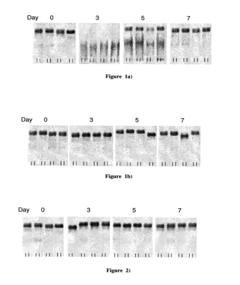
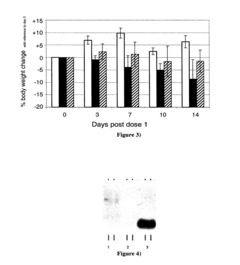
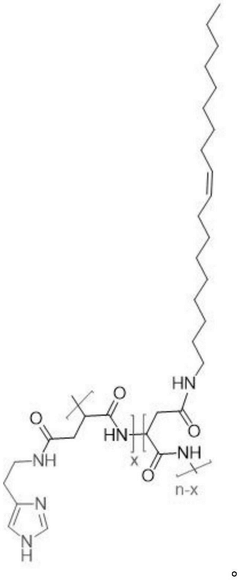
Designing isotonic solutions for targeted siRNA delivery
AUG 19, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
siRNA Delivery Background
RNA interference (RNAi) has emerged as a powerful tool for gene silencing, with small interfering RNA (siRNA) playing a crucial role in this process. Since its discovery in the late 1990s, siRNA has shown immense potential in therapeutic applications, particularly in treating genetic disorders, cancers, and viral infections. The ability of siRNA to specifically target and suppress gene expression has revolutionized the field of molecular biology and opened new avenues for drug development.
The concept of siRNA delivery is rooted in the natural cellular mechanism of post-transcriptional gene silencing. Double-stranded RNA molecules are processed by the enzyme Dicer into short fragments of 21-23 nucleotides, which are then incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). This complex uses the siRNA as a guide to identify and cleave complementary messenger RNA (mRNA), effectively silencing the target gene.
Despite the promising potential of siRNA therapeutics, the primary challenge has been the efficient and targeted delivery of these molecules to specific cells or tissues. siRNA is inherently unstable in biological fluids and susceptible to degradation by nucleases. Moreover, its large size and negative charge hinder cellular uptake, necessitating the development of sophisticated delivery systems.
Early attempts at siRNA delivery focused on viral vectors, which proved efficient but raised safety concerns due to potential immunogenicity and insertional mutagenesis. This led to a shift towards non-viral delivery methods, including lipid-based nanoparticles, polymeric carriers, and conjugate-based approaches. Each of these methods aims to protect the siRNA from degradation, facilitate cellular uptake, and ensure targeted delivery to specific tissues or cell types.
The design of isotonic solutions for siRNA delivery represents a critical aspect of this field. Isotonicity is essential to maintain cellular integrity and prevent osmotic stress during the delivery process. These solutions must balance the need for siRNA stability with physiological compatibility, ensuring that the delivery vehicle can effectively transport the siRNA to its target without causing cellular damage or triggering immune responses.
Recent advancements in siRNA delivery have focused on enhancing the specificity and efficiency of targeting. This includes the development of ligand-conjugated delivery systems that can recognize specific cell surface receptors, as well as stimuli-responsive carriers that release their payload under specific physiological conditions. The integration of these targeting strategies with isotonic delivery solutions presents a promising approach for improving the therapeutic efficacy of siRNA-based treatments.
As the field of siRNA delivery continues to evolve, researchers are exploring innovative approaches to overcome existing challenges. This includes the development of hybrid delivery systems that combine the advantages of different carrier types, as well as the use of novel materials and formulations to enhance stability and targeting efficiency. The ongoing research in this area holds great promise for the future of personalized medicine and targeted gene therapy.
The concept of siRNA delivery is rooted in the natural cellular mechanism of post-transcriptional gene silencing. Double-stranded RNA molecules are processed by the enzyme Dicer into short fragments of 21-23 nucleotides, which are then incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). This complex uses the siRNA as a guide to identify and cleave complementary messenger RNA (mRNA), effectively silencing the target gene.
Despite the promising potential of siRNA therapeutics, the primary challenge has been the efficient and targeted delivery of these molecules to specific cells or tissues. siRNA is inherently unstable in biological fluids and susceptible to degradation by nucleases. Moreover, its large size and negative charge hinder cellular uptake, necessitating the development of sophisticated delivery systems.
