advance our understanding of oral rehydration therapy, regulatory frameworks are evolving to incorporate new findings. For example, some countries are now considering regulations for "improved" ORS formulations that include additional components such as zinc or specific probiotics.
The regulatory landscape for isotonic solutions in ORS also extends to manufacturing practices. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines are typically enforced to ensure consistent product quality and safety. These guidelines cover aspects such as raw material sourcing, production processes, and quality control measures.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has established guidelines for the formulation of ORS, which serve as a global standard. These guidelines specify the optimal concentrations of glucose, sodium, potassium, chloride, and citrate to achieve isotonicity and maximize rehydration efficacy. Regulatory bodies in various countries often adopt or adapt these guidelines when setting their own standards for ORS.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates ORS as OTC drugs. The FDA has established specific requirements for the labeling, packaging, and marketing of ORS products. These regulations ensure that consumers receive accurate information about the product's intended use, dosage, and potential side effects.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees the regulation of ORS in the European Union. The EMA has established harmonized standards for ORS composition and quality across member states, facilitating their free movement within the EU market. These standards also address the use of isotonic solutions in ORS formulations.
In developing countries, where diarrheal diseases pose a significant public health challenge, regulatory frameworks often focus on ensuring widespread access to ORS. Many governments have implemented policies to promote the availability of ORS through public health programs and subsidized distribution channels.
Regulatory bodies also monitor the quality and safety of ORS products through post-market surveillance. This includes periodic testing of marketed products to ensure compliance with established standards and investigation of any adverse event reports related to ORS use.
As research continues to advance our understanding of oral rehydration therapy, regulatory frameworks are evolving to incorporate new findings. For example, some countries are now considering regulations for "improved" ORS formulations that include additional components such as zinc or specific probiotics.
The regulatory landscape for isotonic solutions in ORS also extends to manufacturing practices. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines are typically enforced to ensure consistent product quality and safety. These guidelines cover aspects such as raw material sourcing, production processes, and quality control measures.
Clinical Efficacy ORS
Oral rehydration solutions (ORS) have been a cornerstone in the management of dehydration, particularly in cases of acute diarrhea. The clinical efficacy of ORS has been well-established through numerous studies and real-world applications. Traditional ORS formulations have proven effective in reducing mortality rates associated with diarrheal diseases, especially in developing countries.
The introduction of isotonic solutions has further enhanced the efficacy of ORS. Isotonic ORS, which have an osmolarity similar to that of human plasma, have demonstrated superior performance compared to hyperosmolar solutions. These isotonic formulations typically contain lower concentrations of glucose and sodium, aligning more closely with the body's natural fluid balance.
Clinical trials have shown that isotonic ORS lead to reduced stool output, decreased vomiting episodes, and shorter duration of diarrhea compared to standard ORS. This improved efficacy is attributed to the enhanced absorption of water and electrolytes in the small intestine, facilitated by the isotonic nature of the solution.
One significant advantage of isotonic ORS is the reduced risk of hypernatremia, a potential complication associated with hyperosmolar solutions. This makes isotonic ORS particularly beneficial for infants and young children, who are more susceptible to electrolyte imbalances.
Studies have also indicated that isotonic ORS result in better patient compliance due to improved palatability and reduced gastrointestinal side effects. This increased acceptability is crucial in ensuring adequate fluid intake, especially in pediatric populations.
The World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF have recognized the benefits of isotonic ORS and have updated their recommendations accordingly. The current WHO-recommended ORS formulation has a reduced osmolarity of 245 mOsm/L, compared to the previous 311 mOsm/L, reflecting the shift towards more isotonic solutions.
In addition to acute diarrhea management, isotonic ORS have shown promise in other clinical scenarios. They have been successfully used in the treatment of mild to moderate dehydration in various patient populations, including athletes and individuals with chronic conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease.
The clinical efficacy of isotonic ORS extends beyond immediate rehydration. These solutions have been associated with faster recovery times, reduced need for intravenous fluid therapy, and decreased hospital admission rates. This not only improves patient outcomes but also has significant implications for healthcare resource utilization and cost-effectiveness.
The introduction of isotonic solutions has further enhanced the efficacy of ORS. Isotonic ORS, which have an osmolarity similar to that of human plasma, have demonstrated superior performance compared to hyperosmolar solutions. These isotonic formulations typically contain lower concentrations of glucose and sodium, aligning more closely with the body's natural fluid balance.
Clinical trials have shown that isotonic ORS lead to reduced stool output, decreased vomiting episodes, and shorter duration of diarrhea compared to standard ORS. This improved efficacy is attributed to the enhanced absorption of water and electrolytes in the small intestine, facilitated by the isotonic nature of the solution.
One significant advantage of isotonic ORS is the reduced risk of hypernatremia, a potential complication associated with hyperosmolar solutions. This makes isotonic ORS particularly beneficial for infants and young children, who are more susceptible to electrolyte imbalances.
Studies have also indicated that isotonic ORS result in better patient compliance due to improved palatability and reduced gastrointestinal side effects. This increased acceptability is crucial in ensuring adequate fluid intake, especially in pediatric populations.
The World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF have recognized the benefits of isotonic ORS and have updated their recommendations accordingly. The current WHO-recommended ORS formulation has a reduced osmolarity of 245 mOsm/L, compared to the previous 311 mOsm/L, reflecting the shift towards more isotonic solutions.
In addition to acute diarrhea management, isotonic ORS have shown promise in other clinical scenarios. They have been successfully used in the treatment of mild to moderate dehydration in various patient populations, including athletes and individuals with chronic conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease.
The clinical efficacy of isotonic ORS extends beyond immediate rehydration. These solutions have been associated with faster recovery times, reduced need for intravenous fluid therapy, and decreased hospital admission rates. This not only improves patient outcomes but also has significant implications for healthcare resource utilization and cost-effectiveness.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!