Early attempts at siRNA delivery focused on viral vectors, which proved efficient but raised safety concerns due to potential immunogenicity and insertional mutagenesis. This led to a shift towards non-viral delivery methods, including lipid-based nanoparticles, polymeric carriers, and conjugate-based approaches. Each of these methods aims to protect the siRNA from degradation, facilitate cellular uptake, and ensure targeted delivery to specific tissues or cell types.
The design of isotonic solutions for siRNA delivery represents a critical aspect of this field. Isotonicity is essential to maintain cellular integrity and prevent osmotic stress during the delivery process. These solutions must balance the need for siRNA stability with physiological compatibility, ensuring that the delivery vehicle can effectively transport the siRNA to its target without causing cellular damage or triggering immune responses.
Recent advancements in siRNA delivery have focused on enhancing the specificity and efficiency of targeting. This includes the development of ligand-conjugated delivery systems that can recognize specific cell surface receptors, as well as stimuli-responsive carriers that release their payload under specific physiological conditions. The integration of these targeting strategies with isotonic delivery solutions presents a promising approach for improving the therapeutic efficacy of siRNA-based treatments.
As the field of siRNA delivery continues to evolve, researchers are exploring innovative approaches to overcome existing challenges. This includes the development of hybrid delivery systems that combine the advantages of different carrier types, as well as the use of novel materials and formulations to enhance stability and targeting efficiency. The ongoing research in this area holds great promise for the future of personalized medicine and targeted gene therapy.
Market Analysis
The market for targeted siRNA delivery solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for precision medicine and personalized therapeutics. The global RNA interference (RNAi) therapeutics market, which includes siRNA-based treatments, is projected to expand rapidly in the coming years. This growth is fueled by the potential of siRNA therapies to address previously untreatable diseases and offer more effective alternatives to traditional small molecule drugs.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors are the primary drivers of demand for isotonic solutions designed for targeted siRNA delivery. These industries are investing heavily in research and development of siRNA-based therapies, recognizing their potential to revolutionize treatment approaches for various diseases, including cancer, genetic disorders, and viral infections. The ability to selectively silence specific genes makes siRNA an attractive option for developing highly targeted therapies with potentially fewer side effects than conventional treatments.
Academic research institutions and contract research organizations (CROs) also contribute significantly to the market demand. These entities are actively engaged in fundamental research and preclinical studies, exploring novel delivery mechanisms and optimizing formulations for enhanced siRNA efficacy. The collaboration between academia and industry is fostering innovation and accelerating the development of new siRNA delivery solutions.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for siRNA delivery technologies, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure, robust research ecosystem, and favorable regulatory environment. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years. This expansion is driven by increasing investment in biotechnology research, growing prevalence of chronic diseases, and rising healthcare expenditure in these regions.
The market for isotonic solutions for targeted siRNA delivery is characterized by intense competition and rapid technological advancements. Key players in this space are focusing on developing innovative delivery platforms that can overcome the challenges associated with siRNA stability, cellular uptake, and targeted delivery. Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have emerged as a leading delivery vehicle for siRNA, with several companies investing in the development and optimization of LNP-based formulations.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces several challenges. These include the high cost of siRNA therapies, complex manufacturing processes, and regulatory hurdles associated with novel delivery technologies. Additionally, concerns regarding off-target effects and potential immunogenicity of siRNA formulations need to be addressed to ensure widespread adoption of these therapies.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors are the primary drivers of demand for isotonic solutions designed for targeted siRNA delivery. These industries are investing heavily in research and development of siRNA-based therapies, recognizing their potential to revolutionize treatment approaches for various diseases, including cancer, genetic disorders, and viral infections. The ability to selectively silence specific genes makes siRNA an attractive option for developing highly targeted therapies with potentially fewer side effects than conventional treatments.
Academic research institutions and contract research organizations (CROs) also contribute significantly to the market demand. These entities are actively engaged in fundamental research and preclinical studies, exploring novel delivery mechanisms and optimizing formulations for enhanced siRNA efficacy. The collaboration between academia and industry is fostering innovation and accelerating the development of new siRNA delivery solutions.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market for siRNA delivery technologies, owing to their advanced healthcare infrastructure, robust research ecosystem, and favorable regulatory environment. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, particularly China and India, are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years. This expansion is driven by increasing investment in biotechnology research, growing prevalence of chronic diseases, and rising healthcare expenditure in these regions.
The market for isotonic solutions for targeted siRNA delivery is characterized by intense competition and rapid technological advancements. Key players in this space are focusing on developing innovative delivery platforms that can overcome the challenges associated with siRNA stability, cellular uptake, and targeted delivery. Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have emerged as a leading delivery vehicle for siRNA, with several companies investing in the development and optimization of LNP-based formulations.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces several challenges. These include the high cost of siRNA therapies, complex manufacturing processes, and regulatory hurdles associated with novel delivery technologies. Additionally, concerns regarding off-target effects and potential immunogenicity of siRNA formulations need to be addressed to ensure widespread adoption of these therapies.
Technical Challenges
The development of effective isotonic solutions for targeted siRNA delivery faces several significant technical challenges. One of the primary obstacles is maintaining the stability of siRNA molecules in the delivery solution. siRNA is inherently unstable and prone to degradation by nucleases present in biological fluids. Designing an isotonic solution that can protect siRNA from enzymatic degradation while preserving its structural integrity is crucial for successful delivery.
Another major challenge lies in achieving efficient cellular uptake of siRNA. The large size and negative charge of siRNA molecules hinder their ability to cross cell membranes. Developing isotonic solutions that can facilitate the cellular internalization of siRNA without compromising its activity or causing cellular toxicity remains a complex task. This often requires the incorporation of specialized delivery vehicles or chemical modifications to enhance membrane permeability.
The issue of off-target effects presents a significant hurdle in siRNA delivery. Even when successfully delivered to cells, siRNA can potentially interact with unintended targets, leading to unwanted gene silencing or cellular responses. Designing isotonic solutions that can minimize these off-target effects while maintaining the specificity of siRNA-mediated gene silencing is essential for both efficacy and safety.
Achieving targeted delivery to specific cell types or tissues poses another technical challenge. The isotonic solution must be engineered to selectively deliver siRNA to the desired target cells while avoiding accumulation in non-target tissues. This often requires the incorporation of targeting ligands or the development of advanced nanocarrier systems, which must be compatible with the isotonic environment.
The potential for immune system activation is a critical concern in siRNA delivery. Certain formulations or components of the isotonic solution may trigger innate immune responses, leading to inflammation or rapid clearance of the delivery system. Designing solutions that can evade immune recognition and maintain prolonged circulation times is crucial for effective siRNA delivery.
Scalability and reproducibility in the production of isotonic siRNA delivery solutions present additional technical challenges. Ensuring consistent quality, stability, and performance of the formulation across different batches and production scales is essential for clinical translation and commercial viability.
Lastly, the development of isotonic solutions for siRNA delivery must address the challenge of long-term storage stability. Maintaining the integrity and activity of siRNA and any associated delivery components under various storage conditions is critical for the practical application of these technologies in clinical settings.
Another major challenge lies in achieving efficient cellular uptake of siRNA. The large size and negative charge of siRNA molecules hinder their ability to cross cell membranes. Developing isotonic solutions that can facilitate the cellular internalization of siRNA without compromising its activity or causing cellular toxicity remains a complex task. This often requires the incorporation of specialized delivery vehicles or chemical modifications to enhance membrane permeability.
The issue of off-target effects presents a significant hurdle in siRNA delivery. Even when successfully delivered to cells, siRNA can potentially interact with unintended targets, leading to unwanted gene silencing or cellular responses. Designing isotonic solutions that can minimize these off-target effects while maintaining the specificity of siRNA-mediated gene silencing is essential for both efficacy and safety.
Achieving targeted delivery to specific cell types or tissues poses another technical challenge. The isotonic solution must be engineered to selectively deliver siRNA to the desired target cells while avoiding accumulation in non-target tissues. This often requires the incorporation of targeting ligands or the development of advanced nanocarrier systems, which must be compatible with the isotonic environment.
The potential for immune system activation is a critical concern in siRNA delivery. Certain formulations or components of the isotonic solution may trigger innate immune responses, leading to inflammation or rapid clearance of the delivery system. Designing solutions that can evade immune recognition and maintain prolonged circulation times is crucial for effective siRNA delivery.
Scalability and reproducibility in the production of isotonic siRNA delivery solutions present additional technical challenges. Ensuring consistent quality, stability, and performance of the formulation across different batches and production scales is essential for clinical translation and commercial viability.
Lastly, the development of isotonic solutions for siRNA delivery must address the challenge of long-term storage stability. Maintaining the integrity and activity of siRNA and any associated delivery components under various storage conditions is critical for the practical application of these technologies in clinical settings.
Current Delivery Methods
01 Formulation of isotonic solutions for improved delivery
Isotonic solutions are formulated to match the osmotic pressure of body fluids, enhancing the delivery efficiency of active ingredients. These solutions can be optimized by adjusting the concentration of solutes, such as electrolytes or sugars, to ensure better absorption and distribution of the delivered substances.- Formulation of isotonic solutions for improved delivery: Isotonic solutions are formulated to match the osmotic pressure of body fluids, enhancing the delivery efficiency of active ingredients. These solutions can be optimized by adjusting the concentration of solutes, such as electrolytes or sugars, to ensure better absorption and distribution of the delivered substances.
- Use of nanoparticles in isotonic solutions: Incorporating nanoparticles into isotonic solutions can improve delivery efficiency by enhancing the stability and bioavailability of active ingredients. These nanoparticles can be designed to target specific tissues or cells, allowing for more precise and effective delivery of therapeutic agents.
- Controlled release mechanisms in isotonic solutions: Implementing controlled release mechanisms in isotonic solutions can enhance delivery efficiency by providing sustained and targeted release of active ingredients. This approach can involve the use of polymers, liposomes, or other carrier systems that gradually release the payload over time, improving therapeutic outcomes.
- Optimization of isotonic solution composition: The composition of isotonic solutions can be optimized to improve delivery efficiency by carefully selecting and balancing various components. This may include adjusting pH, adding stabilizers, or incorporating permeation enhancers to facilitate better absorption and distribution of the active ingredients.
- Novel delivery systems for isotonic solutions: Developing novel delivery systems for isotonic solutions can significantly enhance delivery efficiency. These may include advanced pump systems, specialized containers, or innovative application methods that ensure precise dosing and improved absorption of the active ingredients.
02 Use of nanoparticles in isotonic solutions
Incorporating nanoparticles into isotonic solutions can improve delivery efficiency by enhancing the stability and bioavailability of active ingredients. These nanoparticles can be designed to target specific tissues or cells, allowing for more precise and effective delivery of therapeutic agents.Expand Specific Solutions03 Controlled release mechanisms in isotonic solutions
Implementing controlled release mechanisms in isotonic solutions can enhance delivery efficiency by providing sustained and targeted release of active ingredients. This approach can involve the use of polymers, liposomes, or other carrier systems that gradually release the therapeutic agents over time.Expand Specific Solutions04 Optimization of isotonic solution composition
The composition of isotonic solutions can be optimized to improve delivery efficiency by carefully selecting and balancing various components. This may include adjusting pH, adding stabilizers, or incorporating penetration enhancers to facilitate better absorption and distribution of active ingredients.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel delivery systems for isotonic solutions
Developing innovative delivery systems for isotonic solutions can significantly enhance their efficiency. These may include advanced pump systems, specialized containers, or devices that ensure precise dosing and administration of the isotonic solution, leading to improved therapeutic outcomes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The field of designing isotonic solutions for targeted siRNA delivery is in a dynamic growth phase, with significant market potential driven by the increasing demand for RNA-based therapeutics. The market is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and innovative biotech firms, indicating a competitive landscape. Key players like Sirnaomics, Bioneer, and Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals are advancing the technology, while academic institutions such as MIT and Duke University contribute to foundational research. The technology's maturity varies, with some companies like Eli Lilly and Janssen Pharmaceutica leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities to accelerate development. Overall, the field is progressing rapidly, with a focus on improving delivery efficiency and specificity for clinical applications.
Sirnaomics, Inc.
Technical Solution: Sirnaomics has developed a proprietary polypeptide nanoparticle (PNP) delivery system for siRNA therapeutics. Their PNP technology utilizes a unique combination of amino acids to form stable nanoparticles that can effectively encapsulate and deliver siRNA to target cells[1]. The company has optimized the formulation to create isotonic solutions suitable for various administration routes, including intravenous and local delivery. Their PNP-siRNA complexes have demonstrated enhanced stability in biological fluids and improved cellular uptake compared to conventional lipid-based delivery systems[2]. Sirnaomics has also incorporated targeting ligands into their PNP formulations to achieve tissue-specific delivery, particularly for liver and solid tumor applications[3].
Strengths: Versatile delivery platform, enhanced stability, and tissue-specific targeting capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential immunogenicity of peptide-based carriers and limited data on long-term safety in humans.
BIONEER Corp.
Technical Solution: BIONEER has developed an advanced siRNA delivery system called AccuTarget™, which utilizes a novel cationic lipid formulation to create isotonic solutions for targeted siRNA delivery. Their technology incorporates pH-sensitive lipids that facilitate endosomal escape and efficient cytoplasmic release of siRNA[4]. BIONEER's AccuTarget™ system also includes PEGylated lipids to improve the stability and circulation time of the siRNA-lipid complexes in vivo. The company has further enhanced their delivery platform by integrating cell-penetrating peptides and targeting ligands to achieve cell-specific delivery[5]. BIONEER has demonstrated successful in vivo delivery of therapeutic siRNAs to various tissues, including liver, lung, and tumors, with minimal off-target effects[6].
Strengths: Efficient endosomal escape, prolonged circulation time, and versatile targeting options. Weaknesses: Potential toxicity associated with cationic lipids and challenges in large-scale manufacturing of complex lipid formulations.
Innovative Formulations
Small Interfering RNA Delivery
PatentInactiveUS20160081930A1
Innovation
- A method involving the entrapment of double-stranded siRNA in neutral liposomes using the dehydration/rehydration technique, with the addition of sugar to control liposome size and enhance entrapment efficiency, reducing toxicity and immune activation.
Ph-responsive liver-targeted drug delivery carrier, and preparation method and application therefor
PatentWO2024208377A1
Innovation
- Develop a pH-responsive cationic polymer, combine distearoylphosphatidylcholine, cholesterol and targeting molecules to prepare liver-targeted drug delivery carriers, assemble siRNA through ethanol injection precipitation, and use cationic polymers and siRNA The charge attraction effect forms a stable complex and reduces non-specific interactions.
Regulatory Considerations
The regulatory landscape for siRNA-based therapeutics is complex and evolving, requiring careful consideration throughout the development process. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies siRNA therapeutics as biological products, subject to the regulations outlined in the Public Health Service Act and the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Developers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines to ensure product quality, safety, and efficacy.
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees the regulation of siRNA therapeutics. The EMA has established specific guidelines for the quality, non-clinical, and clinical aspects of RNA-based therapeutics, including siRNA. These guidelines address critical issues such as the characterization of the active substance, impurity profiling, and stability testing.
Safety considerations are paramount in the regulatory process for siRNA therapeutics. Regulatory bodies require comprehensive toxicology studies to assess potential off-target effects, immunogenicity, and long-term safety. The design of isotonic solutions for siRNA delivery must take into account these safety requirements, ensuring that the formulation does not introduce additional risks or adverse effects.
Efficacy demonstration is another crucial aspect of the regulatory process. Clinical trials for siRNA therapeutics must be designed to clearly demonstrate the intended therapeutic effect and the specificity of the target gene silencing. The isotonic solution used for delivery plays a vital role in this context, as it directly impacts the bioavailability and cellular uptake of the siRNA.
Regulatory agencies also focus on the manufacturing process and quality control of siRNA therapeutics. The isotonic solution used for delivery must be produced under stringent quality control measures, with well-defined specifications for osmolality, pH, and other critical parameters. Stability studies are required to demonstrate the long-term integrity of the siRNA in the isotonic solution under various storage conditions.
As the field of siRNA therapeutics advances, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Developers must stay informed about emerging guidelines and engage in early discussions with regulatory authorities to address potential challenges in the development and approval process. This proactive approach can help streamline the regulatory pathway and accelerate the translation of innovative siRNA delivery solutions from bench to bedside.
In the European Union, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversees the regulation of siRNA therapeutics. The EMA has established specific guidelines for the quality, non-clinical, and clinical aspects of RNA-based therapeutics, including siRNA. These guidelines address critical issues such as the characterization of the active substance, impurity profiling, and stability testing.
Safety considerations are paramount in the regulatory process for siRNA therapeutics. Regulatory bodies require comprehensive toxicology studies to assess potential off-target effects, immunogenicity, and long-term safety. The design of isotonic solutions for siRNA delivery must take into account these safety requirements, ensuring that the formulation does not introduce additional risks or adverse effects.
Efficacy demonstration is another crucial aspect of the regulatory process. Clinical trials for siRNA therapeutics must be designed to clearly demonstrate the intended therapeutic effect and the specificity of the target gene silencing. The isotonic solution used for delivery plays a vital role in this context, as it directly impacts the bioavailability and cellular uptake of the siRNA.
Regulatory agencies also focus on the manufacturing process and quality control of siRNA therapeutics. The isotonic solution used for delivery must be produced under stringent quality control measures, with well-defined specifications for osmolality, pH, and other critical parameters. Stability studies are required to demonstrate the long-term integrity of the siRNA in the isotonic solution under various storage conditions.
As the field of siRNA therapeutics advances, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. Developers must stay informed about emerging guidelines and engage in early discussions with regulatory authorities to address potential challenges in the development and approval process. This proactive approach can help streamline the regulatory pathway and accelerate the translation of innovative siRNA delivery solutions from bench to bedside.
Biocompatibility Assessment
Biocompatibility assessment is a critical aspect of designing isotonic solutions for targeted siRNA delivery. The evaluation of biocompatibility ensures that the delivery system does not elicit adverse reactions or toxicity in biological systems, thereby maintaining the safety and efficacy of the siRNA therapy.
One of the primary considerations in biocompatibility assessment is the interaction between the isotonic solution and blood components. The solution must not cause hemolysis or platelet aggregation, which could lead to thrombosis or other circulatory complications. Extensive in vitro testing using human blood samples is essential to evaluate these potential interactions.
The impact of the isotonic solution on cellular viability and function is another crucial factor. Cytotoxicity assays using relevant cell lines, such as hepatocytes or immune cells, provide valuable insights into the solution's effects on cellular metabolism and proliferation. Additionally, assessing the solution's influence on cell membrane integrity and intracellular signaling pathways helps predict potential systemic effects.
Immunogenicity is a significant concern in siRNA delivery systems. The isotonic solution and its components must not trigger an excessive immune response, which could lead to rapid clearance of the therapeutic or, in severe cases, anaphylaxis. Evaluating the activation of complement systems and cytokine production in response to the solution is crucial for predicting immunological compatibility.
Long-term effects of repeated administration must also be considered in biocompatibility assessment. Chronic toxicity studies in animal models help identify potential accumulation of delivery components in organs and tissues, as well as any delayed adverse effects that may not be apparent in short-term studies.
The biodegradability and clearance of the isotonic solution components are essential aspects of biocompatibility. Ideally, the delivery system should be metabolized or excreted from the body without leaving harmful residues. Pharmacokinetic studies tracking the distribution, metabolism, and elimination of the solution components provide valuable data for assessing long-term safety.
Compatibility with the target tissue or organ is another critical factor. The isotonic solution must not disrupt the normal physiology or function of the intended delivery site. This is particularly important for targeted delivery systems, where the solution may interact with specific cell types or extracellular matrices.
Lastly, the potential for genotoxicity and carcinogenicity must be evaluated, especially for novel components of the isotonic solution. Standard mutagenicity assays and long-term carcinogenicity studies in animal models are essential for comprehensive safety assessment.
One of the primary considerations in biocompatibility assessment is the interaction between the isotonic solution and blood components. The solution must not cause hemolysis or platelet aggregation, which could lead to thrombosis or other circulatory complications. Extensive in vitro testing using human blood samples is essential to evaluate these potential interactions.
The impact of the isotonic solution on cellular viability and function is another crucial factor. Cytotoxicity assays using relevant cell lines, such as hepatocytes or immune cells, provide valuable insights into the solution's effects on cellular metabolism and proliferation. Additionally, assessing the solution's influence on cell membrane integrity and intracellular signaling pathways helps predict potential systemic effects.
Immunogenicity is a significant concern in siRNA delivery systems. The isotonic solution and its components must not trigger an excessive immune response, which could lead to rapid clearance of the therapeutic or, in severe cases, anaphylaxis. Evaluating the activation of complement systems and cytokine production in response to the solution is crucial for predicting immunological compatibility.
Long-term effects of repeated administration must also be considered in biocompatibility assessment. Chronic toxicity studies in animal models help identify potential accumulation of delivery components in organs and tissues, as well as any delayed adverse effects that may not be apparent in short-term studies.
The biodegradability and clearance of the isotonic solution components are essential aspects of biocompatibility. Ideally, the delivery system should be metabolized or excreted from the body without leaving harmful residues. Pharmacokinetic studies tracking the distribution, metabolism, and elimination of the solution components provide valuable data for assessing long-term safety.
Compatibility with the target tissue or organ is another critical factor. The isotonic solution must not disrupt the normal physiology or function of the intended delivery site. This is particularly important for targeted delivery systems, where the solution may interact with specific cell types or extracellular matrices.
Lastly, the potential for genotoxicity and carcinogenicity must be evaluated, especially for novel components of the isotonic solution. Standard mutagenicity assays and long-term carcinogenicity studies in animal models are essential for comprehensive safety assessment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!